Zikai Song
Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, China
Logical Phase Transitions: Understanding Collapse in LLM Logical Reasoning
Jan 06, 2026Abstract:Symbolic logical reasoning is a critical yet underexplored capability of large language models (LLMs), providing reliable and verifiable decision-making in high-stakes domains such as mathematical reasoning and legal judgment. In this study, we present a systematic analysis of logical reasoning under controlled increases in logical complexity, and reveal a previously unrecognized phenomenon, which we term Logical Phase Transitions: rather than degrading smoothly, logical reasoning performance remains stable within a regime but collapses abruptly beyond a critical logical depth, mirroring physical phase transitions such as water freezing beyond a critical temperature threshold. Building on this insight, we propose Neuro-Symbolic Curriculum Tuning, a principled framework that adaptively aligns natural language with logical symbols to establish a shared representation, and reshapes training dynamics around phase-transition boundaries to progressively strengthen reasoning at increasing logical depths. Experiments on five benchmarks show that our approach effectively mitigates logical reasoning collapse at high complexity, yielding average accuracy gains of +1.26 in naive prompting and +3.95 in CoT, while improving generalization to unseen logical compositions. Code and data are available at https://github.com/AI4SS/Logical-Phase-Transitions.
MCA-RG: Enhancing LLMs with Medical Concept Alignment for Radiology Report Generation
Jul 09, 2025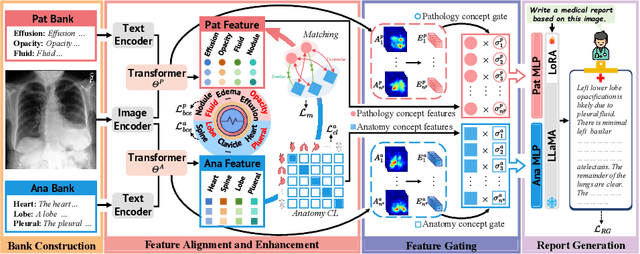
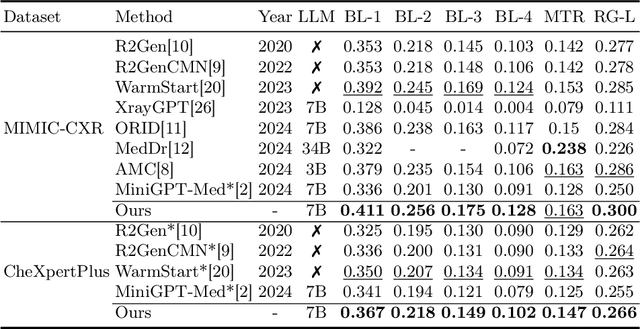
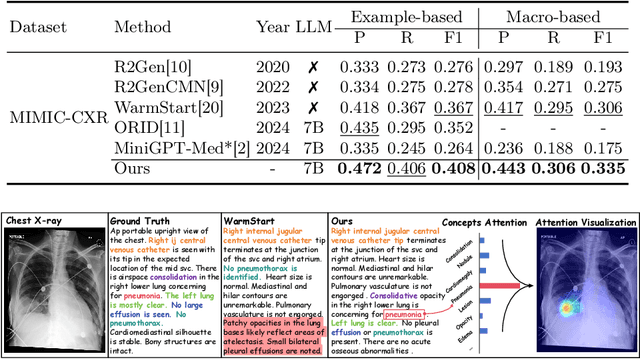
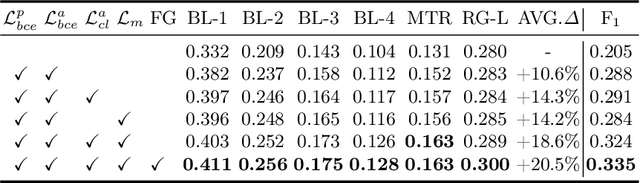
Abstract:Despite significant advancements in adapting Large Language Models (LLMs) for radiology report generation (RRG), clinical adoption remains challenging due to difficulties in accurately mapping pathological and anatomical features to their corresponding text descriptions. Additionally, semantic agnostic feature extraction further hampers the generation of accurate diagnostic reports. To address these challenges, we introduce Medical Concept Aligned Radiology Report Generation (MCA-RG), a knowledge-driven framework that explicitly aligns visual features with distinct medical concepts to enhance the report generation process. MCA-RG utilizes two curated concept banks: a pathology bank containing lesion-related knowledge, and an anatomy bank with anatomical descriptions. The visual features are aligned with these medical concepts and undergo tailored enhancement. We further propose an anatomy-based contrastive learning procedure to improve the generalization of anatomical features, coupled with a matching loss for pathological features to prioritize clinically relevant regions. Additionally, a feature gating mechanism is employed to filter out low-quality concept features. Finally, the visual features are corresponding to individual medical concepts, and are leveraged to guide the report generation process. Experiments on two public benchmarks (MIMIC-CXR and CheXpert Plus) demonstrate that MCA-RG achieves superior performance, highlighting its effectiveness in radiology report generation.
Cross-Modality Masked Learning for Survival Prediction in ICI Treated NSCLC Patients
Jul 09, 2025Abstract:Accurate prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients undergoing immunotherapy is essential for personalized treatment planning, enabling informed patient decisions, and improving both treatment outcomes and quality of life. However, the lack of large, relevant datasets and effective multi-modal feature fusion strategies pose significant challenges in this domain. To address these challenges, we present a large-scale dataset and introduce a novel framework for multi-modal feature fusion aimed at enhancing the accuracy of survival prediction. The dataset comprises 3D CT images and corresponding clinical records from NSCLC patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICI), along with progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) data. We further propose a cross-modality masked learning approach for medical feature fusion, consisting of two distinct branches, each tailored to its respective modality: a Slice-Depth Transformer for extracting 3D features from CT images and a graph-based Transformer for learning node features and relationships among clinical variables in tabular data. The fusion process is guided by a masked modality learning strategy, wherein the model utilizes the intact modality to reconstruct missing components. This mechanism improves the integration of modality-specific features, fostering more effective inter-modality relationships and feature interactions. Our approach demonstrates superior performance in multi-modal integration for NSCLC survival prediction, surpassing existing methods and setting a new benchmark for prognostic models in this context.
HyperFusion: Hierarchical Multimodal Ensemble Learning for Social Media Popularity Prediction
Jul 01, 2025Abstract:Social media popularity prediction plays a crucial role in content optimization, marketing strategies, and user engagement enhancement across digital platforms. However, predicting post popularity remains challenging due to the complex interplay between visual, textual, temporal, and user behavioral factors. This paper presents HyperFusion, a hierarchical multimodal ensemble learning framework for social media popularity prediction. Our approach employs a three-tier fusion architecture that progressively integrates features across abstraction levels: visual representations from CLIP encoders, textual embeddings from transformer models, and temporal-spatial metadata with user characteristics. The framework implements a hierarchical ensemble strategy combining CatBoost, TabNet, and custom multi-layer perceptrons. To address limited labeled data, we propose a two-stage training methodology with pseudo-labeling and iterative refinement. We introduce novel cross-modal similarity measures and hierarchical clustering features that capture inter-modal dependencies. Experimental results demonstrate that HyperFusion achieves competitive performance on the SMP challenge dataset. Our team achieved third place in the SMP Challenge 2025 (Image Track). The source code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/SMPDImage.
MVP: Winning Solution to SMP Challenge 2025 Video Track
Jul 01, 2025Abstract:Social media platforms serve as central hubs for content dissemination, opinion expression, and public engagement across diverse modalities. Accurately predicting the popularity of social media videos enables valuable applications in content recommendation, trend detection, and audience engagement. In this paper, we present Multimodal Video Predictor (MVP), our winning solution to the Video Track of the SMP Challenge 2025. MVP constructs expressive post representations by integrating deep video features extracted from pretrained models with user metadata and contextual information. The framework applies systematic preprocessing techniques, including log-transformations and outlier removal, to improve model robustness. A gradient-boosted regression model is trained to capture complex patterns across modalities. Our approach ranked first in the official evaluation of the Video Track, demonstrating its effectiveness and reliability for multimodal video popularity prediction on social platforms. The source code is available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/SMPDVideo.
Can MLLMs Guide Me Home? A Benchmark Study on Fine-Grained Visual Reasoning from Transit Maps
May 24, 2025Abstract:Multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have recently achieved significant progress in visual tasks, including semantic scene understanding and text-image alignment, with reasoning variants enhancing performance on complex tasks involving mathematics and logic. However, their capacity for reasoning tasks involving fine-grained visual understanding remains insufficiently evaluated. To address this gap, we introduce ReasonMap, a benchmark designed to assess the fine-grained visual understanding and spatial reasoning abilities of MLLMs. ReasonMap encompasses high-resolution transit maps from 30 cities across 13 countries and includes 1,008 question-answer pairs spanning two question types and three templates. Furthermore, we design a two-level evaluation pipeline that properly assesses answer correctness and quality. Comprehensive evaluations of 15 popular MLLMs, including both base and reasoning variants, reveal a counterintuitive pattern: among open-source models, base models outperform reasoning ones, while the opposite trend is observed in closed-source models. Additionally, performance generally degrades when visual inputs are masked, indicating that while MLLMs can leverage prior knowledge to answer some questions, fine-grained visual reasoning tasks still require genuine visual perception for strong performance. Our benchmark study offers new insights into visual reasoning and contributes to investigating the gap between open-source and closed-source models.
SF2T: Self-supervised Fragment Finetuning of Video-LLMs for Fine-Grained Understanding
Apr 10, 2025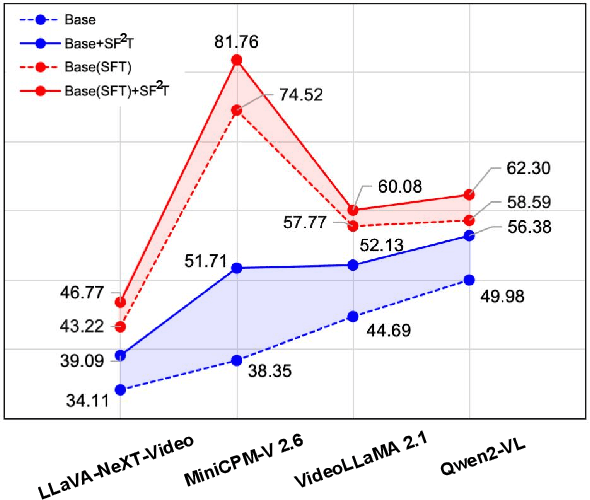



Abstract:Video-based Large Language Models (Video-LLMs) have witnessed substantial advancements in recent years, propelled by the advancement in multi-modal LLMs. Although these models have demonstrated proficiency in providing the overall description of videos, they struggle with fine-grained understanding, particularly in aspects such as visual dynamics and video details inquiries. To tackle these shortcomings, we find that fine-tuning Video-LLMs on self-supervised fragment tasks, greatly improve their fine-grained video understanding abilities. Hence we propose two key contributions:(1) Self-Supervised Fragment Fine-Tuning (SF$^2$T), a novel effortless fine-tuning method, employs the rich inherent characteristics of videos for training, while unlocking more fine-grained understanding ability of Video-LLMs. Moreover, it relieves researchers from labor-intensive annotations and smartly circumvents the limitations of natural language, which often fails to capture the complex spatiotemporal variations in videos; (2) A novel benchmark dataset, namely FineVidBench, for rigorously assessing Video-LLMs' performance at both the scene and fragment levels, offering a comprehensive evaluation of their capabilities. We assessed multiple models and validated the effectiveness of SF$^2$T on them. Experimental results reveal that our approach improves their ability to capture and interpret spatiotemporal details.
Video Anomaly Detection with Motion and Appearance Guided Patch Diffusion Model
Dec 12, 2024



Abstract:A recent endeavor in one class of video anomaly detection is to leverage diffusion models and posit the task as a generation problem, where the diffusion model is trained to recover normal patterns exclusively, thus reporting abnormal patterns as outliers. Yet, existing attempts neglect the various formations of anomaly and predict normal samples at the feature level regardless that abnormal objects in surveillance videos are often relatively small. To address this, a novel patch-based diffusion model is proposed, specifically engineered to capture fine-grained local information. We further observe that anomalies in videos manifest themselves as deviations in both appearance and motion. Therefore, we argue that a comprehensive solution must consider both of these aspects simultaneously to achieve accurate frame prediction. To address this, we introduce innovative motion and appearance conditions that are seamlessly integrated into our patch diffusion model. These conditions are designed to guide the model in generating coherent and contextually appropriate predictions for both semantic content and motion relations. Experimental results in four challenging video anomaly detection datasets empirically substantiate the efficacy of our proposed approach, demonstrating that it consistently outperforms most existing methods in detecting abnormal behaviors.
Ref-GS: Directional Factorization for 2D Gaussian Splatting
Dec 01, 2024



Abstract:In this paper, we introduce Ref-GS, a novel approach for directional light factorization in 2D Gaussian splatting, which enables photorealistic view-dependent appearance rendering and precise geometry recovery. Ref-GS builds upon the deferred rendering of Gaussian splatting and applies directional encoding to the deferred-rendered surface, effectively reducing the ambiguity between orientation and viewing angle. Next, we introduce a spherical Mip-grid to capture varying levels of surface roughness, enabling roughness-aware Gaussian shading. Additionally, we propose a simple yet efficient geometry-lighting factorization that connects geometry and lighting via the vector outer product, significantly reducing renderer overhead when integrating volumetric attributes. Our method achieves superior photorealistic rendering for a range of open-world scenes while also accurately recovering geometry.
IP-MOT: Instance Prompt Learning for Cross-Domain Multi-Object Tracking
Oct 30, 2024Abstract:Multi-Object Tracking (MOT) aims to associate multiple objects across video frames and is a challenging vision task due to inherent complexities in the tracking environment. Most existing approaches train and track within a single domain, resulting in a lack of cross-domain generalizability to data from other domains. While several works have introduced natural language representation to bridge the domain gap in visual tracking, these textual descriptions often provide too high-level a view and fail to distinguish various instances within the same class. In this paper, we address this limitation by developing IP-MOT, an end-to-end transformer model for MOT that operates without concrete textual descriptions. Our approach is underpinned by two key innovations: Firstly, leveraging a pre-trained vision-language model, we obtain instance-level pseudo textual descriptions via prompt-tuning, which are invariant across different tracking scenes; Secondly, we introduce a query-balanced strategy, augmented by knowledge distillation, to further boost the generalization capabilities of our model. Extensive experiments conducted on three widely used MOT benchmarks, including MOT17, MOT20, and DanceTrack, demonstrate that our approach not only achieves competitive performance on same-domain data compared to state-of-the-art models but also significantly improves the performance of query-based trackers by large margins for cross-domain inputs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge