Yichao Wu
Language-based Trial and Error Falls Behind in the Era of Experience
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:While Large Language Models (LLMs) excel in language-based agentic tasks, their applicability to unseen, nonlinguistic environments (e.g., symbolic or spatial tasks) remains limited. Previous work attributes this performance gap to the mismatch between the pretraining distribution and the testing distribution. In this work, we demonstrate the primary bottleneck is the prohibitive cost of exploration: mastering these tasks requires extensive trial-and-error, which is computationally unsustainable for parameter-heavy LLMs operating in a high dimensional semantic space. To address this, we propose SCOUT (Sub-Scale Collaboration On Unseen Tasks), a novel framework that decouples exploration from exploitation. We employ lightweight "scouts" (e.g., small MLPs) to probe environmental dynamics at a speed and scale far exceeding LLMs. The collected trajectories are utilized to bootstrap the LLM via Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), followed by multi-turn Reinforcement Learning (RL) to activate its latent world knowledge. Empirically, SCOUT enables a Qwen2.5-3B-Instruct model to achieve an average score of 0.86, significantly outperforming proprietary models, including Gemini-2.5-Pro (0.60), while saving about 60% GPU hours consumption.
MMRPT: MultiModal Reinforcement Pre-Training via Masked Vision-Dependent Reasoning
Dec 08, 2025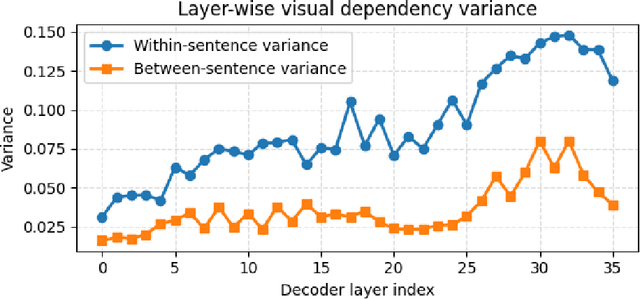
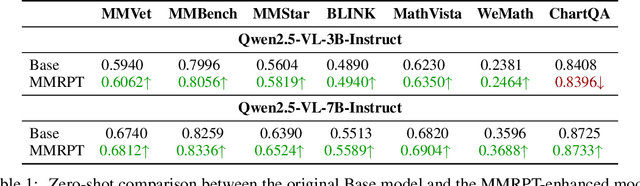

Abstract:Multimodal pre-training remains constrained by the descriptive bias of image-caption pairs, leading models to favor surface linguistic cues over grounded visual understanding. We introduce MMRPT, a masked multimodal reinforcement pre-training framework that strengthens visual reasoning in MLLMs. We are the first to incorporate reinforcement learning directly into the pre-training of large vision-language models, enabling learning signals that reward visual grounding rather than caption imitation. MMRPT constructs masked multimodal data by estimating sentence-level visual dependency via attention over visual tokens and masking highly vision-dependent segments; the model reconstructs these spans through vision-grounded reasoning guided by a semantic-visual reward. Experiments show consistent zero-shot gains across diverse benchmarks and substantially improved robustness under supervised fine-tuning, demonstrating that reinforcement-driven masked reasoning provides a more reliable and generalizable pre-training objective for multimodal models.
Erase to Improve: Erasable Reinforcement Learning for Search-Augmented LLMs
Oct 01, 2025Abstract:While search-augmented large language models (LLMs) exhibit impressive capabilities, their reliability in complex multi-hop reasoning remains limited. This limitation arises from three fundamental challenges: decomposition errors, where tasks are incorrectly broken down; retrieval missing, where key evidence fails to be retrieved; and reasoning errors, where flawed logic propagates through the reasoning chain. A single failure in any of these stages can derail the final answer. We propose Erasable Reinforcement Learning (ERL), a novel framework that transforms fragile reasoning into a robust process. ERL explicitly identifies faulty steps, erases them, and regenerates reasoning in place, preventing defective logic from propagating through the reasoning chain. This targeted correction mechanism turns brittle reasoning into a more resilient process. Models trained with ERL, termed ESearch, achieve substantial improvements on HotpotQA, MuSiQue, 2Wiki, and Bamboogle, with the 3B model achieving +8.48% EM and +11.56% F1, and the 7B model achieving +5.38% EM and +7.22% F1 over previous state-of-the-art(SOTA) results. These findings suggest that erasable reinforcement learning provides a powerful paradigm shift for robust multi-step reasoning in LLMs.
StepSearch: Igniting LLMs Search Ability via Step-Wise Proximal Policy Optimization
May 21, 2025Abstract:Efficient multi-hop reasoning requires Large Language Models (LLMs) based agents to acquire high-value external knowledge iteratively. Previous work has explored reinforcement learning (RL) to train LLMs to perform search-based document retrieval, achieving notable improvements in QA performance, but underperform on complex, multi-hop QA resulting from the sparse rewards from global signal only. To address this gap in existing research, we introduce StepSearch, a framework for search LLMs that trained with step-wise proximal policy optimization method. It consists of richer and more detailed intermediate search rewards and token-level process supervision based on information gain and redundancy penalties to better guide each search step. We constructed a fine-grained question-answering dataset containing sub-question-level search trajectories based on open source datasets through a set of data pipeline method. On standard multi-hop QA benchmarks, it significantly outperforms global-reward baselines, achieving 11.2% and 4.2% absolute improvements for 3B and 7B models over various search with RL baselines using only 19k training data, demonstrating the effectiveness of fine-grained, stepwise supervision in optimizing deep search LLMs. Our implementation is publicly available at https://github.com/zxh20001117/StepSearch.
Piccolo2: General Text Embedding with Multi-task Hybrid Loss Training
May 11, 2024



Abstract:In this report, we introduce Piccolo2, an embedding model that surpasses other models in the comprehensive evaluation over 6 tasks on CMTEB benchmark, setting a new state-of-the-art. Piccolo2 primarily leverages an efficient multi-task hybrid loss training approach, effectively harnessing textual data and labels from diverse downstream tasks. In addition, Piccolo2 scales up the embedding dimension and uses MRL training to support more flexible vector dimensions. The latest information of piccolo models can be accessed via: https://huggingface.co/sensenova/
Maximizing User Experience with LLMOps-Driven Personalized Recommendation Systems
Apr 01, 2024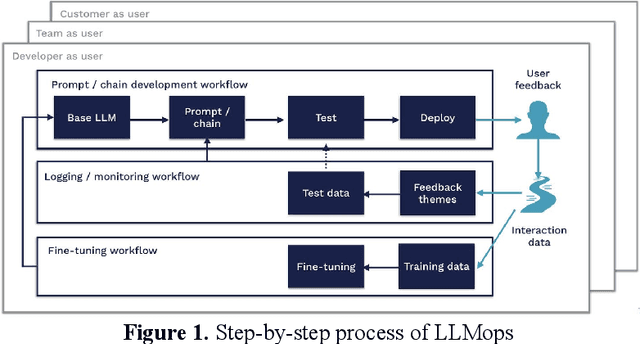
Abstract:The integration of LLMOps into personalized recommendation systems marks a significant advancement in managing LLM-driven applications. This innovation presents both opportunities and challenges for enterprises, requiring specialized teams to navigate the complexity of engineering technology while prioritizing data security and model interpretability. By leveraging LLMOps, enterprises can enhance the efficiency and reliability of large-scale machine learning models, driving personalized recommendations aligned with user preferences. Despite ethical considerations, LLMOps is poised for widespread adoption, promising more efficient and secure machine learning services that elevate user experience and shape the future of personalized recommendation systems.
ViTCN: Vision Transformer Contrastive Network For Reasoning
Mar 15, 2024


Abstract:Machine learning models have achieved significant milestones in various domains, for example, computer vision models have an exceptional result in object recognition, and in natural language processing, where Large Language Models (LLM) like GPT can start a conversation with human-like proficiency. However, abstract reasoning remains a challenge for these models, Can AI really thinking like a human? still be a question yet to be answered. Raven Progressive Matrices (RPM) is a metric designed to assess human reasoning capabilities. It presents a series of eight images as a problem set, where the participant should try to discover the underlying rules among these images and select the most appropriate image from eight possible options that best completes the sequence. This task always be used to test human reasoning abilities and IQ. Zhang et al proposed a dataset called RAVEN which can be used to test Machine Learning model abstract reasoning ability. In this paper, we purposed Vision Transformer Contrastive Network which build on previous work with the Contrastive Perceptual Inference network (CoPiNet), which set a new benchmark for permutationinvariant models Raven Progressive Matrices by incorporating contrast effects from psychology, cognition, and education, and extends this foundation by leveraging the cutting-edge Vision Transformer architecture. This integration aims to further refine the machine ability to process and reason about spatial-temporal information from pixel-level inputs and global wise features on RAVEN dataset.
Research on the Application of Deep Learning-based BERT Model in Sentiment Analysis
Mar 13, 2024



Abstract:This paper explores the application of deep learning techniques, particularly focusing on BERT models, in sentiment analysis. It begins by introducing the fundamental concept of sentiment analysis and how deep learning methods are utilized in this domain. Subsequently, it delves into the architecture and characteristics of BERT models. Through detailed explanation, it elucidates the application effects and optimization strategies of BERT models in sentiment analysis, supported by experimental validation. The experimental findings indicate that BERT models exhibit robust performance in sentiment analysis tasks, with notable enhancements post fine-tuning. Lastly, the paper concludes by summarizing the potential applications of BERT models in sentiment analysis and suggests directions for future research and practical implementations.
Emerging Synergies Between Large Language Models and Machine Learning in Ecommerce Recommendations
Mar 12, 2024



Abstract:With the boom of e-commerce and web applications, recommender systems have become an important part of our daily lives, providing personalized recommendations based on the user's preferences. Although deep neural networks (DNNs) have made significant progress in improving recommendation systems by simulating the interaction between users and items and incorporating their textual information, these DNN-based approaches still have some limitations, such as the difficulty of effectively understanding users' interests and capturing textual information. It is not possible to generalize to different seen/unseen recommendation scenarios and reason about their predictions. At the same time, the emergence of large language models (LLMs), represented by ChatGPT and GPT-4, has revolutionized the fields of natural language processing (NLP) and artificial intelligence (AI) due to their superior capabilities in the basic tasks of language understanding and generation, and their impressive generalization and reasoning capabilities. As a result, recent research has sought to harness the power of LLM to improve recommendation systems. Given the rapid development of this research direction in the field of recommendation systems, there is an urgent need for a systematic review of existing LLM-driven recommendation systems for researchers and practitioners in related fields to gain insight into. More specifically, we first introduced a representative approach to learning user and item representations using LLM as a feature encoder. We then reviewed the latest advances in LLMs techniques for collaborative filtering enhanced recommendation systems from the three paradigms of pre-training, fine-tuning, and prompting. Finally, we had a comprehensive discussion on the future direction of this emerging field.
LoRA-SP: Streamlined Partial Parameter Adaptation for Resource-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models
Feb 28, 2024Abstract:In addressing the computational and memory demands of fine-tuning Large Language Models(LLMs), we propose LoRA-SP(Streamlined Partial Parameter Adaptation), a novel approach utilizing randomized half-selective parameter freezing within the Low-Rank Adaptation(LoRA)framework. This method efficiently balances pre-trained knowledge retention and adaptability for task-specific optimizations. Through a randomized mechanism, LoRA-SP determines which parameters to update or freeze, significantly reducing computational and memory requirements without compromising model performance. We evaluated LoRA-SP across several benchmark NLP tasks, demonstrating its ability to achieve competitive performance with substantially lower resource consumption compared to traditional full-parameter fine-tuning and other parameter-efficient techniques. LoRA-SP innovative approach not only facilitates the deployment of advanced NLP models in resource-limited settings but also opens new research avenues into effective and efficient model adaptation strategies.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge