Linda Moy
A Multi-Modal AI System for Screening Mammography: Integrating 2D and 3D Imaging to Improve Breast Cancer Detection in a Prospective Clinical Study
Apr 08, 2025
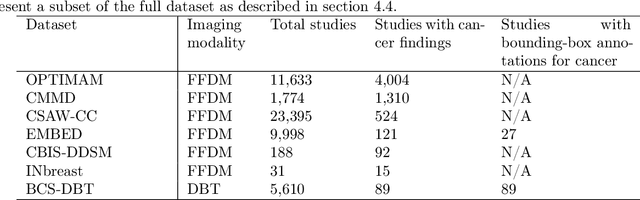
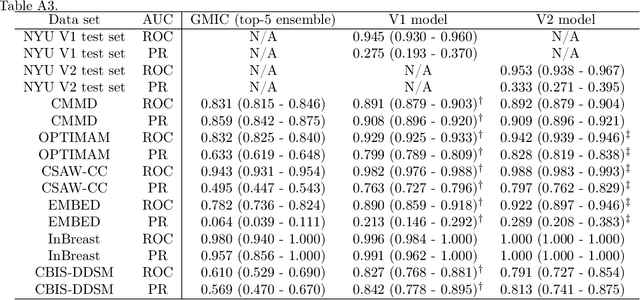
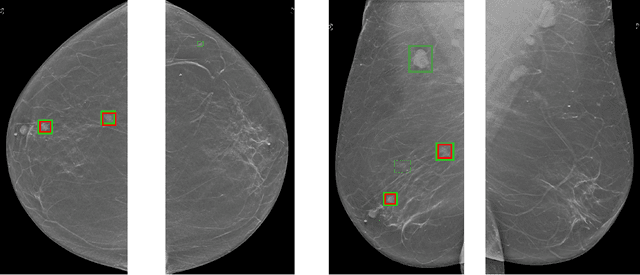
Abstract:Although digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) improves diagnostic performance over full-field digital mammography (FFDM), false-positive recalls remain a concern in breast cancer screening. We developed a multi-modal artificial intelligence system integrating FFDM, synthetic mammography, and DBT to provide breast-level predictions and bounding-box localizations of suspicious findings. Our AI system, trained on approximately 500,000 mammography exams, achieved 0.945 AUROC on an internal test set. It demonstrated capacity to reduce recalls by 31.7% and radiologist workload by 43.8% while maintaining 100% sensitivity, underscoring its potential to improve clinical workflows. External validation confirmed strong generalizability, reducing the gap to a perfect AUROC by 35.31%-69.14% relative to strong baselines. In prospective deployment across 18 sites, the system reduced recall rates for low-risk cases. An improved version, trained on over 750,000 exams with additional labels, further reduced the gap by 18.86%-56.62% across large external datasets. Overall, these results underscore the importance of utilizing all available imaging modalities, demonstrate the potential for clinical impact, and indicate feasibility of further reduction of the test error with increased training set when using large-capacity neural networks.
fastMRI Breast: A publicly available radial k-space dataset of breast dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI
Jun 07, 2024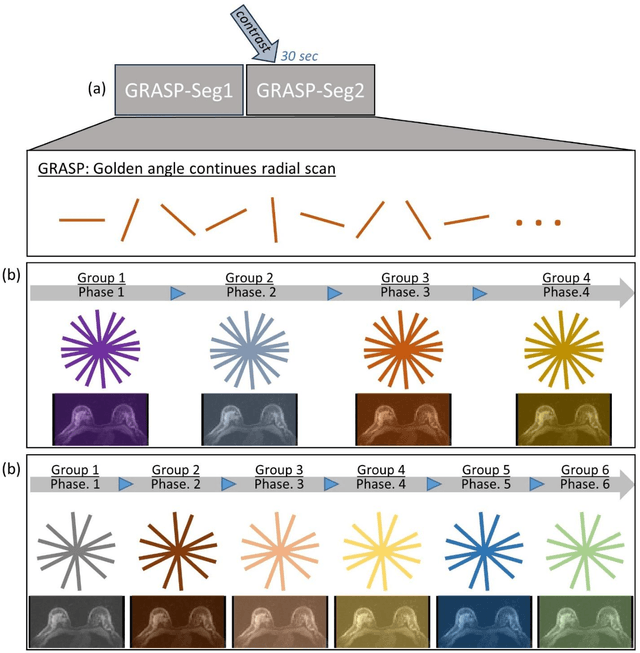
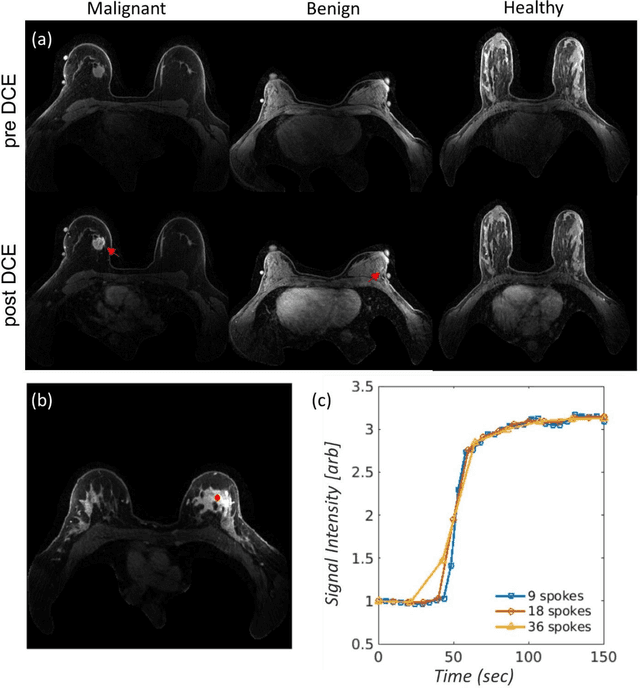
Abstract:This data curation work introduces the first large-scale dataset of radial k-space and DICOM data for breast DCE-MRI acquired in diagnostic breast MRI exams. Our dataset includes case-level labels indicating patient age, menopause status, lesion status (negative, benign, and malignant), and lesion type for each case. The public availability of this dataset and accompanying reconstruction code will support research and development of fast and quantitative breast image reconstruction and machine learning methods.
RIDGE: Reproducibility, Integrity, Dependability, Generalizability, and Efficiency Assessment of Medical Image Segmentation Models
Jan 16, 2024
Abstract:Deep learning techniques, despite their potential, often suffer from a lack of reproducibility and generalizability, impeding their clinical adoption. Image segmentation is one of the critical tasks in medical image analysis, in which one or several regions/volumes of interest should be annotated. This paper introduces the RIDGE checklist, a framework for assessing the Reproducibility, Integrity, Dependability, Generalizability, and Efficiency of deep learning-based medical image segmentation models. The checklist serves as a guide for researchers to enhance the quality and transparency of their work, ensuring that segmentation models are not only scientifically sound but also clinically relevant.
3D-GMIC: an efficient deep neural network to find small objects in large 3D images
Oct 16, 2022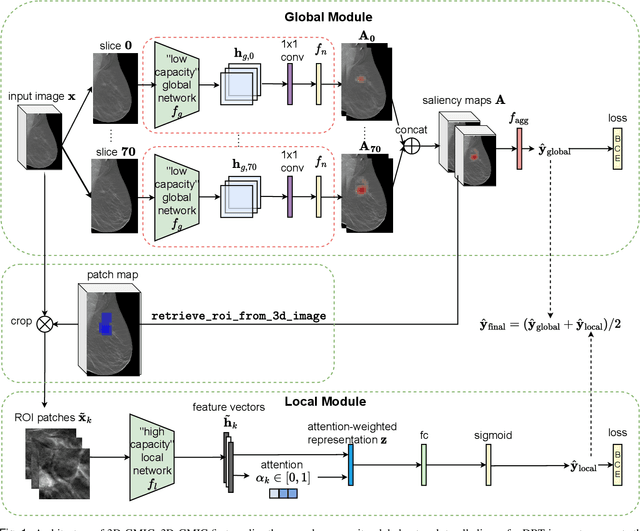
Abstract:3D imaging enables a more accurate diagnosis by providing spatial information about organ anatomy. However, using 3D images to train AI models is computationally challenging because they consist of tens or hundreds of times more pixels than their 2D counterparts. To train with high-resolution 3D images, convolutional neural networks typically resort to downsampling them or projecting them to two dimensions. In this work, we propose an effective alternative, a novel neural network architecture that enables computationally efficient classification of 3D medical images in their full resolution. Compared to off-the-shelf convolutional neural networks, 3D-GMIC uses 77.98%-90.05% less GPU memory and 91.23%-96.02% less computation. While our network is trained only with image-level labels, without segmentation labels, it explains its classification predictions by providing pixel-level saliency maps. On a dataset collected at NYU Langone Health, including 85,526 patients with full-field 2D mammography (FFDM), synthetic 2D mammography, and 3D mammography (DBT), our model, the 3D Globally-Aware Multiple Instance Classifier (3D-GMIC), achieves a breast-wise AUC of 0.831 (95% CI: 0.769-0.887) in classifying breasts with malignant findings using DBT images. As DBT and 2D mammography capture different information, averaging predictions on 2D and 3D mammography together leads to a diverse ensemble with an improved breast-wise AUC of 0.841 (95% CI: 0.768-0.895). Our model generalizes well to an external dataset from Duke University Hospital, achieving an image-wise AUC of 0.848 (95% CI: 0.798-0.896) in classifying DBT images with malignant findings.
Best Practices and Scoring System on Reviewing A.I. based Medical Imaging Papers: Part 1 Classification
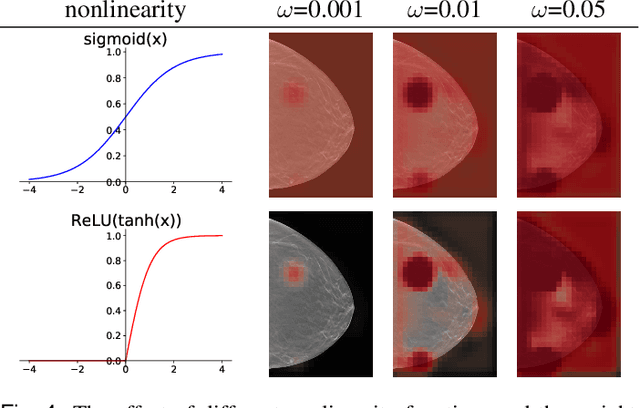
Feb 03, 2022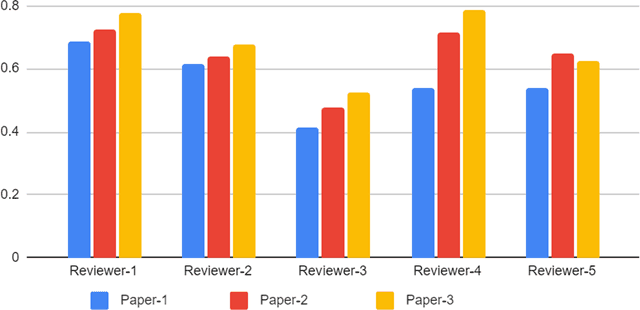
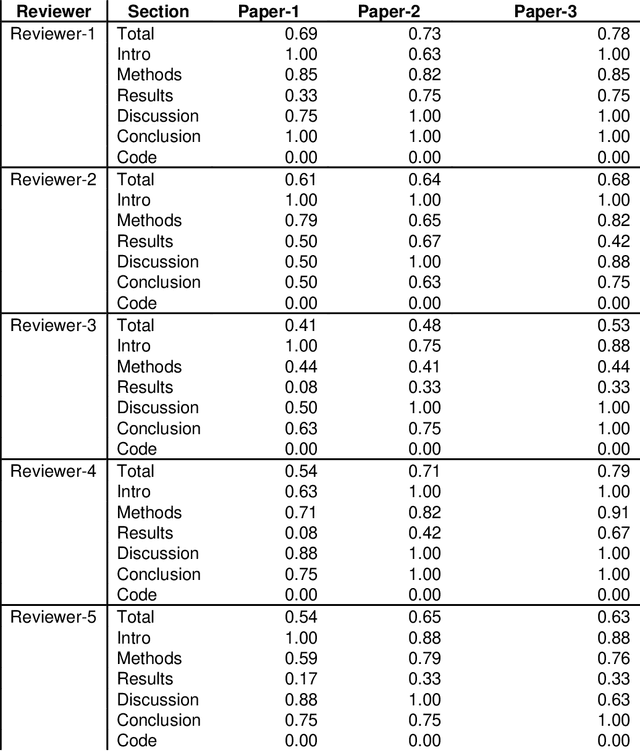
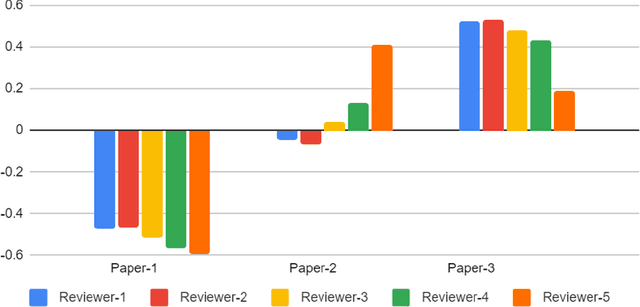
Abstract:With the recent advances in A.I. methodologies and their application to medical imaging, there has been an explosion of related research programs utilizing these techniques to produce state-of-the-art classification performance. Ultimately, these research programs culminate in submission of their work for consideration in peer reviewed journals. To date, the criteria for acceptance vs. rejection is often subjective; however, reproducible science requires reproducible review. The Machine Learning Education Sub-Committee of SIIM has identified a knowledge gap and a serious need to establish guidelines for reviewing these studies. Although there have been several recent papers with this goal, this present work is written from the machine learning practitioners standpoint. In this series, the committee will address the best practices to be followed in an A.I.-based study and present the required sections in terms of examples and discussion of what should be included to make the studies cohesive, reproducible, accurate, and self-contained. This first entry in the series focuses on the task of image classification. Elements such as dataset curation, data pre-processing steps, defining an appropriate reference standard, data partitioning, model architecture and training are discussed. The sections are presented as they would be detailed in a typical manuscript, with content describing the necessary information that should be included to make sure the study is of sufficient quality to be considered for publication. The goal of this series is to provide resources to not only help improve the review process for A.I.-based medical imaging papers, but to facilitate a standard for the information that is presented within all components of the research study. We hope to provide quantitative metrics in what otherwise may be a qualitative review process.
Differences between human and machine perception in medical diagnosis
Nov 28, 2020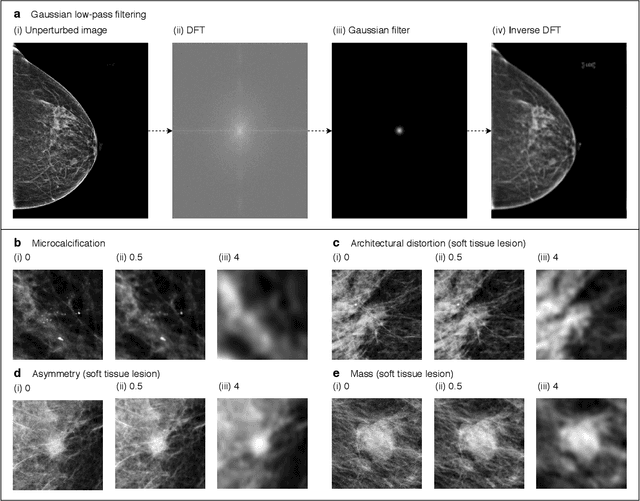
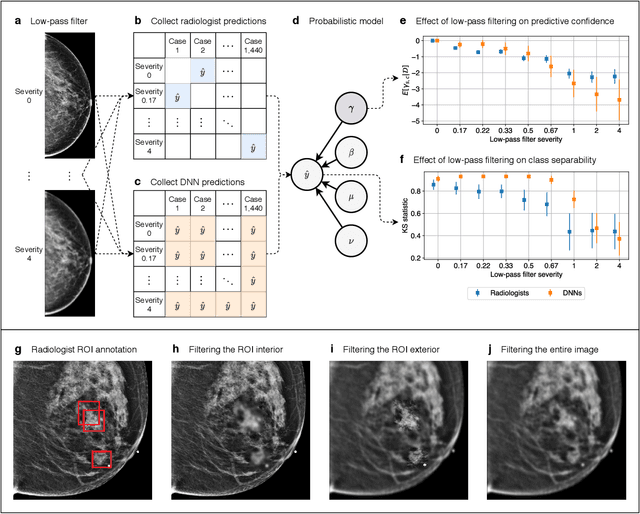
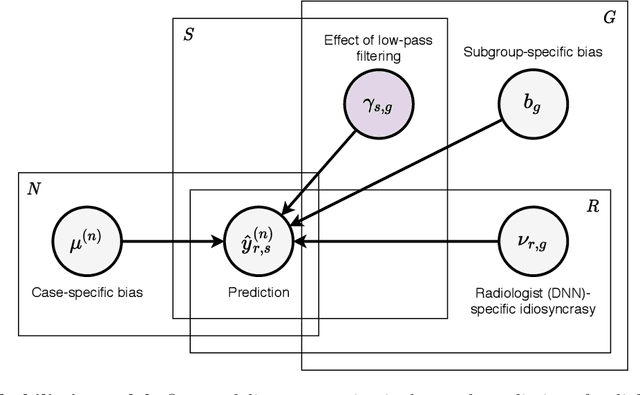
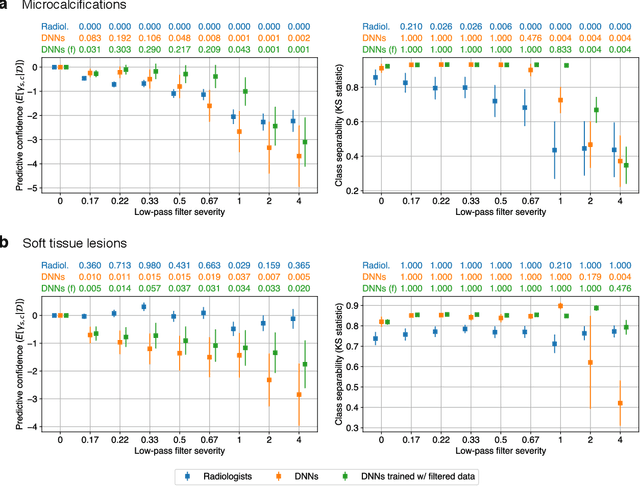
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) show promise in image-based medical diagnosis, but cannot be fully trusted since their performance can be severely degraded by dataset shifts to which human perception remains invariant. If we can better understand the differences between human and machine perception, we can potentially characterize and mitigate this effect. We therefore propose a framework for comparing human and machine perception in medical diagnosis. The two are compared with respect to their sensitivity to the removal of clinically meaningful information, and to the regions of an image deemed most suspicious. Drawing inspiration from the natural image domain, we frame both comparisons in terms of perturbation robustness. The novelty of our framework is that separate analyses are performed for subgroups with clinically meaningful differences. We argue that this is necessary in order to avert Simpson's paradox and draw correct conclusions. We demonstrate our framework with a case study in breast cancer screening, and reveal significant differences between radiologists and DNNs. We compare the two with respect to their robustness to Gaussian low-pass filtering, performing a subgroup analysis on microcalcifications and soft tissue lesions. For microcalcifications, DNNs use a separate set of high frequency components than radiologists, some of which lie outside the image regions considered most suspicious by radiologists. These features run the risk of being spurious, but if not, could represent potential new biomarkers. For soft tissue lesions, the divergence between radiologists and DNNs is even starker, with DNNs relying heavily on spurious high frequency components ignored by radiologists. Importantly, this deviation in soft tissue lesions was only observable through subgroup analysis, which highlights the importance of incorporating medical domain knowledge into our comparison framework.
Reducing false-positive biopsies with deep neural networks that utilize local and global information in screening mammograms
Sep 19, 2020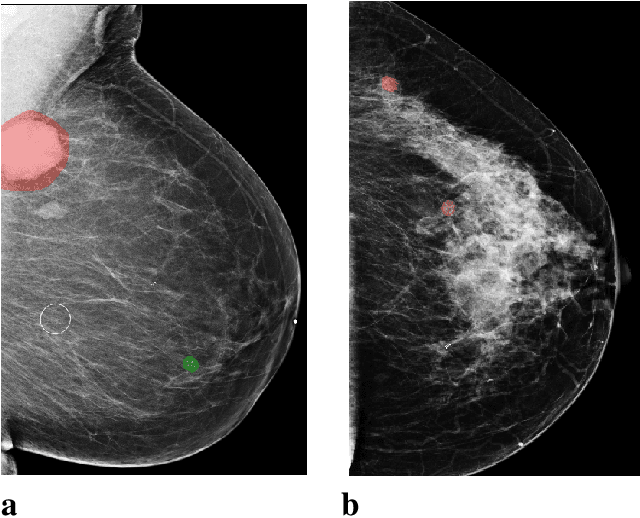
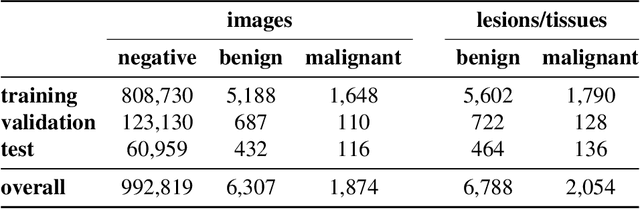
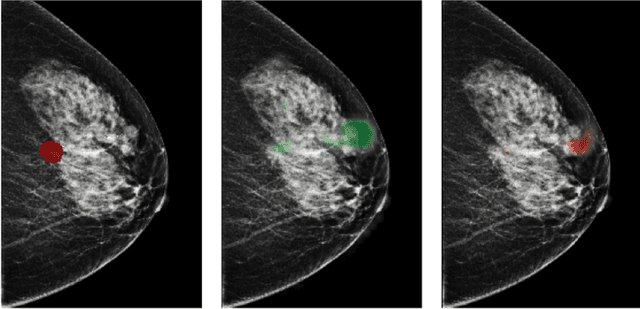
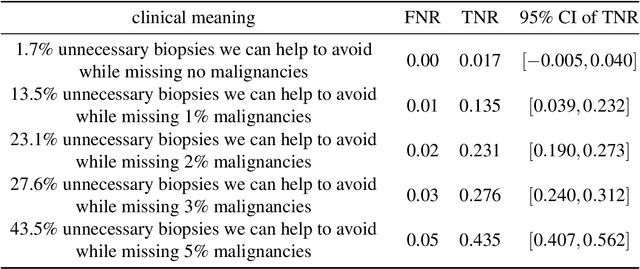
Abstract:Breast cancer is the most common cancer in women, and hundreds of thousands of unnecessary biopsies are done around the world at a tremendous cost. It is crucial to reduce the rate of biopsies that turn out to be benign tissue. In this study, we build deep neural networks (DNNs) to classify biopsied lesions as being either malignant or benign, with the goal of using these networks as second readers serving radiologists to further reduce the number of false positive findings. We enhance the performance of DNNs that are trained to learn from small image patches by integrating global context provided in the form of saliency maps learned from the entire image into their reasoning, similar to how radiologists consider global context when evaluating areas of interest. Our experiments are conducted on a dataset of 229,426 screening mammography exams from 141,473 patients. We achieve an AUC of 0.8 on a test set consisting of 464 benign and 136 malignant lesions.
Understanding the robustness of deep neural network classifiers for breast cancer screening
Mar 23, 2020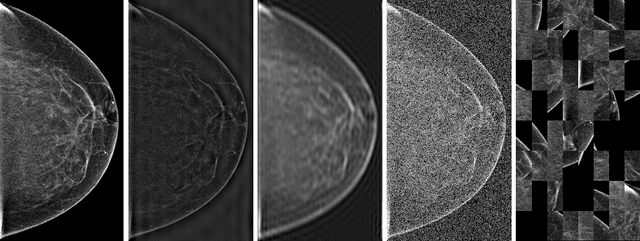
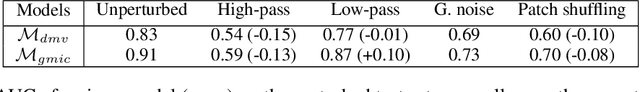
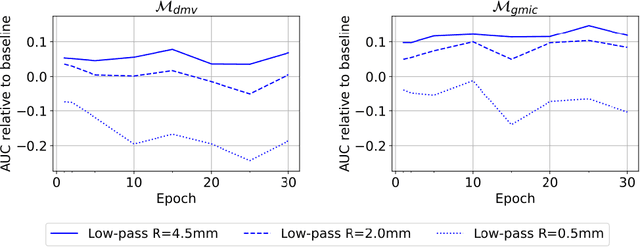
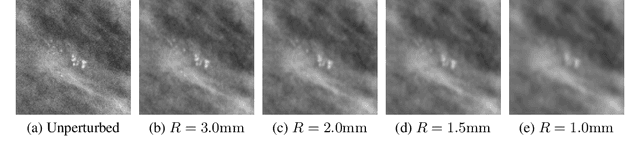
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) show promise in breast cancer screening, but their robustness to input perturbations must be better understood before they can be clinically implemented. There exists extensive literature on this subject in the context of natural images that can potentially be built upon. However, it cannot be assumed that conclusions about robustness will transfer from natural images to mammogram images, due to significant differences between the two image modalities. In order to determine whether conclusions will transfer, we measure the sensitivity of a radiologist-level screening mammogram image classifier to four commonly studied input perturbations that natural image classifiers are sensitive to. We find that mammogram image classifiers are also sensitive to these perturbations, which suggests that we can build on the existing literature. We also perform a detailed analysis on the effects of low-pass filtering, and find that it degrades the visibility of clinically meaningful features called microcalcifications. Since low-pass filtering removes semantically meaningful information that is predictive of breast cancer, we argue that it is undesirable for mammogram image classifiers to be invariant to it. This is in contrast to natural images, where we do not want DNNs to be sensitive to low-pass filtering due to its tendency to remove information that is human-incomprehensible.
An interpretable classifier for high-resolution breast cancer screening images utilizing weakly supervised localization
Feb 13, 2020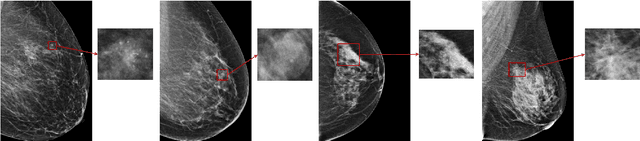
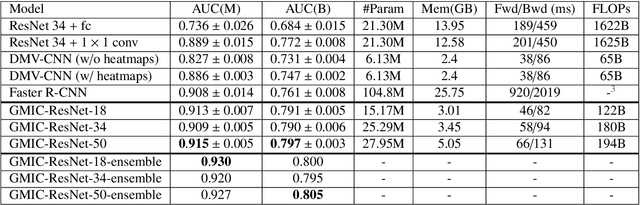
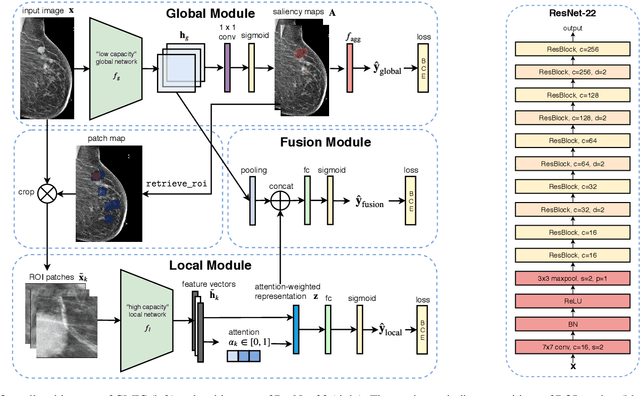
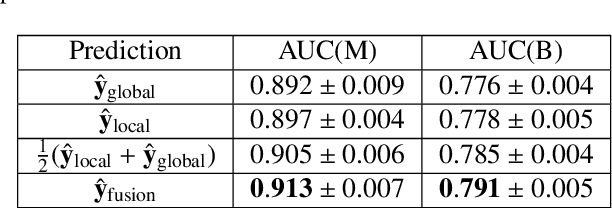
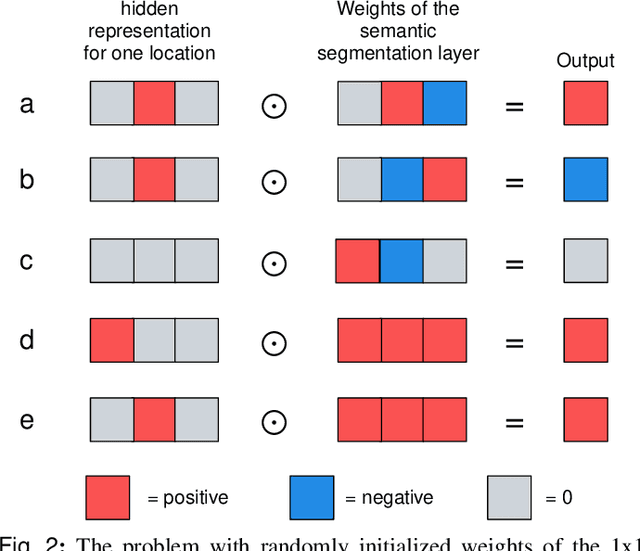
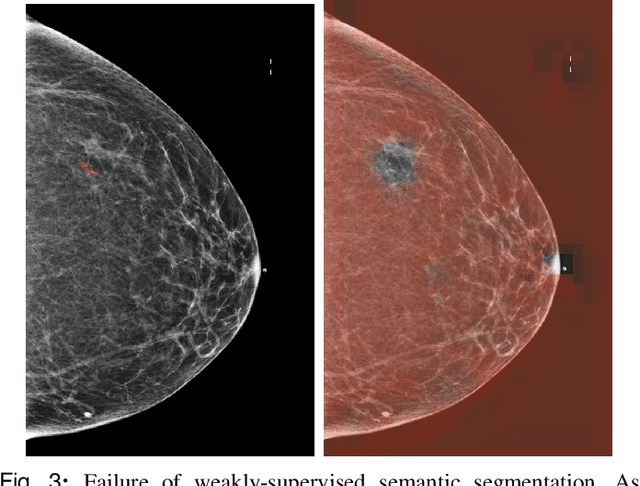
Abstract:Medical images differ from natural images in significantly higher resolutions and smaller regions of interest. Because of these differences, neural network architectures that work well for natural images might not be applicable to medical image analysis. In this work, we extend the globally-aware multiple instance classifier, a framework we proposed to address these unique properties of medical images. This model first uses a low-capacity, yet memory-efficient, network on the whole image to identify the most informative regions. It then applies another higher-capacity network to collect details from chosen regions. Finally, it employs a fusion module that aggregates global and local information to make a final prediction. While existing methods often require lesion segmentation during training, our model is trained with only image-level labels and can generate pixel-level saliency maps indicating possible malignant findings. We apply the model to screening mammography interpretation: predicting the presence or absence of benign and malignant lesions. On the NYU Breast Cancer Screening Dataset, consisting of more than one million images, our model achieves an AUC of 0.93 in classifying breasts with malignant findings, outperforming ResNet-34 and Faster R-CNN. Compared to ResNet-34, our model is 4.1x faster for inference while using 78.4% less GPU memory. Furthermore, we demonstrate, in a reader study, that our model surpasses radiologist-level AUC by a margin of 0.11. The proposed model is available online: https://github.com/nyukat/GMIC.
Improving localization-based approaches for breast cancer screening exam classification
Aug 01, 2019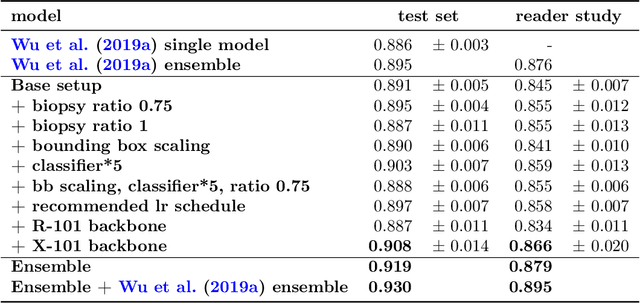
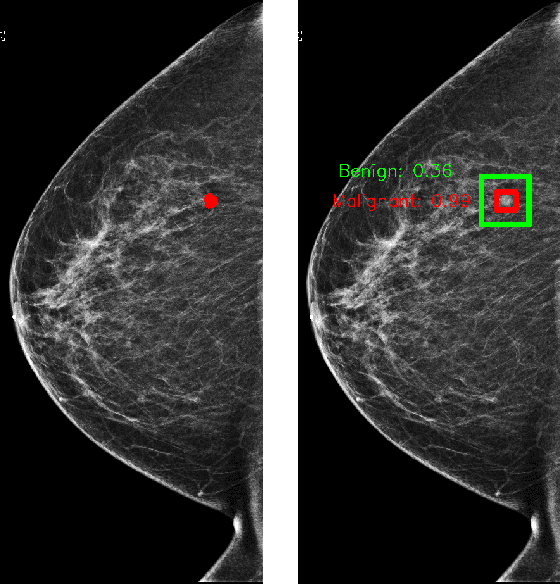
Abstract:We trained and evaluated a localization-based deep CNN for breast cancer screening exam classification on over 200,000 exams (over 1,000,000 images). Our model achieves an AUC of 0.919 in predicting malignancy in patients undergoing breast cancer screening, reducing the error rate of the baseline (Wu et al., 2019a) by 23%. In addition, the models generates bounding boxes for benign and malignant findings, providing interpretable predictions.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge