Beatrice Brown-Mulry
Feature Quality and Adaptability of Medical Foundation Models: A Comparative Evaluation for Radiographic Classification and Segmentation
Nov 12, 2025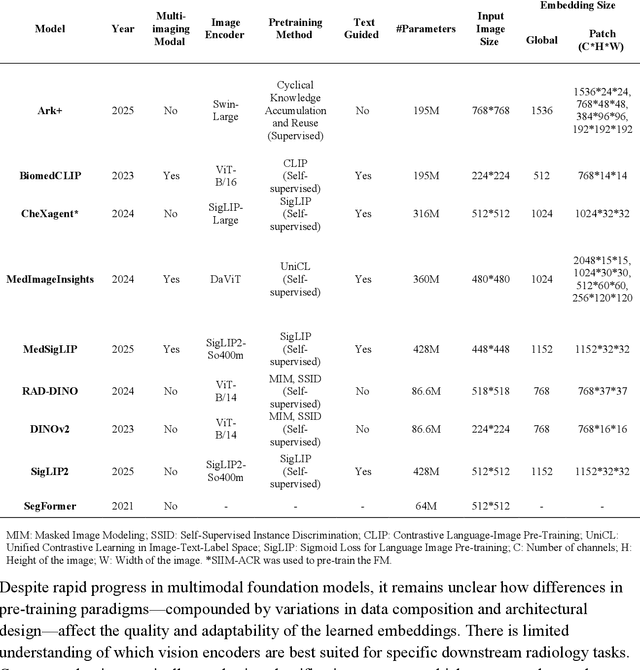
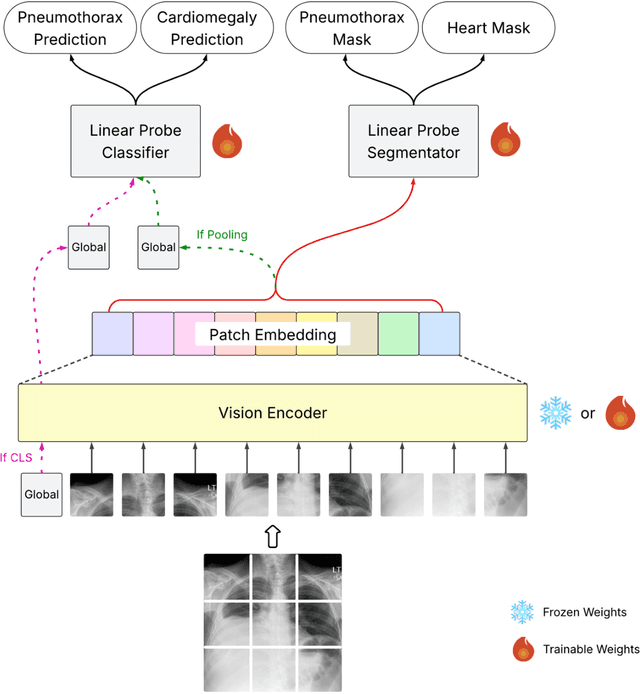
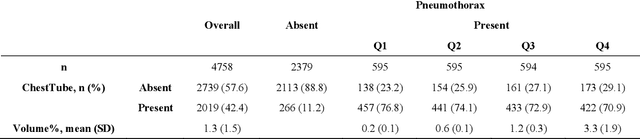
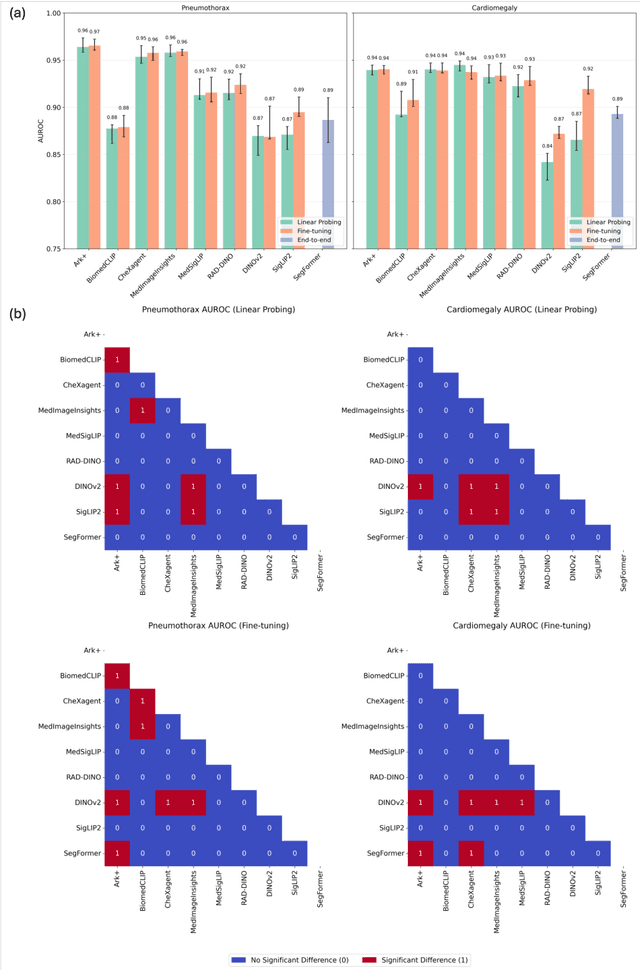
Abstract:Foundation models (FMs) promise to generalize medical imaging, but their effectiveness varies. It remains unclear how pre-training domain (medical vs. general), paradigm (e.g., text-guided), and architecture influence embedding quality, hindering the selection of optimal encoders for specific radiology tasks. To address this, we evaluate vision encoders from eight medical and general-domain FMs for chest X-ray analysis. We benchmark classification (pneumothorax, cardiomegaly) and segmentation (pneumothorax, cardiac boundary) using linear probing and fine-tuning. Our results show that domain-specific pre-training provides a significant advantage; medical FMs consistently outperformed general-domain models in linear probing, establishing superior initial feature quality. However, feature utility is highly task-dependent. Pre-trained embeddings were strong for global classification and segmenting salient anatomy (e.g., heart). In contrast, for segmenting complex, subtle pathologies (e.g., pneumothorax), all FMs performed poorly without significant fine-tuning, revealing a critical gap in localizing subtle disease. Subgroup analysis showed FMs use confounding shortcuts (e.g., chest tubes for pneumothorax) for classification, a strategy that fails for precise segmentation. We also found that expensive text-image alignment is not a prerequisite; image-only (RAD-DINO) and label-supervised (Ark+) FMs were among top performers. Notably, a supervised, end-to-end baseline remained highly competitive, matching or exceeding the best FMs on segmentation tasks. These findings show that while medical pre-training is beneficial, architectural choices (e.g., multi-scale) are critical, and pre-trained features are not universally effective, especially for complex localization tasks where supervised models remain a strong alternative.
A Multi-Modal AI System for Screening Mammography: Integrating 2D and 3D Imaging to Improve Breast Cancer Detection in a Prospective Clinical Study
Apr 08, 2025
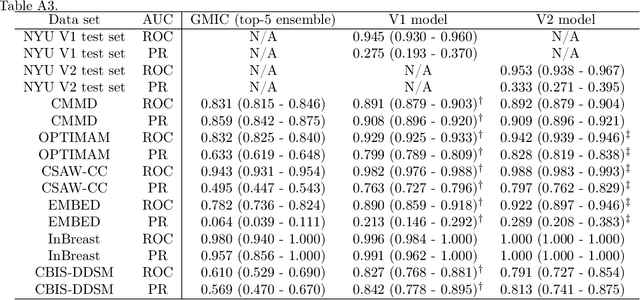
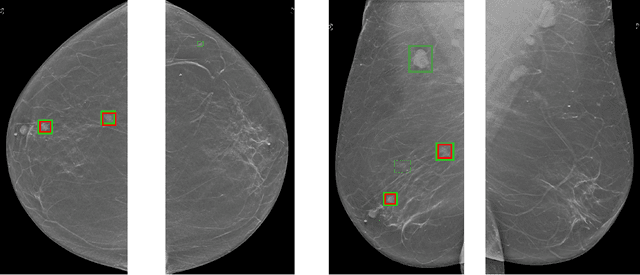
Abstract:Although digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) improves diagnostic performance over full-field digital mammography (FFDM), false-positive recalls remain a concern in breast cancer screening. We developed a multi-modal artificial intelligence system integrating FFDM, synthetic mammography, and DBT to provide breast-level predictions and bounding-box localizations of suspicious findings. Our AI system, trained on approximately 500,000 mammography exams, achieved 0.945 AUROC on an internal test set. It demonstrated capacity to reduce recalls by 31.7% and radiologist workload by 43.8% while maintaining 100% sensitivity, underscoring its potential to improve clinical workflows. External validation confirmed strong generalizability, reducing the gap to a perfect AUROC by 35.31%-69.14% relative to strong baselines. In prospective deployment across 18 sites, the system reduced recall rates for low-risk cases. An improved version, trained on over 750,000 exams with additional labels, further reduced the gap by 18.86%-56.62% across large external datasets. Overall, these results underscore the importance of utilizing all available imaging modalities, demonstrate the potential for clinical impact, and indicate feasibility of further reduction of the test error with increased training set when using large-capacity neural networks.
Subgroup Performance of a Commercial Digital Breast Tomosynthesis Model for Breast Cancer Detection
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:While research has established the potential of AI models for mammography to improve breast cancer screening outcomes, there have not been any detailed subgroup evaluations performed to assess the strengths and weaknesses of commercial models for digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) imaging. This study presents a granular evaluation of the Lunit INSIGHT DBT model on a large retrospective cohort of 163,449 screening mammography exams from the Emory Breast Imaging Dataset (EMBED). Model performance was evaluated in a binary context with various negative exam types (162,081 exams) compared against screen detected cancers (1,368 exams) as the positive class. The analysis was stratified across demographic, imaging, and pathologic subgroups to identify potential disparities. The model achieved an overall AUC of 0.91 (95% CI: 0.90-0.92) with a precision of 0.08 (95% CI: 0.08-0.08), and a recall of 0.73 (95% CI: 0.71-0.76). Performance was found to be robust across demographics, but cases with non-invasive cancers (AUC: 0.85, 95% CI: 0.83-0.87), calcifications (AUC: 0.80, 95% CI: 0.78-0.82), and dense breast tissue (AUC: 0.90, 95% CI: 0.88-0.91) were associated with significantly lower performance compared to other groups. These results highlight the need for detailed evaluation of model characteristics and vigilance in considering adoption of new tools for clinical deployment.
Novel AI-Based Quantification of Breast Arterial Calcification to Predict Cardiovascular Risk
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:Women are underdiagnosed and undertreated for cardiovascular disease. Automatic quantification of breast arterial calcification on screening mammography can identify women at risk for cardiovascular disease and enable earlier treatment and management of disease. In this retrospective study of 116,135 women from two healthcare systems, a transformer-based neural network quantified BAC severity (no BAC, mild, moderate, and severe) on screening mammograms. Outcomes included major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) and all-cause mortality. BAC severity was independently associated with MACE after adjusting for cardiovascular risk factors, with increasing hazard ratios from mild (HR 1.18-1.22), moderate (HR 1.38-1.47), to severe BAC (HR 2.03-2.22) across datasets (all p<0.001). This association remained significant across all age groups, with even mild BAC indicating increased risk in women under 50. BAC remained an independent predictor when analyzed alongside ASCVD risk scores, showing significant associations with myocardial infarction, stroke, heart failure, and mortality (all p<0.005). Automated BAC quantification enables opportunistic cardiovascular risk assessment during routine mammography without additional radiation or cost. This approach provides value beyond traditional risk factors, particularly in younger women, offering potential for early CVD risk stratification in the millions of women undergoing annual mammography.
Emory Knee Radiograph (MRKR) Dataset
Oct 30, 2024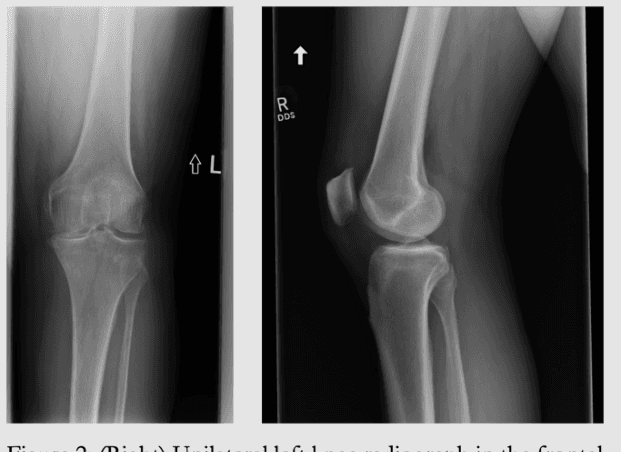
Abstract:The Emory Knee Radiograph (MRKR) dataset is a large, demographically diverse collection of 503,261 knee radiographs from 83,011 patients, 40% of which are African American. This dataset provides imaging data in DICOM format along with detailed clinical information, including patient-reported pain scores, diagnostic codes, and procedural codes, which are not commonly available in similar datasets. The MRKR dataset also features imaging metadata such as image laterality, view type, and presence of hardware, enhancing its value for research and model development. MRKR addresses significant gaps in existing datasets by offering a more representative sample for studying osteoarthritis and related outcomes, particularly among minority populations, thereby providing a valuable resource for clinicians and researchers.
Performance Gaps of Artificial Intelligence Models Screening Mammography -- Towards Fair and Interpretable Models
May 08, 2023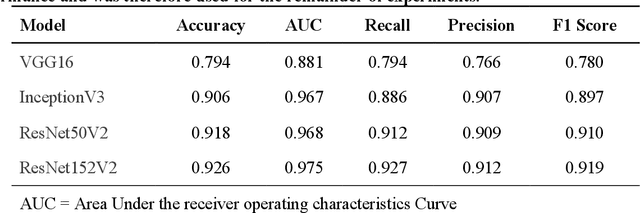
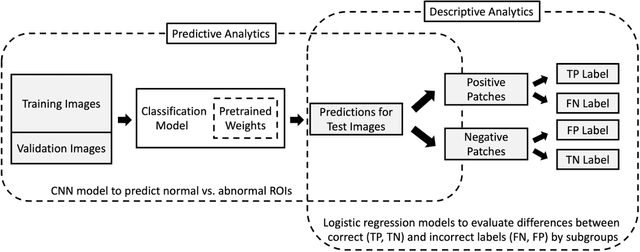
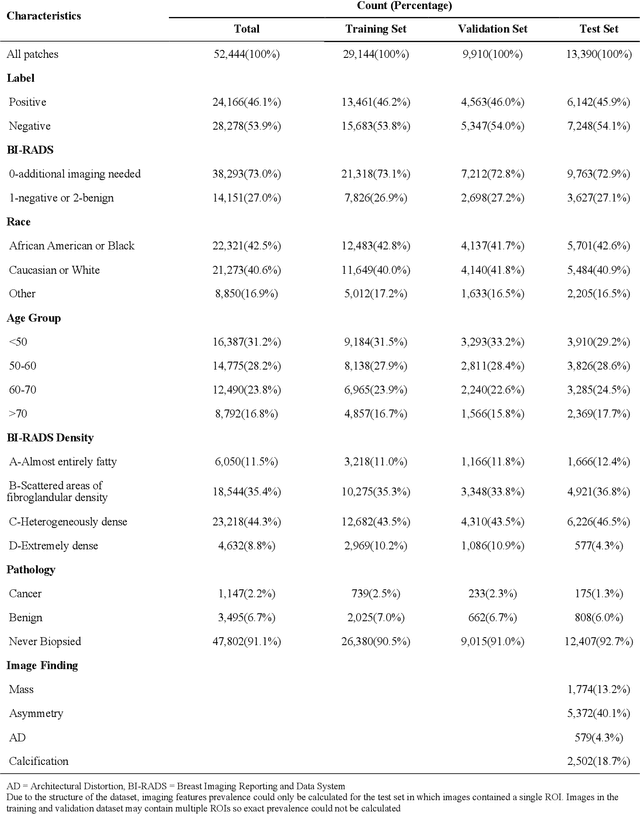
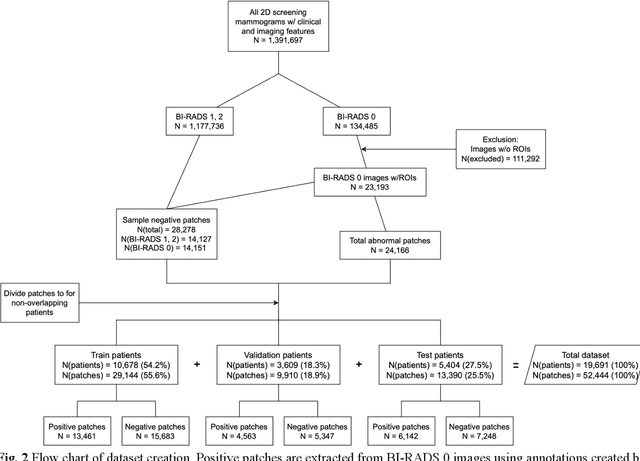
Abstract:Purpose: To analyze the demographic and imaging characteristics associated with increased risk of failure for abnormality classification in screening mammograms. Materials and Methods: This retrospective study used data from the Emory BrEast Imaging Dataset (EMBED) which includes mammograms from 115,931 patients imaged at Emory University Healthcare between 2013 to 2020. Clinical and imaging data includes Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS) assessment, region of interest coordinates for abnormalities, imaging features, pathologic outcomes, and patient demographics. Multiple deep learning models were developed to distinguish between patches of abnormal tissue and randomly selected patches of normal tissue from the screening mammograms. We assessed model performance overall and within subgroups defined by age, race, pathologic outcome, and imaging characteristics to evaluate reasons for misclassifications. Results: On a test set size of 5,810 studies (13,390 patches), a ResNet152V2 model trained to classify normal versus abnormal tissue patches achieved an accuracy of 92.6% (95% CI = 92.0-93.2%), and area under the receiver operative characteristics curve 0.975 (95% CI = 0.972-0.978). Imaging characteristics associated with higher misclassifications of images include higher tissue densities (risk ratio [RR]=1.649; p=.010, BI-RADS density C and RR=2.026; p=.003, BI-RADS density D), and presence of architectural distortion (RR=1.026; p<.001). Conclusion: Even though deep learning models for abnormality classification can perform well in screening mammography, we demonstrate certain imaging features that result in worse model performance. This is the first such work to systematically evaluate breast abnormality classification by various subgroups and better-informed developers and end-users of population subgroups which are likely to experience biased model performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge