Mang Wang
Baichuan-M1: Pushing the Medical Capability of Large Language Models
Feb 18, 2025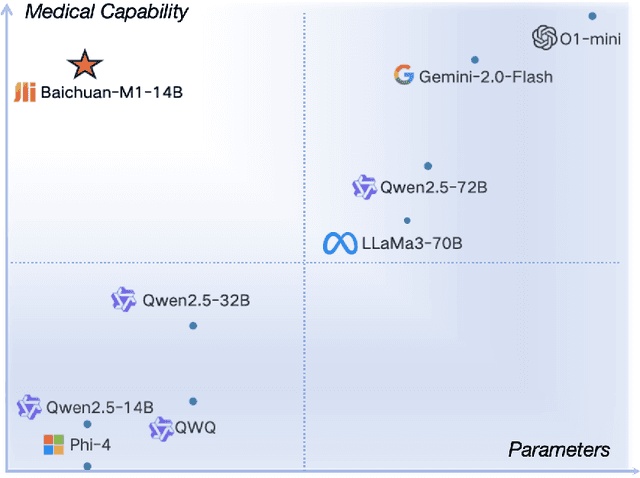
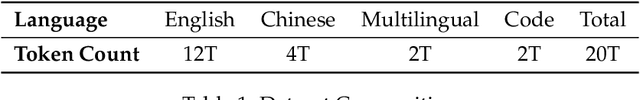
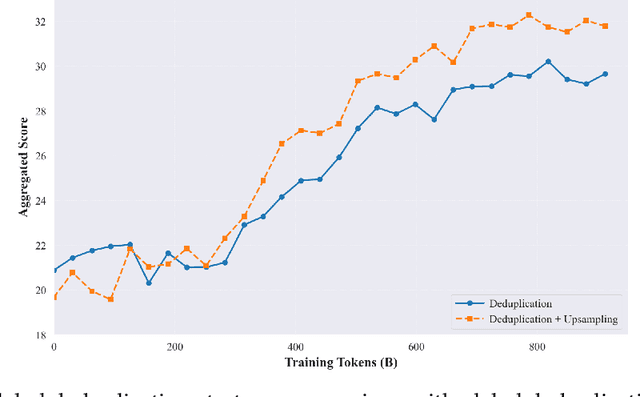
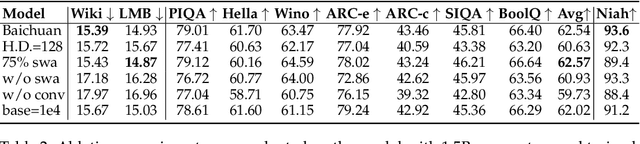
Abstract:The current generation of large language models (LLMs) is typically designed for broad, general-purpose applications, while domain-specific LLMs, especially in vertical fields like medicine, remain relatively scarce. In particular, the development of highly efficient and practical LLMs for the medical domain is challenging due to the complexity of medical knowledge and the limited availability of high-quality data. To bridge this gap, we introduce Baichuan-M1, a series of large language models specifically optimized for medical applications. Unlike traditional approaches that simply continue pretraining on existing models or apply post-training to a general base model, Baichuan-M1 is trained from scratch with a dedicated focus on enhancing medical capabilities. Our model is trained on 20 trillion tokens and incorporates a range of effective training methods that strike a balance between general capabilities and medical expertise. As a result, Baichuan-M1 not only performs strongly across general domains such as mathematics and coding but also excels in specialized medical fields. We have open-sourced Baichuan-M1-14B, a mini version of our model, which can be accessed through the following links.
Baichuan-Omni-1.5 Technical Report
Jan 26, 2025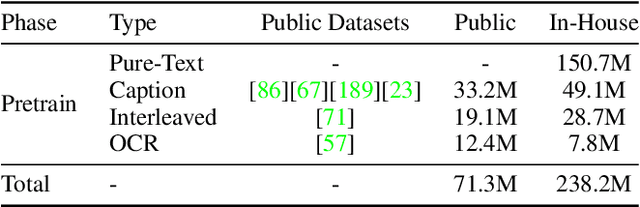
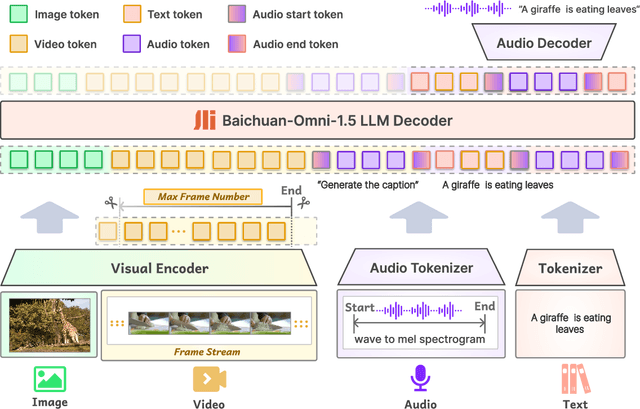
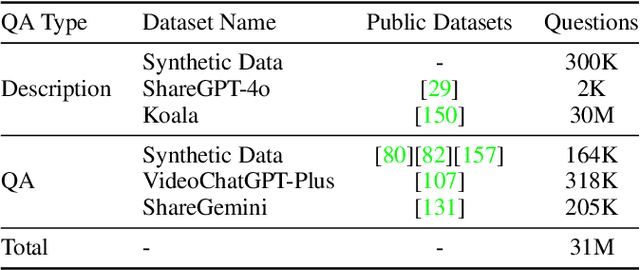
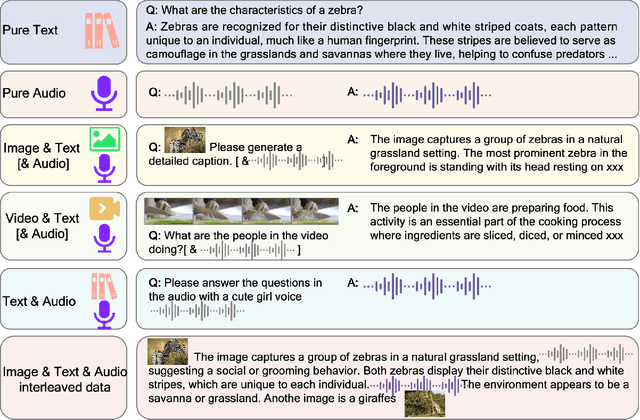
Abstract:We introduce Baichuan-Omni-1.5, an omni-modal model that not only has omni-modal understanding capabilities but also provides end-to-end audio generation capabilities. To achieve fluent and high-quality interaction across modalities without compromising the capabilities of any modality, we prioritized optimizing three key aspects. First, we establish a comprehensive data cleaning and synthesis pipeline for multimodal data, obtaining about 500B high-quality data (text, audio, and vision). Second, an audio-tokenizer (Baichuan-Audio-Tokenizer) has been designed to capture both semantic and acoustic information from audio, enabling seamless integration and enhanced compatibility with MLLM. Lastly, we designed a multi-stage training strategy that progressively integrates multimodal alignment and multitask fine-tuning, ensuring effective synergy across all modalities. Baichuan-Omni-1.5 leads contemporary models (including GPT4o-mini and MiniCPM-o 2.6) in terms of comprehensive omni-modal capabilities. Notably, it achieves results comparable to leading models such as Qwen2-VL-72B across various multimodal medical benchmarks.
From Novice to Expert: LLM Agent Policy Optimization via Step-wise Reinforcement Learning
Nov 06, 2024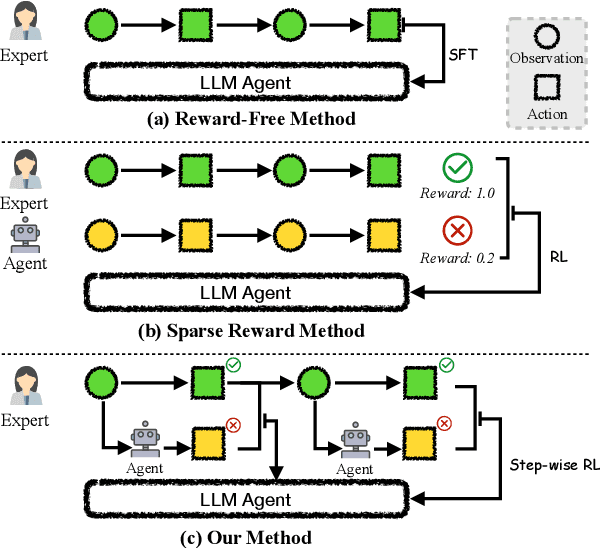
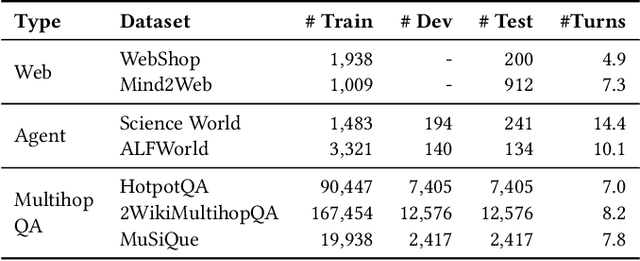

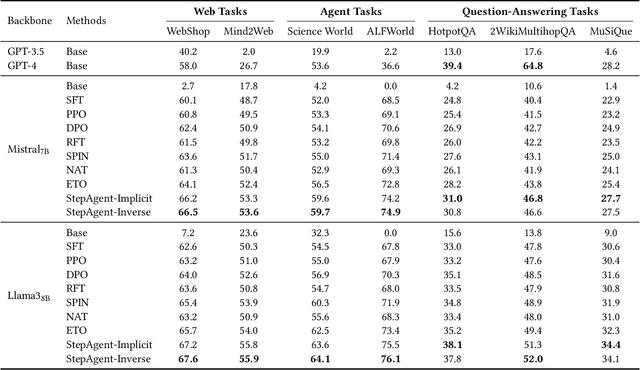
Abstract:The outstanding capabilities of large language models (LLMs) render them a crucial component in various autonomous agent systems. While traditional methods depend on the inherent knowledge of LLMs without fine-tuning, more recent approaches have shifted toward the reinforcement learning strategy to further enhance agents' ability to solve complex interactive tasks with environments and tools. However, previous approaches are constrained by the sparse reward issue, where existing datasets solely provide a final scalar reward for each multi-step reasoning chain, potentially leading to ineffectiveness and inefficiency in policy learning. In this paper, we introduce StepAgent, which utilizes step-wise reward to optimize the agent's reinforcement learning process. Inheriting the spirit of novice-to-expert theory, we first compare the actions of the expert and the agent to automatically generate intermediate rewards for fine-grained optimization. Additionally, we propose implicit-reward and inverse reinforcement learning techniques to facilitate agent reflection and policy adjustment. Further theoretical analysis demonstrates that the action distribution of the agent can converge toward the expert action distribution over multiple training cycles. Experimental results across various datasets indicate that StepAgent outperforms existing baseline methods.
HtmlRAG: HTML is Better Than Plain Text for Modeling Retrieved Knowledge in RAG Systems
Nov 05, 2024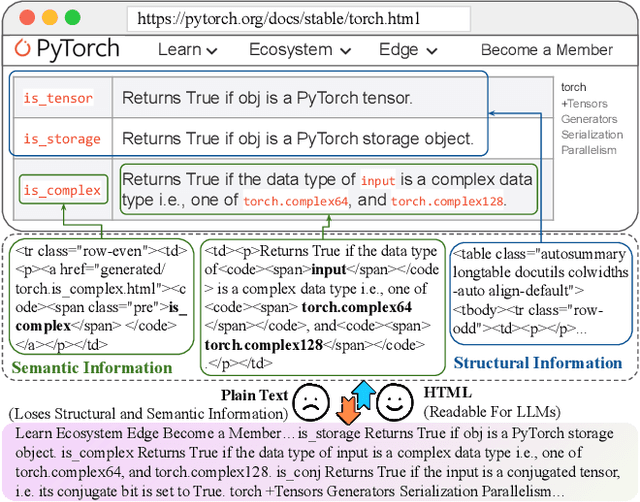
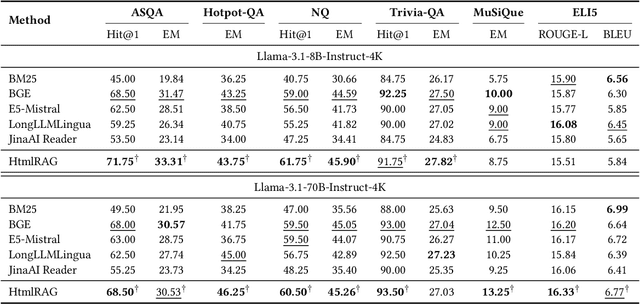
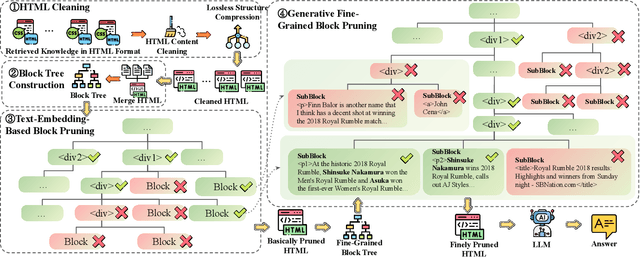
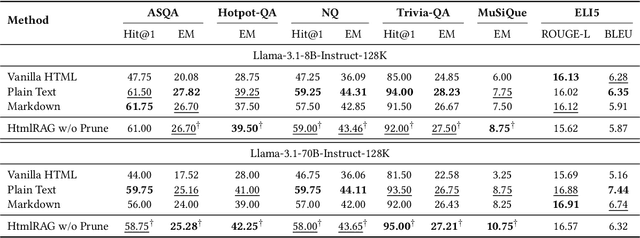
Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has been shown to improve knowledge capabilities and alleviate the hallucination problem of LLMs. The Web is a major source of external knowledge used in RAG systems, and many commercial systems such as ChatGPT and Perplexity have used Web search engines as their major retrieval systems. Typically, such RAG systems retrieve search results, download HTML sources of the results, and then extract plain texts from the HTML sources. Plain text documents or chunks are fed into the LLMs to augment the generation. However, much of the structural and semantic information inherent in HTML, such as headings and table structures, is lost during this plain-text-based RAG process. To alleviate this problem, we propose HtmlRAG, which uses HTML instead of plain text as the format of retrieved knowledge in RAG. We believe HTML is better than plain text in modeling knowledge in external documents, and most LLMs possess robust capacities to understand HTML. However, utilizing HTML presents new challenges. HTML contains additional content such as tags, JavaScript, and CSS specifications, which bring extra input tokens and noise to the RAG system. To address this issue, we propose HTML cleaning, compression, and pruning strategies, to shorten the HTML while minimizing the loss of information. Specifically, we design a two-step block-tree-based pruning method that prunes useless HTML blocks and keeps only the relevant part of the HTML. Experiments on six QA datasets confirm the superiority of using HTML in RAG systems.
Baichuan Alignment Technical Report
Oct 19, 2024



Abstract:We introduce Baichuan Alignment, a detailed analysis of the alignment techniques employed in the Baichuan series of models. This represents the industry's first comprehensive account of alignment methodologies, offering valuable insights for advancing AI research. We investigate the critical components that enhance model performance during the alignment process, including optimization methods, data strategies, capability enhancements, and evaluation processes. The process spans three key stages: Prompt Augmentation System (PAS), Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), and Preference Alignment. The problems encountered, the solutions applied, and the improvements made are thoroughly recorded. Through comparisons across well-established benchmarks, we highlight the technological advancements enabled by Baichuan Alignment. Baichuan-Instruct is an internal model, while Qwen2-Nova-72B and Llama3-PBM-Nova-70B are instruct versions of the Qwen2-72B and Llama-3-70B base models, optimized through Baichuan Alignment. Baichuan-Instruct demonstrates significant improvements in core capabilities, with user experience gains ranging from 17% to 28%, and performs exceptionally well on specialized benchmarks. In open-source benchmark evaluations, both Qwen2-Nova-72B and Llama3-PBM-Nova-70B consistently outperform their respective official instruct versions across nearly all datasets. This report aims to clarify the key technologies behind the alignment process, fostering a deeper understanding within the community. Llama3-PBM-Nova-70B model is available at https://huggingface.co/PKU-Baichuan-MLSystemLab/Llama3-PBM-Nova-70B.
RichRAG: Crafting Rich Responses for Multi-faceted Queries in Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jun 18, 2024



Abstract:Retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) effectively addresses issues of static knowledge and hallucination in large language models. Existing studies mostly focus on question scenarios with clear user intents and concise answers. However, it is prevalent that users issue broad, open-ended queries with diverse sub-intents, for which they desire rich and long-form answers covering multiple relevant aspects. To tackle this important yet underexplored problem, we propose a novel RAG framework, namely RichRAG. It includes a sub-aspect explorer to identify potential sub-aspects of input questions, a multi-faceted retriever to build a candidate pool of diverse external documents related to these sub-aspects, and a generative list-wise ranker, which is a key module to provide the top-k most valuable documents for the final generator. These ranked documents sufficiently cover various query aspects and are aware of the generator's preferences, hence incentivizing it to produce rich and comprehensive responses for users. The training of our ranker involves a supervised fine-tuning stage to ensure the basic coverage of documents, and a reinforcement learning stage to align downstream LLM's preferences to the ranking of documents. Experimental results on two publicly available datasets prove that our framework effectively and efficiently provides comprehensive and satisfying responses to users.
Make Continual Learning Stronger via C-Flat
Apr 01, 2024Abstract:Model generalization ability upon incrementally acquiring dynamically updating knowledge from sequentially arriving tasks is crucial to tackle the sensitivity-stability dilemma in Continual Learning (CL). Weight loss landscape sharpness minimization seeking for flat minima lying in neighborhoods with uniform low loss or smooth gradient is proven to be a strong training regime improving model generalization compared with loss minimization based optimizer like SGD. Yet only a few works have discussed this training regime for CL, proving that dedicated designed zeroth-order sharpness optimizer can improve CL performance. In this work, we propose a Continual Flatness (C-Flat) method featuring a flatter loss landscape tailored for CL. C-Flat could be easily called with only one line of code and is plug-and-play to any CL methods. A general framework of C-Flat applied to all CL categories and a thorough comparison with loss minima optimizer and flat minima based CL approaches is presented in this paper, showing that our method can boost CL performance in almost all cases. Code will be publicly available upon publication.
Baichuan 2: Open Large-scale Language Models
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance on a variety of natural language tasks based on just a few examples of natural language instructions, reducing the need for extensive feature engineering. However, most powerful LLMs are closed-source or limited in their capability for languages other than English. In this technical report, we present Baichuan 2, a series of large-scale multilingual language models containing 7 billion and 13 billion parameters, trained from scratch, on 2.6 trillion tokens. Baichuan 2 matches or outperforms other open-source models of similar size on public benchmarks like MMLU, CMMLU, GSM8K, and HumanEval. Furthermore, Baichuan 2 excels in vertical domains such as medicine and law. We will release all pre-training model checkpoints to benefit the research community in better understanding the training dynamics of Baichuan 2.
Progressive Learning without Forgetting
Nov 28, 2022Abstract:Learning from changing tasks and sequential experience without forgetting the obtained knowledge is a challenging problem for artificial neural networks. In this work, we focus on two challenging problems in the paradigm of Continual Learning (CL) without involving any old data: (i) the accumulation of catastrophic forgetting caused by the gradually fading knowledge space from which the model learns the previous knowledge; (ii) the uncontrolled tug-of-war dynamics to balance the stability and plasticity during the learning of new tasks. In order to tackle these problems, we present Progressive Learning without Forgetting (PLwF) and a credit assignment regime in the optimizer. PLwF densely introduces model functions from previous tasks to construct a knowledge space such that it contains the most reliable knowledge on each task and the distribution information of different tasks, while credit assignment controls the tug-of-war dynamics by removing gradient conflict through projection. Extensive ablative experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of PLwF and credit assignment. In comparison with other CL methods, we report notably better results even without relying on any raw data.
Overcoming Catastrophic Forgetting in Incremental Object Detection via Elastic Response Distillation
Apr 05, 2022



Abstract:Traditional object detectors are ill-equipped for incremental learning. However, fine-tuning directly on a well-trained detection model with only new data will lead to catastrophic forgetting. Knowledge distillation is a flexible way to mitigate catastrophic forgetting. In Incremental Object Detection (IOD), previous work mainly focuses on distilling for the combination of features and responses. However, they under-explore the information that contains in responses. In this paper, we propose a response-based incremental distillation method, dubbed Elastic Response Distillation (ERD), which focuses on elastically learning responses from the classification head and the regression head. Firstly, our method transfers category knowledge while equipping student detector with the ability to retain localization information during incremental learning. In addition, we further evaluate the quality of all locations and provide valuable responses by the Elastic Response Selection (ERS) strategy. Finally, we elucidate that the knowledge from different responses should be assigned with different importance during incremental distillation. Extensive experiments conducted on MS COCO demonstrate our method achieves state-of-the-art result, which substantially narrows the performance gap towards full training.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge