Yutong Dai
WALT: Web Agents that Learn Tools
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Web agents promise to automate complex browser tasks, but current methods remain brittle -- relying on step-by-step UI interactions and heavy LLM reasoning that break under dynamic layouts and long horizons. Humans, by contrast, exploit website-provided functionality through high-level operations like search, filter, and sort. We introduce WALT (Web Agents that Learn Tools), a framework that reverse-engineers latent website functionality into reusable invocable tools. Rather than hypothesizing ad-hoc skills, WALT exposes robust implementations of automations already designed into websites -- spanning discovery (search, filter, sort), communication (post, comment, upvote), and content management (create, edit, delete). Tools abstract away low-level execution: instead of reasoning about how to click and type, agents simply call search(query) or create(listing). This shifts the computational burden from fragile step-by-step reasoning to reliable tool invocation. On VisualWebArena and WebArena, WALT achieves higher success with fewer steps and less LLM-dependent reasoning, establishing a robust and generalizable paradigm for browser automation.
GUI-KV: Efficient GUI Agents via KV Cache with Spatio-Temporal Awareness
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:Graphical user interface (GUI) agents built on vision-language models have emerged as a promising approach to automate human-computer workflows. However, they also face the inefficiency challenge as they process long sequences of high-resolution screenshots and solving long-horizon tasks, making inference slow, costly and memory-bound. While key-value (KV) caching can mitigate this, storing the full cache is prohibitive for image-heavy contexts. Existing cache-compression methods are sub-optimal as they do not account for the spatial and temporal redundancy of GUIs. In this work, we first analyze attention patterns in GUI agent workloads and find that, unlike in natural images, attention sparsity is uniformly high across all transformer layers. This insight motivates a simple uniform budget allocation strategy, which we show empirically outperforms more complex layer-varying schemes. Building on this, we introduce GUI-KV, a plug-and-play KV cache compression method for GUI agents that requires no retraining. GUI-KV combines two novel techniques: (i) spatial saliency guidance, which augments attention scores with the L2 norm of hidden states to better preserve semantically important visual tokens, and (ii) temporal redundancy scoring, which projects previous frames' keys onto the current frame's key subspace to preferentially prune redundant history. Across standard GUI agent benchmarks and models, GUI-KV outperforms competitive KV compression baselines, closely matching full-cache accuracy at modest budgets. Notably, in a 5-screenshot setting on the AgentNetBench benchmark, GUI-KV reduces decoding FLOPs by 38.9% while increasing step accuracy by 4.1% over the full-cache baseline. These results demonstrate that exploiting GUI-specific redundancies enables efficient and reliable agent performance.
SCUBA: Salesforce Computer Use Benchmark
Sep 30, 2025

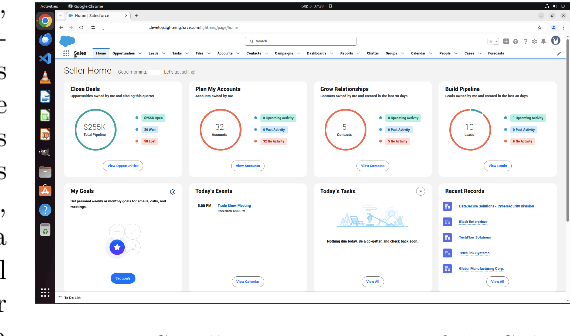
Abstract:We introduce SCUBA, a benchmark designed to evaluate computer-use agents on customer relationship management (CRM) workflows within the Salesforce platform. SCUBA contains 300 task instances derived from real user interviews, spanning three primary personas, platform administrators, sales representatives, and service agents. The tasks test a range of enterprise-critical abilities, including Enterprise Software UI navigation, data manipulation, workflow automation, information retrieval, and troubleshooting. To ensure realism, SCUBA operates in Salesforce sandbox environments with support for parallel execution and fine-grained evaluation metrics to capture milestone progress. We benchmark a diverse set of agents under both zero-shot and demonstration-augmented settings. We observed huge performance gaps in different agent design paradigms and gaps between the open-source model and the closed-source model. In the zero-shot setting, open-source model powered computer-use agents that have strong performance on related benchmarks like OSWorld only have less than 5\% success rate on SCUBA, while methods built on closed-source models can still have up to 39% task success rate. In the demonstration-augmented settings, task success rates can be improved to 50\% while simultaneously reducing time and costs by 13% and 16%, respectively. These findings highlight both the challenges of enterprise tasks automation and the promise of agentic solutions. By offering a realistic benchmark with interpretable evaluation, SCUBA aims to accelerate progress in building reliable computer-use agents for complex business software ecosystems.
CoAct-1: Computer-using Agents with Coding as Actions
Aug 05, 2025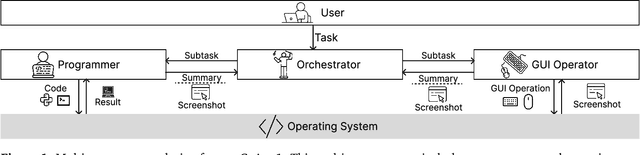
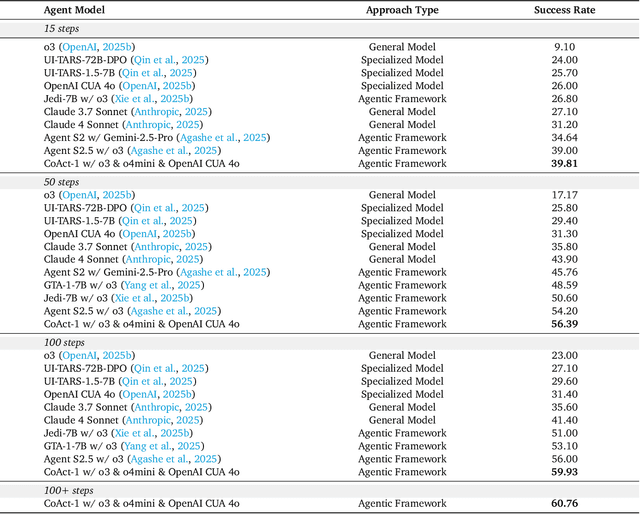
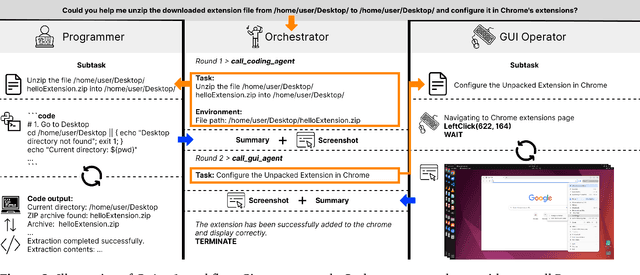
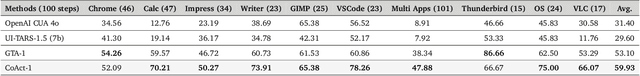
Abstract:Autonomous agents that operate computers via Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) often struggle with efficiency and reliability on complex, long-horizon tasks. While augmenting these agents with planners can improve task decomposition, they remain constrained by the inherent limitations of performing all actions through GUI manipulation, leading to brittleness and inefficiency. In this work, we introduce a more robust and flexible paradigm: enabling agents to use coding as a enhanced action. We present CoAct-1, a novel multi-agent system that synergistically combines GUI-based control with direct programmatic execution. CoAct-1 features an Orchestrator that dynamically delegates subtasks to either a conventional GUI Operator or a specialized Programmer agent, which can write and execute Python or Bash scripts. This hybrid approach allows the agent to bypass inefficient GUI action sequences for tasks like file management and data processing, while still leveraging visual interaction when necessary. We evaluate our system on the challenging OSWorld benchmark, where CoAct-1 achieves a new state-of-the-art success rate of 60.76%, significantly outperforming prior methods. Furthermore, our approach dramatically improves efficiency, reducing the average number of steps required to complete a task to just 10.15, compared to 15 for leading GUI agents. Our results demonstrate that integrating coding as a core action provides a more powerful, efficient, and scalable path toward generalized computer automation.
Collaborative Learning of On-Device Small Model and Cloud-Based Large Model: Advances and Future Directions
Apr 17, 2025Abstract:The conventional cloud-based large model learning framework is increasingly constrained by latency, cost, personalization, and privacy concerns. In this survey, we explore an emerging paradigm: collaborative learning between on-device small model and cloud-based large model, which promises low-latency, cost-efficient, and personalized intelligent services while preserving user privacy. We provide a comprehensive review across hardware, system, algorithm, and application layers. At each layer, we summarize key problems and recent advances from both academia and industry. In particular, we categorize collaboration algorithms into data-based, feature-based, and parameter-based frameworks. We also review publicly available datasets and evaluation metrics with user-level or device-level consideration tailored to collaborative learning settings. We further highlight real-world deployments, ranging from recommender systems and mobile livestreaming to personal intelligent assistants. We finally point out open research directions to guide future development in this rapidly evolving field.
xGen-MM (BLIP-3): A Family of Open Large Multimodal Models
Aug 16, 2024



Abstract:This report introduces xGen-MM (also known as BLIP-3), a framework for developing Large Multimodal Models (LMMs). The framework comprises meticulously curated datasets, a training recipe, model architectures, and a resulting suite of LMMs. xGen-MM, short for xGen-MultiModal, expands the Salesforce xGen initiative on foundation AI models. Our models undergo rigorous evaluation across a range of tasks, including both single and multi-image benchmarks. Our pre-trained base model exhibits strong in-context learning capabilities and the instruction-tuned model demonstrates competitive performance among open-source LMMs with similar model sizes. In addition, we introduce a safety-tuned model with DPO, aiming to mitigate harmful behaviors such as hallucinations and improve safety. We open-source our models, curated large-scale datasets, and our fine-tuning codebase to facilitate further advancements in LMM research. Associated resources will be available on our project page above.
Variational Bayes for Federated Continual Learning
May 23, 2024



Abstract:Federated continual learning (FCL) has received increasing attention due to its potential in handling real-world streaming data, characterized by evolving data distributions and varying client classes over time. The constraints of storage limitations and privacy concerns confine local models to exclusively access the present data within each learning cycle. Consequently, this restriction induces performance degradation in model training on previous data, termed "catastrophic forgetting". However, existing FCL approaches need to identify or know changes in data distribution, which is difficult in the real world. To release these limitations, this paper directs attention to a broader continuous framework. Within this framework, we introduce Federated Bayesian Neural Network (FedBNN), a versatile and efficacious framework employing a variational Bayesian neural network across all clients. Our method continually integrates knowledge from local and historical data distributions into a single model, adeptly learning from new data distributions while retaining performance on historical distributions. We rigorously evaluate FedBNN's performance against prevalent methods in federated learning and continual learning using various metrics. Experimental analyses across diverse datasets demonstrate that FedBNN achieves state-of-the-art results in mitigating forgetting.
Unleashing the Power of Multi-Task Learning: A Comprehensive Survey Spanning Traditional, Deep, and Pretrained Foundation Model Eras
Apr 29, 2024



Abstract:MTL is a learning paradigm that effectively leverages both task-specific and shared information to address multiple related tasks simultaneously. In contrast to STL, MTL offers a suite of benefits that enhance both the training process and the inference efficiency. MTL's key advantages encompass streamlined model architecture, performance enhancement, and cross-domain generalizability. Over the past twenty years, MTL has become widely recognized as a flexible and effective approach in various fields, including CV, NLP, recommendation systems, disease prognosis and diagnosis, and robotics. This survey provides a comprehensive overview of the evolution of MTL, encompassing the technical aspects of cutting-edge methods from traditional approaches to deep learning and the latest trend of pretrained foundation models. Our survey methodically categorizes MTL techniques into five key areas: regularization, relationship learning, feature propagation, optimization, and pre-training. This categorization not only chronologically outlines the development of MTL but also dives into various specialized strategies within each category. Furthermore, the survey reveals how the MTL evolves from handling a fixed set of tasks to embracing a more flexible approach free from task or modality constraints. It explores the concepts of task-promptable and -agnostic training, along with the capacity for ZSL, which unleashes the untapped potential of this historically coveted learning paradigm. Overall, we hope this survey provides the research community with a comprehensive overview of the advancements in MTL from its inception in 1997 to the present in 2023. We address present challenges and look ahead to future possibilities, shedding light on the opportunities and potential avenues for MTL research in a broad manner. This project is publicly available at https://github.com/junfish/Awesome-Multitask-Learning.
Toward Robust Imperceptible Perturbation against Unauthorized Text-to-image Diffusion-based Synthesis
Nov 22, 2023



Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models allow seamless generation of personalized images from scant reference photos. Yet, these tools, in the wrong hands, can fabricate misleading or harmful content, endangering individuals. To address this problem, existing poisoning-based approaches perturb user images in an imperceptible way to render them "unlearnable" from malicious uses. We identify two limitations of these defending approaches: i) sub-optimal due to the hand-crafted heuristics for solving the intractable bilevel optimization and ii) lack of robustness against simple data transformations like Gaussian filtering. To solve these challenges, we propose MetaCloak, which solves the bi-level poisoning problem with a meta-learning framework with an additional transformation sampling process to craft transferable and robust perturbation. Specifically, we employ a pool of surrogate diffusion models to craft transferable and model-agnostic perturbation. Furthermore, by incorporating an additional transformation process, we design a simple denoising-error maximization loss that is sufficient for causing transformation-robust semantic distortion and degradation in a personalized generation. Extensive experiments on the VGGFace2 and CelebA-HQ datasets show that MetaCloak outperforms existing approaches. Notably, MetaCloak can successfully fool online training services like Replicate, in a black-box manner, demonstrating the effectiveness of MetaCloak in real-world scenarios. Our code is available at https://github.com/liuyixin-louis/MetaCloak.
Joint Demosaicing and Denoising with Double Deep Image Priors
Sep 18, 2023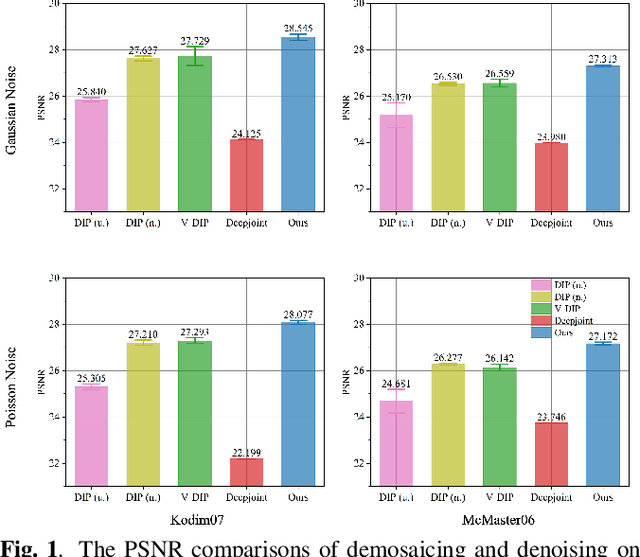
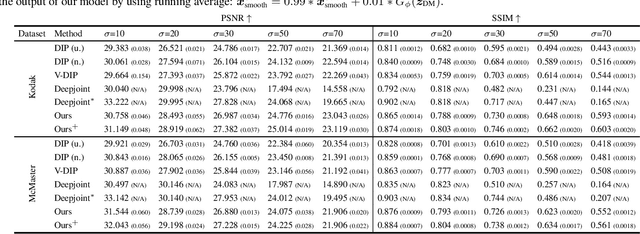
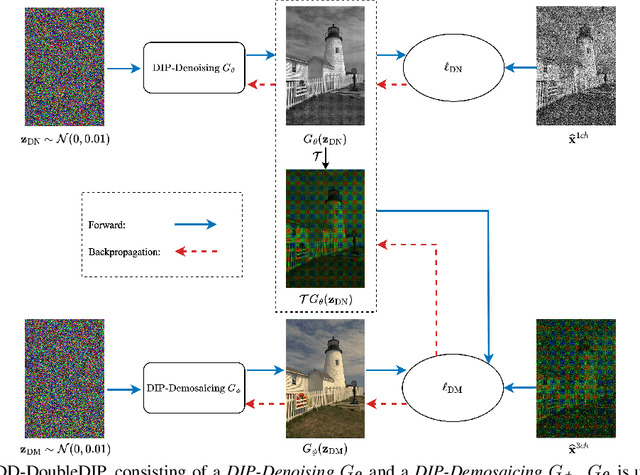
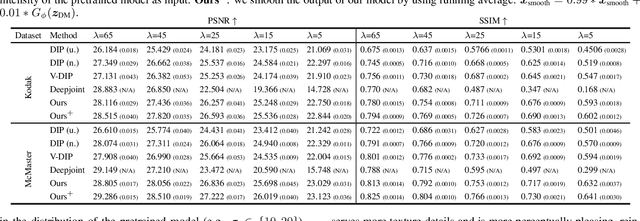
Abstract:Demosaicing and denoising of RAW images are crucial steps in the processing pipeline of modern digital cameras. As only a third of the color information required to produce a digital image is captured by the camera sensor, the process of demosaicing is inherently ill-posed. The presence of noise further exacerbates this problem. Performing these two steps sequentially may distort the content of the captured RAW images and accumulate errors from one step to another. Recent deep neural-network-based approaches have shown the effectiveness of joint demosaicing and denoising to mitigate such challenges. However, these methods typically require a large number of training samples and do not generalize well to different types and intensities of noise. In this paper, we propose a novel joint demosaicing and denoising method, dubbed JDD-DoubleDIP, which operates directly on a single RAW image without requiring any training data. We validate the effectiveness of our method on two popular datasets -- Kodak and McMaster -- with various noises and noise intensities. The experimental results show that our method consistently outperforms other compared methods in terms of PSNR, SSIM, and qualitative visual perception.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge