Xiangfei Qiu
SEER: Transformer-based Robust Time Series Forecasting via Automated Patch Enhancement and Replacement
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Time series forecasting is important in many fields that require accurate predictions for decision-making. Patching techniques, commonly used and effective in time series modeling, help capture temporal dependencies by dividing the data into patches. However, existing patch-based methods fail to dynamically select patches and typically use all patches during the prediction process. In real-world time series, there are often low-quality issues during data collection, such as missing values, distribution shifts, anomalies and white noise, which may cause some patches to contain low-quality information, negatively impacting the prediction results. To address this issue, this study proposes a robust time series forecasting framework called SEER. Firstly, we propose an Augmented Embedding Module, which improves patch-wise representations using a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture and obtains series-wise token representations through a channel-adaptive perception mechanism. Secondly, we introduce a Learnable Patch Replacement Module, which enhances forecasting robustness and model accuracy through a two-stage process: 1) a dynamic filtering mechanism eliminates negative patch-wise tokens; 2) a replaced attention module substitutes the identified low-quality patches with global series-wise token, further refining their representations through a causal attention mechanism. Comprehensive experimental results demonstrate the SOTA performance of SEER.
Bridging Time and Frequency: A Joint Modeling Framework for Irregular Multivariate Time Series Forecasting
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Irregular multivariate time series forecasting (IMTSF) is challenging due to non-uniform sampling and variable asynchronicity. These irregularities violate the equidistant assumptions of standard models, hindering local temporal modeling and rendering classical frequency-domain methods ineffective for capturing global periodic structures. To address this challenge, we propose TFMixer, a joint time-frequency modeling framework for IMTS forecasting. Specifically, TFMixer incorporates a Global Frequency Module that employs a learnable Non-Uniform Discrete Fourier Transform (NUDFT) to directly extract spectral representations from irregular timestamps. In parallel, the Local Time Module introduces a query-based patch mixing mechanism to adaptively aggregate informative temporal patches and alleviate information density imbalance. Finally, TFMixer fuses the time-domain and frequency-domain representations to generate forecasts and further leverages inverse NUDFT for explicit seasonal extrapolation. Extensive experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate the state--of-the-art performance of TFMixer.
TimeART: Towards Agentic Time Series Reasoning via Tool-Augmentation
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Time series data widely exist in real-world cyber-physical systems. Though analyzing and interpreting them contributes to significant values, e.g, disaster prediction and financial risk control, current workflows mainly rely on human data scientists, which requires significant labor costs and lacks automation. To tackle this, we introduce TimeART, a framework fusing the analytical capability of strong out-of-the-box tools and the reasoning capability of Large Language Models (LLMs), which serves as a fully agentic data scientist for Time Series Question Answering (TSQA). To teach the LLM-based Time Series Reasoning Models (TSRMs) strategic tool-use, we also collect a 100k expert trajectory corpus called TimeToolBench. To enhance TSRMs' generalization capability, we then devise a four-stage training strategy, which boosts TSRMs through learning from their own early experiences and self-reflections. Experimentally, we train an 8B TSRM on TimeToolBench and equip it with the TimeART framework, and it achieves consistent state-of-the-art performance on multiple TSQA tasks, which pioneers a novel approach towards agentic time series reasoning.
FLAME: Flow Enhanced Legendre Memory Models for General Time Series Forecasting
Dec 16, 2025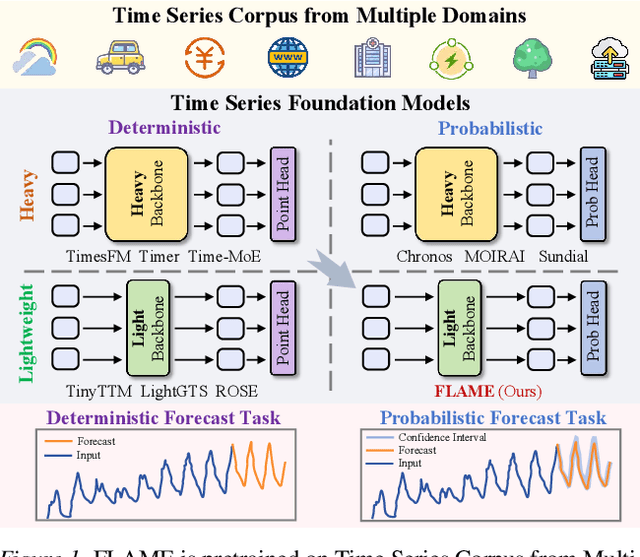
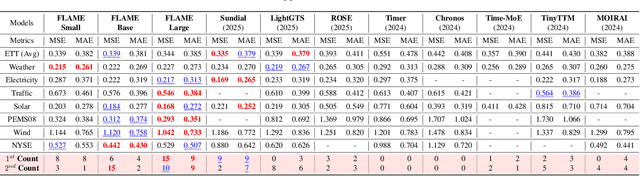
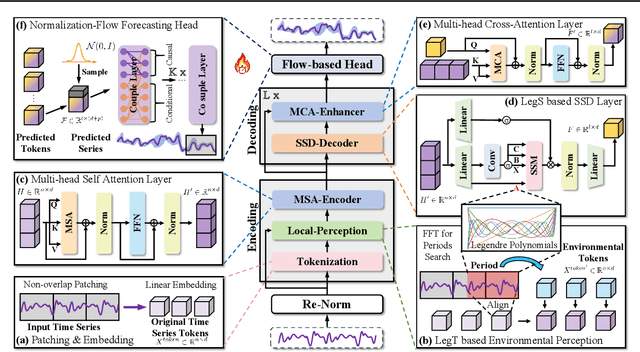
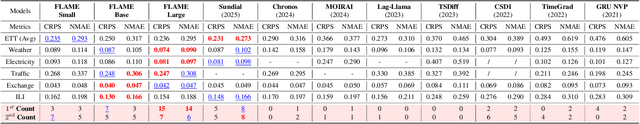
Abstract:In this work, we introduce FLAME, a family of extremely lightweight and capable Time Series Foundation Models, which support both deterministic and probabilistic forecasting via generative probabilistic modeling, thus ensuring both efficiency and robustness. FLAME utilizes the Legendre Memory for strong generalization capabilities. Through adapting variants of Legendre Memory, i.e., translated Legendre (LegT) and scaled Legendre (LegS), in the Encoding and Decoding phases, FLAME can effectively capture the inherent inductive bias within data and make efficient long-range inferences. To enhance the accuracy of probabilistic forecasting while keeping efficient, FLAME adopts a Normalization Flow based forecasting head, which can model the arbitrarily intricate distributions over the forecasting horizon in a generative manner. Comprehensive experiments on well-recognized benchmarks, including TSFM-Bench and ProbTS, demonstrate the consistent state-of-the-art zero-shot performance of FLAME on both deterministic and probabilistic forecasting tasks.
An Encode-then-Decompose Approach to Unsupervised Time Series Anomaly Detection on Contaminated Training Data--Extended Version
Oct 21, 2025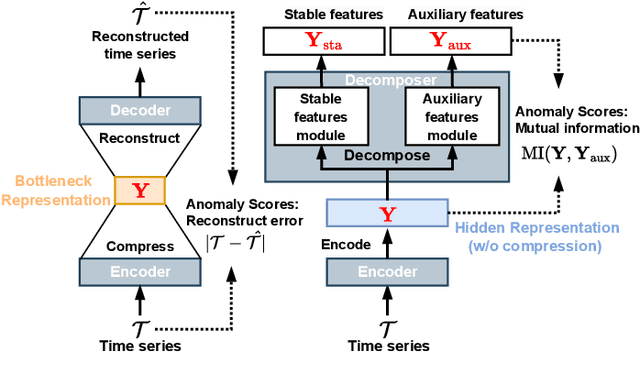
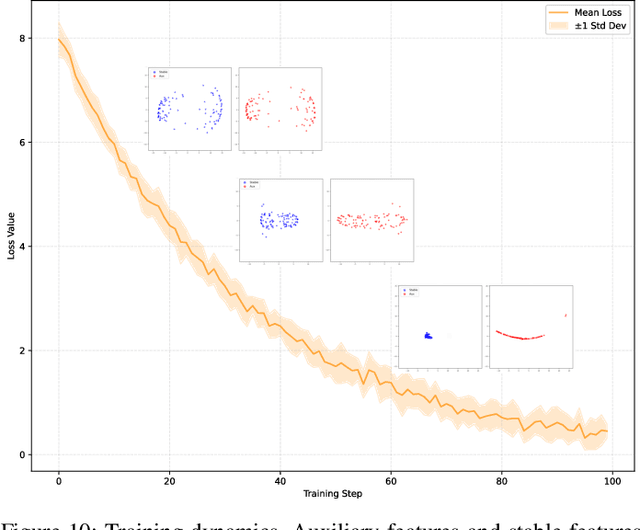
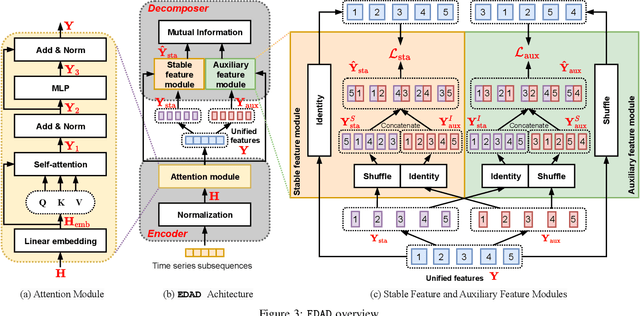
Abstract:Time series anomaly detection is important in modern large-scale systems and is applied in a variety of domains to analyze and monitor the operation of diverse systems. Unsupervised approaches have received widespread interest, as they do not require anomaly labels during training, thus avoiding potentially high costs and having wider applications. Among these, autoencoders have received extensive attention. They use reconstruction errors from compressed representations to define anomaly scores. However, representations learned by autoencoders are sensitive to anomalies in training time series, causing reduced accuracy. We propose a novel encode-then-decompose paradigm, where we decompose the encoded representation into stable and auxiliary representations, thereby enhancing the robustness when training with contaminated time series. In addition, we propose a novel mutual information based metric to replace the reconstruction errors for identifying anomalies. Our proposal demonstrates competitive or state-of-the-art performance on eight commonly used multi- and univariate time series benchmarks and exhibits robustness to time series with different contamination ratios.
Enhancing Time Series Forecasting through Selective Representation Spaces: A Patch Perspective
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:Time Series Forecasting has made significant progress with the help of Patching technique, which partitions time series into multiple patches to effectively retain contextual semantic information into a representation space beneficial for modeling long-term dependencies. However, conventional patching partitions a time series into adjacent patches, which causes a fixed representation space, thus resulting in insufficiently expressful representations. In this paper, we pioneer the exploration of constructing a selective representation space to flexibly include the most informative patches for forecasting. Specifically, we propose the Selective Representation Space (SRS) module, which utilizes the learnable Selective Patching and Dynamic Reassembly techniques to adaptively select and shuffle the patches from the contextual time series, aiming at fully exploiting the information of contextual time series to enhance the forecasting performance of patch-based models. To demonstrate the effectiveness of SRS module, we propose a simple yet effective SRSNet consisting of SRS and an MLP head, which achieves state-of-the-art performance on real-world datasets from multiple domains. Furthermore, as a novel plugin-and-play module, SRS can also enhance the performance of existing patch-based models. The resources are available at https://github.com/decisionintelligence/SRSNet.
Unlocking the Power of Mixture-of-Experts for Task-Aware Time Series Analytics
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Time Series Analysis is widely used in various real-world applications such as weather forecasting, financial fraud detection, imputation for missing data in IoT systems, and classification for action recognization. Mixture-of-Experts (MoE), as a powerful architecture, though demonstrating effectiveness in NLP, still falls short in adapting to versatile tasks in time series analytics due to its task-agnostic router and the lack of capability in modeling channel correlations. In this study, we propose a novel, general MoE-based time series framework called PatchMoE to support the intricate ``knowledge'' utilization for distinct tasks, thus task-aware. Based on the observation that hierarchical representations often vary across tasks, e.g., forecasting vs. classification, we propose a Recurrent Noisy Gating to utilize the hierarchical information in routing, thus obtaining task-sepcific capability. And the routing strategy is operated on time series tokens in both temporal and channel dimensions, and encouraged by a meticulously designed Temporal \& Channel Load Balancing Loss to model the intricate temporal and channel correlations. Comprehensive experiments on five downstream tasks demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance of PatchMoE.
DAG: A Dual Causal Network for Time Series Forecasting with Exogenous Variables
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Time series forecasting is crucial in various fields such as economics, traffic, and AIOps. However, in real-world applications, focusing solely on the endogenous variables (i.e., target variables), is often insufficient to ensure accurate predictions. Considering exogenous variables (i.e., covariates) provides additional predictive information, thereby improving forecasting accuracy. However, existing methods for time series forecasting with exogenous variables (TSF-X) have the following shortcomings: 1) they do not leverage future exogenous variables, 2) they fail to account for the causal relationships between endogenous and exogenous variables. As a result, their performance is suboptimal. In this study, to better leverage exogenous variables, especially future exogenous variable, we propose a general framework DAG, which utilizes dual causal network along both the temporal and channel dimensions for time series forecasting with exogenous variables. Specifically, we first introduce the Temporal Causal Module, which includes a causal discovery module to capture how historical exogenous variables affect future exogenous variables. Following this, we construct a causal injection module that incorporates the discovered causal relationships into the process of forecasting future endogenous variables based on historical endogenous variables. Next, we propose the Channel Causal Module, which follows a similar design principle. It features a causal discovery module models how historical exogenous variables influence historical endogenous variables, and a causal injection module incorporates the discovered relationships to enhance the prediction of future endogenous variables based on future exogenous variables.
$K^2$VAE: A Koopman-Kalman Enhanced Variational AutoEncoder for Probabilistic Time Series Forecasting
May 29, 2025



Abstract:Probabilistic Time Series Forecasting (PTSF) plays a crucial role in decision-making across various fields, including economics, energy, and transportation. Most existing methods excell at short-term forecasting, while overlooking the hurdles of Long-term Probabilistic Time Series Forecasting (LPTSF). As the forecast horizon extends, the inherent nonlinear dynamics have a significant adverse effect on prediction accuracy, and make generative models inefficient by increasing the cost of each iteration. To overcome these limitations, we introduce $K^2$VAE, an efficient VAE-based generative model that leverages a KoopmanNet to transform nonlinear time series into a linear dynamical system, and devises a KalmanNet to refine predictions and model uncertainty in such linear system, which reduces error accumulation in long-term forecasting. Extensive experiments demonstrate that $K^2$VAE outperforms state-of-the-art methods in both short- and long-term PTSF, providing a more efficient and accurate solution.
Rethinking Irregular Time Series Forecasting: A Simple yet Effective Baseline
May 16, 2025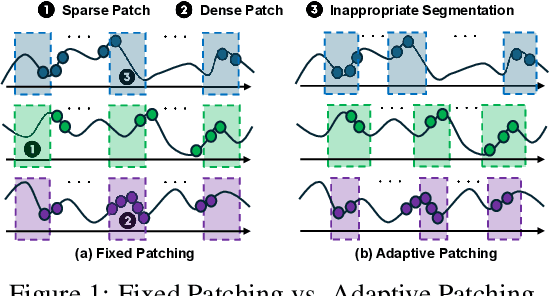
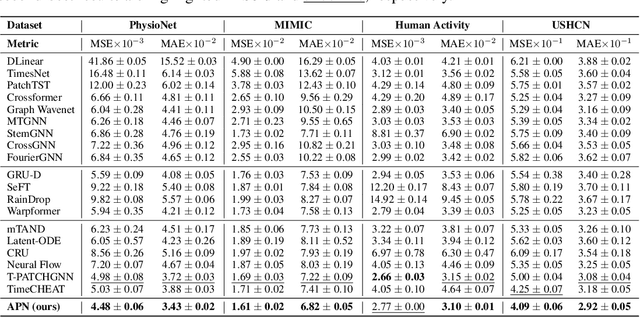
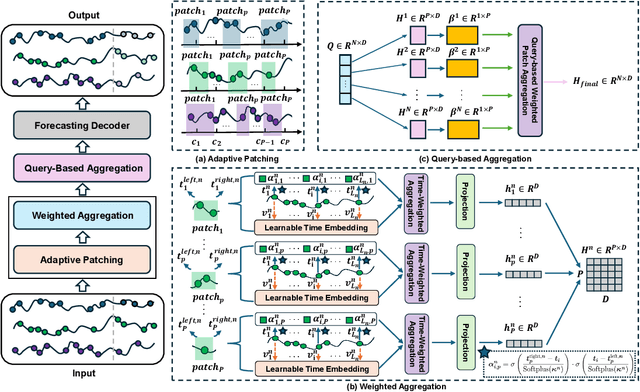
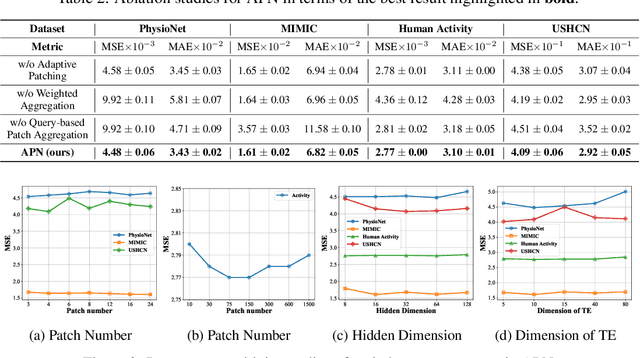
Abstract:The forecasting of irregular multivariate time series (IMTS) is crucial in key areas such as healthcare, biomechanics, climate science, and astronomy. However, achieving accurate and practical predictions is challenging due to two main factors. First, the inherent irregularity and data missingness in irregular time series make modeling difficult. Second, most existing methods are typically complex and resource-intensive. In this study, we propose a general framework called APN to address these challenges. Specifically, we design a novel Time-Aware Patch Aggregation (TAPA) module that achieves adaptive patching. By learning dynamically adjustable patch boundaries and a time-aware weighted averaging strategy, TAPA transforms the original irregular sequences into high-quality, regularized representations in a channel-independent manner. Additionally, we use a simple query module to effectively integrate historical information while maintaining the model's efficiency. Finally, predictions are made by a shallow MLP. Experimental results on multiple real-world datasets show that APN outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in both efficiency and accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge