Alexa Lintner
SwissADT: An Audio Description Translation System for Swiss Languages
Nov 22, 2024Abstract:Audio description (AD) is a crucial accessibility service provided to blind persons and persons with visual impairment, designed to convey visual information in acoustic form. Despite recent advancements in multilingual machine translation research, the lack of well-crafted and time-synchronized AD data impedes the development of audio description translation (ADT) systems that address the needs of multilingual countries such as Switzerland. Furthermore, since the majority of ADT systems rely solely on text, uncertainty exists as to whether incorporating visual information from the corresponding video clips can enhance the quality of ADT outputs. In this work, we present SwissADT, the first ADT system implemented for three main Swiss languages and English. By collecting well-crafted AD data augmented with video clips in German, French, Italian, and English, and leveraging the power of Large Language Models (LLMs), we aim to enhance information accessibility for diverse language populations in Switzerland by automatically translating AD scripts to the desired Swiss language. Our extensive experimental ADT results, composed of both automatic and human evaluations of ADT quality, demonstrate the promising capability of SwissADT for the ADT task. We believe that combining human expertise with the generation power of LLMs can further enhance the performance of ADT systems, ultimately benefiting a larger multilingual target population.
Audio Description Generation in the Era of LLMs and VLMs: A Review of Transferable Generative AI Technologies
Oct 11, 2024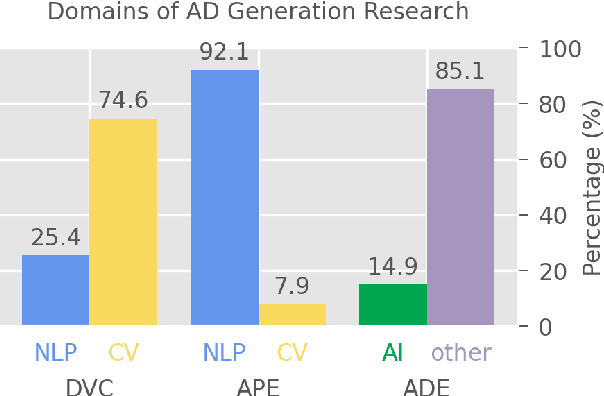


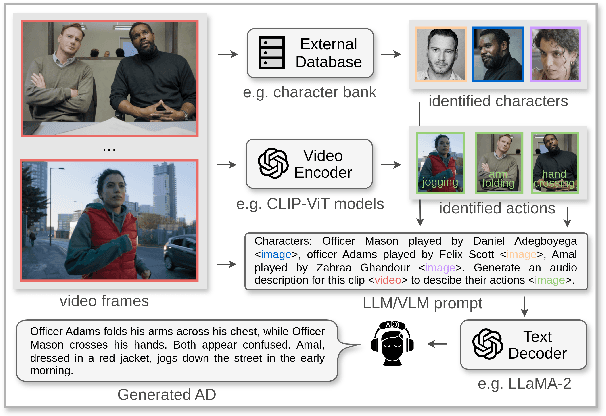
Abstract:Audio descriptions (ADs) function as acoustic commentaries designed to assist blind persons and persons with visual impairments in accessing digital media content on television and in movies, among other settings. As an accessibility service typically provided by trained AD professionals, the generation of ADs demands significant human effort, making the process both time-consuming and costly. Recent advancements in natural language processing (NLP) and computer vision (CV), particularly in large language models (LLMs) and vision-language models (VLMs), have allowed for getting a step closer to automatic AD generation. This paper reviews the technologies pertinent to AD generation in the era of LLMs and VLMs: we discuss how state-of-the-art NLP and CV technologies can be applied to generate ADs and identify essential research directions for the future.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge