Ken Chen
Discovering Process-Outcome Credit in Multi-Step LLM Reasoning
Feb 01, 2026Abstract:Reinforcement Learning (RL) serves as a potent paradigm for enhancing reasoning capabilities in Large Language Models (LLMs), yet standard outcome-based approaches often suffer from reward sparsity and inefficient credit assignment. In this paper, we propose a novel framework designed to provide continuous reward signals, which introduces a Step-wise Marginal Information Gain (MIG) mechanism that quantifies the intrinsic value of reasoning steps against a Monotonic Historical Watermark, effectively filtering out training noise. To ensure disentangled credit distribution, we implement a Decoupled Masking Strategy, applying process-oriented rewards specifically to the chain-of-thought (CoT) and outcome-oriented rewards to the full completion. Additionally, we incorporate a Dual-Gated SFT objective to stabilize training with high-quality structural and factual signals. Extensive experiments across textual and multi-modal benchmarks (e.g., MATH, Super-CLEVR) demonstrate that our approach consistently outperforms baselines such as GRPO in both sample efficiency and final accuracy. Furthermore, our model exhibits superior out-of-distribution robustness, demonstrating promising zero-shot transfer capabilities to unseen and challenging reasoning tasks.
Unmasking the Unknown: Facial Deepfake Detection in the Open-Set Paradigm
Mar 11, 2025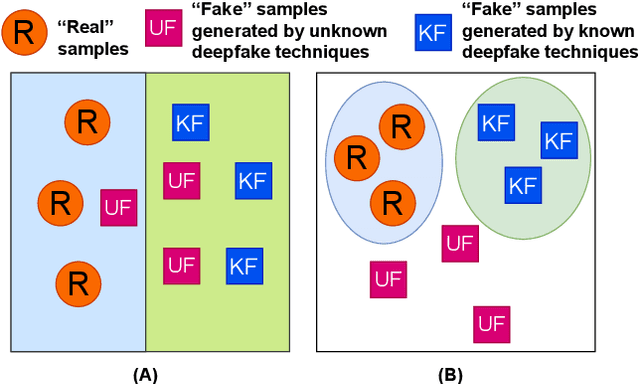
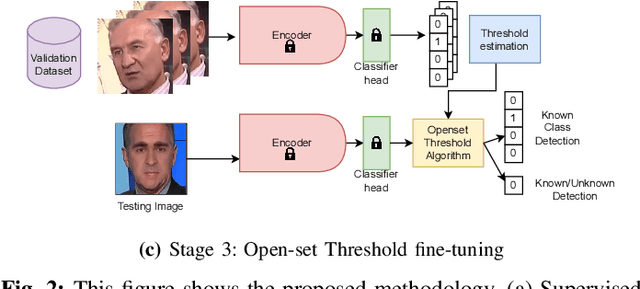
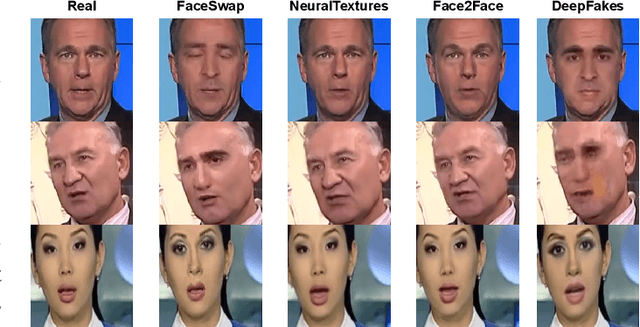
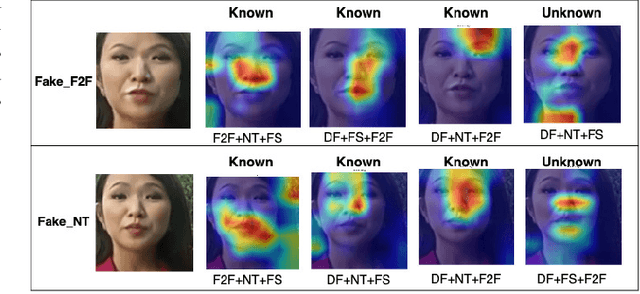
Abstract:Facial forgery methods such as deepfakes can be misused for identity manipulation and spreading misinformation. They have evolved alongside advancements in generative AI, leading to new and more sophisticated forgery techniques that diverge from existing 'known' methods. Conventional deepfake detection methods use the closedset paradigm, thus limiting their applicability to detecting forgeries created using methods that are not part of the training dataset. In this paper, we propose a shift from the closed-set paradigm for deepfake detection. In the open-set paradigm, models are designed not only to identify images created by known facial forgery methods but also to identify and flag those produced by previously unknown methods as 'unknown' and not as unforged/real/unmanipulated. In this paper, we propose an open-set deepfake classification algorithm based on supervised contrastive learning. The open-set paradigm used in our model allows it to function as a more robust tool capable of handling emerging and unseen deepfake techniques, enhancing reliability and confidence, and complementing forensic analysis. In open-set paradigm, we identify three groups including the "unknown group that is neither considered known deepfake nor real. We investigate deepfake open-set classification across three scenarios, classifying deepfakes from unknown methods not as real, distinguishing real images from deepfakes, and classifying deepfakes from known methods, using the FaceForensics++ dataset as a benchmark. Our method achieves state of the art results in the first two tasks and competitive results in the third task.
AniFaceDiff: High-Fidelity Face Reenactment via Facial Parametric Conditioned Diffusion Models
Jun 19, 2024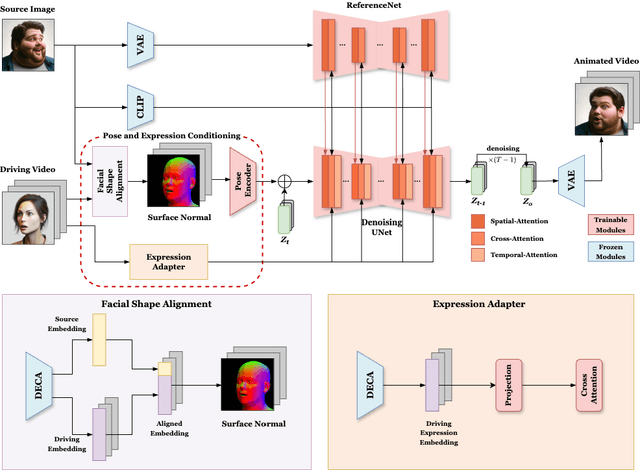
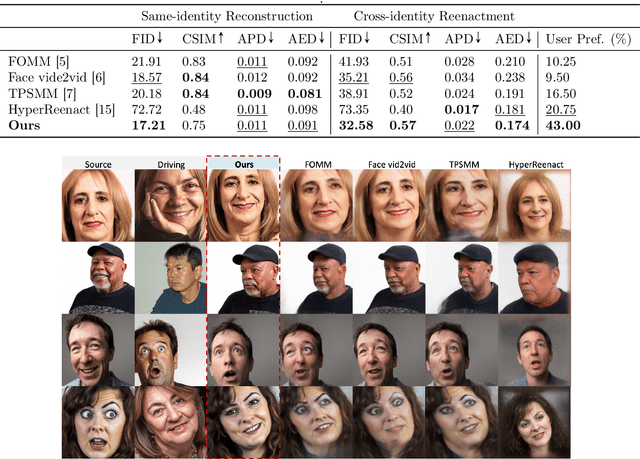
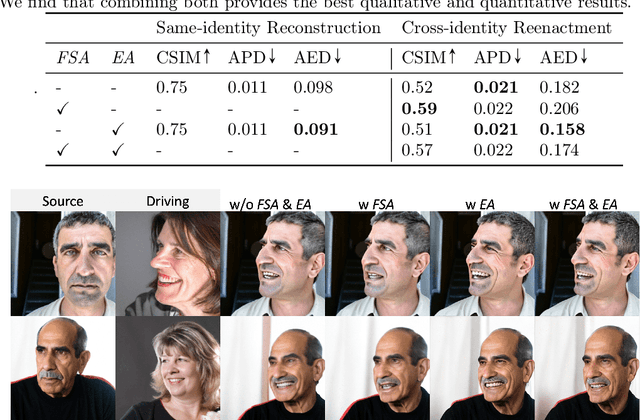
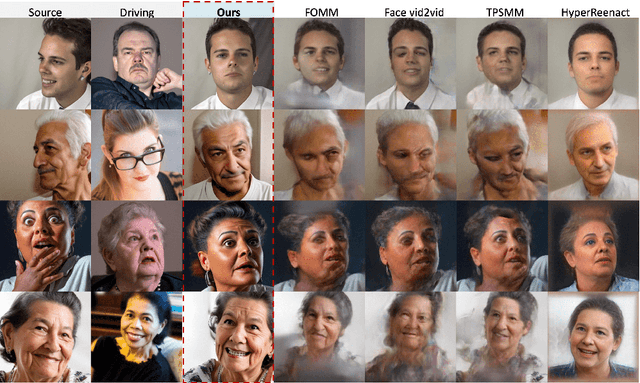
Abstract:Face reenactment refers to the process of transferring the pose and facial expressions from a reference (driving) video onto a static facial (source) image while maintaining the original identity of the source image. Previous research in this domain has made significant progress by training controllable deep generative models to generate faces based on specific identity, pose and expression conditions. However, the mechanisms used in these methods to control pose and expression often inadvertently introduce identity information from the driving video, while also causing a loss of expression-related details. This paper proposes a new method based on Stable Diffusion, called AniFaceDiff, incorporating a new conditioning module for high-fidelity face reenactment. First, we propose an enhanced 2D facial snapshot conditioning approach by facial shape alignment to prevent the inclusion of identity information from the driving video. Then, we introduce an expression adapter conditioning mechanism to address the potential loss of expression-related information. Our approach effectively preserves pose and expression fidelity from the driving video while retaining the identity and fine details of the source image. Through experiments on the VoxCeleb dataset, we demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art results in face reenactment, showcasing superior image quality, identity preservation, and expression accuracy, especially for cross-identity scenarios. Considering the ethical concerns surrounding potential misuse, we analyze the implications of our method, evaluate current state-of-the-art deepfake detectors, and identify their shortcomings to guide future research.
RoScenes: A Large-scale Multi-view 3D Dataset for Roadside Perception
May 17, 2024



Abstract:We introduce RoScenes, the largest multi-view roadside perception dataset, which aims to shed light on the development of vision-centric Bird's Eye View (BEV) approaches for more challenging traffic scenes. The highlights of RoScenes include significantly large perception area, full scene coverage and crowded traffic. More specifically, our dataset achieves surprising 21.13M 3D annotations within 64,000 $m^2$. To relieve the expensive costs of roadside 3D labeling, we present a novel BEV-to-3D joint annotation pipeline to efficiently collect such a large volume of data. After that, we organize a comprehensive study for current BEV methods on RoScenes in terms of effectiveness and efficiency. Tested methods suffer from the vast perception area and variation of sensor layout across scenes, resulting in performance levels falling below expectations. To this end, we propose RoBEV that incorporates feature-guided position embedding for effective 2D-3D feature assignment. With its help, our method outperforms state-of-the-art by a large margin without extra computational overhead on validation set. Our dataset and devkit will be made available at https://github.com/xiaosu-zhu/RoScenes.
Source Prompt: Coordinated Pre-training of Language Models on Diverse Corpora from Multiple Sources
Nov 16, 2023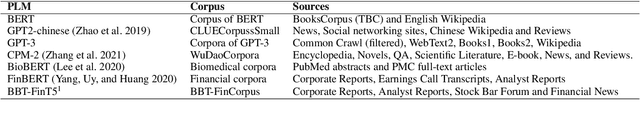
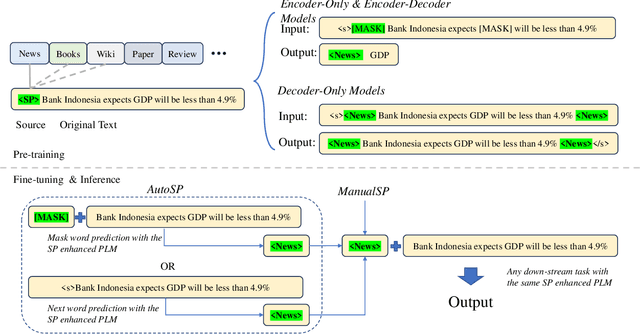
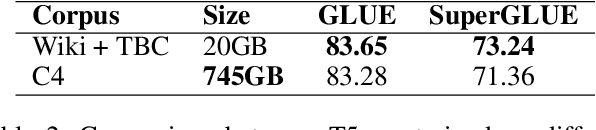
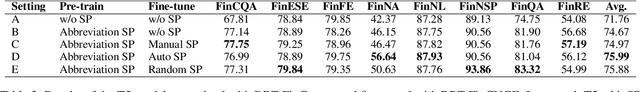
Abstract:Pre-trained language models (PLMs) have established the new paradigm in the field of NLP. For more powerful PLMs, one of the most popular and successful way is to continuously scale up sizes of the models and the pre-training corpora. These large corpora are generally obtained by converging smaller ones from multiple sources, they are thus growing increasingly diverse. However, the side-effects of these colossal converged corpora remain understudied. In this paper, we identify the disadvantage of heterogeneous corpora from multiple sources for pre-training PLMs. Towards coordinated pre-training on diverse corpora, we further propose source prompts (SP), which explicitly prompt the model of the data source at the pre-training and fine-tuning stages. Results of extensive experiments demonstrate that PLMs pre-trained with SP on diverse corpora gain significant improvement in various downstream tasks.
Robotic Assembly Control Reconfiguration Based on Transfer Reinforcement Learning for Objects with Different Geometric Features
Nov 04, 2022



Abstract:Robotic force-based compliance control is a preferred approach to achieve high-precision assembly tasks. When the geometric features of assembly objects are asymmetric or irregular, reinforcement learning (RL) agents are gradually incorporated into the compliance controller to adapt to complex force-pose mapping which is hard to model analytically. Since force-pose mapping is strongly dependent on geometric features, a compliance controller is only optimal for current geometric features. To reduce the learning cost of assembly objects with different geometric features, this paper is devoted to answering how to reconfigure existing controllers for new assembly objects with different geometric features. In this paper, model-based parameters are first reconfigured based on the proposed Equivalent Theory of Compliance Law (ETCL). Then the RL agent is transferred based on the proposed Weighted Dimensional Policy Distillation (WDPD) method. The experiment results demonstrate that the control reconfiguration method costs less time and achieves better control performance, which confirms the validity of proposed methods.
Local Connection Reinforcement Learning Method for Efficient Control of Robotic Peg-in-Hole Assembly
Oct 24, 2022



Abstract:Traditional control methods of robotic peg-in-hole assembly rely on complex contact state analysis. Reinforcement learning (RL) is gradually becoming a preferred method of controlling robotic peg-in-hole assembly tasks. However, the training process of RL is quite time-consuming because RL methods are always globally connected, which means all state components are assumed to be the input of policies for all action components, thus increasing action space and state space to be explored. In this paper, we first define continuous space serialized Shapley value (CS3) and construct a connection graph to clarify the correlativity of action components on state components. Then we propose a local connection reinforcement learning (LCRL) method based on the connection graph, which eliminates the influence of irrelevant state components on the selection of action components. The simulation and experiment results demonstrate that the control strategy obtained through LCRL method improves the stability and rapidity of the control process. LCRL method will enhance the data-efficiency and increase the final reward of the training process.
Progressive extension of reinforcement learning action dimension for asymmetric assembly tasks
Apr 06, 2021



Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) is always the preferred embodiment to construct the control strategy of complex tasks, like asymmetric assembly tasks. However, the convergence speed of reinforcement learning severely restricts its practical application. In this paper, the convergence is first accelerated by combining RL and compliance control. Then a completely innovative progressive extension of action dimension (PEAD) mechanism is proposed to optimize the convergence of RL algorithms. The PEAD method is verified in DDPG and PPO. The results demonstrate the PEAD method will enhance the data-efficiency and time-efficiency of RL algorithms as well as increase the stable reward, which provides more potential for the application of RL.
LAW: Learning to Auto Weight
May 27, 2019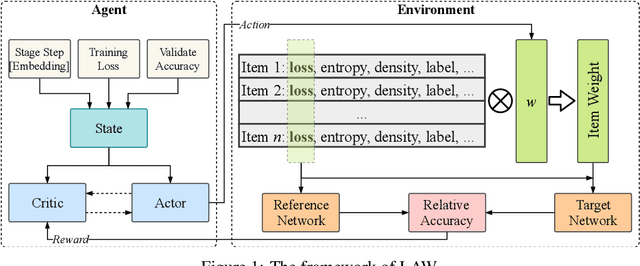

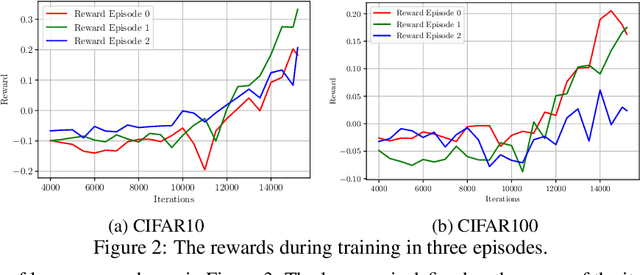
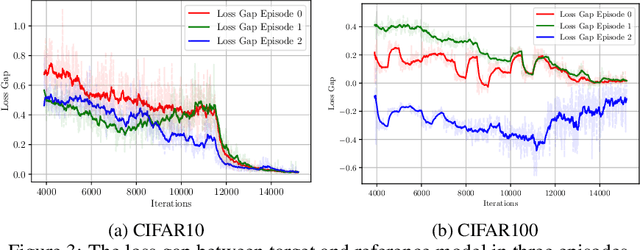
Abstract:Example weighting algorithm is an effective solution to the training bias problem. However, typical methods are usually limited to human knowledge and require laborious tuning of hyperparameters. In this study, we propose a novel example weighting framework called Learning to Auto Weight (LAW), which can learn weighting policy from data adaptively based on reinforcement learning (RL). To shrink the huge searching space in a complete training process, we divide the training procedure consisting of numerous iterations into a small number of stages, and then search a low-deformational continuous vector as action, which determines the weight of each sample. To make training more efficient, we make an innovative design of the reward to remove randomness during the RL process. Experimental results demonstrate the superiority of weighting policy explored by LAW over standard training pipeline. Especially, compared with baselines, LAW can find a better weighting schedule which achieves higher accuracy in the origin CIFAR dataset, and over 10% higher in accuracy on the contaminated CIFAR dataset with 30% label noises. Our code will be released soon.
Fast Skill Learning for Variable Compliance Robotic Assembly
May 11, 2019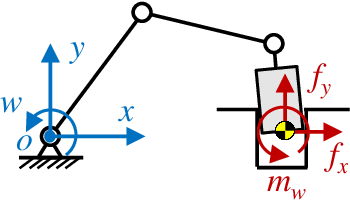
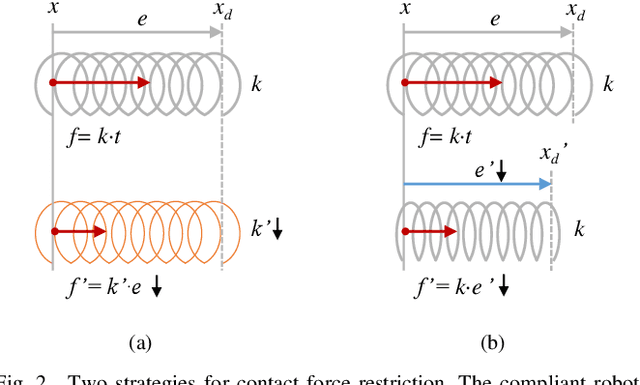
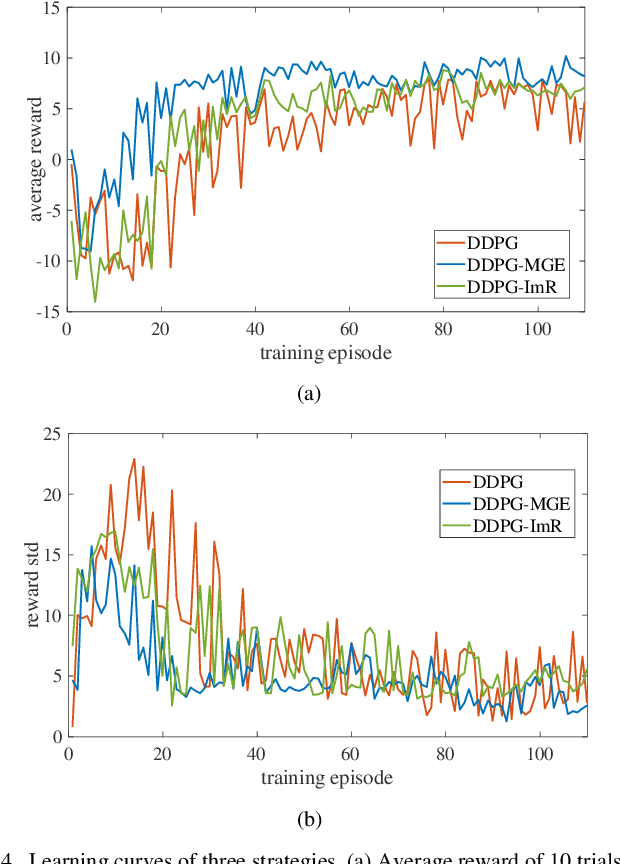
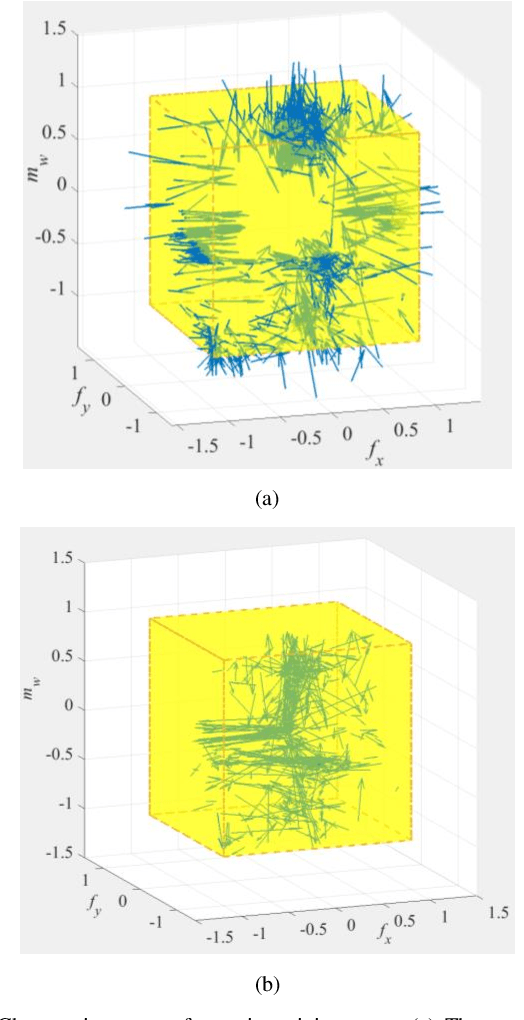
Abstract:The robotic assembly represents a group of benchmark problems for reinforcement learning and variable compliance control that features sophisticated contact manipulation. One of the key challenges in applying reinforcement learning to physical robot is the sample complexity, the requirement of large amounts of experience for learning. We mitigate this sample complexity problem by incorporating an iteratively refitted model into the learning process through model-guided exploration. Yet, fitting a local model of the physical environment is of major difficulties. In this work, a Kalman filter is used to combine the adaptive linear dynamics with a coarse prior model from analytical description, and proves to give more accurate predictions than the existing method. Experimental results show that the proposed model fitting strategy can be incorporated into a model predictive controller to generate good exploration behaviors for learning acceleration, while preserving the benefits of model-free reinforcement learning for uncertain environments. In addition to the sample complexity, the inevitable robot overloaded during operation also tends to limit the learning efficiency. To address this problem, we present a method to restrict the largest possible potential energy in the compliance control system and therefore keep the contact force within the legitimate range.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge