Eric Undersander
PARTNR: A Benchmark for Planning and Reasoning in Embodied Multi-agent Tasks
Oct 31, 2024
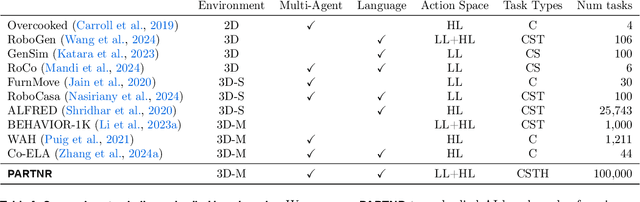

Abstract:We present a benchmark for Planning And Reasoning Tasks in humaN-Robot collaboration (PARTNR) designed to study human-robot coordination in household activities. PARTNR tasks exhibit characteristics of everyday tasks, such as spatial, temporal, and heterogeneous agent capability constraints. We employ a semi-automated task generation pipeline using Large Language Models (LLMs), incorporating simulation in the loop for grounding and verification. PARTNR stands as the largest benchmark of its kind, comprising 100,000 natural language tasks, spanning 60 houses and 5,819 unique objects. We analyze state-of-the-art LLMs on PARTNR tasks, across the axes of planning, perception and skill execution. The analysis reveals significant limitations in SoTA models, such as poor coordination and failures in task tracking and recovery from errors. When LLMs are paired with real humans, they require 1.5x as many steps as two humans collaborating and 1.1x more steps than a single human, underscoring the potential for improvement in these models. We further show that fine-tuning smaller LLMs with planning data can achieve performance on par with models 9 times larger, while being 8.6x faster at inference. Overall, PARTNR highlights significant challenges facing collaborative embodied agents and aims to drive research in this direction.
Habitat 3.0: A Co-Habitat for Humans, Avatars and Robots
Oct 19, 2023



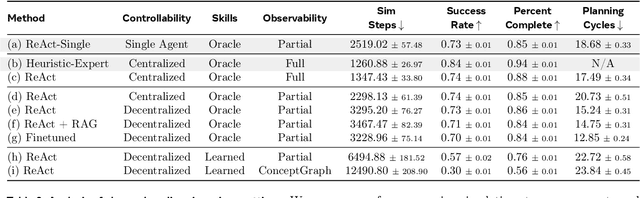
Abstract:We present Habitat 3.0: a simulation platform for studying collaborative human-robot tasks in home environments. Habitat 3.0 offers contributions across three dimensions: (1) Accurate humanoid simulation: addressing challenges in modeling complex deformable bodies and diversity in appearance and motion, all while ensuring high simulation speed. (2) Human-in-the-loop infrastructure: enabling real human interaction with simulated robots via mouse/keyboard or a VR interface, facilitating evaluation of robot policies with human input. (3) Collaborative tasks: studying two collaborative tasks, Social Navigation and Social Rearrangement. Social Navigation investigates a robot's ability to locate and follow humanoid avatars in unseen environments, whereas Social Rearrangement addresses collaboration between a humanoid and robot while rearranging a scene. These contributions allow us to study end-to-end learned and heuristic baselines for human-robot collaboration in-depth, as well as evaluate them with humans in the loop. Our experiments demonstrate that learned robot policies lead to efficient task completion when collaborating with unseen humanoid agents and human partners that might exhibit behaviors that the robot has not seen before. Additionally, we observe emergent behaviors during collaborative task execution, such as the robot yielding space when obstructing a humanoid agent, thereby allowing the effective completion of the task by the humanoid agent. Furthermore, our experiments using the human-in-the-loop tool demonstrate that our automated evaluation with humanoids can provide an indication of the relative ordering of different policies when evaluated with real human collaborators. Habitat 3.0 unlocks interesting new features in simulators for Embodied AI, and we hope it paves the way for a new frontier of embodied human-AI interaction capabilities.
Habitat Synthetic Scenes Dataset (HSSD-200): An Analysis of 3D Scene Scale and Realism Tradeoffs for ObjectGoal Navigation
Jun 21, 2023Abstract:We contribute the Habitat Synthetic Scene Dataset, a dataset of 211 high-quality 3D scenes, and use it to test navigation agent generalization to realistic 3D environments. Our dataset represents real interiors and contains a diverse set of 18,656 models of real-world objects. We investigate the impact of synthetic 3D scene dataset scale and realism on the task of training embodied agents to find and navigate to objects (ObjectGoal navigation). By comparing to synthetic 3D scene datasets from prior work, we find that scale helps in generalization, but the benefits quickly saturate, making visual fidelity and correlation to real-world scenes more important. Our experiments show that agents trained on our smaller-scale dataset can match or outperform agents trained on much larger datasets. Surprisingly, we observe that agents trained on just 122 scenes from our dataset outperform agents trained on 10,000 scenes from the ProcTHOR-10K dataset in terms of zero-shot generalization in real-world scanned environments.
Galactic: Scaling End-to-End Reinforcement Learning for Rearrangement at 100k Steps-Per-Second
Jun 13, 2023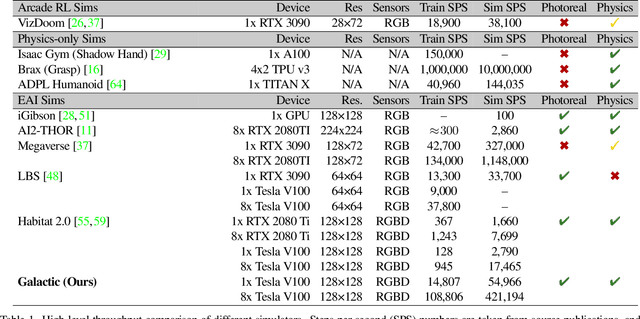
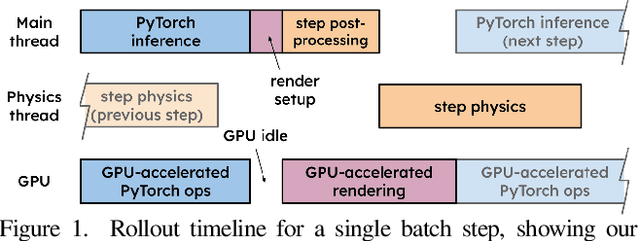
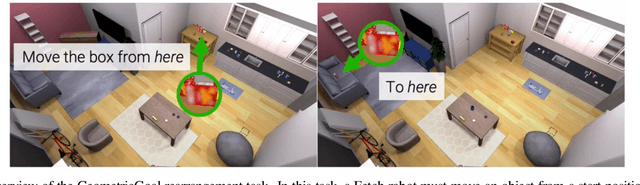

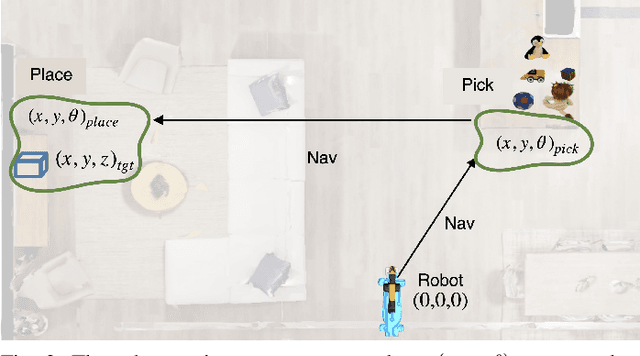
Abstract:We present Galactic, a large-scale simulation and reinforcement-learning (RL) framework for robotic mobile manipulation in indoor environments. Specifically, a Fetch robot (equipped with a mobile base, 7DoF arm, RGBD camera, egomotion, and onboard sensing) is spawned in a home environment and asked to rearrange objects - by navigating to an object, picking it up, navigating to a target location, and then placing the object at the target location. Galactic is fast. In terms of simulation speed (rendering + physics), Galactic achieves over 421,000 steps-per-second (SPS) on an 8-GPU node, which is 54x faster than Habitat 2.0 (7699 SPS). More importantly, Galactic was designed to optimize the entire rendering + physics + RL interplay since any bottleneck in the interplay slows down training. In terms of simulation+RL speed (rendering + physics + inference + learning), Galactic achieves over 108,000 SPS, which 88x faster than Habitat 2.0 (1243 SPS). These massive speed-ups not only drastically cut the wall-clock training time of existing experiments, but also unlock an unprecedented scale of new experiments. First, Galactic can train a mobile pick skill to >80% accuracy in under 16 minutes, a 100x speedup compared to the over 24 hours it takes to train the same skill in Habitat 2.0. Second, we use Galactic to perform the largest-scale experiment to date for rearrangement using 5B steps of experience in 46 hours, which is equivalent to 20 years of robot experience. This scaling results in a single neural network composed of task-agnostic components achieving 85% success in GeometricGoal rearrangement, compared to 0% success reported in Habitat 2.0 for the same approach. The code is available at github.com/facebookresearch/galactic.
Adaptive Skill Coordination for Robotic Mobile Manipulation
Apr 01, 2023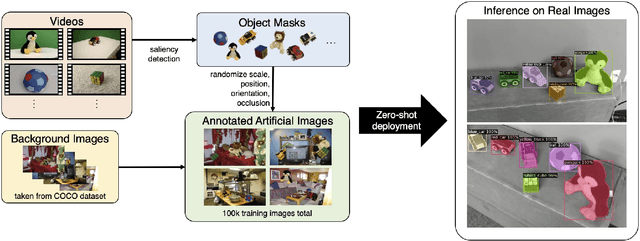
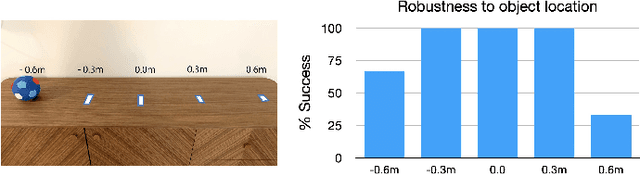

Abstract:We present Adaptive Skill Coordination (ASC) - an approach for accomplishing long-horizon tasks (e.g., mobile pick-and-place, consisting of navigating to an object, picking it, navigating to another location, placing it, repeating). ASC consists of three components - (1) a library of basic visuomotor skills (navigation, pick, place), (2) a skill coordination policy that chooses which skills are appropriate to use when, and (3) a corrective policy that adapts pre-trained skills when out-of-distribution states are perceived. All components of ASC rely only on onboard visual and proprioceptive sensing, without access to privileged information like pre-built maps or precise object locations, easing real-world deployment. We train ASC in simulated indoor environments, and deploy it zero-shot in two novel real-world environments on the Boston Dynamics Spot robot. ASC achieves near-perfect performance at mobile pick-and-place, succeeding in 59/60 (98%) episodes, while sequentially executing skills succeeds in only 44/60 (73%) episodes. It is robust to hand-off errors, changes in the environment layout, dynamic obstacles (e.g., people), and unexpected disturbances, making it an ideal framework for complex, long-horizon tasks. Supplementary videos available at adaptiveskillcoordination.github.io.
Transformers are Adaptable Task Planners
Jul 06, 2022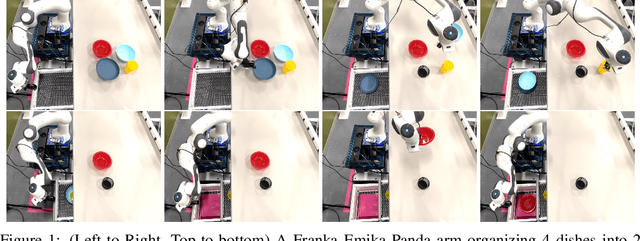
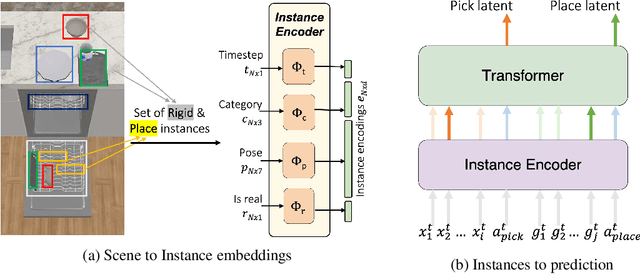
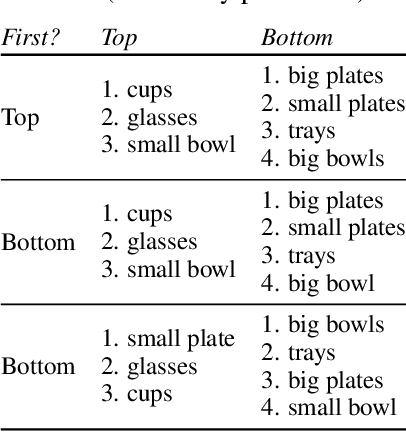
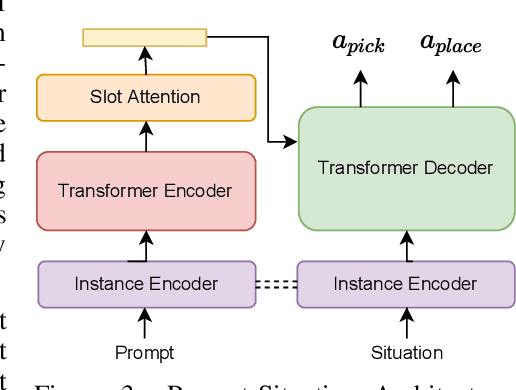
Abstract:Every home is different, and every person likes things done in their particular way. Therefore, home robots of the future need to both reason about the sequential nature of day-to-day tasks and generalize to user's preferences. To this end, we propose a Transformer Task Planner(TTP) that learns high-level actions from demonstrations by leveraging object attribute-based representations. TTP can be pre-trained on multiple preferences and shows generalization to unseen preferences using a single demonstration as a prompt in a simulated dishwasher loading task. Further, we demonstrate real-world dish rearrangement using TTP with a Franka Panda robotic arm, prompted using a single human demonstration.
Habitat-Web: Learning Embodied Object-Search Strategies from Human Demonstrations at Scale
Apr 08, 2022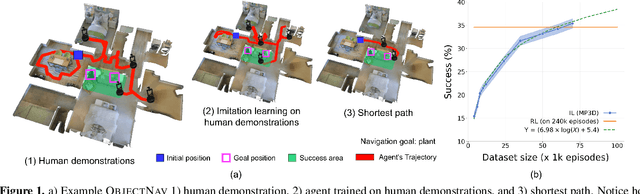

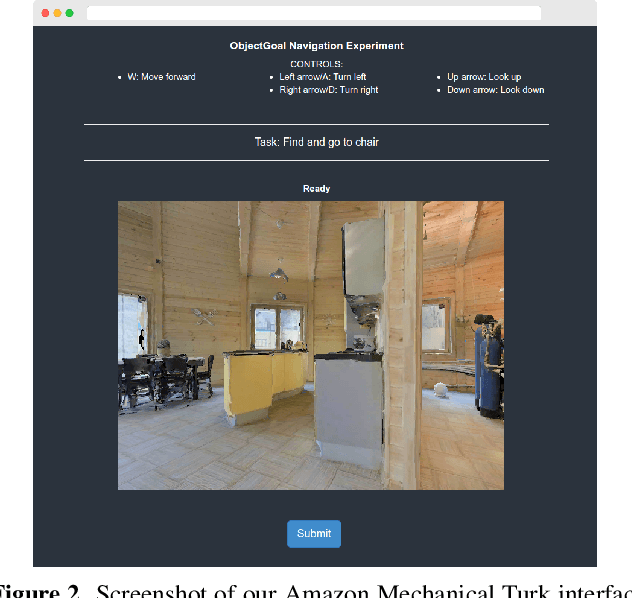
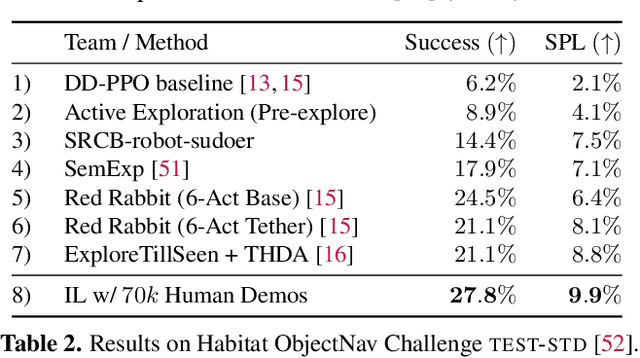
Abstract:We present a large-scale study of imitating human demonstrations on tasks that require a virtual robot to search for objects in new environments -- (1) ObjectGoal Navigation (e.g. 'find & go to a chair') and (2) Pick&Place (e.g. 'find mug, pick mug, find counter, place mug on counter'). First, we develop a virtual teleoperation data-collection infrastructure -- connecting Habitat simulator running in a web browser to Amazon Mechanical Turk, allowing remote users to teleoperate virtual robots, safely and at scale. We collect 80k demonstrations for ObjectNav and 12k demonstrations for Pick&Place, which is an order of magnitude larger than existing human demonstration datasets in simulation or on real robots. Second, we attempt to answer the question -- how does large-scale imitation learning (IL) (which hasn't been hitherto possible) compare to reinforcement learning (RL) (which is the status quo)? On ObjectNav, we find that IL (with no bells or whistles) using 70k human demonstrations outperforms RL using 240k agent-gathered trajectories. The IL-trained agent demonstrates efficient object-search behavior -- it peeks into rooms, checks corners for small objects, turns in place to get a panoramic view -- none of these are exhibited as prominently by the RL agent, and to induce these behaviors via RL would require tedious reward engineering. Finally, accuracy vs. training data size plots show promising scaling behavior, suggesting that simply collecting more demonstrations is likely to advance the state of art further. On Pick&Place, the comparison is starker -- IL agents achieve ${\sim}$18% success on episodes with new object-receptacle locations when trained with 9.5k human demonstrations, while RL agents fail to get beyond 0%. Overall, our work provides compelling evidence for investing in large-scale imitation learning. Project page: https://ram81.github.io/projects/habitat-web.
Habitat-Matterport 3D Dataset (HM3D): 1000 Large-scale 3D Environments for Embodied AI
Sep 16, 2021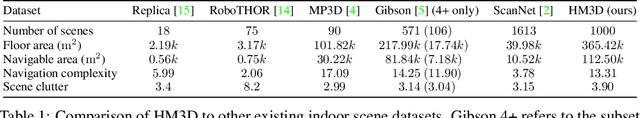

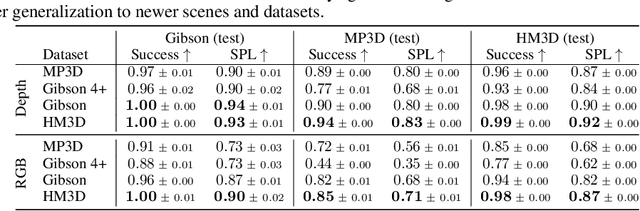
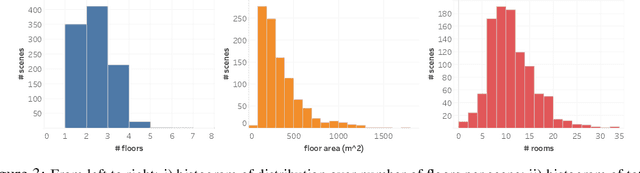
Abstract:We present the Habitat-Matterport 3D (HM3D) dataset. HM3D is a large-scale dataset of 1,000 building-scale 3D reconstructions from a diverse set of real-world locations. Each scene in the dataset consists of a textured 3D mesh reconstruction of interiors such as multi-floor residences, stores, and other private indoor spaces. HM3D surpasses existing datasets available for academic research in terms of physical scale, completeness of the reconstruction, and visual fidelity. HM3D contains 112.5k m^2 of navigable space, which is 1.4 - 3.7x larger than other building-scale datasets such as MP3D and Gibson. When compared to existing photorealistic 3D datasets such as Replica, MP3D, Gibson, and ScanNet, images rendered from HM3D have 20 - 85% higher visual fidelity w.r.t. counterpart images captured with real cameras, and HM3D meshes have 34 - 91% fewer artifacts due to incomplete surface reconstruction. The increased scale, fidelity, and diversity of HM3D directly impacts the performance of embodied AI agents trained using it. In fact, we find that HM3D is `pareto optimal' in the following sense -- agents trained to perform PointGoal navigation on HM3D achieve the highest performance regardless of whether they are evaluated on HM3D, Gibson, or MP3D. No similar claim can be made about training on other datasets. HM3D-trained PointNav agents achieve 100% performance on Gibson-test dataset, suggesting that it might be time to retire that episode dataset.
Habitat 2.0: Training Home Assistants to Rearrange their Habitat
Jun 28, 2021
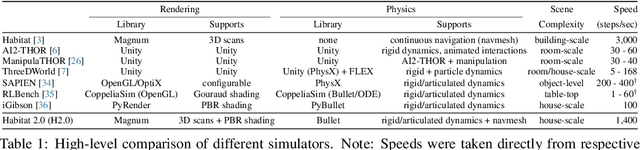

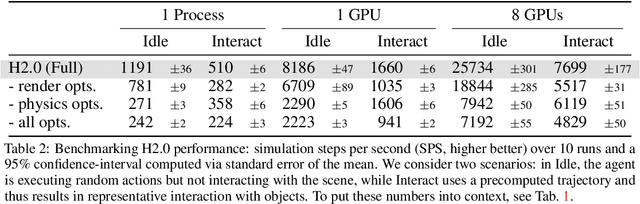
Abstract:We introduce Habitat 2.0 (H2.0), a simulation platform for training virtual robots in interactive 3D environments and complex physics-enabled scenarios. We make comprehensive contributions to all levels of the embodied AI stack - data, simulation, and benchmark tasks. Specifically, we present: (i) ReplicaCAD: an artist-authored, annotated, reconfigurable 3D dataset of apartments (matching real spaces) with articulated objects (e.g. cabinets and drawers that can open/close); (ii) H2.0: a high-performance physics-enabled 3D simulator with speeds exceeding 25,000 simulation steps per second (850x real-time) on an 8-GPU node, representing 100x speed-ups over prior work; and, (iii) Home Assistant Benchmark (HAB): a suite of common tasks for assistive robots (tidy the house, prepare groceries, set the table) that test a range of mobile manipulation capabilities. These large-scale engineering contributions allow us to systematically compare deep reinforcement learning (RL) at scale and classical sense-plan-act (SPA) pipelines in long-horizon structured tasks, with an emphasis on generalization to new objects, receptacles, and layouts. We find that (1) flat RL policies struggle on HAB compared to hierarchical ones; (2) a hierarchy with independent skills suffers from 'hand-off problems', and (3) SPA pipelines are more brittle than RL policies.
Block-Sparse Recurrent Neural Networks
Nov 08, 2017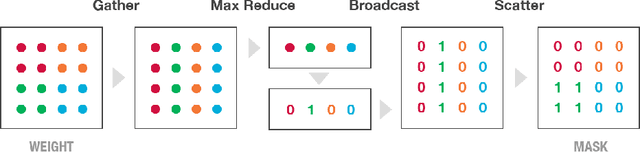
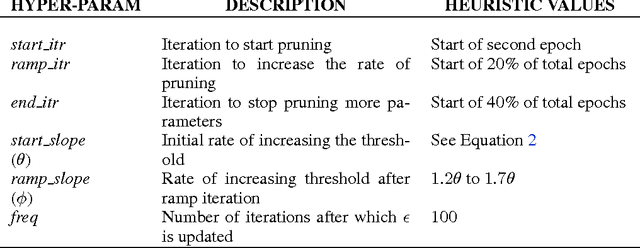
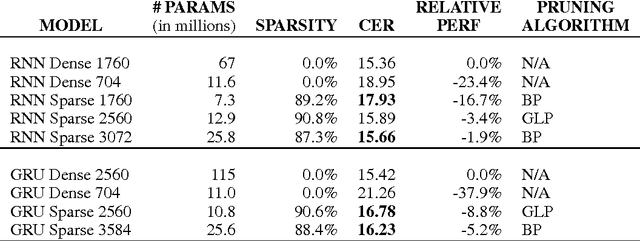
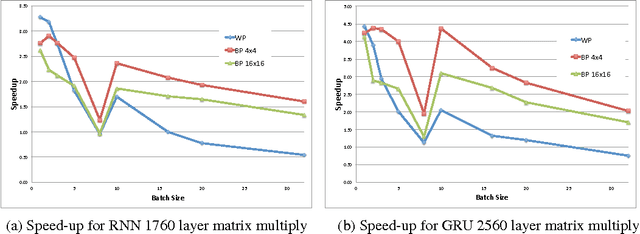
Abstract:Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) are used in state-of-the-art models in domains such as speech recognition, machine translation, and language modelling. Sparsity is a technique to reduce compute and memory requirements of deep learning models. Sparse RNNs are easier to deploy on devices and high-end server processors. Even though sparse operations need less compute and memory relative to their dense counterparts, the speed-up observed by using sparse operations is less than expected on different hardware platforms. In order to address this issue, we investigate two different approaches to induce block sparsity in RNNs: pruning blocks of weights in a layer and using group lasso regularization to create blocks of weights with zeros. Using these techniques, we demonstrate that we can create block-sparse RNNs with sparsity ranging from 80% to 90% with small loss in accuracy. This allows us to reduce the model size by roughly 10x. Additionally, we can prune a larger dense network to recover this loss in accuracy while maintaining high block sparsity and reducing the overall parameter count. Our technique works with a variety of block sizes up to 32x32. Block-sparse RNNs eliminate overheads related to data storage and irregular memory accesses while increasing hardware efficiency compared to unstructured sparsity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge