Zhengjie Huang
ERNIE 5.0 Technical Report
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:In this report, we introduce ERNIE 5.0, a natively autoregressive foundation model desinged for unified multimodal understanding and generation across text, image, video, and audio. All modalities are trained from scratch under a unified next-group-of-tokens prediction objective, based on an ultra-sparse mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture with modality-agnostic expert routing. To address practical challenges in large-scale deployment under diverse resource constraints, ERNIE 5.0 adopts a novel elastic training paradigm. Within a single pre-training run, the model learns a family of sub-models with varying depths, expert capacities, and routing sparsity, enabling flexible trade-offs among performance, model size, and inference latency in memory- or time-constrained scenarios. Moreover, we systematically address the challenges of scaling reinforcement learning to unified foundation models, thereby guaranteeing efficient and stable post-training under ultra-sparse MoE architectures and diverse multimodal settings. Extensive experiments demonstrate that ERNIE 5.0 achieves strong and balanced performance across multiple modalities. To the best of our knowledge, among publicly disclosed models, ERNIE 5.0 represents the first production-scale realization of a trillion-parameter unified autoregressive model that supports both multimodal understanding and generation. To facilitate further research, we present detailed visualizations of modality-agnostic expert routing in the unified model, alongside comprehensive empirical analysis of elastic training, aiming to offer profound insights to the community.
HGAMN: Heterogeneous Graph Attention Matching Network for Multilingual POI Retrieval at Baidu Maps
Sep 05, 2024



Abstract:The increasing interest in international travel has raised the demand of retrieving point of interests in multiple languages. This is even superior to find local venues such as restaurants and scenic spots in unfamiliar languages when traveling abroad. Multilingual POI retrieval, enabling users to find desired POIs in a demanded language using queries in numerous languages, has become an indispensable feature of today's global map applications such as Baidu Maps. This task is non-trivial because of two key challenges: (1) visiting sparsity and (2) multilingual query-POI matching. To this end, we propose a Heterogeneous Graph Attention Matching Network (HGAMN) to concurrently address both challenges. Specifically, we construct a heterogeneous graph that contains two types of nodes: POI node and query node using the search logs of Baidu Maps. To alleviate challenge \#1, we construct edges between different POI nodes to link the low-frequency POIs with the high-frequency ones, which enables the transfer of knowledge from the latter to the former. To mitigate challenge \#2, we construct edges between POI and query nodes based on the co-occurrences between queries and POIs, where queries in different languages and formulations can be aggregated for individual POIs. Moreover, we develop an attention-based network to jointly learn node representations of the heterogeneous graph and further design a cross-attention module to fuse the representations of both types of nodes for query-POI relevance scoring. Extensive experiments conducted on large-scale real-world datasets from Baidu Maps demonstrate the superiority and effectiveness of HGAMN. In addition, HGAMN has already been deployed in production at Baidu Maps, and it successfully keeps serving hundreds of millions of requests every day.
Spectral Heterogeneous Graph Convolutions via Positive Noncommutative Polynomials
May 31, 2023Abstract:Heterogeneous Graph Neural Networks (HGNNs) have gained significant popularity in various heterogeneous graph learning tasks. However, most HGNNs rely on spatial domain-based message passing and attention modules for information propagation and aggregation. These spatial-based HGNNs neglect the utilization of spectral graph convolutions, which are the foundation of Graph Convolutional Networks (GCN) on homogeneous graphs. Inspired by the effectiveness and scalability of spectral-based GNNs on homogeneous graphs, this paper explores the extension of spectral-based GNNs to heterogeneous graphs. We propose PSHGCN, a novel heterogeneous convolutional network based on positive noncommutative polynomials. PSHGCN provides a simple yet effective approach for learning spectral graph convolutions on heterogeneous graphs. Moreover, we demonstrate the rationale of PSHGCN in graph optimization. We conducted an extensive experimental study to show that PSHGCN can learn diverse spectral heterogeneous graph convolutions and achieve superior performance in node classification tasks. Our code is available at https://github.com/ivam-he/PSHGCN.
Label Information Enhanced Fraud Detection against Low Homophily in Graphs
Feb 21, 2023



Abstract:Node classification is a substantial problem in graph-based fraud detection. Many existing works adopt Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) to enhance fraud detectors. While promising, currently most GNN-based fraud detectors fail to generalize to the low homophily setting. Besides, label utilization has been proved to be significant factor for node classification problem. But we find they are less effective in fraud detection tasks due to the low homophily in graphs. In this work, we propose GAGA, a novel Group AGgregation enhanced TrAnsformer, to tackle the above challenges. Specifically, the group aggregation provides a portable method to cope with the low homophily issue. Such an aggregation explicitly integrates the label information to generate distinguishable neighborhood information. Along with group aggregation, an attempt towards end-to-end trainable group encoding is proposed which augments the original feature space with the class labels. Meanwhile, we devise two additional learnable encodings to recognize the structural and relational context. Then, we combine the group aggregation and the learnable encodings into a Transformer encoder to capture the semantic information. Experimental results clearly show that GAGA outperforms other competitive graph-based fraud detectors by up to 24.39% on two trending public datasets and a real-world industrial dataset from Anonymous. Even more, the group aggregation is demonstrated to outperform other label utilization methods (e.g., C&S, BoT/UniMP) in the low homophily setting.
Layout-aware Webpage Quality Assessment
Feb 05, 2023Abstract:Identifying high-quality webpages is fundamental for real-world search engines, which can fulfil users' information need with the less cognitive burden. Early studies of \emph{webpage quality assessment} usually design hand-crafted features that may only work on particular categories of webpages (e.g., shopping websites, medical websites). They can hardly be applied to real-world search engines that serve trillions of webpages with various types and purposes. In this paper, we propose a novel layout-aware webpage quality assessment model currently deployed in our search engine. Intuitively, layout is a universal and critical dimension for the quality assessment of different categories of webpages. Based on this, we directly employ the meta-data that describes a webpage, i.e., Document Object Model (DOM) tree, as the input of our model. The DOM tree data unifies the representation of webpages with different categories and purposes and indicates the layout of webpages. To assess webpage quality from complex DOM tree data, we propose a graph neural network (GNN) based method that extracts rich layout-aware information that implies webpage quality in an end-to-end manner. Moreover, we improve the GNN method with an attentive readout function, external web categories and a category-aware sampling method. We conduct rigorous offline and online experiments to show that our proposed solution is effective in real search engines, improving the overall usability and user experience.
Who is Gambling? Finding Cryptocurrency Gamblers Using Multi-modal Retrieval Methods
Nov 27, 2022Abstract:With the popularity of cryptocurrencies and the remarkable development of blockchain technology, decentralized applications emerged as a revolutionary force for the Internet. Meanwhile, decentralized applications have also attracted intense attention from the online gambling community, with more and more decentralized gambling platforms created through the help of smart contracts. Compared with conventional gambling platforms, decentralized gambling have transparent rules and a low participation threshold, attracting a substantial number of gamblers. In order to discover gambling behaviors and identify the contracts and addresses involved in gambling, we propose a tool termed ETHGamDet. The tool is able to automatically detect the smart contracts and addresses involved in gambling by scrutinizing the smart contract code and address transaction records. Interestingly, we present a novel LightGBM model with memory components, which possesses the ability to learn from its own misclassifications. As a side contribution, we construct and release a large-scale gambling dataset at https://github.com/AwesomeHuang/Bitcoin-Gambling-Dataset to facilitate future research in this field. Empirically, ETHGamDet achieves a F1-score of 0.72 and 0.89 in address classification and contract classification respectively, and offers novel and interesting insights.
Demystifying Bitcoin Address Behavior via Graph Neural Networks
Nov 26, 2022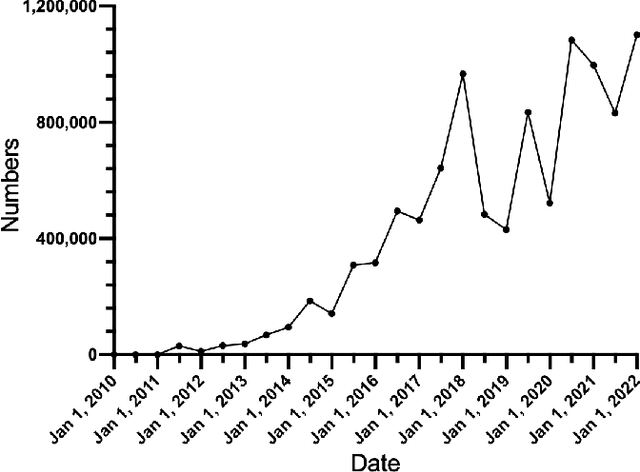
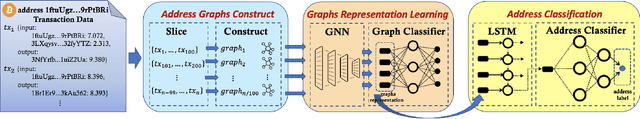
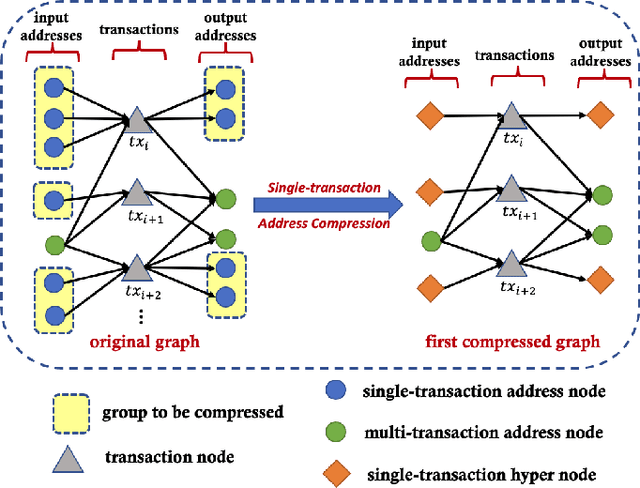

Abstract:Bitcoin is one of the decentralized cryptocurrencies powered by a peer-to-peer blockchain network. Parties who trade in the bitcoin network are not required to disclose any personal information. Such property of anonymity, however, precipitates potential malicious transactions to a certain extent. Indeed, various illegal activities such as money laundering, dark network trading, and gambling in the bitcoin network are nothing new now. While a proliferation of work has been developed to identify malicious bitcoin transactions, the behavior analysis and classification of bitcoin addresses are largely overlooked by existing tools. In this paper, we propose BAClassifier, a tool that can automatically classify bitcoin addresses based on their behaviors. Technically, we come up with the following three key designs. First, we consider casting the transactions of the bitcoin address into an address graph structure, of which we introduce a graph node compression technique and a graph structure augmentation method to characterize a unified graph representation. Furthermore, we leverage a graph feature network to learn the graph representations of each address and generate the graph embeddings. Finally, we aggregate all graph embeddings of an address into the address-level representation, and engage in a classification model to give the address behavior classification. As a side contribution, we construct and release a large-scale annotated dataset that consists of over 2 million real-world bitcoin addresses and concerns 4 types of address behaviors. Experimental results demonstrate that our proposed framework outperforms state-of-the-art bitcoin address classifiers and existing classification models, where the precision and F1-score are 96% and 95%, respectively. Our implementation and dataset are released, hoping to inspire others.
ERNIE-Layout: Layout Knowledge Enhanced Pre-training for Visually-rich Document Understanding
Oct 14, 2022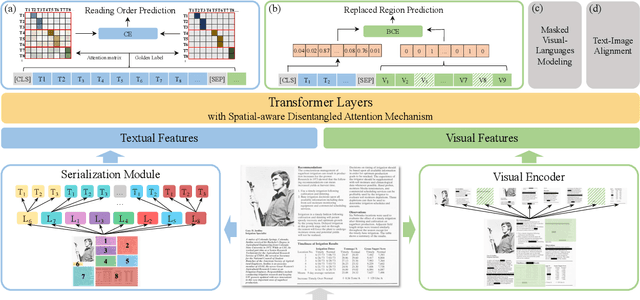



Abstract:Recent years have witnessed the rise and success of pre-training techniques in visually-rich document understanding. However, most existing methods lack the systematic mining and utilization of layout-centered knowledge, leading to sub-optimal performances. In this paper, we propose ERNIE-Layout, a novel document pre-training solution with layout knowledge enhancement in the whole workflow, to learn better representations that combine the features from text, layout, and image. Specifically, we first rearrange input sequences in the serialization stage, and then present a correlative pre-training task, reading order prediction, to learn the proper reading order of documents. To improve the layout awareness of the model, we integrate a spatial-aware disentangled attention into the multi-modal transformer and a replaced regions prediction task into the pre-training phase. Experimental results show that ERNIE-Layout achieves superior performance on various downstream tasks, setting new state-of-the-art on key information extraction, document image classification, and document question answering datasets. The code and models are publicly available at http://github.com/PaddlePaddle/PaddleNLP/tree/develop/model_zoo/ernie-layout.
Text detection and recognition based on a lensless imaging system
Oct 09, 2022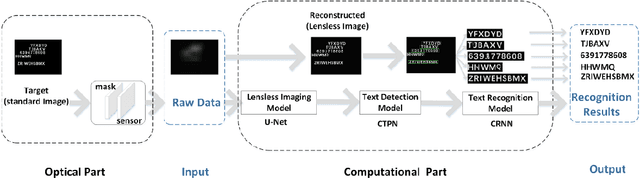
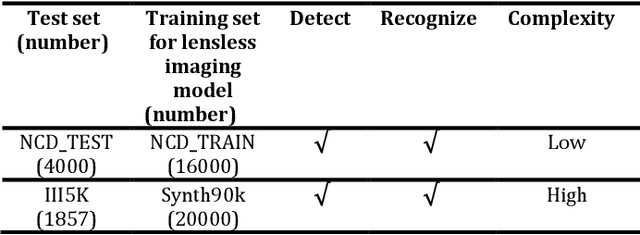
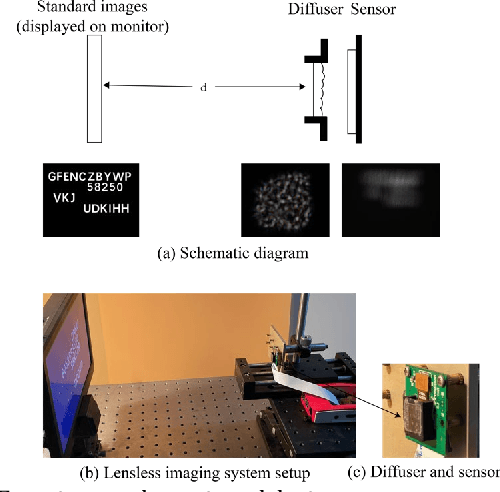
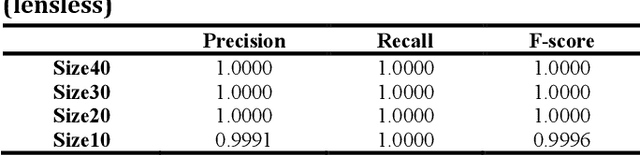
Abstract:Lensless cameras are characterized by several advantages (e.g., miniaturization, ease of manufacture, and low cost) as compared with conventional cameras. However, they have not been extensively employed due to their poor image clarity and low image resolution, especially for tasks that have high requirements on image quality and details such as text detection and text recognition. To address the problem, a framework of deep-learning-based pipeline structure was built to recognize text with three steps from raw data captured by employing lensless cameras. This pipeline structure consisted of the lensless imaging model U-Net, the text detection model connectionist text proposal network (CTPN), and the text recognition model convolutional recurrent neural network (CRNN). Compared with the method focusing only on image reconstruction, UNet in the pipeline was able to supplement the imaging details by enhancing factors related to character categories in the reconstruction process, so the textual information can be more effectively detected and recognized by CTPN and CRNN with fewer artifacts and high-clarity reconstructed lensless images. By performing experiments on datasets of different complexities, the applicability to text detection and recognition on lensless cameras was verified. This study reasonably demonstrates text detection and recognition tasks in the lensless camera system,and develops a basic method for novel applications.
ERNIE-mmLayout: Multi-grained MultiModal Transformer for Document Understanding
Sep 18, 2022


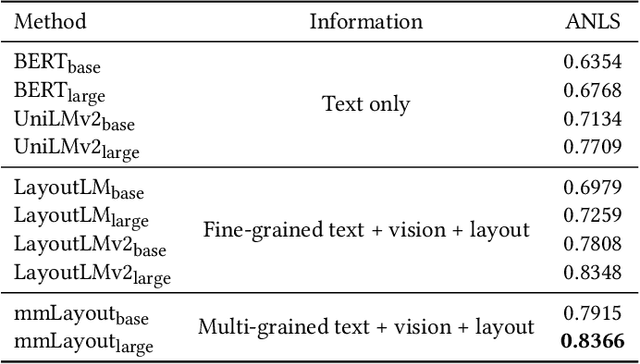
Abstract:Recent efforts of multimodal Transformers have improved Visually Rich Document Understanding (VrDU) tasks via incorporating visual and textual information. However, existing approaches mainly focus on fine-grained elements such as words and document image patches, making it hard for them to learn from coarse-grained elements, including natural lexical units like phrases and salient visual regions like prominent image regions. In this paper, we attach more importance to coarse-grained elements containing high-density information and consistent semantics, which are valuable for document understanding. At first, a document graph is proposed to model complex relationships among multi-grained multimodal elements, in which salient visual regions are detected by a cluster-based method. Then, a multi-grained multimodal Transformer called mmLayout is proposed to incorporate coarse-grained information into existing pre-trained fine-grained multimodal Transformers based on the graph. In mmLayout, coarse-grained information is aggregated from fine-grained, and then, after further processing, is fused back into fine-grained for final prediction. Furthermore, common sense enhancement is introduced to exploit the semantic information of natural lexical units. Experimental results on four tasks, including information extraction and document question answering, show that our method can improve the performance of multimodal Transformers based on fine-grained elements and achieve better performance with fewer parameters. Qualitative analyses show that our method can capture consistent semantics in coarse-grained elements.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge