Yulu Gong
Northern Arizona University
Application of Computer Deep Learning Model in Diagnosis of Pulmonary Nodules
Jun 19, 2024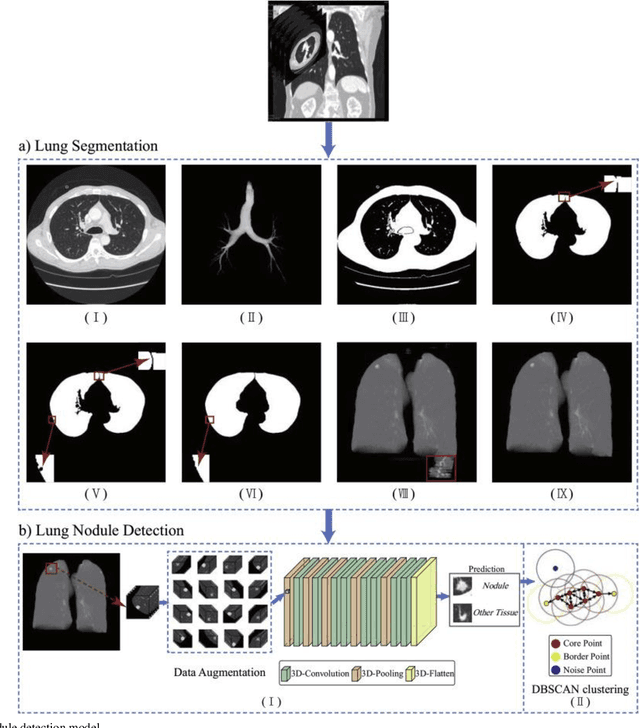
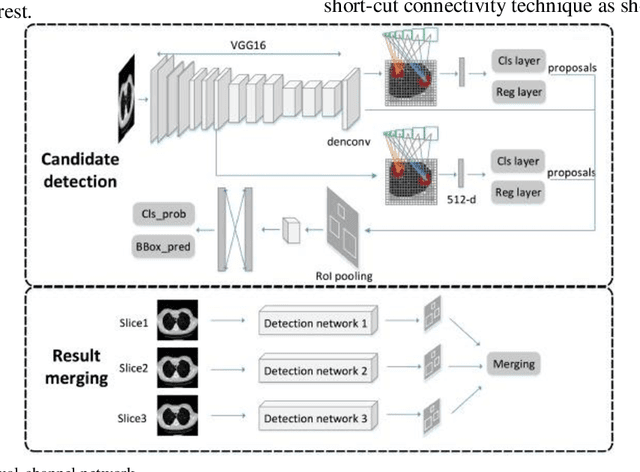
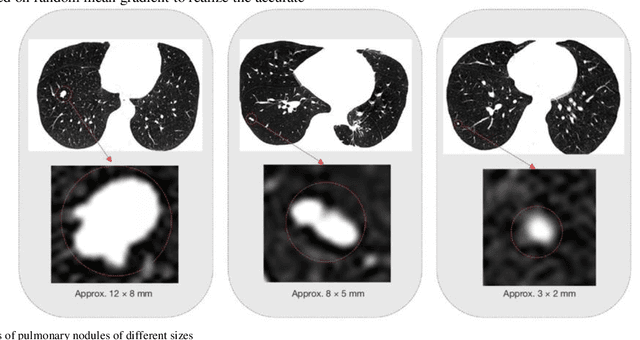
Abstract:The 3D simulation model of the lung was established by using the reconstruction method. A computer aided pulmonary nodule detection model was constructed. The process iterates over the images to refine the lung nodule recognition model based on neural networks. It is integrated with 3D virtual modeling technology to improve the interactivity of the system, so as to achieve intelligent recognition of lung nodules. A 3D RCNN (Region-based Convolutional Neural Network) was utilized for feature extraction and nodule identification. The LUNA16 large sample database was used as the research dataset. FROC (Free-response Receiver Operating Characteristic) analysis was applied to evaluate the model, calculating sensitivity at various false positive rates to derive the average FROC. Compared with conventional diagnostic methods, the recognition rate was significantly improved. This technique facilitates the detection of pulmonary abnormalities at an initial phase, which holds immense value for the prompt diagnosis of lung malignancies.
Enhancing Text Authenticity: A Novel Hybrid Approach for AI-Generated Text Detection
Jun 01, 2024


Abstract:The rapid advancement of Large Language Models (LLMs) has ushered in an era where AI-generated text is increasingly indistinguishable from human-generated content. Detecting AI-generated text has become imperative to combat misinformation, ensure content authenticity, and safeguard against malicious uses of AI. In this paper, we propose a novel hybrid approach that combines traditional TF-IDF techniques with advanced machine learning models, including Bayesian classifiers, Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD), Categorical Gradient Boosting (CatBoost), and 12 instances of Deberta-v3-large models. Our approach aims to address the challenges associated with detecting AI-generated text by leveraging the strengths of both traditional feature extraction methods and state-of-the-art deep learning models. Through extensive experiments on a comprehensive dataset, we demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method in accurately distinguishing between human and AI-generated text. Our approach achieves superior performance compared to existing methods. This research contributes to the advancement of AI-generated text detection techniques and lays the foundation for developing robust solutions to mitigate the challenges posed by AI-generated content.
Research on Intelligent Aided Diagnosis System of Medical Image Based on Computer Deep Learning
Apr 29, 2024Abstract:This paper combines Struts and Hibernate two architectures together, using DAO (Data Access Object) to store and access data. Then a set of dual-mode humidity medical image library suitable for deep network is established, and a dual-mode medical image assisted diagnosis method based on the image is proposed. Through the test of various feature extraction methods, the optimal operating characteristic under curve product (AUROC) is 0.9985, the recall rate is 0.9814, and the accuracy is 0.9833. This method can be applied to clinical diagnosis, and it is a practical method. Any outpatient doctor can register quickly through the system, or log in to the platform to upload the image to obtain more accurate images. Through the system, each outpatient physician can quickly register or log in to the platform for image uploading, thus obtaining more accurate images. The segmentation of images can guide doctors in clinical departments. Then the image is analyzed to determine the location and nature of the tumor, so as to make targeted treatment.
Practical Applications of Advanced Cloud Services and Generative AI Systems in Medical Image Analysis
Mar 26, 2024Abstract:The medical field is one of the important fields in the application of artificial intelligence technology. With the explosive growth and diversification of medical data, as well as the continuous improvement of medical needs and challenges, artificial intelligence technology is playing an increasingly important role in the medical field. Artificial intelligence technologies represented by computer vision, natural language processing, and machine learning have been widely penetrated into diverse scenarios such as medical imaging, health management, medical information, and drug research and development, and have become an important driving force for improving the level and quality of medical services.The article explores the transformative potential of generative AI in medical imaging, emphasizing its ability to generate syntheticACM-2 data, enhance images, aid in anomaly detection, and facilitate image-to-image translation. Despite challenges like model complexity, the applications of generative models in healthcare, including Med-PaLM 2 technology, show promising results. By addressing limitations in dataset size and diversity, these models contribute to more accurate diagnoses and improved patient outcomes. However, ethical considerations and collaboration among stakeholders are essential for responsible implementation. Through experiments leveraging GANs to augment brain tumor MRI datasets, the study demonstrates how generative AI can enhance image quality and diversity, ultimately advancing medical diagnostics and patient care.
Leveraging Deep Learning and Xception Architecture for High-Accuracy MRI Classification in Alzheimer Diagnosis
Mar 24, 2024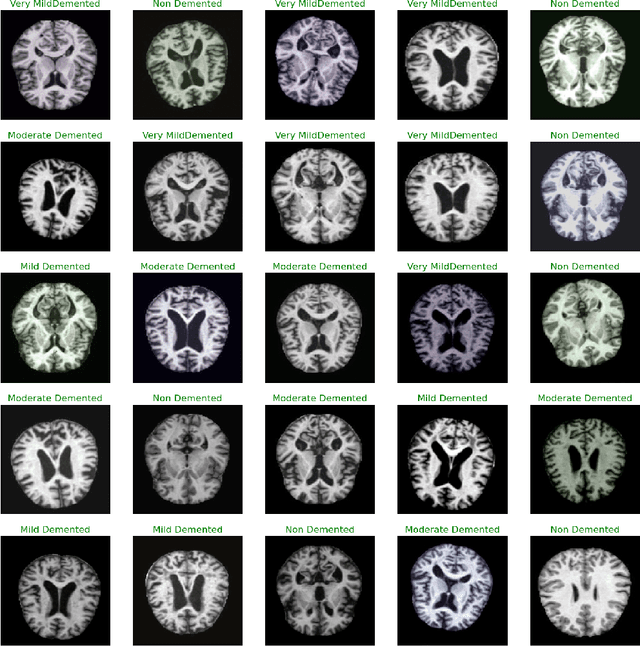
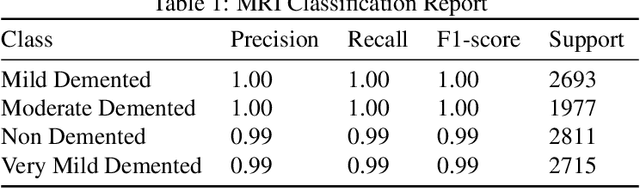
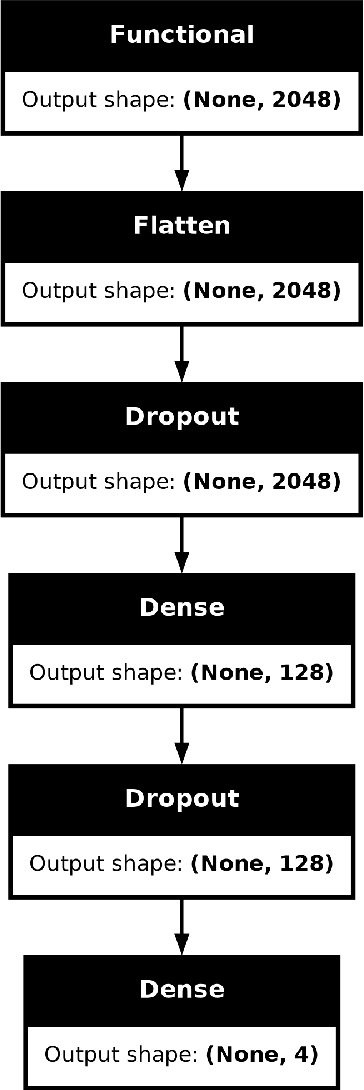
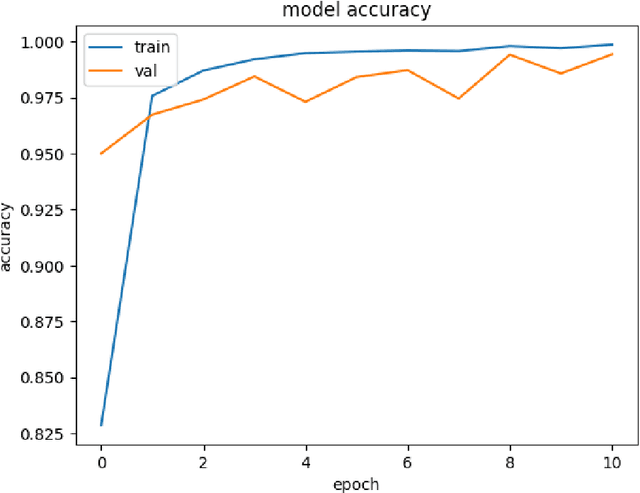
Abstract:Exploring the application of deep learning technologies in the field of medical diagnostics, Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) provides a unique perspective for observing and diagnosing complex neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer Disease (AD). With advancements in deep learning, particularly in Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and the Xception network architecture, we are now able to analyze and classify vast amounts of MRI data with unprecedented accuracy. The progress of this technology not only enhances our understanding of brain structural changes but also opens up new avenues for monitoring disease progression through non-invasive means and potentially allows for precise diagnosis in the early stages of the disease. This study aims to classify MRI images using deep learning models to identify different stages of Alzheimer Disease through a series of innovative data processing and model construction steps. Our experimental results show that the deep learning framework based on the Xception model achieved a 99.6% accuracy rate in the multi-class MRI image classification task, demonstrating its potential application value in assistive diagnosis. Future research will focus on expanding the dataset, improving model interpretability, and clinical validation to further promote the application of deep learning technology in the medical field, with the hope of bringing earlier diagnosis and more personalized treatment plans to Alzheimer Disease patients.
Utilizing the LightGBM Algorithm for Operator User Credit Assessment Research
Mar 21, 2024



Abstract:Mobile Internet user credit assessment is an important way for communication operators to establish decisions and formulate measures, and it is also a guarantee for operators to obtain expected benefits. However, credit evaluation methods have long been monopolized by financial industries such as banks and credit. As supporters and providers of platform network technology and network resources, communication operators are also builders and maintainers of communication networks. Internet data improves the user's credit evaluation strategy. This paper uses the massive data provided by communication operators to carry out research on the operator's user credit evaluation model based on the fusion LightGBM algorithm. First, for the massive data related to user evaluation provided by operators, key features are extracted by data preprocessing and feature engineering methods, and a multi-dimensional feature set with statistical significance is constructed; then, linear regression, decision tree, LightGBM, and other machine learning algorithms build multiple basic models to find the best basic model; finally, integrates Averaging, Voting, Blending, Stacking and other integrated algorithms to refine multiple fusion models, and finally establish the most suitable fusion model for operator user evaluation.
Dynamic Resource Allocation for Virtual Machine Migration Optimization using Machine Learning
Mar 20, 2024Abstract:The paragraph is grammatically correct and logically coherent. It discusses the importance of mobile terminal cloud computing migration technology in meeting the demands of evolving computer and cloud computing technologies. It emphasizes the need for efficient data access and storage, as well as the utilization of cloud computing migration technology to prevent additional time delays. The paragraph also highlights the contributions of cloud computing migration technology to expanding cloud computing services. Additionally, it acknowledges the role of virtualization as a fundamental capability of cloud computing while emphasizing that cloud computing and virtualization are not inherently interconnected. Finally, it introduces machine learning-based virtual machine migration optimization and dynamic resource allocation as a critical research direction in cloud computing, citing the limitations of static rules or manual settings in traditional cloud computing environments. Overall, the paragraph effectively communicates the importance of machine learning technology in addressing resource allocation and virtual machine migration challenges in cloud computing.
Ensemble Methodology:Innovations in Credit Default Prediction Using LightGBM, XGBoost, and LocalEnsemble
Feb 28, 2024Abstract:In the realm of consumer lending, accurate credit default prediction stands as a critical element in risk mitigation and lending decision optimization. Extensive research has sought continuous improvement in existing models to enhance customer experiences and ensure the sound economic functioning of lending institutions. This study responds to the evolving landscape of credit default prediction, challenging conventional models and introducing innovative approaches. By building upon foundational research and recent innovations, our work aims to redefine the standards of accuracy in credit default prediction, setting a new benchmark for the industry. To overcome these challenges, we present an Ensemble Methods framework comprising LightGBM, XGBoost, and LocalEnsemble modules, each making unique contributions to amplify diversity and improve generalization. By utilizing distinct feature sets, our methodology directly tackles limitations identified in previous studies, with the overarching goal of establishing a novel standard for credit default prediction accuracy. Our experimental findings validate the effectiveness of the ensemble model on the dataset, signifying substantial contributions to the field. This innovative approach not only addresses existing obstacles but also sets a precedent for advancing the accuracy and robustness of credit default prediction models.
LoRA-SP: Streamlined Partial Parameter Adaptation for Resource-Efficient Fine-Tuning of Large Language Models
Feb 28, 2024Abstract:In addressing the computational and memory demands of fine-tuning Large Language Models(LLMs), we propose LoRA-SP(Streamlined Partial Parameter Adaptation), a novel approach utilizing randomized half-selective parameter freezing within the Low-Rank Adaptation(LoRA)framework. This method efficiently balances pre-trained knowledge retention and adaptability for task-specific optimizations. Through a randomized mechanism, LoRA-SP determines which parameters to update or freeze, significantly reducing computational and memory requirements without compromising model performance. We evaluated LoRA-SP across several benchmark NLP tasks, demonstrating its ability to achieve competitive performance with substantially lower resource consumption compared to traditional full-parameter fine-tuning and other parameter-efficient techniques. LoRA-SP innovative approach not only facilitates the deployment of advanced NLP models in resource-limited settings but also opens new research avenues into effective and efficient model adaptation strategies.
Application of Machine Learning Optimization in Cloud Computing Resource Scheduling and Management
Feb 27, 2024



Abstract:In recent years, cloud computing has been widely used. Cloud computing refers to the centralized computing resources, users through the access to the centralized resources to complete the calculation, the cloud computing center will return the results of the program processing to the user. Cloud computing is not only for individual users, but also for enterprise users. By purchasing a cloud server, users do not have to buy a large number of computers, saving computing costs. According to a report by China Economic News Network, the scale of cloud computing in China has reached 209.1 billion yuan. At present, the more mature cloud service providers in China are Ali Cloud, Baidu Cloud, Huawei Cloud and so on. Therefore, this paper proposes an innovative approach to solve complex problems in cloud computing resource scheduling and management using machine learning optimization techniques. Through in-depth study of challenges such as low resource utilization and unbalanced load in the cloud environment, this study proposes a comprehensive solution, including optimization methods such as deep learning and genetic algorithm, to improve system performance and efficiency, and thus bring new breakthroughs and progress in the field of cloud computing resource management.Rational allocation of resources plays a crucial role in cloud computing. In the resource allocation of cloud computing, the cloud computing center has limited cloud resources, and users arrive in sequence. Each user requests the cloud computing center to use a certain number of cloud resources at a specific time.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge