Zhou Li
Arce: Augmented Roberta with Contextualized Elucidations for Ner in Automated Rule Checking
Aug 10, 2025Abstract:Accurate information extraction from specialized texts is a critical challenge, particularly for named entity recognition (NER) in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) domain to support automated rule checking (ARC). The performance of standard pre-trained models is often constrained by the domain gap, as they struggle to interpret the specialized terminology and complex relational contexts inherent in AEC texts. Although this issue can be mitigated by further pre-training on large, human-curated domain corpora, as exemplified by methods like ARCBERT, this approach is both labor-intensive and cost-prohibitive. Consequently, leveraging large language models (LLMs) for automated knowledge generation has emerged as a promising alternative. However, the optimal strategy for generating knowledge that can genuinely enhance smaller, efficient models remains an open question. To address this, we propose ARCE (augmented RoBERTa with contextualized elucidations), a novel approach that systematically explores and optimizes this generation process. ARCE employs an LLM to first generate a corpus of simple, direct explanations, which we term Cote, and then uses this corpus to incrementally pre-train a RoBERTa model prior to its fine-tuning on the downstream task. Our extensive experiments show that ARCE establishes a new state-of-the-art on a benchmark AEC dataset, achieving a Macro-F1 score of 77.20%. This result also reveals a key finding: simple, explanation-based knowledge proves surprisingly more effective than complex, role-based rationales for this task. The code is publicly available at:https://github.com/nxcc-lab/ARCE.
Information-Theoretic Decentralized Secure Aggregation with Collusion Resilience
Aug 01, 2025Abstract:In decentralized federated learning (FL), multiple clients collaboratively learn a shared machine learning (ML) model by leveraging their privately held datasets distributed across the network, through interactive exchange of the intermediate model updates. To ensure data security, cryptographic techniques are commonly employed to protect model updates during aggregation. Despite growing interest in secure aggregation, existing works predominantly focus on protocol design and computational guarantees, with limited understanding of the fundamental information-theoretic limits of such systems. Moreover, optimal bounds on communication and key usage remain unknown in decentralized settings, where no central aggregator is available. Motivated by these gaps, we study the problem of decentralized secure aggregation (DSA) from an information-theoretic perspective. Specifically, we consider a network of $K$ fully-connected users, each holding a private input -- an abstraction of local training data -- who aim to securely compute the sum of all inputs. The security constraint requires that no user learns anything beyond the input sum, even when colluding with up to $T$ other users. We characterize the optimal rate region, which specifies the minimum achievable communication and secret key rates for DSA. In particular, we show that to securely compute one symbol of the desired input sum, each user must (i) transmit at least one symbol to others, (ii) hold at least one symbol of secret key, and (iii) all users must collectively hold no fewer than $K - 1$ independent key symbols. Our results establish the fundamental performance limits of DSA, providing insights for the design of provably secure and communication-efficient protocols in distributed learning systems.
Dynamic Risk Assessments for Offensive Cybersecurity Agents
May 23, 2025



Abstract:Foundation models are increasingly becoming better autonomous programmers, raising the prospect that they could also automate dangerous offensive cyber-operations. Current frontier model audits probe the cybersecurity risks of such agents, but most fail to account for the degrees of freedom available to adversaries in the real world. In particular, with strong verifiers and financial incentives, agents for offensive cybersecurity are amenable to iterative improvement by would-be adversaries. We argue that assessments should take into account an expanded threat model in the context of cybersecurity, emphasizing the varying degrees of freedom that an adversary may possess in stateful and non-stateful environments within a fixed compute budget. We show that even with a relatively small compute budget (8 H100 GPU Hours in our study), adversaries can improve an agent's cybersecurity capability on InterCode CTF by more than 40\% relative to the baseline -- without any external assistance. These results highlight the need to evaluate agents' cybersecurity risk in a dynamic manner, painting a more representative picture of risk.
FetalFlex: Anatomy-Guided Diffusion Model for Flexible Control on Fetal Ultrasound Image Synthesis
Mar 19, 2025Abstract:Fetal ultrasound (US) examinations require the acquisition of multiple planes, each providing unique diagnostic information to evaluate fetal development and screening for congenital anomalies. However, obtaining a comprehensive, multi-plane annotated fetal US dataset remains challenging, particularly for rare or complex anomalies owing to their low incidence and numerous subtypes. This poses difficulties in training novice radiologists and developing robust AI models, especially for detecting abnormal fetuses. In this study, we introduce a Flexible Fetal US image generation framework (FetalFlex) to address these challenges, which leverages anatomical structures and multimodal information to enable controllable synthesis of fetal US images across diverse planes. Specifically, FetalFlex incorporates a pre-alignment module to enhance controllability and introduces a repaint strategy to ensure consistent texture and appearance. Moreover, a two-stage adaptive sampling strategy is developed to progressively refine image quality from coarse to fine levels. We believe that FetalFlex is the first method capable of generating both in-distribution normal and out-of-distribution abnormal fetal US images, without requiring any abnormal data. Experiments on multi-center datasets demonstrate that FetalFlex achieved state-of-the-art performance across multiple image quality metrics. A reader study further confirms the close alignment of the generated results with expert visual assessments. Furthermore, synthetic images by FetalFlex significantly improve the performance of six typical deep models in downstream classification and anomaly detection tasks. Lastly, FetalFlex's anatomy-level controllable generation offers a unique advantage for anomaly simulation and creating paired or counterfactual data at the pixel level. The demo is available at: https://dyf1023.github.io/FetalFlex/.
Fundamental Limits of Hierarchical Secure Aggregation with Cyclic User Association
Mar 07, 2025Abstract:Secure aggregation is motivated by federated learning (FL) where a cloud server aims to compute an averaged model (i.e., weights of deep neural networks) of the locally-trained models of numerous clients, while adhering to data security requirements. Hierarchical secure aggregation (HSA) extends this concept to a three-layer network, where clustered users communicate with the server through an intermediate layer of relays. In HSA, beyond conventional server security, relay security is also enforced to ensure that the relays remain oblivious to the users' inputs (an abstraction of the local models in FL). Existing study on HSA assumes that each user is associated with only one relay, limiting opportunities for coding across inter-cluster users to achieve efficient communication and key generation. In this paper, we consider HSA with a cyclic association pattern where each user is connected to $B$ consecutive relays in a wrap-around manner. We propose an efficient aggregation scheme which includes a message design for the inputs inspired by gradient coding-a well-known technique for efficient communication in distributed computing-along with a highly nontrivial security key design. We also derive novel converse bounds on the minimum achievable communication and key rates using information-theoretic arguments.
AutoAttacker: A Large Language Model Guided System to Implement Automatic Cyber-attacks
Mar 02, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated impressive results on natural language tasks, and security researchers are beginning to employ them in both offensive and defensive systems. In cyber-security, there have been multiple research efforts that utilize LLMs focusing on the pre-breach stage of attacks like phishing and malware generation. However, so far there lacks a comprehensive study regarding whether LLM-based systems can be leveraged to simulate the post-breach stage of attacks that are typically human-operated, or "hands-on-keyboard" attacks, under various attack techniques and environments. As LLMs inevitably advance, they may be able to automate both the pre- and post-breach attack stages. This shift may transform organizational attacks from rare, expert-led events to frequent, automated operations requiring no expertise and executed at automation speed and scale. This risks fundamentally changing global computer security and correspondingly causing substantial economic impacts, and a goal of this work is to better understand these risks now so we can better prepare for these inevitable ever-more-capable LLMs on the horizon. On the immediate impact side, this research serves three purposes. First, an automated LLM-based, post-breach exploitation framework can help analysts quickly test and continually improve their organization's network security posture against previously unseen attacks. Second, an LLM-based penetration test system can extend the effectiveness of red teams with a limited number of human analysts. Finally, this research can help defensive systems and teams learn to detect novel attack behaviors preemptively before their use in the wild....
A Comprehensive Study of Privacy Risks in Curriculum Learning
Oct 16, 2023Abstract:Training a machine learning model with data following a meaningful order, i.e., from easy to hard, has been proven to be effective in accelerating the training process and achieving better model performance. The key enabling technique is curriculum learning (CL), which has seen great success and has been deployed in areas like image and text classification. Yet, how CL affects the privacy of machine learning is unclear. Given that CL changes the way a model memorizes the training data, its influence on data privacy needs to be thoroughly evaluated. To fill this knowledge gap, we perform the first study and leverage membership inference attack (MIA) and attribute inference attack (AIA) as two vectors to quantify the privacy leakage caused by CL. Our evaluation of nine real-world datasets with attack methods (NN-based, metric-based, label-only MIA, and NN-based AIA) revealed new insights about CL. First, MIA becomes slightly more effective when CL is applied, but the impact is much more prominent to a subset of training samples ranked as difficult. Second, a model trained under CL is less vulnerable under AIA, compared to MIA. Third, the existing defense techniques like DP-SGD, MemGuard, and MixupMMD are still effective under CL, though DP-SGD has a significant impact on target model accuracy. Finally, based on our insights into CL, we propose a new MIA, termed Diff-Cali, which exploits the difficulty scores for result calibration and is demonstrated to be effective against all CL methods and the normal training method. With this study, we hope to draw the community's attention to the unintended privacy risks of emerging machine-learning techniques and develop new attack benchmarks and defense solutions.
Maestro: A Gamified Platform for Teaching AI Robustness
Jun 14, 2023Abstract:Although the prevention of AI vulnerabilities is critical to preserve the safety and privacy of users and businesses, educational tools for robust AI are still underdeveloped worldwide. We present the design, implementation, and assessment of Maestro. Maestro is an effective open-source game-based platform that contributes to the advancement of robust AI education. Maestro provides goal-based scenarios where college students are exposed to challenging life-inspired assignments in a competitive programming environment. We assessed Maestro's influence on students' engagement, motivation, and learning success in robust AI. This work also provides insights into the design features of online learning tools that promote active learning opportunities in the robust AI domain. We analyzed the reflection responses (measured with Likert scales) of 147 undergraduate students using Maestro in two quarterly college courses in AI. According to the results, students who felt the acquisition of new skills in robust AI tended to appreciate highly Maestro and scored highly on material consolidation, curiosity, and mastery in robust AI. Moreover, the leaderboard, our key gamification element in Maestro, has effectively contributed to students' engagement and learning. Results also indicate that Maestro can be effectively adapted to any course length and depth without losing its educational quality.
Attacking Point Cloud Segmentation with Color-only Perturbation
Dec 18, 2021
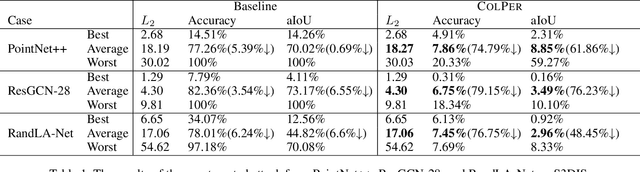
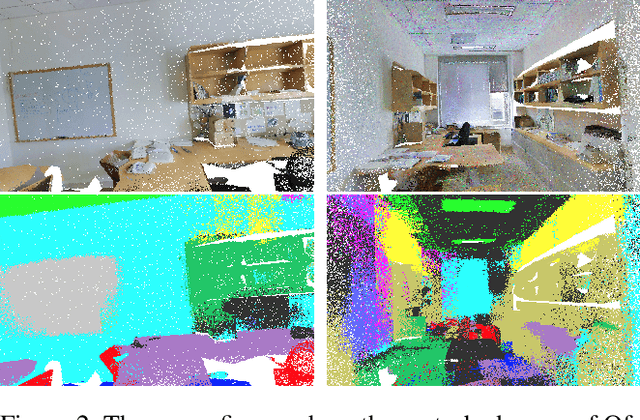

Abstract:Recent research efforts on 3D point-cloud semantic segmentation have achieved outstanding performance by adopting deep CNN (convolutional neural networks) and GCN (graph convolutional networks). However, the robustness of these complex models has not been systematically analyzed. Given that semantic segmentation has been applied in many safety-critical applications (e.g., autonomous driving, geological sensing), it is important to fill this knowledge gap, in particular, how these models are affected under adversarial samples. While adversarial attacks against point cloud have been studied, we found all of them were targeting single-object recognition, and the perturbation is done on the point coordinates. We argue that the coordinate-based perturbation is unlikely to realize under the physical-world constraints. Hence, we propose a new color-only perturbation method named COLPER, and tailor it to semantic segmentation. By evaluating COLPER on an indoor dataset (S3DIS) and an outdoor dataset (Semantic3D) against three point cloud segmentation models (PointNet++, DeepGCNs, and RandLA-Net), we found color-only perturbation is sufficient to significantly drop the segmentation accuracy and aIoU, under both targeted and non-targeted attack settings.
Continuous Release of Data Streams under both Centralized and Local Differential Privacy
May 24, 2020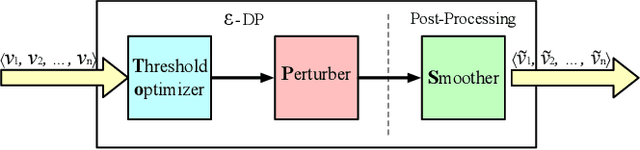
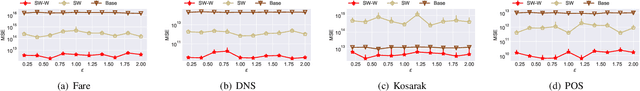
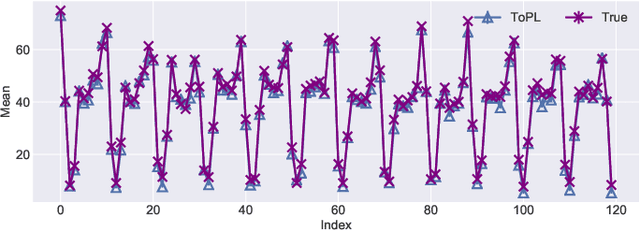
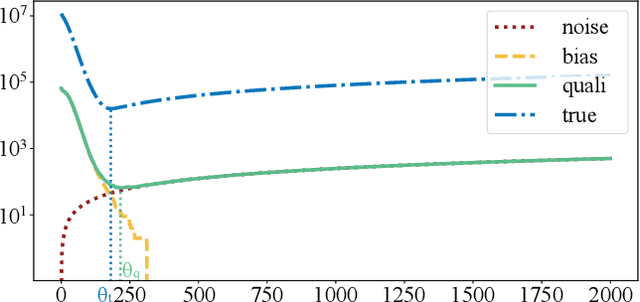
Abstract:In this paper, we study the problem of publishing a stream of real-valued data satisfying differential privacy (DP). One major challenge is that the maximal possible value can be quite large; thus it is necessary to estimate a threshold so that numbers above it are truncated to reduce the amount of noise that is required to all the data. The estimation must be done based on the data in a private fashion. We develop such a method that uses the Exponential Mechanism with a quality function that approximates well the utility goal while maintaining a low sensitivity. Given the threshold, we then propose a novel online hierarchical method and several post-processing techniques. Building on these ideas, we formalize the steps into a framework for private publishing of stream data. Our framework consists of three components: a threshold optimizer that privately estimates the threshold, a perturber that adds calibrated noises to the stream, and a smoother that improves the result using post-processing. Within our framework, we design an algorithm satisfying the more stringent setting of DP called local DP (LDP). To our knowledge, this is the first LDP algorithm for publishing streaming data. Using four real-world datasets, we demonstrate that our mechanism outperforms the state-of-the-art by a factor of 6-10 orders of magnitude in terms of utility (measured by the mean squared error of answering a random range query).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge