Nan Wu
DanQing: An Up-to-Date Large-Scale Chinese Vision-Language Pre-training Dataset
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:Vision-Language Pre-training (VLP) models demonstrate strong performance across various downstream tasks by learning from large-scale image-text pairs through contrastive pretraining. The release of extensive English image-text datasets (e.g., COYO-700M and LAION-400M) has enabled widespread adoption of models such as CLIP and SigLIP in tasks including cross-modal retrieval and image captioning. However, the advancement of Chinese vision-language pretraining has substantially lagged behind, due to the scarcity of high-quality Chinese image-text data. To address this gap, we develop a comprehensive pipeline for constructing a high-quality Chinese cross-modal dataset. As a result, we propose DanQing, which contains 100 million image-text pairs collected from Common Crawl. Different from existing datasets, DanQing is curated through a more rigorous selection process, yielding superior data quality. Moreover, DanQing is primarily built from 2024-2025 web data, enabling models to better capture evolving semantic trends and thus offering greater practical utility. We compare DanQing with existing datasets by continual pre-training of the SigLIP2 model. Experimental results show that DanQing consistently achieves superior performance across a range of Chinese downstream tasks, including zero-shot classification, cross-modal retrieval, and LMM-based evaluations. To facilitate further research in Chinese vision-language pre-training, we will open-source the DanQing dataset under the Creative Common CC-BY 4.0 license.
Step-GUI Technical Report
Dec 19, 2025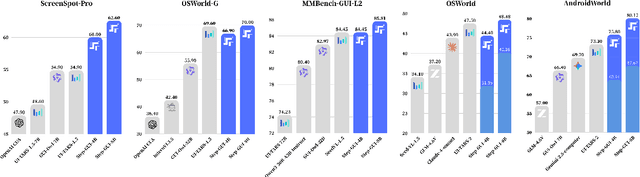
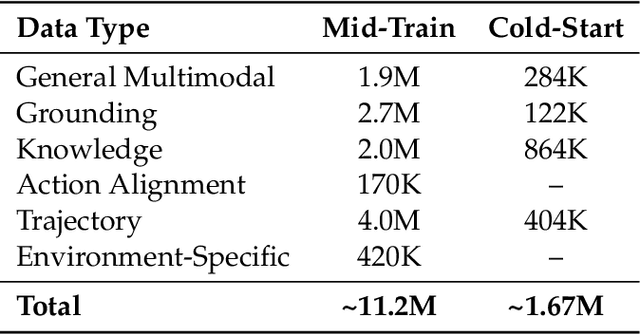
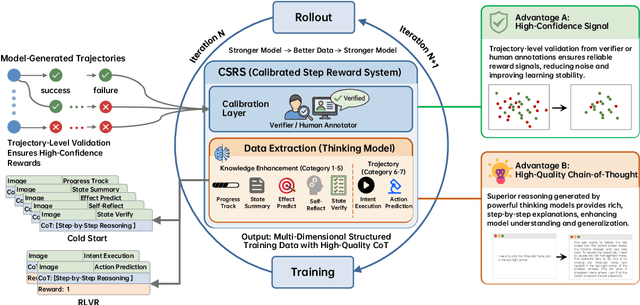

Abstract:Recent advances in multimodal large language models unlock unprecedented opportunities for GUI automation. However, a fundamental challenge remains: how to efficiently acquire high-quality training data while maintaining annotation reliability? We introduce a self-evolving training pipeline powered by the Calibrated Step Reward System, which converts model-generated trajectories into reliable training signals through trajectory-level calibration, achieving >90% annotation accuracy with 10-100x lower cost. Leveraging this pipeline, we introduce Step-GUI, a family of models (4B/8B) that achieves state-of-the-art GUI performance (8B: 80.2% AndroidWorld, 48.5% OSWorld, 62.6% ScreenShot-Pro) while maintaining robust general capabilities. As GUI agent capabilities improve, practical deployment demands standardized interfaces across heterogeneous devices while protecting user privacy. To this end, we propose GUI-MCP, the first Model Context Protocol for GUI automation with hierarchical architecture that combines low-level atomic operations and high-level task delegation to local specialist models, enabling high-privacy execution where sensitive data stays on-device. Finally, to assess whether agents can handle authentic everyday usage, we introduce AndroidDaily, a benchmark grounded in real-world mobile usage patterns with 3146 static actions and 235 end-to-end tasks across high-frequency daily scenarios (8B: static 89.91%, end-to-end 52.50%). Our work advances the development of practical GUI agents and demonstrates strong potential for real-world deployment in everyday digital interactions.
Bandwidth-Efficient Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts via Low-Rank Compensation
Dec 18, 2025



Abstract:Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) models scale capacity via sparse activation but stress memory and bandwidth. Offloading alleviates GPU memory by fetching experts on demand, yet token-level routing causes irregular transfers that make inference I/O-bound. Static uniform quantization reduces traffic but degrades accuracy under aggressive compression by ignoring expert heterogeneity. We present Bandwidth-Efficient Adaptive Mixture-of-Experts via Low-Rank Compensation, which performs router-guided precision restoration using precomputed low-rank compensators. At inference time, our method transfers compact low-rank factors with Top-n (n<k) experts per token and applies compensation to them, keeping others low-bit. Integrated with offloading on GPU and GPU-NDP systems, our method delivers a superior bandwidth-accuracy trade-off and improved throughput.
zkUnlearner: A Zero-Knowledge Framework for Verifiable Unlearning with Multi-Granularity and Forgery-Resistance
Sep 08, 2025Abstract:As the demand for exercising the "right to be forgotten" grows, the need for verifiable machine unlearning has become increasingly evident to ensure both transparency and accountability. We present {\em zkUnlearner}, the first zero-knowledge framework for verifiable machine unlearning, specifically designed to support {\em multi-granularity} and {\em forgery-resistance}. First, we propose a general computational model that employs a {\em bit-masking} technique to enable the {\em selectivity} of existing zero-knowledge proofs of training for gradient descent algorithms. This innovation enables not only traditional {\em sample-level} unlearning but also more advanced {\em feature-level} and {\em class-level} unlearning. Our model can be translated to arithmetic circuits, ensuring compatibility with a broad range of zero-knowledge proof systems. Furthermore, our approach overcomes key limitations of existing methods in both efficiency and privacy. Second, forging attacks present a serious threat to the reliability of unlearning. Specifically, in Stochastic Gradient Descent optimization, gradients from unlearned data, or from minibatches containing it, can be forged using alternative data samples or minibatches that exclude it. We propose the first effective strategies to resist state-of-the-art forging attacks. Finally, we benchmark a zkSNARK-based instantiation of our framework and perform comprehensive performance evaluations to validate its practicality.
Step-Audio 2 Technical Report
Jul 24, 2025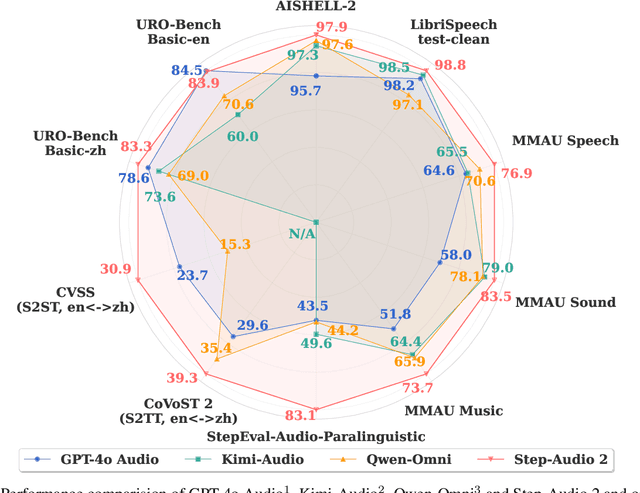

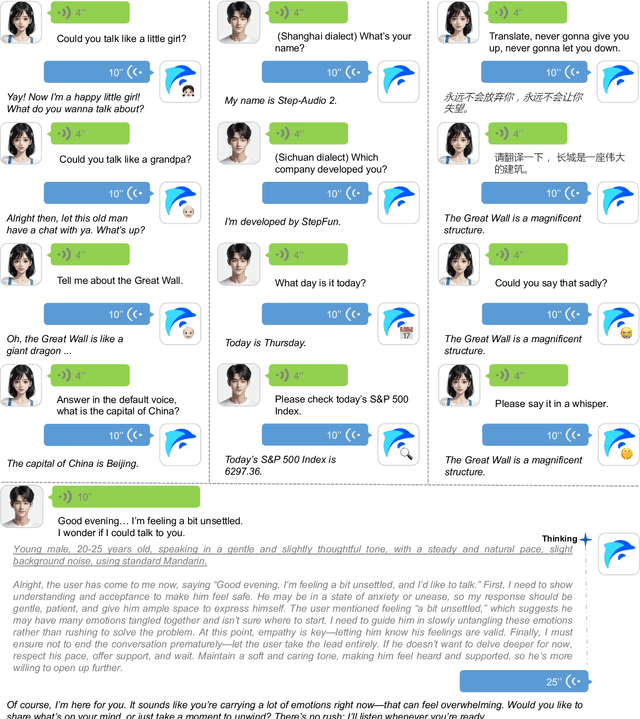

Abstract:This paper presents Step-Audio 2, an end-to-end multi-modal large language model designed for industry-strength audio understanding and speech conversation. By integrating a latent audio encoder and reasoning-centric reinforcement learning (RL), Step-Audio 2 achieves promising performance in automatic speech recognition (ASR) and audio understanding. To facilitate genuine end-to-end speech conversation, Step-Audio 2 incorporates the generation of discrete audio tokens into language modeling, significantly enhancing its responsiveness to paralinguistic information such as speaking styles and emotions. To effectively leverage the rich textual and acoustic knowledge in real-world data, Step-Audio 2 integrates retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) and is able to call external tools such as web search to mitigate hallucination and audio search to switch timbres. Trained on millions of hours of speech and audio data, Step-Audio 2 delivers intelligence and expressiveness across diverse conversational scenarios. Evaluation results demonstrate that Step-Audio 2 achieves state-of-the-art performance on various audio understanding and conversational benchmarks compared to other open-source and commercial solutions. Please visit https://github.com/stepfun-ai/Step-Audio2 for more information.
Forecast-Then-Optimize Deep Learning Methods
Jun 16, 2025Abstract:Time series forecasting underpins vital decision-making across various sectors, yet raw predictions from sophisticated models often harbor systematic errors and biases. We examine the Forecast-Then-Optimize (FTO) framework, pioneering its systematic synopsis. Unlike conventional Predict-Then-Optimize (PTO) methods, FTO explicitly refines forecasts through optimization techniques such as ensemble methods, meta-learners, and uncertainty adjustments. Furthermore, deep learning and large language models have established superiority over traditional parametric forecasting models for most enterprise applications. This paper surveys significant advancements from 2016 to 2025, analyzing mainstream deep learning FTO architectures. Focusing on real-world applications in operations management, we demonstrate FTO's crucial role in enhancing predictive accuracy, robustness, and decision efficacy. Our study establishes foundational guidelines for future forecasting methodologies, bridging theory and operational practicality.
SwiLTra-Bench: The Swiss Legal Translation Benchmark
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:In Switzerland legal translation is uniquely important due to the country's four official languages and requirements for multilingual legal documentation. However, this process traditionally relies on professionals who must be both legal experts and skilled translators -- creating bottlenecks and impacting effective access to justice. To address this challenge, we introduce SwiLTra-Bench, a comprehensive multilingual benchmark of over 180K aligned Swiss legal translation pairs comprising laws, headnotes, and press releases across all Swiss languages along with English, designed to evaluate LLM-based translation systems. Our systematic evaluation reveals that frontier models achieve superior translation performance across all document types, while specialized translation systems excel specifically in laws but under-perform in headnotes. Through rigorous testing and human expert validation, we demonstrate that while fine-tuning open SLMs significantly improves their translation quality, they still lag behind the best zero-shot prompted frontier models such as Claude-3.5-Sonnet. Additionally, we present SwiLTra-Judge, a specialized LLM evaluation system that aligns best with human expert assessments.
From Tokens to Materials: Leveraging Language Models for Scientific Discovery
Oct 21, 2024



Abstract:Exploring the predictive capabilities of language models in material science is an ongoing interest. This study investigates the application of language model embeddings to enhance material property prediction in materials science. By evaluating various contextual embedding methods and pre-trained models, including Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers (BERT) and Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPT), we demonstrate that domain-specific models, particularly MatBERT significantly outperform general-purpose models in extracting implicit knowledge from compound names and material properties. Our findings reveal that information-dense embeddings from the third layer of MatBERT, combined with a context-averaging approach, offer the most effective method for capturing material-property relationships from the scientific literature. We also identify a crucial "tokenizer effect," highlighting the importance of specialized text processing techniques that preserve complete compound names while maintaining consistent token counts. These insights underscore the value of domain-specific training and tokenization in materials science applications and offer a promising pathway for accelerating the discovery and development of new materials through AI-driven approaches.
A Benchmark on Directed Graph Representation Learning in Hardware Designs
Oct 09, 2024Abstract:To keep pace with the rapid advancements in design complexity within modern computing systems, directed graph representation learning (DGRL) has become crucial, particularly for encoding circuit netlists, computational graphs, and developing surrogate models for hardware performance prediction. However, DGRL remains relatively unexplored, especially in the hardware domain, mainly due to the lack of comprehensive and user-friendly benchmarks. This study presents a novel benchmark comprising five hardware design datasets and 13 prediction tasks spanning various levels of circuit abstraction. We evaluate 21 DGRL models, employing diverse graph neural networks and graph transformers (GTs) as backbones, enhanced by positional encodings (PEs) tailored for directed graphs. Our results highlight that bidirected (BI) message passing neural networks (MPNNs) and robust PEs significantly enhance model performance. Notably, the top-performing models include PE-enhanced GTs interleaved with BI-MPNN layers and BI-Graph Isomorphism Network, both surpassing baselines across the 13 tasks. Additionally, our investigation into out-of-distribution (OOD) performance emphasizes the urgent need to improve OOD generalization in DGRL models. This benchmark, implemented with a modular codebase, streamlines the evaluation of DGRL models for both hardware and ML practitioners
Predicting Lung Cancer Patient Prognosis with Large Language Models
Aug 15, 2024Abstract:Prognosis prediction is crucial for determining optimal treatment plans for lung cancer patients. Traditionally, such predictions relied on models developed from retrospective patient data. Recently, large language models (LLMs) have gained attention for their ability to process and generate text based on extensive learned knowledge. In this study, we evaluate the potential of GPT-4o mini and GPT-3.5 in predicting the prognosis of lung cancer patients. We collected two prognosis datasets, i.e., survival and post-operative complication datasets, and designed multiple tasks to assess the models' performance comprehensively. Logistic regression models were also developed as baselines for comparison. The experimental results demonstrate that LLMs can achieve competitive, and in some tasks superior, performance in lung cancer prognosis prediction compared to data-driven logistic regression models despite not using additional patient data. These findings suggest that LLMs can be effective tools for prognosis prediction in lung cancer, particularly when patient data is limited or unavailable.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge