Piotr Gaiński
Torsional-GFN: a conditional conformation generator for small molecules
Jul 15, 2025Abstract:Generating stable molecular conformations is crucial in several drug discovery applications, such as estimating the binding affinity of a molecule to a target. Recently, generative machine learning methods have emerged as a promising, more efficient method than molecular dynamics for sampling of conformations from the Boltzmann distribution. In this paper, we introduce Torsional-GFN, a conditional GFlowNet specifically designed to sample conformations of molecules proportionally to their Boltzmann distribution, using only a reward function as training signal. Conditioned on a molecular graph and its local structure (bond lengths and angles), Torsional-GFN samples rotations of its torsion angles. Our results demonstrate that Torsional-GFN is able to sample conformations approximately proportional to the Boltzmann distribution for multiple molecules with a single model, and allows for zero-shot generalization to unseen bond lengths and angles coming from the MD simulations for such molecules. Our work presents a promising avenue for scaling the proposed approach to larger molecular systems, achieving zero-shot generalization to unseen molecules, and including the generation of the local structure into the GFlowNet model.
Chimera: Accurate retrosynthesis prediction by ensembling models with diverse inductive biases
Dec 06, 2024



Abstract:Planning and conducting chemical syntheses remains a major bottleneck in the discovery of functional small molecules, and prevents fully leveraging generative AI for molecular inverse design. While early work has shown that ML-based retrosynthesis models can predict reasonable routes, their low accuracy for less frequent, yet important reactions has been pointed out. As multi-step search algorithms are limited to reactions suggested by the underlying model, the applicability of those tools is inherently constrained by the accuracy of retrosynthesis prediction. Inspired by how chemists use different strategies to ideate reactions, we propose Chimera: a framework for building highly accurate reaction models that combine predictions from diverse sources with complementary inductive biases using a learning-based ensembling strategy. We instantiate the framework with two newly developed models, which already by themselves achieve state of the art in their categories. Through experiments across several orders of magnitude in data scale and time-splits, we show Chimera outperforms all major models by a large margin, owing both to the good individual performance of its constituents, but also to the scalability of our ensembling strategy. Moreover, we find that PhD-level organic chemists prefer predictions from Chimera over baselines in terms of quality. Finally, we transfer the largest-scale checkpoint to an internal dataset from a major pharmaceutical company, showing robust generalization under distribution shift. With the new dimension that our framework unlocks, we anticipate further acceleration in the development of even more accurate models.
RetroGFN: Diverse and Feasible Retrosynthesis using GFlowNets
Jun 26, 2024Abstract:Single-step retrosynthesis aims to predict a set of reactions that lead to the creation of a target molecule, which is a crucial task in molecular discovery. Although a target molecule can often be synthesized with multiple different reactions, it is not clear how to verify the feasibility of a reaction, because the available datasets cover only a tiny fraction of the possible solutions. Consequently, the existing models are not encouraged to explore the space of possible reactions sufficiently. In this paper, we propose a novel single-step retrosynthesis model, RetroGFN, that can explore outside the limited dataset and return a diverse set of feasible reactions by leveraging a feasibility proxy model during the training. We show that RetroGFN achieves competitive results on standard top-k accuracy while outperforming existing methods on round-trip accuracy. Moreover, we provide empirical arguments in favor of using round-trip accuracy which expands the notion of feasibility with respect to the standard top-k accuracy metric.
Re-evaluating Retrosynthesis Algorithms with Syntheseus
Oct 30, 2023Abstract:The planning of how to synthesize molecules, also known as retrosynthesis, has been a growing focus of the machine learning and chemistry communities in recent years. Despite the appearance of steady progress, we argue that imperfect benchmarks and inconsistent comparisons mask systematic shortcomings of existing techniques. To remedy this, we present a benchmarking library called syntheseus which promotes best practice by default, enabling consistent meaningful evaluation of single-step and multi-step retrosynthesis algorithms. We use syntheseus to re-evaluate a number of previous retrosynthesis algorithms, and find that the ranking of state-of-the-art models changes when evaluated carefully. We end with guidance for future works in this area.
ChiENN: Embracing Molecular Chirality with Graph Neural Networks
Jul 10, 2023Abstract:Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) play a fundamental role in many deep learning problems, in particular in cheminformatics. However, typical GNNs cannot capture the concept of chirality, which means they do not distinguish between the 3D graph of a chemical compound and its mirror image (enantiomer). The ability to distinguish between enantiomers is important especially in drug discovery because enantiomers can have very distinct biochemical properties. In this paper, we propose a theoretically justified message-passing scheme, which makes GNNs sensitive to the order of node neighbors. We apply that general concept in the context of molecular chirality to construct Chiral Edge Neural Network (ChiENN) layer which can be appended to any GNN model to enable chirality-awareness. Our experiments show that adding ChiENN layers to a GNN outperforms current state-of-the-art methods in chiral-sensitive molecular property prediction tasks.
Step by Step Loss Goes Very Far: Multi-Step Quantization for Adversarial Text Attacks
Feb 10, 2023



Abstract:We propose a novel gradient-based attack against transformer-based language models that searches for an adversarial example in a continuous space of token probabilities. Our algorithm mitigates the gap between adversarial loss for continuous and discrete text representations by performing multi-step quantization in a quantization-compensation loop. Experiments show that our method significantly outperforms other approaches on various natural language processing (NLP) tasks.
Relative Molecule Self-Attention Transformer
Oct 12, 2021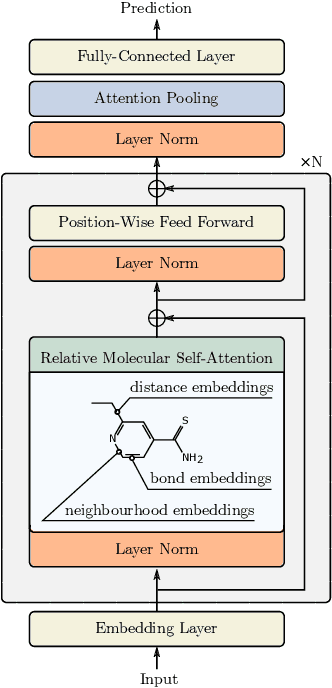
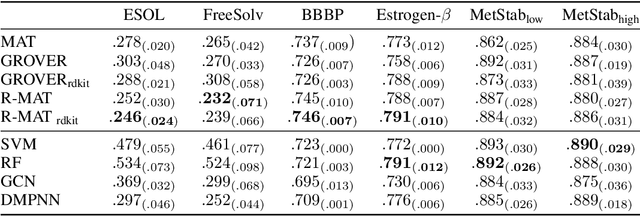
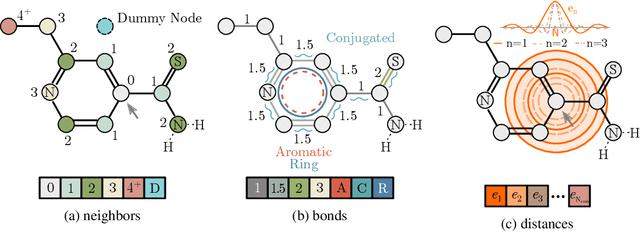
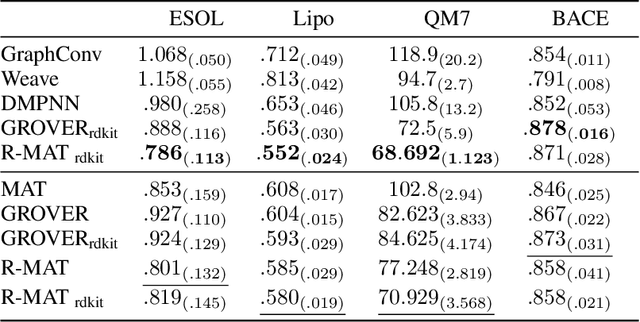
Abstract:Self-supervised learning holds promise to revolutionize molecule property prediction - a central task to drug discovery and many more industries - by enabling data efficient learning from scarce experimental data. Despite significant progress, non-pretrained methods can be still competitive in certain settings. We reason that architecture might be a key bottleneck. In particular, enriching the backbone architecture with domain-specific inductive biases has been key for the success of self-supervised learning in other domains. In this spirit, we methodologically explore the design space of the self-attention mechanism tailored to molecular data. We identify a novel variant of self-attention adapted to processing molecules, inspired by the relative self-attention layer, which involves fusing embedded graph and distance relationships between atoms. Our main contribution is Relative Molecule Attention Transformer (R-MAT): a novel Transformer-based model based on the developed self-attention layer that achieves state-of-the-art or very competitive results across a~wide range of molecule property prediction tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge