Zhengyu Li
DiMo: Discrete Diffusion Modeling for Motion Generation and Understanding
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Prior masked modeling motion generation methods predominantly study text-to-motion. We present DiMo, a discrete diffusion-style framework, which extends masked modeling to bidirectional text--motion understanding and generation. Unlike GPT-style autoregressive approaches that tokenize motion and decode sequentially, DiMo performs iterative masked token refinement, unifying Text-to-Motion (T2M), Motion-to-Text (M2T), and text-free Motion-to-Motion (M2M) within a single model. This decoding paradigm naturally enables a quality-latency trade-off at inference via the number of refinement steps.We further improve motion token fidelity with residual vector quantization (RVQ) and enhance alignment and controllability with Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO). Experiments on HumanML3D and KIT-ML show strong motion quality and competitive bidirectional understanding under a unified framework. In addition, we demonstrate model ability in text-free motion completion, text-guided motion prediction and motion caption correction without architectural change.Additional qualitative results are available on our project page: https://animotionlab.github.io/DiMo/.
TimeART: Towards Agentic Time Series Reasoning via Tool-Augmentation
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Time series data widely exist in real-world cyber-physical systems. Though analyzing and interpreting them contributes to significant values, e.g, disaster prediction and financial risk control, current workflows mainly rely on human data scientists, which requires significant labor costs and lacks automation. To tackle this, we introduce TimeART, a framework fusing the analytical capability of strong out-of-the-box tools and the reasoning capability of Large Language Models (LLMs), which serves as a fully agentic data scientist for Time Series Question Answering (TSQA). To teach the LLM-based Time Series Reasoning Models (TSRMs) strategic tool-use, we also collect a 100k expert trajectory corpus called TimeToolBench. To enhance TSRMs' generalization capability, we then devise a four-stage training strategy, which boosts TSRMs through learning from their own early experiences and self-reflections. Experimentally, we train an 8B TSRM on TimeToolBench and equip it with the TimeART framework, and it achieves consistent state-of-the-art performance on multiple TSQA tasks, which pioneers a novel approach towards agentic time series reasoning.
FLAME: Flow Enhanced Legendre Memory Models for General Time Series Forecasting
Dec 16, 2025
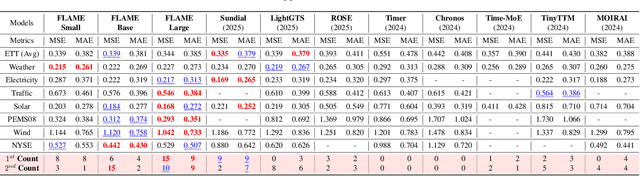
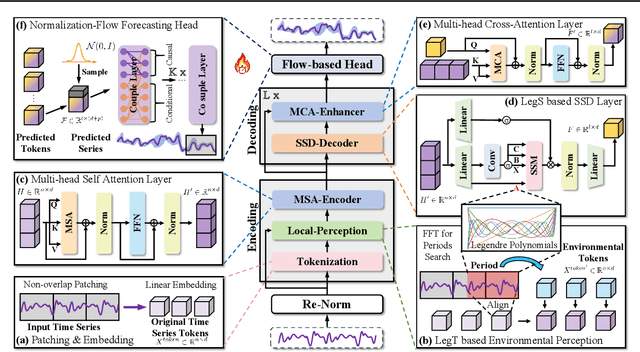
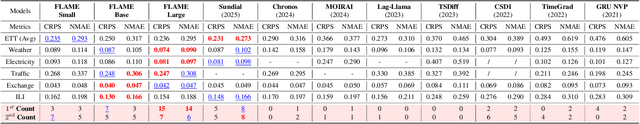
Abstract:In this work, we introduce FLAME, a family of extremely lightweight and capable Time Series Foundation Models, which support both deterministic and probabilistic forecasting via generative probabilistic modeling, thus ensuring both efficiency and robustness. FLAME utilizes the Legendre Memory for strong generalization capabilities. Through adapting variants of Legendre Memory, i.e., translated Legendre (LegT) and scaled Legendre (LegS), in the Encoding and Decoding phases, FLAME can effectively capture the inherent inductive bias within data and make efficient long-range inferences. To enhance the accuracy of probabilistic forecasting while keeping efficient, FLAME adopts a Normalization Flow based forecasting head, which can model the arbitrarily intricate distributions over the forecasting horizon in a generative manner. Comprehensive experiments on well-recognized benchmarks, including TSFM-Bench and ProbTS, demonstrate the consistent state-of-the-art zero-shot performance of FLAME on both deterministic and probabilistic forecasting tasks.
MoCapAnything: Unified 3D Motion Capture for Arbitrary Skeletons from Monocular Videos
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Motion capture now underpins content creation far beyond digital humans, yet most existing pipelines remain species- or template-specific. We formalize this gap as Category-Agnostic Motion Capture (CAMoCap): given a monocular video and an arbitrary rigged 3D asset as a prompt, the goal is to reconstruct a rotation-based animation such as BVH that directly drives the specific asset. We present MoCapAnything, a reference-guided, factorized framework that first predicts 3D joint trajectories and then recovers asset-specific rotations via constraint-aware inverse kinematics. The system contains three learnable modules and a lightweight IK stage: (1) a Reference Prompt Encoder that extracts per-joint queries from the asset's skeleton, mesh, and rendered images; (2) a Video Feature Extractor that computes dense visual descriptors and reconstructs a coarse 4D deforming mesh to bridge the gap between video and joint space; and (3) a Unified Motion Decoder that fuses these cues to produce temporally coherent trajectories. We also curate Truebones Zoo with 1038 motion clips, each providing a standardized skeleton-mesh-render triad. Experiments on both in-domain benchmarks and in-the-wild videos show that MoCapAnything delivers high-quality skeletal animations and exhibits meaningful cross-species retargeting across heterogeneous rigs, enabling scalable, prompt-driven 3D motion capture for arbitrary assets. Project page: https://animotionlab.github.io/MoCapAnything/
SWiT-4D: Sliding-Window Transformer for Lossless and Parameter-Free Temporal 4D Generation
Dec 11, 2025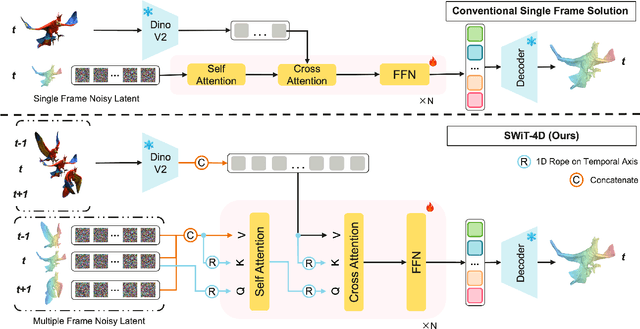
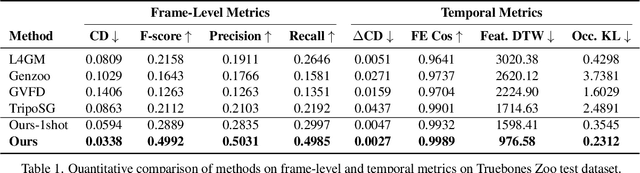
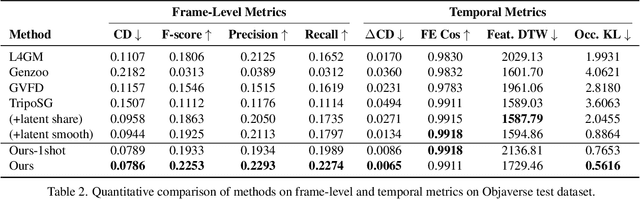
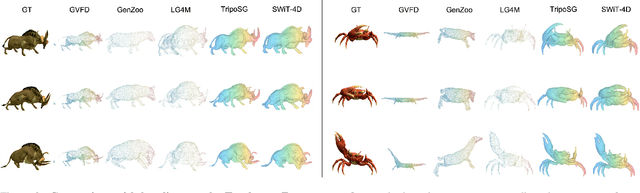
Abstract:Despite significant progress in 4D content generation, the conversion of monocular videos into high-quality animated 3D assets with explicit 4D meshes remains considerably challenging. The scarcity of large-scale, naturally captured 4D mesh datasets further limits the ability to train generalizable video-to-4D models from scratch in a purely data-driven manner. Meanwhile, advances in image-to-3D generation, supported by extensive datasets, offer powerful prior models that can be leveraged. To better utilize these priors while minimizing reliance on 4D supervision, we introduce SWiT-4D, a Sliding-Window Transformer for lossless, parameter-free temporal 4D mesh generation. SWiT-4D integrates seamlessly with any Diffusion Transformer (DiT)-based image-to-3D generator, adding spatial-temporal modeling across video frames while preserving the original single-image forward process, enabling 4D mesh reconstruction from videos of arbitrary length. To recover global translation, we further introduce an optimization-based trajectory module tailored for static-camera monocular videos. SWiT-4D demonstrates strong data efficiency: with only a single short (<10s) video for fine-tuning, it achieves high-fidelity geometry and stable temporal consistency, indicating practical deployability under extremely limited 4D supervision. Comprehensive experiments on both in-domain zoo-test sets and challenging out-of-domain benchmarks (C4D, Objaverse, and in-the-wild videos) show that SWiT-4D consistently outperforms existing baselines in temporal smoothness. Project page: https://animotionlab.github.io/SWIT4D/
Enhancing Time Series Forecasting through Selective Representation Spaces: A Patch Perspective
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Time Series Forecasting has made significant progress with the help of Patching technique, which partitions time series into multiple patches to effectively retain contextual semantic information into a representation space beneficial for modeling long-term dependencies. However, conventional patching partitions a time series into adjacent patches, which causes a fixed representation space, thus resulting in insufficiently expressful representations. In this paper, we pioneer the exploration of constructing a selective representation space to flexibly include the most informative patches for forecasting. Specifically, we propose the Selective Representation Space (SRS) module, which utilizes the learnable Selective Patching and Dynamic Reassembly techniques to adaptively select and shuffle the patches from the contextual time series, aiming at fully exploiting the information of contextual time series to enhance the forecasting performance of patch-based models. To demonstrate the effectiveness of SRS module, we propose a simple yet effective SRSNet consisting of SRS and an MLP head, which achieves state-of-the-art performance on real-world datasets from multiple domains. Furthermore, as a novel plugin-and-play module, SRS can also enhance the performance of existing patch-based models. The resources are available at https://github.com/decisionintelligence/SRSNet.
Unlocking the Power of Mixture-of-Experts for Task-Aware Time Series Analytics
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Time Series Analysis is widely used in various real-world applications such as weather forecasting, financial fraud detection, imputation for missing data in IoT systems, and classification for action recognization. Mixture-of-Experts (MoE), as a powerful architecture, though demonstrating effectiveness in NLP, still falls short in adapting to versatile tasks in time series analytics due to its task-agnostic router and the lack of capability in modeling channel correlations. In this study, we propose a novel, general MoE-based time series framework called PatchMoE to support the intricate ``knowledge'' utilization for distinct tasks, thus task-aware. Based on the observation that hierarchical representations often vary across tasks, e.g., forecasting vs. classification, we propose a Recurrent Noisy Gating to utilize the hierarchical information in routing, thus obtaining task-sepcific capability. And the routing strategy is operated on time series tokens in both temporal and channel dimensions, and encouraged by a meticulously designed Temporal \& Channel Load Balancing Loss to model the intricate temporal and channel correlations. Comprehensive experiments on five downstream tasks demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of PatchMoE.
DAG: A Dual Causal Network for Time Series Forecasting with Exogenous Variables
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Time series forecasting is crucial in various fields such as economics, traffic, and AIOps. However, in real-world applications, focusing solely on the endogenous variables (i.e., target variables), is often insufficient to ensure accurate predictions. Considering exogenous variables (i.e., covariates) provides additional predictive information, thereby improving forecasting accuracy. However, existing methods for time series forecasting with exogenous variables (TSF-X) have the following shortcomings: 1) they do not leverage future exogenous variables, 2) they fail to account for the causal relationships between endogenous and exogenous variables. As a result, their performance is suboptimal. In this study, to better leverage exogenous variables, especially future exogenous variable, we propose a general framework DAG, which utilizes dual causal network along both the temporal and channel dimensions for time series forecasting with exogenous variables. Specifically, we first introduce the Temporal Causal Module, which includes a causal discovery module to capture how historical exogenous variables affect future exogenous variables. Following this, we construct a causal injection module that incorporates the discovered causal relationships into the process of forecasting future endogenous variables based on historical endogenous variables. Next, we propose the Channel Causal Module, which follows a similar design principle. It features a causal discovery module models how historical exogenous variables influence historical endogenous variables, and a causal injection module incorporates the discovered relationships to enhance the prediction of future endogenous variables based on future exogenous variables.
Rethinking Irregular Time Series Forecasting: A Simple yet Effective Baseline
May 16, 2025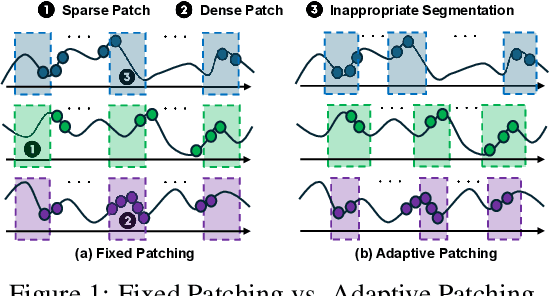
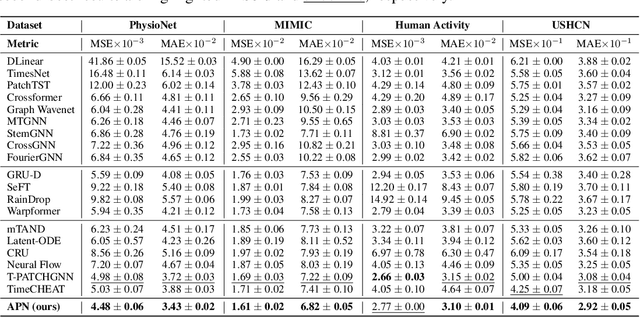
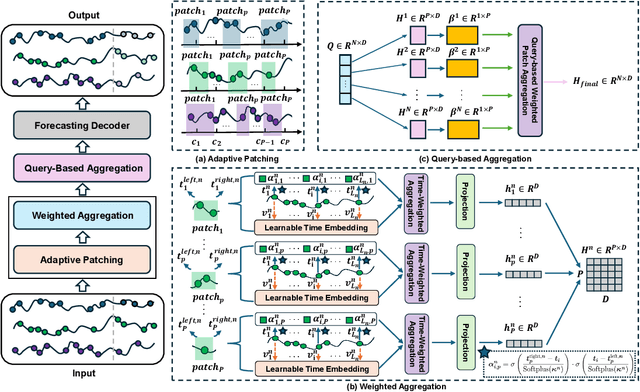
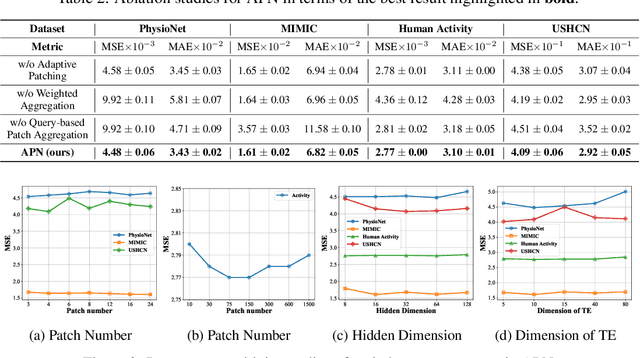
Abstract:The forecasting of irregular multivariate time series (IMTS) is crucial in key areas such as healthcare, biomechanics, climate science, and astronomy. However, achieving accurate and practical predictions is challenging due to two main factors. First, the inherent irregularity and data missingness in irregular time series make modeling difficult. Second, most existing methods are typically complex and resource-intensive. In this study, we propose a general framework called APN to address these challenges. Specifically, we design a novel Time-Aware Patch Aggregation (TAPA) module that achieves adaptive patching. By learning dynamically adjustable patch boundaries and a time-aware weighted averaging strategy, TAPA transforms the original irregular sequences into high-quality, regularized representations in a channel-independent manner. Additionally, we use a simple query module to effectively integrate historical information while maintaining the model's efficiency. Finally, predictions are made by a shallow MLP. Experimental results on multiple real-world datasets show that APN outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in both efficiency and accuracy.
Transferable Mask Transformer: Cross-domain Semantic Segmentation with Region-adaptive Transferability Estimation
Apr 08, 2025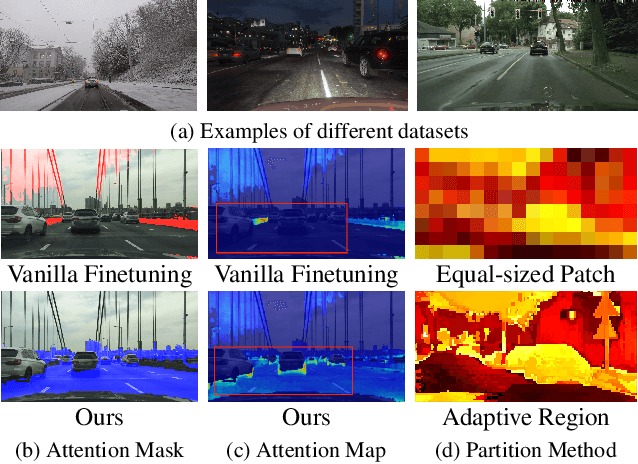
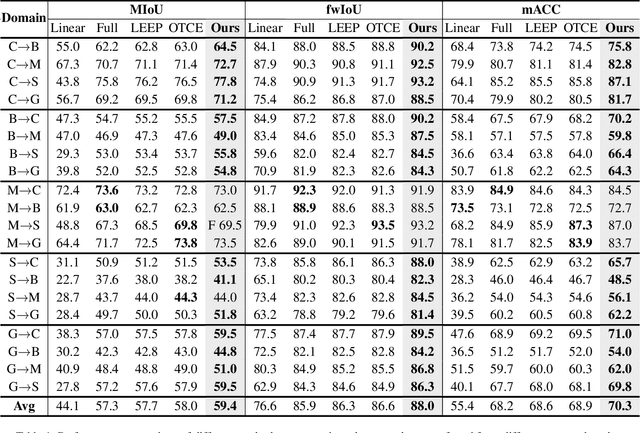
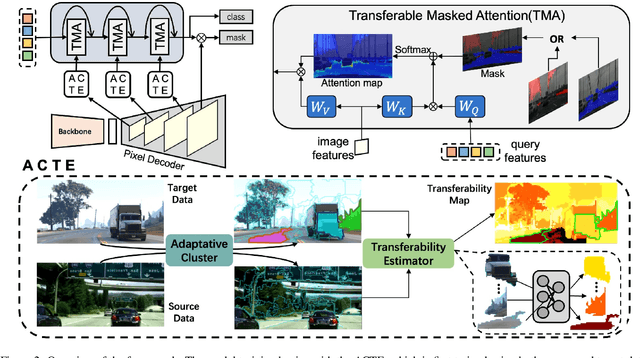
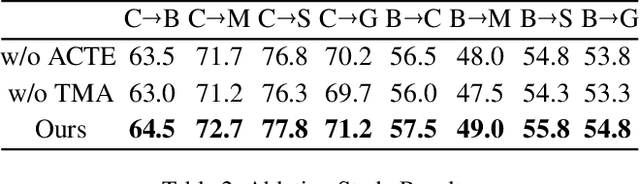
Abstract:Recent advances in Vision Transformers (ViTs) have set new benchmarks in semantic segmentation. However, when adapting pretrained ViTs to new target domains, significant performance degradation often occurs due to distribution shifts, resulting in suboptimal global attention. Since self-attention mechanisms are inherently data-driven, they may fail to effectively attend to key objects when source and target domains exhibit differences in texture, scale, or object co-occurrence patterns. While global and patch-level domain adaptation methods provide partial solutions, region-level adaptation with dynamically shaped regions is crucial due to spatial heterogeneity in transferability across different image areas. We present Transferable Mask Transformer (TMT), a novel region-level adaptation framework for semantic segmentation that aligns cross-domain representations through spatial transferability analysis. TMT consists of two key components: (1) An Adaptive Cluster-based Transferability Estimator (ACTE) that dynamically segments images into structurally and semantically coherent regions for localized transferability assessment, and (2) A Transferable Masked Attention (TMA) module that integrates region-specific transferability maps into ViTs' attention mechanisms, prioritizing adaptation in regions with low transferability and high semantic uncertainty. Comprehensive evaluations across 20 cross-domain pairs demonstrate TMT's superiority, achieving an average 2% MIoU improvement over vanilla fine-tuning and a 1.28% increase compared to state-of-the-art baselines. The source code will be publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge