Lintao Ma
TableCache: Primary Foreign Key Guided KV Cache Precomputation for Low Latency Text-to-SQL
Jan 13, 2026Abstract:In Text-to-SQL tasks, existing LLM-based methods often include extensive database schemas in prompts, leading to long context lengths and increased prefilling latency. While user queries typically focus on recurrent table sets-offering an opportunity for KV cache sharing across queries-current inference engines, such as SGLang and vLLM, generate redundant prefix cache copies when processing user queries with varying table orders. To address this inefficiency, we propose precomputing table representations as KV caches offline and querying the required ones online. A key aspect of our approach is the computation of table caches while preserving primary foreign key relationships between tables. Additionally, we construct a Table Trie structure to facilitate efficient KV cache lookups during inference. To enhance cache performance, we introduce a cache management system with a query reranking strategy to improve cache hit rates and a computation loading pipeline for parallelizing model inference and cache loading. Experimental results show that our proposed TableCache achieves up to a 3.62x speedup in Time to First Token (TTFT) with negligible performance degradation.
Adaptive Two-Stage Cloud Resource Scaling via Hierarchical Multi-Indicator Forecasting and Bayesian Decision-Making
Aug 02, 2024Abstract:The surging demand for cloud computing resources, driven by the rapid growth of sophisticated large-scale models and data centers, underscores the critical importance of efficient and adaptive resource allocation. As major tech enterprises deploy massive infrastructures with thousands of GPUs, existing cloud platforms still struggle with low resource utilization due to key challenges: capturing hierarchical indicator structures, modeling non-Gaussian distributions, and decision-making under uncertainty. To address these challenges, we propose HRAMONY, an adaptive Hierarchical Attention-based Resource Modeling and Decision-Making System. HARMONY combines hierarchical multi-indicator distribution forecasting and uncertainty-aware Bayesian decision-making. It introduces a novel hierarchical attention mechanism that comprehensively models complex inter-indicator dependencies, enabling accurate predictions that can adapt to evolving environment states. By transforming Gaussian projections into adaptive non-Gaussian distributions via Normalizing Flows. Crucially, HARMONY leverages the full predictive distributions in an adaptive Bayesian process, proactively incorporating uncertainties to optimize resource allocation while robustly meeting SLA constraints under varying conditions. Extensive evaluations across four large-scale cloud datasets demonstrate HARMONY's state-of-the-art performance, significantly outperforming nine established methods. A month-long real-world deployment validated HARMONY's substantial practical impact, realizing over 35,000 GPU hours in savings and translating to $100K+ in cost reduction, showcasing its remarkable economic value through adaptive, uncertainty-aware scaling. Our code is available at https://github.com/Floating-LY/HARMONY1.
Autogenic Language Embedding for Coherent Point Tracking
Jul 30, 2024
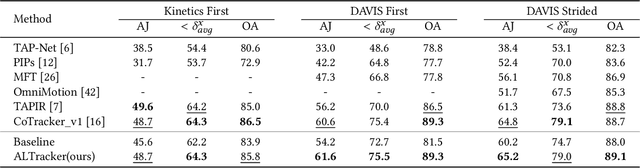


Abstract:Point tracking is a challenging task in computer vision, aiming to establish point-wise correspondence across long video sequences. Recent advancements have primarily focused on temporal modeling techniques to improve local feature similarity, often overlooking the valuable semantic consistency inherent in tracked points. In this paper, we introduce a novel approach leveraging language embeddings to enhance the coherence of frame-wise visual features related to the same object. Our proposed method, termed autogenic language embedding for visual feature enhancement, strengthens point correspondence in long-term sequences. Unlike existing visual-language schemes, our approach learns text embeddings from visual features through a dedicated mapping network, enabling seamless adaptation to various tracking tasks without explicit text annotations. Additionally, we introduce a consistency decoder that efficiently integrates text tokens into visual features with minimal computational overhead. Through enhanced visual consistency, our approach significantly improves tracking trajectories in lengthy videos with substantial appearance variations. Extensive experiments on widely-used tracking benchmarks demonstrate the superior performance of our method, showcasing notable enhancements compared to trackers relying solely on visual cues.
Multiscale Representation Enhanced Temporal Flow Fusion Model for Long-Term Workload Forecasting
Jul 29, 2024



Abstract:Accurate workload forecasting is critical for efficient resource management in cloud computing systems, enabling effective scheduling and autoscaling. Despite recent advances with transformer-based forecasting models, challenges remain due to the non-stationary, nonlinear characteristics of workload time series and the long-term dependencies. In particular, inconsistent performance between long-term history and near-term forecasts hinders long-range predictions. This paper proposes a novel framework leveraging self-supervised multiscale representation learning to capture both long-term and near-term workload patterns. The long-term history is encoded through multiscale representations while the near-term observations are modeled via temporal flow fusion. These representations of different scales are fused using an attention mechanism and characterized with normalizing flows to handle non-Gaussian/non-linear distributions of time series. Extensive experiments on 9 benchmarks demonstrate superiority over existing methods.
GMP-AR: Granularity Message Passing and Adaptive Reconciliation for Temporal Hierarchy Forecasting
Jun 18, 2024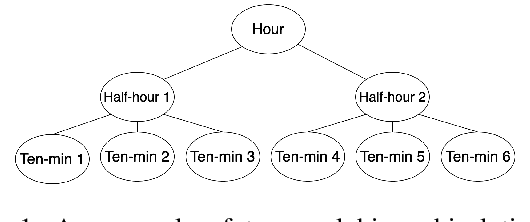
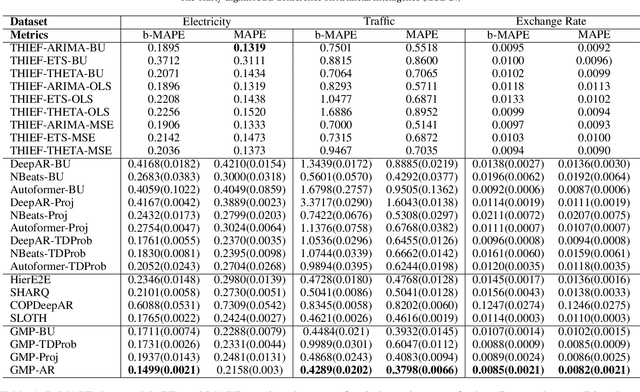
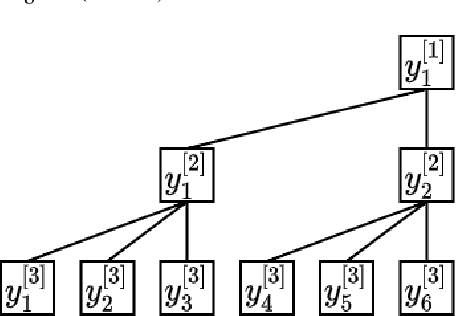
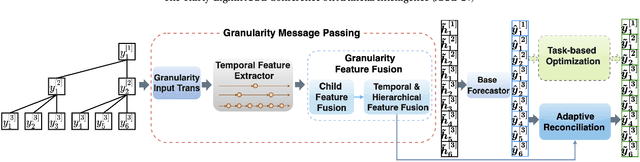
Abstract:Time series forecasts of different temporal granularity are widely used in real-world applications, e.g., sales prediction in days and weeks for making different inventory plans. However, these tasks are usually solved separately without ensuring coherence, which is crucial for aligning downstream decisions. Previous works mainly focus on ensuring coherence with some straightforward methods, e.g., aggregation from the forecasts of fine granularity to the coarse ones, and allocation from the coarse granularity to the fine ones. These methods merely take the temporal hierarchical structure to maintain coherence without improving the forecasting accuracy. In this paper, we propose a novel granularity message-passing mechanism (GMP) that leverages temporal hierarchy information to improve forecasting performance and also utilizes an adaptive reconciliation (AR) strategy to maintain coherence without performance loss. Furthermore, we introduce an optimization module to achieve task-based targets while adhering to more real-world constraints. Experiments on real-world datasets demonstrate that our framework (GMP-AR) achieves superior performances on temporal hierarchical forecasting tasks compared to state-of-the-art methods. In addition, our framework has been successfully applied to a real-world task of payment traffic management in Alipay by integrating with the task-based optimization module.
TimeMixer: Decomposable Multiscale Mixing for Time Series Forecasting
May 23, 2024



Abstract:Time series forecasting is widely used in extensive applications, such as traffic planning and weather forecasting. However, real-world time series usually present intricate temporal variations, making forecasting extremely challenging. Going beyond the mainstream paradigms of plain decomposition and multiperiodicity analysis, we analyze temporal variations in a novel view of multiscale-mixing, which is based on an intuitive but important observation that time series present distinct patterns in different sampling scales. The microscopic and the macroscopic information are reflected in fine and coarse scales respectively, and thereby complex variations can be inherently disentangled. Based on this observation, we propose TimeMixer as a fully MLP-based architecture with Past-Decomposable-Mixing (PDM) and Future-Multipredictor-Mixing (FMM) blocks to take full advantage of disentangled multiscale series in both past extraction and future prediction phases. Concretely, PDM applies the decomposition to multiscale series and further mixes the decomposed seasonal and trend components in fine-to-coarse and coarse-to-fine directions separately, which successively aggregates the microscopic seasonal and macroscopic trend information. FMM further ensembles multiple predictors to utilize complementary forecasting capabilities in multiscale observations. Consequently, TimeMixer is able to achieve consistent state-of-the-art performances in both long-term and short-term forecasting tasks with favorable run-time efficiency.
A Survey on Diffusion Models for Time Series and Spatio-Temporal Data
Apr 29, 2024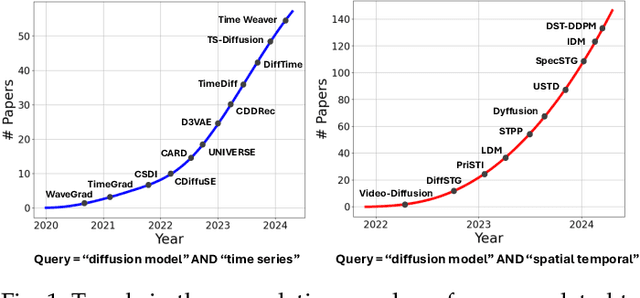
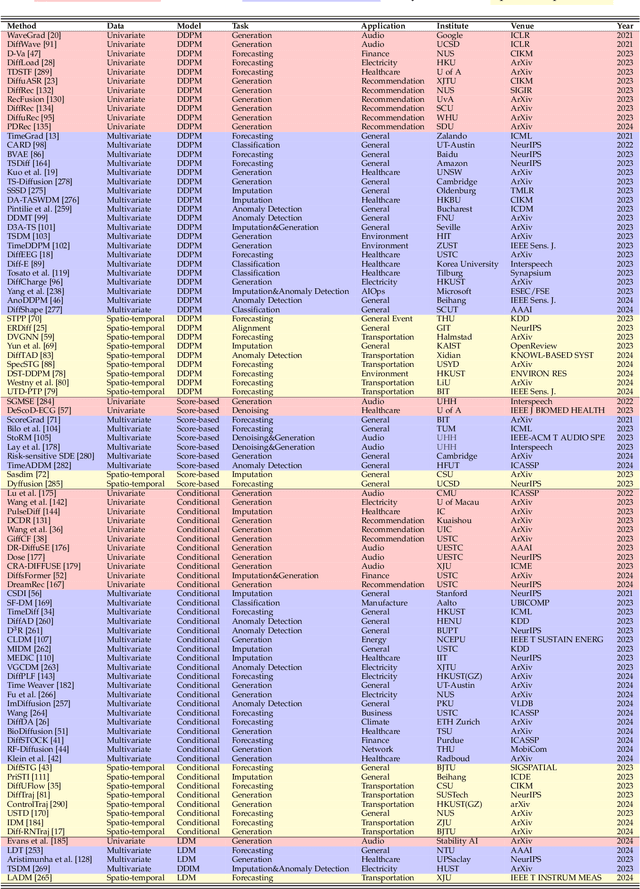
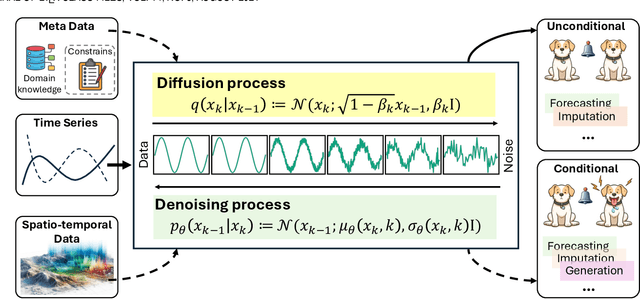
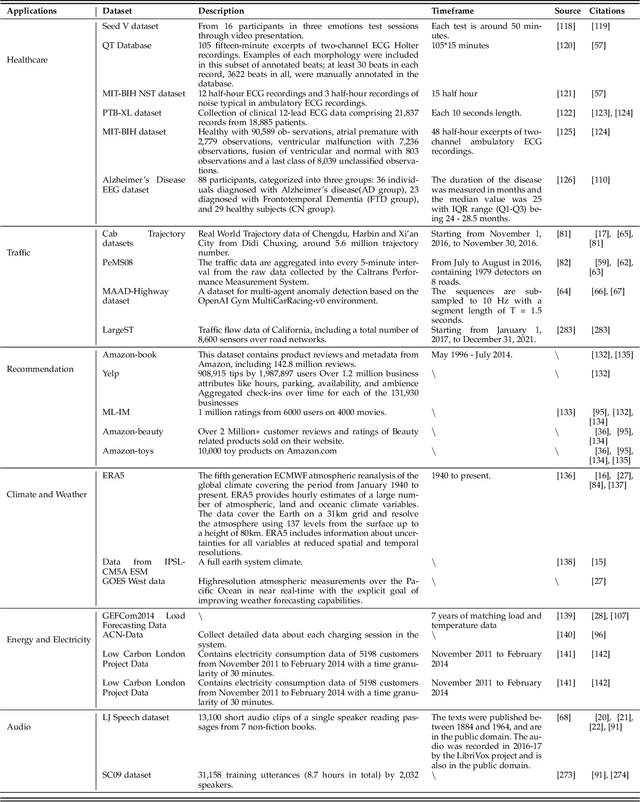
Abstract:The study of time series data is crucial for understanding trends and anomalies over time, enabling predictive insights across various sectors. Spatio-temporal data, on the other hand, is vital for analyzing phenomena in both space and time, providing a dynamic perspective on complex system interactions. Recently, diffusion models have seen widespread application in time series and spatio-temporal data mining. Not only do they enhance the generative and inferential capabilities for sequential and temporal data, but they also extend to other downstream tasks. In this survey, we comprehensively and thoroughly review the use of diffusion models in time series and spatio-temporal data, categorizing them by model category, task type, data modality, and practical application domain. In detail, we categorize diffusion models into unconditioned and conditioned types and discuss time series data and spatio-temporal data separately. Unconditioned models, which operate unsupervised, are subdivided into probability-based and score-based models, serving predictive and generative tasks such as forecasting, anomaly detection, classification, and imputation. Conditioned models, on the other hand, utilize extra information to enhance performance and are similarly divided for both predictive and generative tasks. Our survey extensively covers their application in various fields, including healthcare, recommendation, climate, energy, audio, and transportation, providing a foundational understanding of how these models analyze and generate data. Through this structured overview, we aim to provide researchers and practitioners with a comprehensive understanding of diffusion models for time series and spatio-temporal data analysis, aiming to direct future innovations and applications by addressing traditional challenges and exploring innovative solutions within the diffusion model framework.
iTransformer: Inverted Transformers Are Effective for Time Series Forecasting
Oct 10, 2023



Abstract:The recent boom of linear forecasting models questions the ongoing passion for architectural modifications of Transformer-based forecasters. These forecasters leverage Transformers to model the global dependencies over temporal tokens of time series, with each token formed by multiple variates of the same timestamp. However, Transformer is challenged in forecasting series with larger lookback windows due to performance degradation and computation explosion. Besides, the unified embedding for each temporal token fuses multiple variates with potentially unaligned timestamps and distinct physical measurements, which may fail in learning variate-centric representations and result in meaningless attention maps. In this work, we reflect on the competent duties of Transformer components and repurpose the Transformer architecture without any adaptation on the basic components. We propose iTransformer that simply inverts the duties of the attention mechanism and the feed-forward network. Specifically, the time points of individual series are embedded into variate tokens which are utilized by the attention mechanism to capture multivariate correlations; meanwhile, the feed-forward network is applied for each variate token to learn nonlinear representations. The iTransformer model achieves consistent state-of-the-art on several real-world datasets, which further empowers the Transformer family with promoted performance, generalization ability across different variates, and better utilization of arbitrary lookback windows, making it a nice alternative as the fundamental backbone of time series forecasting.
Continuous Invariance Learning
Oct 09, 2023



Abstract:Invariance learning methods aim to learn invariant features in the hope that they generalize under distributional shifts. Although many tasks are naturally characterized by continuous domains, current invariance learning techniques generally assume categorically indexed domains. For example, auto-scaling in cloud computing often needs a CPU utilization prediction model that generalizes across different times (e.g., time of a day and date of a year), where `time' is a continuous domain index. In this paper, we start by theoretically showing that existing invariance learning methods can fail for continuous domain problems. Specifically, the naive solution of splitting continuous domains into discrete ones ignores the underlying relationship among domains, and therefore potentially leads to suboptimal performance. To address this challenge, we then propose Continuous Invariance Learning (CIL), which extracts invariant features across continuously indexed domains. CIL is a novel adversarial procedure that measures and controls the conditional independence between the labels and continuous domain indices given the extracted features. Our theoretical analysis demonstrates the superiority of CIL over existing invariance learning methods. Empirical results on both synthetic and real-world datasets (including data collected from production systems) show that CIL consistently outperforms strong baselines among all the tasks.
Time-LLM: Time Series Forecasting by Reprogramming Large Language Models
Oct 03, 2023



Abstract:Time series forecasting holds significant importance in many real-world dynamic systems and has been extensively studied. Unlike natural language process (NLP) and computer vision (CV), where a single large model can tackle multiple tasks, models for time series forecasting are often specialized, necessitating distinct designs for different tasks and applications. While pre-trained foundation models have made impressive strides in NLP and CV, their development in time series domains has been constrained by data sparsity. Recent studies have revealed that large language models (LLMs) possess robust pattern recognition and reasoning abilities over complex sequences of tokens. However, the challenge remains in effectively aligning the modalities of time series data and natural language to leverage these capabilities. In this work, we present Time-LLM, a reprogramming framework to repurpose LLMs for general time series forecasting with the backbone language models kept intact. We begin by reprogramming the input time series with text prototypes before feeding it into the frozen LLM to align the two modalities. To augment the LLM's ability to reason with time series data, we propose Prompt-as-Prefix (PaP), which enriches the input context and directs the transformation of reprogrammed input patches. The transformed time series patches from the LLM are finally projected to obtain the forecasts. Our comprehensive evaluations demonstrate that Time-LLM is a powerful time series learner that outperforms state-of-the-art, specialized forecasting models. Moreover, Time-LLM excels in both few-shot and zero-shot learning scenarios.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge