Zhenli Sheng
SEFraud: Graph-based Self-Explainable Fraud Detection via Interpretative Mask Learning
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Graph-based fraud detection has widespread application in modern industry scenarios, such as spam review and malicious account detection. While considerable efforts have been devoted to designing adequate fraud detectors, the interpretability of their results has often been overlooked. Previous works have attempted to generate explanations for specific instances using post-hoc explaining methods such as a GNNExplainer. However, post-hoc explanations can not facilitate the model predictions and the computational cost of these methods cannot meet practical requirements, thus limiting their application in real-world scenarios. To address these issues, we propose SEFraud, a novel graph-based self-explainable fraud detection framework that simultaneously tackles fraud detection and result in interpretability. Concretely, SEFraud first leverages customized heterogeneous graph transformer networks with learnable feature masks and edge masks to learn expressive representations from the informative heterogeneously typed transactions. A new triplet loss is further designed to enhance the performance of mask learning. Empirical results on various datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of SEFraud as it shows considerable advantages in both the fraud detection performance and interpretability of prediction results. Moreover, SEFraud has been deployed and offers explainable fraud detection service for the largest bank in China, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China Limited (ICBC). Results collected from the production environment of ICBC show that SEFraud can provide accurate detection results and comprehensive explanations that align with the expert business understanding, confirming its efficiency and applicability in large-scale online services.
Investigating Memory Failure Prediction Across CPU Architectures
Jun 08, 2024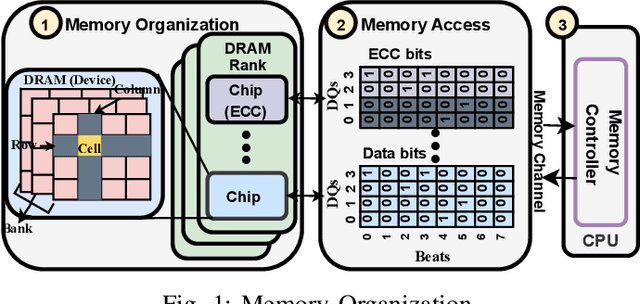
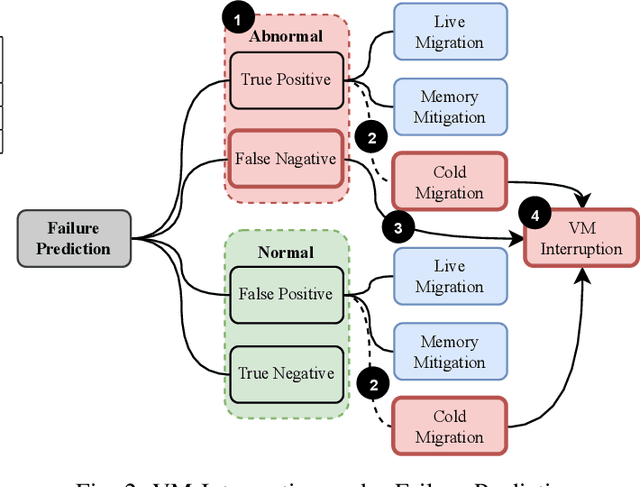
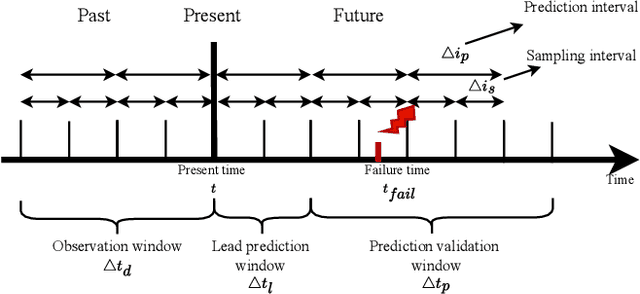
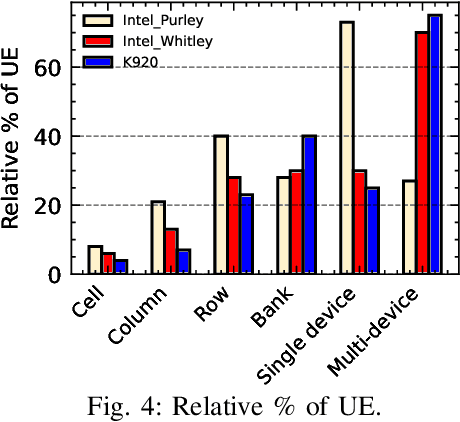
Abstract:Large-scale datacenters often experience memory failures, where Uncorrectable Errors (UEs) highlight critical malfunction in Dual Inline Memory Modules (DIMMs). Existing approaches primarily utilize Correctable Errors (CEs) to predict UEs, yet they typically neglect how these errors vary between different CPU architectures, especially in terms of Error Correction Code (ECC) applicability. In this paper, we investigate the correlation between CEs and UEs across different CPU architectures, including X86 and ARM. Our analysis identifies unique patterns of memory failure associated with each processor platform. Leveraging Machine Learning (ML) techniques on production datasets, we conduct the memory failure prediction in different processors' platforms, achieving up to 15% improvements in F1-score compared to the existing algorithm. Finally, an MLOps (Machine Learning Operations) framework is provided to consistently improve the failure prediction in the production environment.
TFB: Towards Comprehensive and Fair Benchmarking of Time Series Forecasting Methods
Apr 08, 2024



Abstract:Time series are generated in diverse domains such as economic, traffic, health, and energy, where forecasting of future values has numerous important applications. Not surprisingly, many forecasting methods are being proposed. To ensure progress, it is essential to be able to study and compare such methods empirically in a comprehensive and reliable manner. To achieve this, we propose TFB, an automated benchmark for Time Series Forecasting (TSF) methods. TFB advances the state-of-the-art by addressing shortcomings related to datasets, comparison methods, and evaluation pipelines: 1) insufficient coverage of data domains, 2) stereotype bias against traditional methods, and 3) inconsistent and inflexible pipelines. To achieve better domain coverage, we include datasets from 10 different domains: traffic, electricity, energy, the environment, nature, economic, stock markets, banking, health, and the web. We also provide a time series characterization to ensure that the selected datasets are comprehensive. To remove biases against some methods, we include a diverse range of methods, including statistical learning, machine learning, and deep learning methods, and we also support a variety of evaluation strategies and metrics to ensure a more comprehensive evaluations of different methods. To support the integration of different methods into the benchmark and enable fair comparisons, TFB features a flexible and scalable pipeline that eliminates biases. Next, we employ TFB to perform a thorough evaluation of 21 Univariate Time Series Forecasting (UTSF) methods on 8,068 univariate time series and 14 Multivariate Time Series Forecasting (MTSF) methods on 25 datasets. The benchmark code and data are available at https://github.com/decisionintelligence/TFB.
Enhancing Multi-field B2B Cloud Solution Matching via Contrastive Pre-training
Feb 11, 2024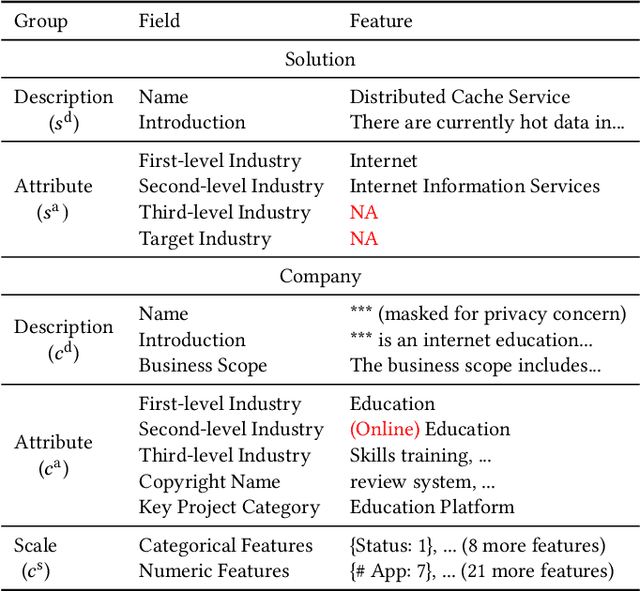
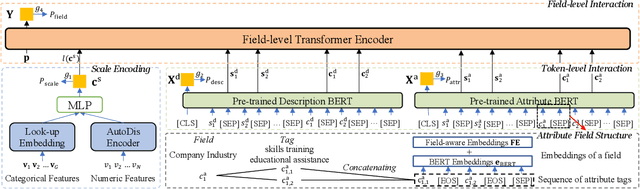
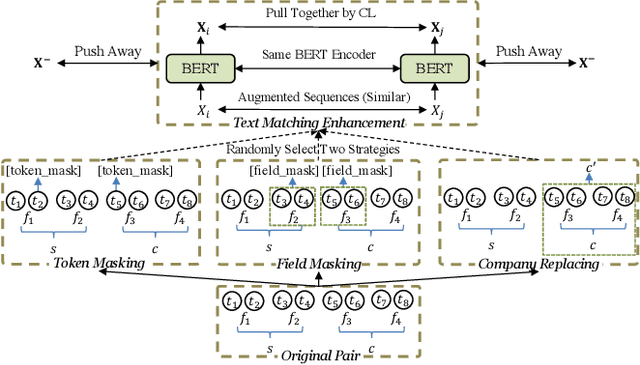
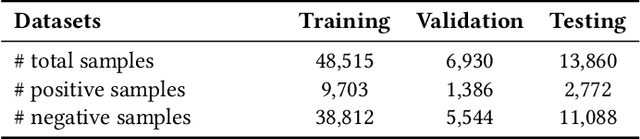
Abstract:Cloud solutions have gained significant popularity in the technology industry as they offer a combination of services and tools to tackle specific problems. However, despite their widespread use, the task of identifying appropriate company customers for a specific target solution to the sales team of a solution provider remains a complex business problem that existing matching systems have yet to adequately address. In this work, we study the B2B solution matching problem and identify two main challenges of this scenario: (1) the modeling of complex multi-field features and (2) the limited, incomplete, and sparse transaction data. To tackle these challenges, we propose a framework CAMA, which is built with a hierarchical multi-field matching structure as its backbone and supplemented by three data augmentation strategies and a contrastive pre-training objective to compensate for the imperfections in the available data. Through extensive experiments on a real-world dataset, we demonstrate that CAMA outperforms several strong baseline matching models significantly. Furthermore, we have deployed our matching framework on a system of Huawei Cloud. Our observations indicate an improvement of about 30% compared to the previous online model in terms of Conversion Rate (CVR), which demonstrates its great business value.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge