Nianlong Gu
MODOC: A Modular Interface for Flexible Interlinking of Text Retrieval and Text Generation Functions
Aug 26, 2024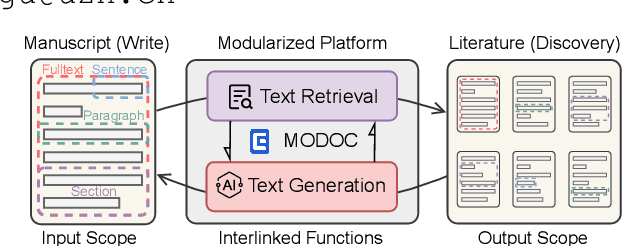
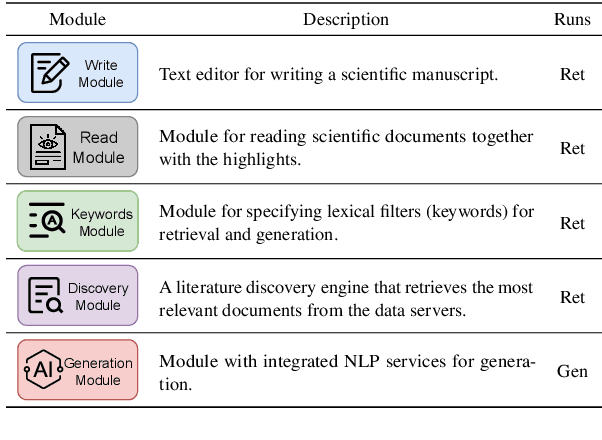
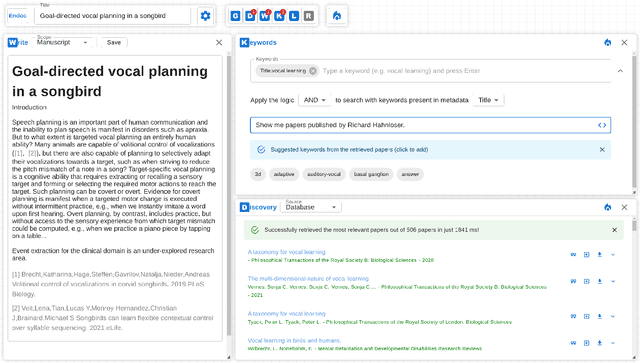
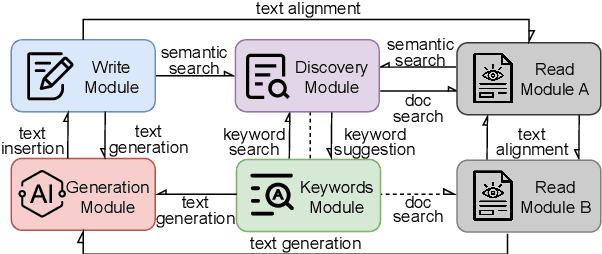
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) produce eloquent texts but often the content they generate needs to be verified. Traditional information retrieval systems can assist with this task, but most systems have not been designed with LLM-generated queries in mind. As such, there is a compelling need for integrated systems that provide both retrieval and generation functionality within a single user interface. We present MODOC, a modular user interface that leverages the capabilities of LLMs and provides assistance with detecting their confabulations, promoting integrity in scientific writing. MODOC represents a significant step forward in scientific writing assistance. Its modular architecture supports flexible functions for retrieving information and for writing and generating text in a single, user-friendly interface.
Large language models surpass human experts in predicting neuroscience results
Mar 14, 2024Abstract:Scientific discoveries often hinge on synthesizing decades of research, a task that potentially outstrips human information processing capacities. Large language models (LLMs) offer a solution. LLMs trained on the vast scientific literature could potentially integrate noisy yet interrelated findings to forecast novel results better than human experts. To evaluate this possibility, we created BrainBench, a forward-looking benchmark for predicting neuroscience results. We find that LLMs surpass experts in predicting experimental outcomes. BrainGPT, an LLM we tuned on the neuroscience literature, performed better yet. Like human experts, when LLMs were confident in their predictions, they were more likely to be correct, which presages a future where humans and LLMs team together to make discoveries. Our approach is not neuroscience-specific and is transferable to other knowledge-intensive endeavors.
MemSum-DQA: Adapting An Efficient Long Document Extractive Summarizer for Document Question Answering
Oct 10, 2023Abstract:We introduce MemSum-DQA, an efficient system for document question answering (DQA) that leverages MemSum, a long document extractive summarizer. By prefixing each text block in the parsed document with the provided question and question type, MemSum-DQA selectively extracts text blocks as answers from documents. On full-document answering tasks, this approach yields a 9% improvement in exact match accuracy over prior state-of-the-art baselines. Notably, MemSum-DQA excels in addressing questions related to child-relationship understanding, underscoring the potential of extractive summarization techniques for DQA tasks.
SciLit: A Platform for Joint Scientific Literature Discovery, Summarization and Citation Generation
Jun 06, 2023Abstract:Scientific writing involves retrieving, summarizing, and citing relevant papers, which can be time-consuming processes in large and rapidly evolving fields. By making these processes inter-operable, natural language processing (NLP) provides opportunities for creating end-to-end assistive writing tools. We propose SciLit, a pipeline that automatically recommends relevant papers, extracts highlights, and suggests a reference sentence as a citation of a paper, taking into consideration the user-provided context and keywords. SciLit efficiently recommends papers from large databases of hundreds of millions of papers using a two-stage pre-fetching and re-ranking literature search system that flexibly deals with addition and removal of a paper database. We provide a convenient user interface that displays the recommended papers as extractive summaries and that offers abstractively-generated citing sentences which are aligned with the provided context and which mention the chosen keyword(s). Our assistive tool for literature discovery and scientific writing is available at https://scilit.vercel.app
Unsupervised Scientific Abstract Segmentation with Normalized Mutual Information
May 19, 2023Abstract:The abstracts of scientific papers consist of premises and conclusions. Structured abstracts explicitly highlight the conclusion sentences, whereas non-structured abstracts may have conclusion sentences at uncertain positions. This implicit nature of conclusion positions makes the automatic segmentation of scientific abstracts into premises and conclusions a challenging task. In this work, we empirically explore using Normalized Mutual Information (NMI) for abstract segmentation. We consider each abstract as a recurrent cycle of sentences and place segmentation boundaries by greedily optimizing the NMI score between premises and conclusions. On non-structured abstracts, our proposed unsupervised approach GreedyCAS achieves the best performance across all evaluation metrics; on structured abstracts, GreedyCAS outperforms all baseline methods measured by $P_k$. The strong correlation of NMI to our evaluation metrics reveals the effectiveness of NMI for abstract segmentation.
Legal Extractive Summarization of U.S. Court Opinions
May 15, 2023



Abstract:This paper tackles the task of legal extractive summarization using a dataset of 430K U.S. court opinions with key passages annotated. According to automated summary quality metrics, the reinforcement-learning-based MemSum model is best and even out-performs transformer-based models. In turn, expert human evaluation shows that MemSum summaries effectively capture the key points of lengthy court opinions. Motivated by these results, we open-source our models to the general public. This represents progress towards democratizing law and making U.S. court opinions more accessible to the general public.
Controllable Citation Text Generation
Nov 14, 2022



Abstract:The aim of citation generation is usually to automatically generate a citation sentence that refers to a chosen paper in the context of a manuscript. However, a rigid citation generation process is at odds with an author's desire to control the generated text based on certain attributes, such as 1) the citation intent of e.g. either introducing background information or comparing results; 2) keywords that should appear in the citation text; or 3) specific sentences in the cited paper that characterize the citation content. To provide these degrees of freedom, we present a controllable citation generation system. In data from a large corpus, we first parse the attributes of each citation sentence and use these as additional input sources during training of the BART-based abstractive summarizer. We further develop an attribute suggestion module that infers the citation intent and suggests relevant keywords and sentences that users can select to tune the generation. Our framework gives users more control over generated citations, outperforming citation generation models without attribute awareness in both ROUGE and human evaluations.
Local Citation Recommendation with Hierarchical-Attention Text Encoder and SciBERT-based Reranking
Dec 02, 2021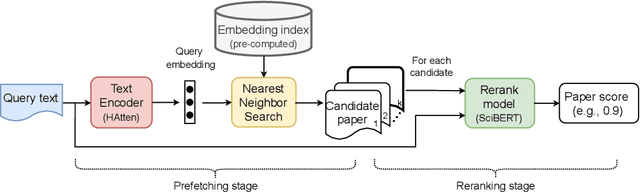
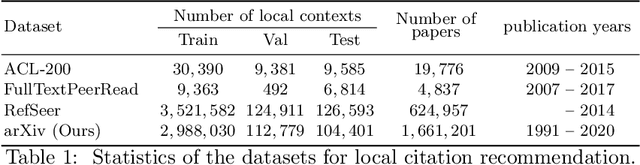
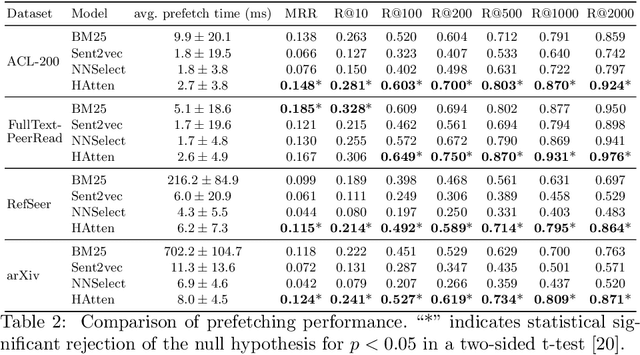
Abstract:The goal of local citation recommendation is to recommend a missing reference from the local citation context and optionally also from the global context. To balance the tradeoff between speed and accuracy of citation recommendation in the context of a large-scale paper database, a viable approach is to first prefetch a limited number of relevant documents using efficient ranking methods and then to perform a fine-grained reranking using more sophisticated models. In that vein, BM25 has been found to be a tough-to-beat approach to prefetching, which is why recent work has focused mainly on the reranking step. Even so, we explore prefetching with nearest neighbor search among text embeddings constructed by a hierarchical attention network. When coupled with a SciBERT reranker fine-tuned on local citation recommendation tasks, our hierarchical Attention encoder (HAtten) achieves high prefetch recall for a given number of candidates to be reranked. Consequently, our reranker needs to rerank fewer prefetch candidates, yet still achieves state-of-the-art performance on various local citation recommendation datasets such as ACL-200, FullTextPeerRead, RefSeer, and arXiv.
MemSum: Extractive Summarization of Long Documents using Multi-step Episodic Markov Decision Processes
Jul 19, 2021



Abstract:We introduce MemSum (Multi-step Episodic Markov decision process extractive SUMmarizer), a reinforcement-learning-based extractive summarizer enriched at any given time step with information on the current extraction history. Similar to previous models in this vein, MemSum iteratively selects sentences into the summary. Our innovation is in considering a broader information set when summarizing that would intuitively also be used by humans in this task: 1) the text content of the sentence, 2) the global text context of the rest of the document, and 3) the extraction history consisting of the set of sentences that have already been extracted. With a lightweight architecture, MemSum nonetheless obtains state-of-the-art test-set performance (ROUGE score) on long document datasets (PubMed, arXiv, and GovReport). Supporting analysis demonstrates that the added awareness of extraction history gives MemSum robustness against redundancy in the source document.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge