Yingqiang Gao
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Direct Preference Optimization for Personalizing German Automatic Text Simplifications for Persons with Intellectual Disabilities
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:Automatic text simplification (ATS) aims to enhance language accessibility for various target groups, particularly persons with intellectual disabilities. Recent advancements in generative AI, especially large language models (LLMs), have substantially improved the quality of machine-generated text simplifications, thereby mitigating information barriers for the target group. However, existing LLM-based ATS systems do not incorporate preference feedback on text simplifications during training, resulting in a lack of personalization tailored to the specific needs of target group representatives. In this work, we extend the standard supervised fine-tuning (SFT) approach for adapting LLM-based ATS models by leveraging a computationally efficient LLM alignment technique -- direct preference optimization (DPO). Specifically, we post-train LLM-based ATS models using human feedback collected from persons with intellectual disabilities, reflecting their preferences on paired text simplifications generated by mainstream LLMs. Furthermore, we propose a pipeline for developing personalized LLM-based ATS systems, encompassing data collection, model selection, SFT and DPO post-training, and evaluation. Our findings underscore the necessity of active participation of target group persons in designing personalized AI accessibility solutions aligned with human expectations. This work represents a step towards personalizing inclusive AI systems at the target-group level, incorporating insights not only from text simplification experts but also from target group persons themselves.
Digitally Supported Analysis of Spontaneous Speech (DigiSpon): Benchmarking NLP-Supported Language Sample Analysis of Swiss Children's Speech
Apr 01, 2025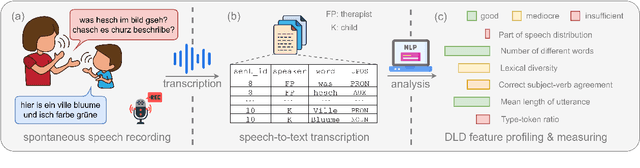
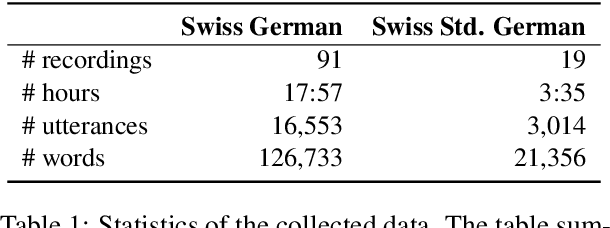

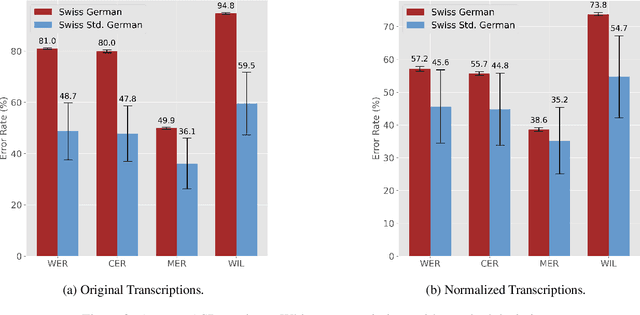
Abstract:Language sample analysis (LSA) is a process that complements standardized psychometric tests for diagnosing, for example, developmental language disorder (DLD) in children. However, its labor-intensive nature has limited its use in speech-language pathology practice. We introduce an approach that leverages natural language processing (NLP) methods not based on commercial large language models (LLMs) applied to transcribed speech data from 119 children in the German speaking part of Switzerland with typical and atypical language development. The study aims to identify optimal practices that support speech-language pathologists in diagnosing DLD more efficiently within a human-in-the-loop framework, without relying on potentially unethical implementations that leverage commercial LLMs. Preliminary findings underscore the potential of integrating locally deployed NLP methods into the process of semi-automatic LSA.
SwiLTra-Bench: The Swiss Legal Translation Benchmark
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:In Switzerland legal translation is uniquely important due to the country's four official languages and requirements for multilingual legal documentation. However, this process traditionally relies on professionals who must be both legal experts and skilled translators -- creating bottlenecks and impacting effective access to justice. To address this challenge, we introduce SwiLTra-Bench, a comprehensive multilingual benchmark of over 180K aligned Swiss legal translation pairs comprising laws, headnotes, and press releases across all Swiss languages along with English, designed to evaluate LLM-based translation systems. Our systematic evaluation reveals that frontier models achieve superior translation performance across all document types, while specialized translation systems excel specifically in laws but under-perform in headnotes. Through rigorous testing and human expert validation, we demonstrate that while fine-tuning open SLMs significantly improves their translation quality, they still lag behind the best zero-shot prompted frontier models such as Claude-3.5-Sonnet. Additionally, we present SwiLTra-Judge, a specialized LLM evaluation system that aligns best with human expert assessments.
SwissADT: An Audio Description Translation System for Swiss Languages
Nov 22, 2024Abstract:Audio description (AD) is a crucial accessibility service provided to blind persons and persons with visual impairment, designed to convey visual information in acoustic form. Despite recent advancements in multilingual machine translation research, the lack of well-crafted and time-synchronized AD data impedes the development of audio description translation (ADT) systems that address the needs of multilingual countries such as Switzerland. Furthermore, since the majority of ADT systems rely solely on text, uncertainty exists as to whether incorporating visual information from the corresponding video clips can enhance the quality of ADT outputs. In this work, we present SwissADT, the first ADT system implemented for three main Swiss languages and English. By collecting well-crafted AD data augmented with video clips in German, French, Italian, and English, and leveraging the power of Large Language Models (LLMs), we aim to enhance information accessibility for diverse language populations in Switzerland by automatically translating AD scripts to the desired Swiss language. Our extensive experimental ADT results, composed of both automatic and human evaluations of ADT quality, demonstrate the promising capability of SwissADT for the ADT task. We believe that combining human expertise with the generation power of LLMs can further enhance the performance of ADT systems, ultimately benefiting a larger multilingual target population.
Audio Description Generation in the Era of LLMs and VLMs: A Review of Transferable Generative AI Technologies
Oct 11, 2024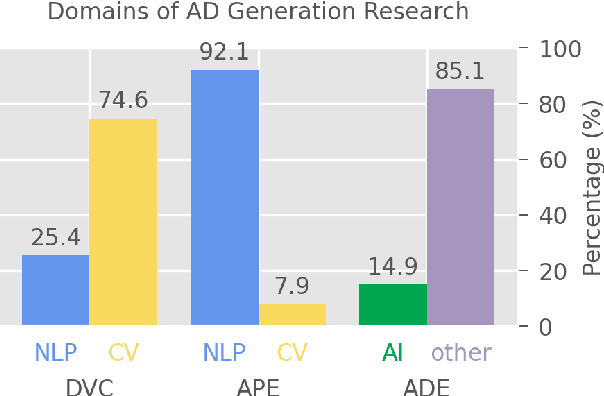


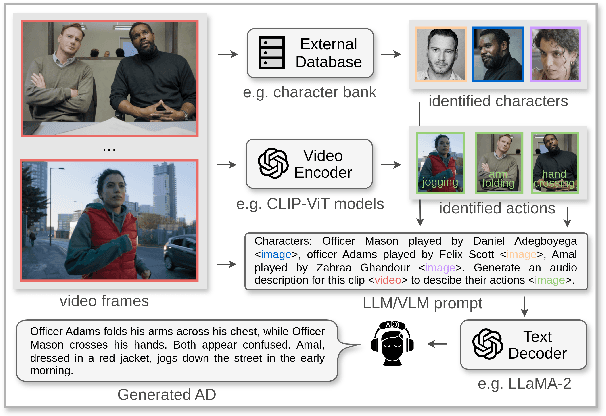
Abstract:Audio descriptions (ADs) function as acoustic commentaries designed to assist blind persons and persons with visual impairments in accessing digital media content on television and in movies, among other settings. As an accessibility service typically provided by trained AD professionals, the generation of ADs demands significant human effort, making the process both time-consuming and costly. Recent advancements in natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision (CV), particularly in large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs), have allowed for getting a step closer to automatic AD generation. This paper reviews the technologies pertinent to AD generation in the era of LLMs and VLMs: we discuss how state-of-the-art NLP and CV technologies can be applied to generate ADs and identify essential research directions for the future.
MODOC: A Modular Interface for Flexible Interlinking of Text Retrieval and Text Generation Functions
Aug 26, 2024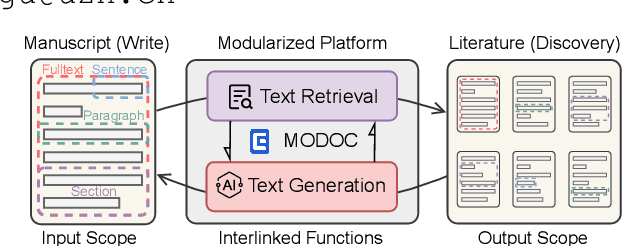
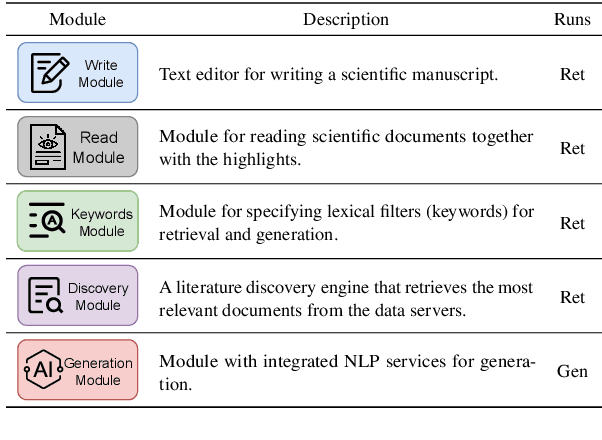
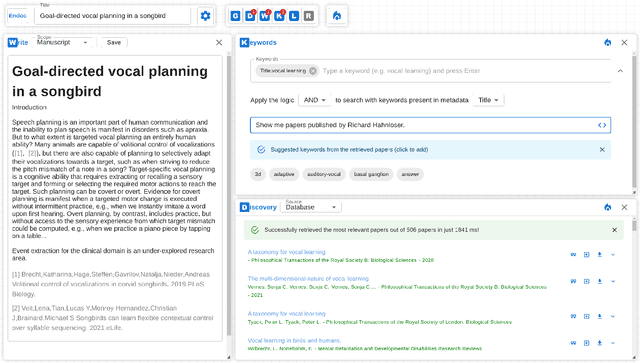
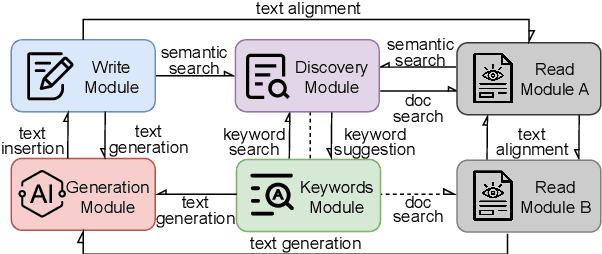
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) produce eloquent texts but often the content they generate needs to be verified. Traditional information retrieval systems can assist with this task, but most systems have not been designed with LLM-generated queries in mind. As such, there is a compelling need for integrated systems that provide both retrieval and generation functionality within a single user interface. We present MODOC, a modular user interface that leverages the capabilities of LLMs and provides assistance with detecting their confabulations, promoting integrity in scientific writing. MODOC represents a significant step forward in scientific writing assistance. Its modular architecture supports flexible functions for retrieving information and for writing and generating text in a single, user-friendly interface.
MemSum-DQA: Adapting An Efficient Long Document Extractive Summarizer for Document Question Answering
Oct 10, 2023Abstract:We introduce MemSum-DQA, an efficient system for document question answering (DQA) that leverages MemSum, a long document extractive summarizer. By prefixing each text block in the parsed document with the provided question and question type, MemSum-DQA selectively extracts text blocks as answers from documents. On full-document answering tasks, this approach yields a 9% improvement in exact match accuracy over prior state-of-the-art baselines. Notably, MemSum-DQA excels in addressing questions related to child-relationship understanding, underscoring the potential of extractive summarization techniques for DQA tasks.
Unsupervised Scientific Abstract Segmentation with Normalized Mutual Information
May 19, 2023Abstract:The abstracts of scientific papers consist of premises and conclusions. Structured abstracts explicitly highlight the conclusion sentences, whereas non-structured abstracts may have conclusion sentences at uncertain positions. This implicit nature of conclusion positions makes the automatic segmentation of scientific abstracts into premises and conclusions a challenging task. In this work, we empirically explore using Normalized Mutual Information (NMI) for abstract segmentation. We consider each abstract as a recurrent cycle of sentences and place segmentation boundaries by greedily optimizing the NMI score between premises and conclusions. On non-structured abstracts, our proposed unsupervised approach GreedyCAS achieves the best performance across all evaluation metrics; on structured abstracts, GreedyCAS outperforms all baseline methods measured by $P_k$. The strong correlation of NMI to our evaluation metrics reveals the effectiveness of NMI for abstract segmentation.
Local Citation Recommendation with Hierarchical-Attention Text Encoder and SciBERT-based Reranking
Dec 02, 2021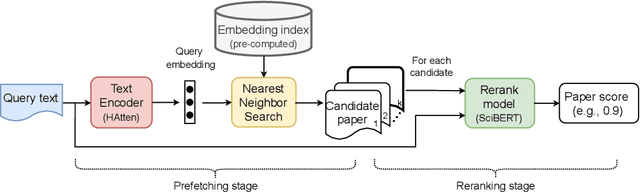
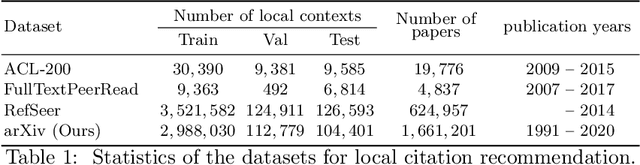
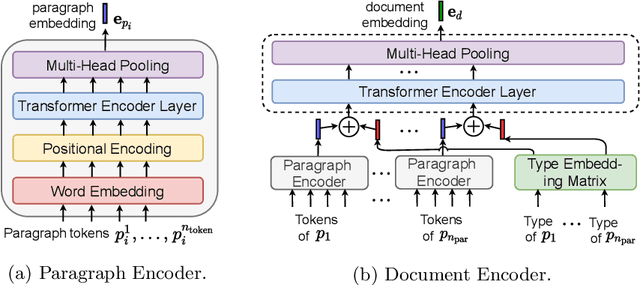
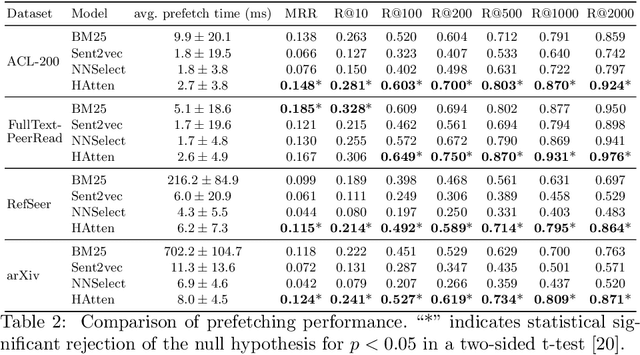
Abstract:The goal of local citation recommendation is to recommend a missing reference from the local citation context and optionally also from the global context. To balance the tradeoff between speed and accuracy of citation recommendation in the context of a large-scale paper database, a viable approach is to first prefetch a limited number of relevant documents using efficient ranking methods and then to perform a fine-grained reranking using more sophisticated models. In that vein, BM25 has been found to be a tough-to-beat approach to prefetching, which is why recent work has focused mainly on the reranking step. Even so, we explore prefetching with nearest neighbor search among text embeddings constructed by a hierarchical attention network. When coupled with a SciBERT reranker fine-tuned on local citation recommendation tasks, our hierarchical Attention encoder (HAtten) achieves high prefetch recall for a given number of candidates to be reranked. Consequently, our reranker needs to rerank fewer prefetch candidates, yet still achieves state-of-the-art performance on various local citation recommendation datasets such as ACL-200, FullTextPeerRead, RefSeer, and arXiv.
Character-Level Translation with Self-attention
Apr 30, 2020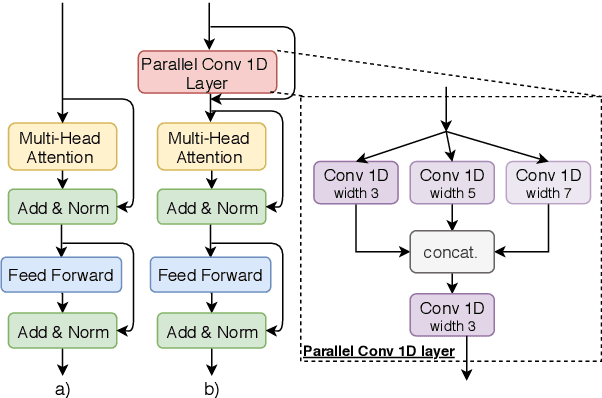
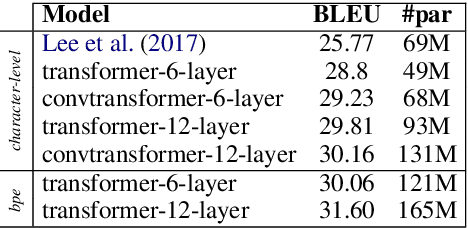
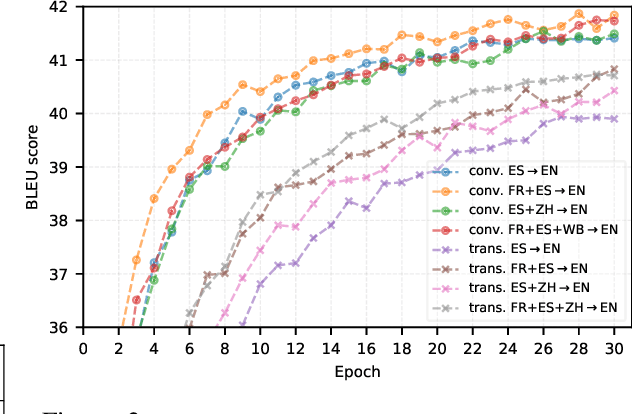
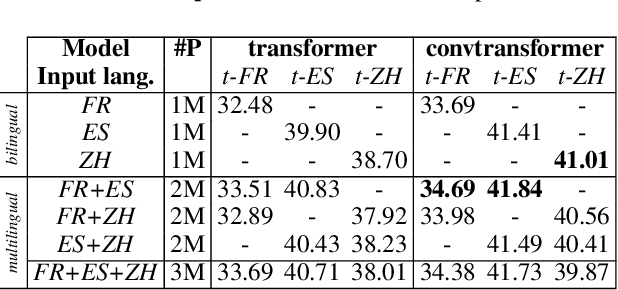
Abstract:We explore the suitability of self-attention models for character-level neural machine translation. We test the standard transformer model, as well as a novel variant in which the encoder block combines information from nearby characters using convolutions. We perform extensive experiments on WMT and UN datasets, testing both bilingual and multilingual translation to English using up to three input languages (French, Spanish, and Chinese). Our transformer variant consistently outperforms the standard transformer at the character-level and converges faster while learning more robust character-level alignments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge