Shaodian Zhang
TGE-PS: Text-driven Graph Embedding with Pairs Sampling
Sep 12, 2018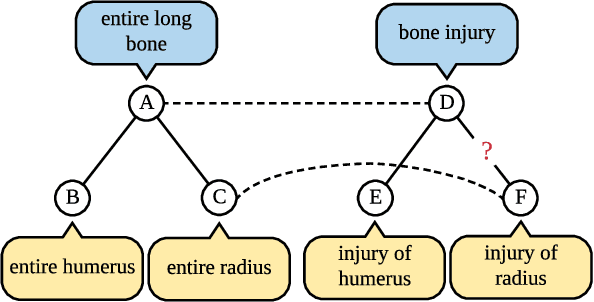
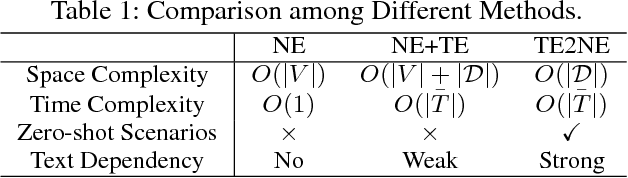
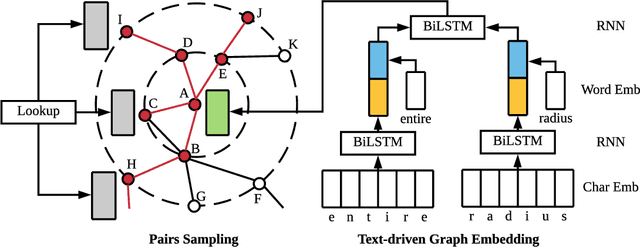
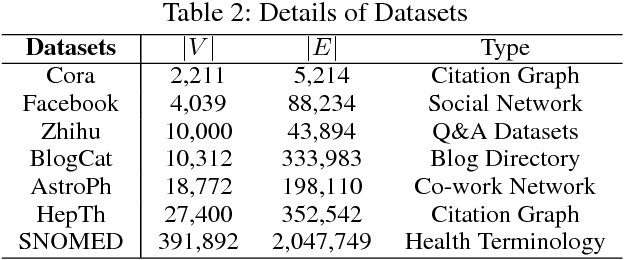
Abstract:In graphs with rich text information, constructing expressive graph representations requires incorporating textual information with structural information. Graph embedding models are becoming more and more popular in representing graphs, yet they are faced with two issues: sampling efficiency and text utilization. Through analyzing existing models, we find their training objectives are composed of pairwise proximities, and there are large amounts of redundant node pairs in Random Walk-based methods. Besides, inferring graph structures directly from texts (also known as zero-shot scenario) is a problem that requires higher text utilization. To solve these problems, we propose a novel Text-driven Graph Embedding with Pairs Sampling (TGE-PS) framework. TGE-PS uses Pairs Sampling (PS) to generate training samples which reduces ~99% training samples and is competitive compared to Random Walk. TGE-PS uses Text-driven Graph Embedding (TGE) which adopts word- and character-level embeddings to generate node embeddings. We evaluate TGE-PS on several real-world datasets, and experimental results demonstrate that TGE-PS produces state-of-the-art results in traditional and zero-shot link prediction tasks.
Label-aware Double Transfer Learning for Cross-Specialty Medical Named Entity Recognition
Apr 28, 2018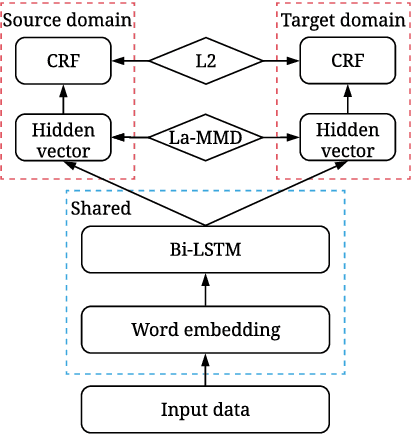
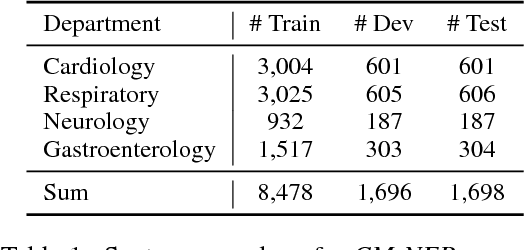
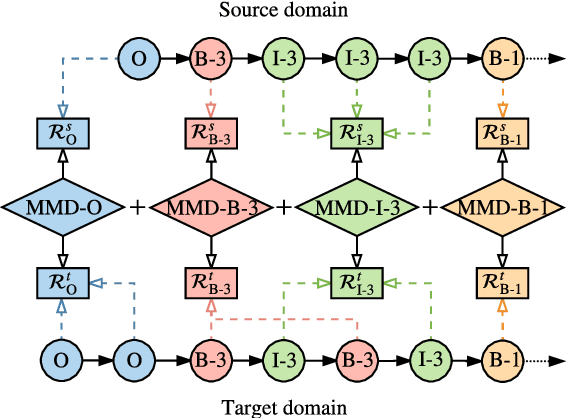
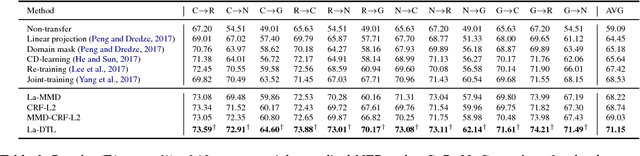
Abstract:We study the problem of named entity recognition (NER) from electronic medical records, which is one of the most fundamental and critical problems for medical text mining. Medical records which are written by clinicians from different specialties usually contain quite different terminologies and writing styles. The difference of specialties and the cost of human annotation makes it particularly difficult to train a universal medical NER system. In this paper, we propose a label-aware double transfer learning framework (La-DTL) for cross-specialty NER, so that a medical NER system designed for one specialty could be conveniently applied to another one with minimal annotation efforts. The transferability is guaranteed by two components: (i) we propose label-aware MMD for feature representation transfer, and (ii) we perform parameter transfer with a theoretical upper bound which is also label aware. We conduct extensive experiments on 12 cross-specialty NER tasks. The experimental results demonstrate that La-DTL provides consistent accuracy improvement over strong baselines. Besides, the promising experimental results on non-medical NER scenarios indicate that La-DTL is potential to be seamlessly adapted to a wide range of NER tasks.
Longitudinal Analysis of Discussion Topics in an Online Breast Cancer Community using Convolutional Neural Networks
Apr 07, 2016
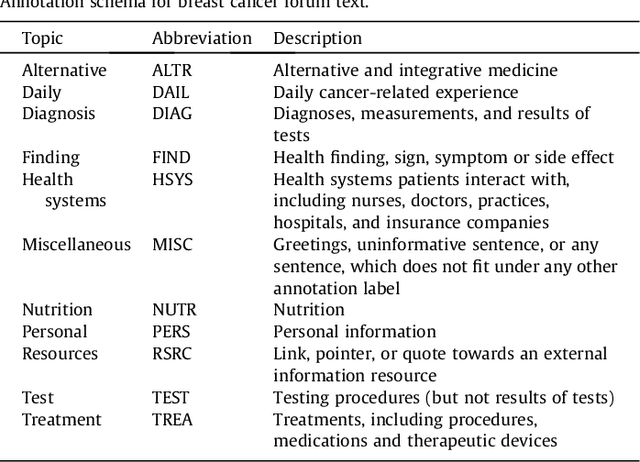

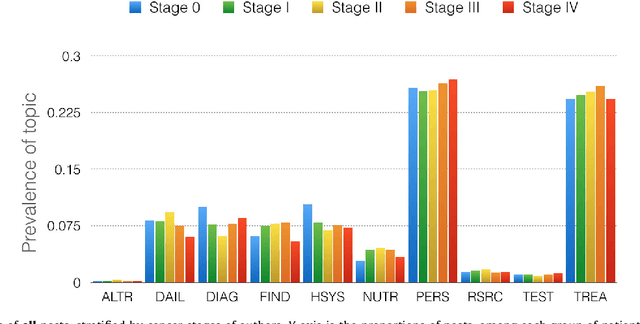
Abstract:Identifying topics of discussions in online health communities (OHC) is critical to various applications, but can be difficult because topics of OHC content are usually heterogeneous and domain-dependent. In this paper, we provide a multi-class schema, an annotated dataset, and supervised classifiers based on convolutional neural network (CNN) and other models for the task of classifying discussion topics. We apply the CNN classifier to the most popular breast cancer online community, and carry out a longitudinal analysis to show topic distributions and topic changes throughout members' participation. Our experimental results suggest that CNN outperforms other classifiers in the task of topic classification, and that certain trajectories can be detected with respect to topic changes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge