Sanjay Saha
Unmasking the Unknown: Facial Deepfake Detection in the Open-Set Paradigm
Mar 11, 2025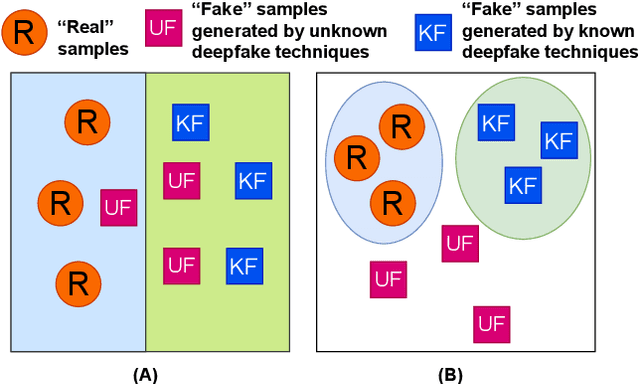
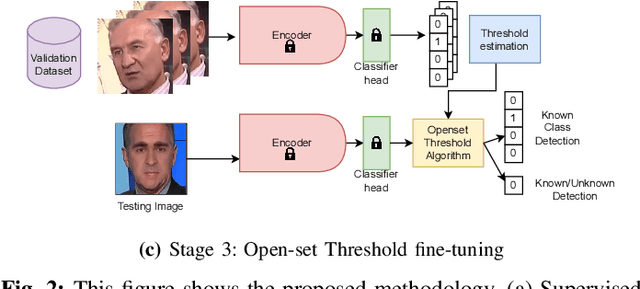
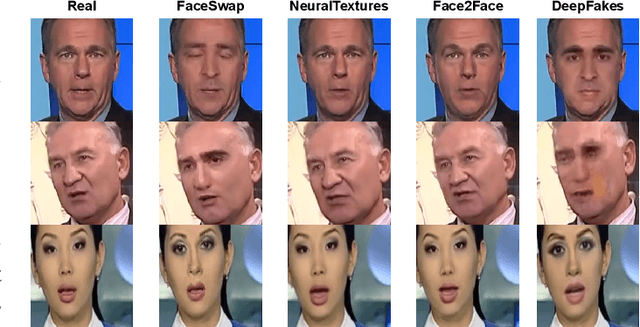
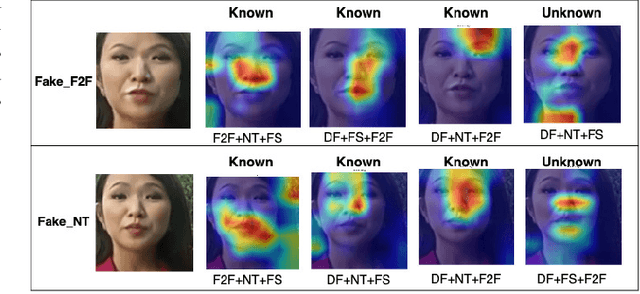
Abstract:Facial forgery methods such as deepfakes can be misused for identity manipulation and spreading misinformation. They have evolved alongside advancements in generative AI, leading to new and more sophisticated forgery techniques that diverge from existing 'known' methods. Conventional deepfake detection methods use the closedset paradigm, thus limiting their applicability to detecting forgeries created using methods that are not part of the training dataset. In this paper, we propose a shift from the closed-set paradigm for deepfake detection. In the open-set paradigm, models are designed not only to identify images created by known facial forgery methods but also to identify and flag those produced by previously unknown methods as 'unknown' and not as unforged/real/unmanipulated. In this paper, we propose an open-set deepfake classification algorithm based on supervised contrastive learning. The open-set paradigm used in our model allows it to function as a more robust tool capable of handling emerging and unseen deepfake techniques, enhancing reliability and confidence, and complementing forensic analysis. In open-set paradigm, we identify three groups including the "unknown group that is neither considered known deepfake nor real. We investigate deepfake open-set classification across three scenarios, classifying deepfakes from unknown methods not as real, distinguishing real images from deepfakes, and classifying deepfakes from known methods, using the FaceForensics++ dataset as a benchmark. Our method achieves state of the art results in the first two tasks and competitive results in the third task.
KVC-onGoing: Keystroke Verification Challenge
Dec 29, 2024



Abstract:This article presents the Keystroke Verification Challenge - onGoing (KVC-onGoing), on which researchers can easily benchmark their systems in a common platform using large-scale public databases, the Aalto University Keystroke databases, and a standard experimental protocol. The keystroke data consist of tweet-long sequences of variable transcript text from over 185,000 subjects, acquired through desktop and mobile keyboards simulating real-life conditions. The results on the evaluation set of KVC-onGoing have proved the high discriminative power of keystroke dynamics, reaching values as low as 3.33% of Equal Error Rate (EER) and 11.96% of False Non-Match Rate (FNMR) @1% False Match Rate (FMR) in the desktop scenario, and 3.61% of EER and 17.44% of FNMR @1% at FMR in the mobile scenario, significantly improving previous state-of-the-art results. Concerning demographic fairness, the analyzed scores reflect the subjects' age and gender to various extents, not negligible in a few cases. The framework runs on CodaLab.
Face Anonymization Made Simple
Nov 01, 2024



Abstract:Current face anonymization techniques often depend on identity loss calculated by face recognition models, which can be inaccurate and unreliable. Additionally, many methods require supplementary data such as facial landmarks and masks to guide the synthesis process. In contrast, our approach uses diffusion models with only a reconstruction loss, eliminating the need for facial landmarks or masks while still producing images with intricate, fine-grained details. We validated our results on two public benchmarks through both quantitative and qualitative evaluations. Our model achieves state-of-the-art performance in three key areas: identity anonymization, facial attribute preservation, and image quality. Beyond its primary function of anonymization, our model can also perform face swapping tasks by incorporating an additional facial image as input, demonstrating its versatility and potential for diverse applications. Our code and models are available at https://github.com/hanweikung/face_anon_simple .
AniFaceDiff: High-Fidelity Face Reenactment via Facial Parametric Conditioned Diffusion Models
Jun 19, 2024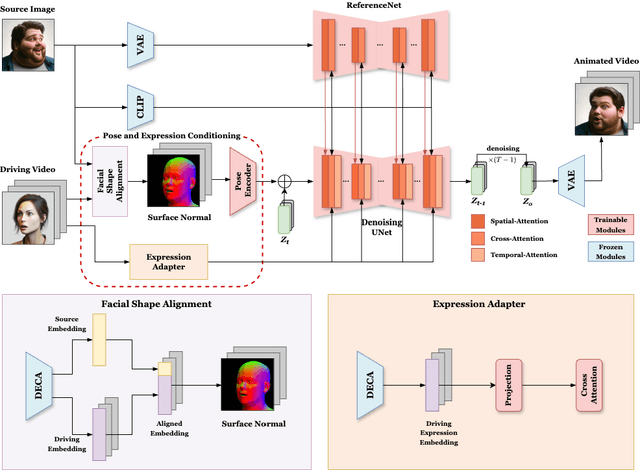
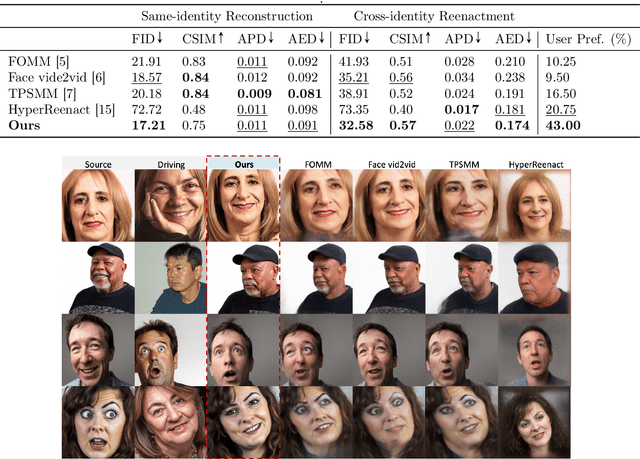
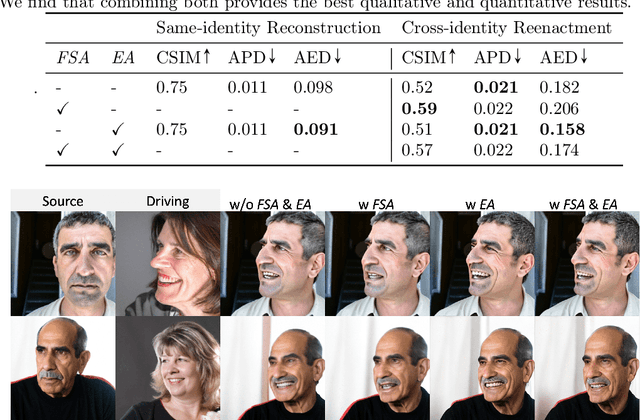
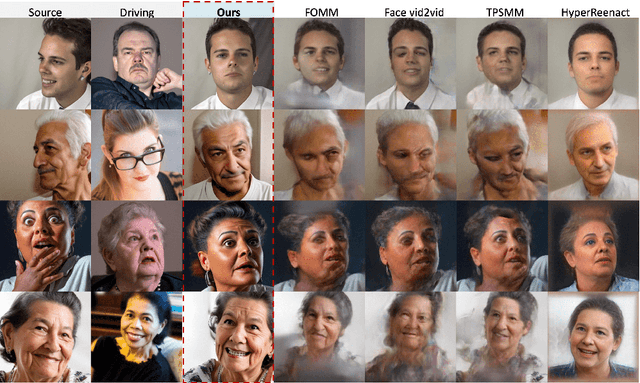
Abstract:Face reenactment refers to the process of transferring the pose and facial expressions from a reference (driving) video onto a static facial (source) image while maintaining the original identity of the source image. Previous research in this domain has made significant progress by training controllable deep generative models to generate faces based on specific identity, pose and expression conditions. However, the mechanisms used in these methods to control pose and expression often inadvertently introduce identity information from the driving video, while also causing a loss of expression-related details. This paper proposes a new method based on Stable Diffusion, called AniFaceDiff, incorporating a new conditioning module for high-fidelity face reenactment. First, we propose an enhanced 2D facial snapshot conditioning approach by facial shape alignment to prevent the inclusion of identity information from the driving video. Then, we introduce an expression adapter conditioning mechanism to address the potential loss of expression-related information. Our approach effectively preserves pose and expression fidelity from the driving video while retaining the identity and fine details of the source image. Through experiments on the VoxCeleb dataset, we demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art results in face reenactment, showcasing superior image quality, identity preservation, and expression accuracy, especially for cross-identity scenarios. Considering the ethical concerns surrounding potential misuse, we analyze the implications of our method, evaluate current state-of-the-art deepfake detectors, and identify their shortcomings to guide future research.
IEEE BigData 2023 Keystroke Verification Challenge (KVC)
Jan 29, 2024Abstract:This paper describes the results of the IEEE BigData 2023 Keystroke Verification Challenge (KVC), that considers the biometric verification performance of Keystroke Dynamics (KD), captured as tweet-long sequences of variable transcript text from over 185,000 subjects. The data are obtained from two of the largest public databases of KD up to date, the Aalto Desktop and Mobile Keystroke Databases, guaranteeing a minimum amount of data per subject, age and gender annotations, absence of corrupted data, and avoiding excessively unbalanced subject distributions with respect to the considered demographic attributes. Several neural architectures were proposed by the participants, leading to global Equal Error Rates (EERs) as low as 3.33% and 3.61% achieved by the best team respectively in the desktop and mobile scenario, outperforming the current state of the art biometric verification performance for KD. Hosted on CodaLab, the KVC will be made ongoing to represent a useful tool for the research community to compare different approaches under the same experimental conditions and to deepen the knowledge of the field.
Undercover Deepfakes: Detecting Fake Segments in Videos
May 16, 2023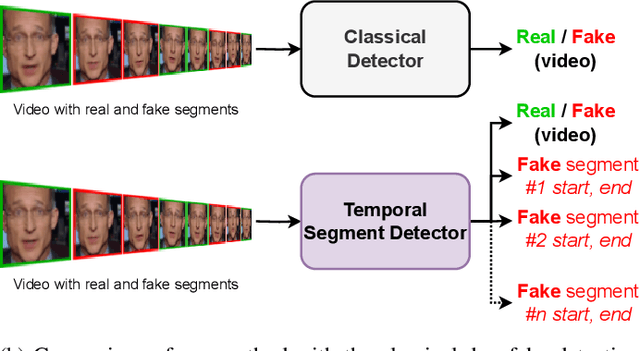
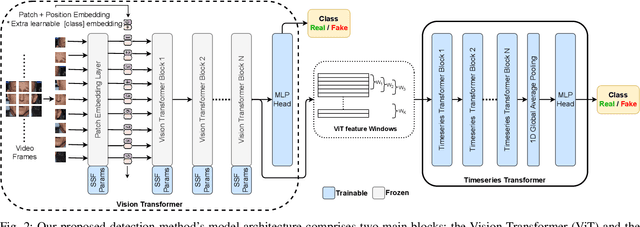

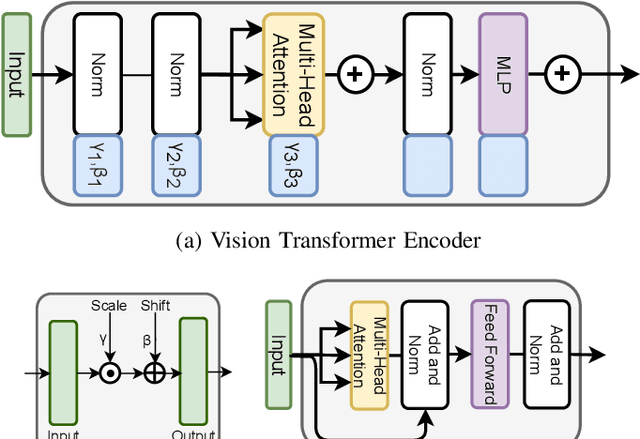
Abstract:The recent renaissance in generative models, driven primarily by the advent of diffusion models and iterative improvement in GAN methods, has enabled many creative applications. However, each advancement is also accompanied by a rise in the potential for misuse. In the arena of deepfake generation this is a key societal issue. In particular, the ability to modify segments of videos using such generative techniques creates a new paradigm of deepfakes which are mostly real videos altered slightly to distort the truth. Current deepfake detection methods in the academic literature are not evaluated on this paradigm. In this paper, we present a deepfake detection method able to address this issue by performing both frame and video level deepfake prediction. To facilitate testing our method we create a new benchmark dataset where videos have both real and fake frame sequences. Our method utilizes the Vision Transformer, Scaling and Shifting pretraining and Timeseries Transformer to temporally segment videos to help facilitate the interpretation of possible deepfakes. Extensive experiments on a variety of deepfake generation methods show excellent results on temporal segmentation and classical video level predictions as well. In particular, the paradigm we introduce will form a powerful tool for the moderation of deepfakes, where human oversight can be better targeted to the parts of videos suspected of being deepfakes. All experiments can be reproduced at: https://github.com/sanjaysaha1311/temporal-deepfake-segmentation.
Is Face Recognition Safe from Realizable Attacks?
Oct 15, 2022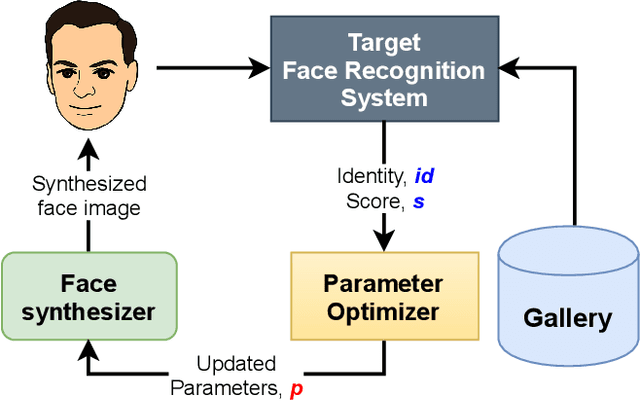
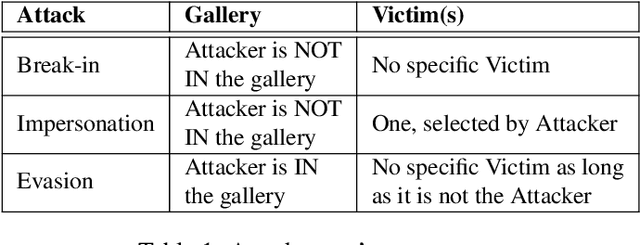

Abstract:Face recognition is a popular form of biometric authentication and due to its widespread use, attacks have become more common as well. Recent studies show that Face Recognition Systems are vulnerable to attacks and can lead to erroneous identification of faces. Interestingly, most of these attacks are white-box, or they are manipulating facial images in ways that are not physically realizable. In this paper, we propose an attack scheme where the attacker can generate realistic synthesized face images with subtle perturbations and physically realize that onto his face to attack black-box face recognition systems. Comprehensive experiments and analyses show that subtle perturbations realized on attackers face can create successful attacks on state-of-the-art face recognition systems in black-box settings. Our study exposes the underlying vulnerability posed by the Face Recognition Systems against realizable black-box attacks.
Hand Sign to Bangla Speech: A Deep Learning in Vision based system for Recognizing Hand Sign Digits and Generating Bangla Speech
Jan 17, 2019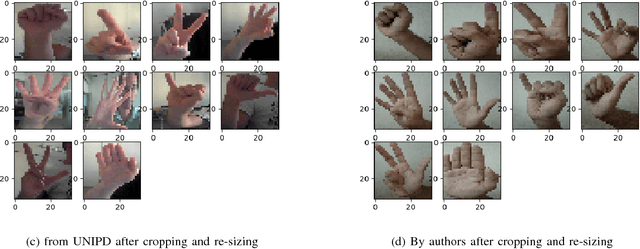

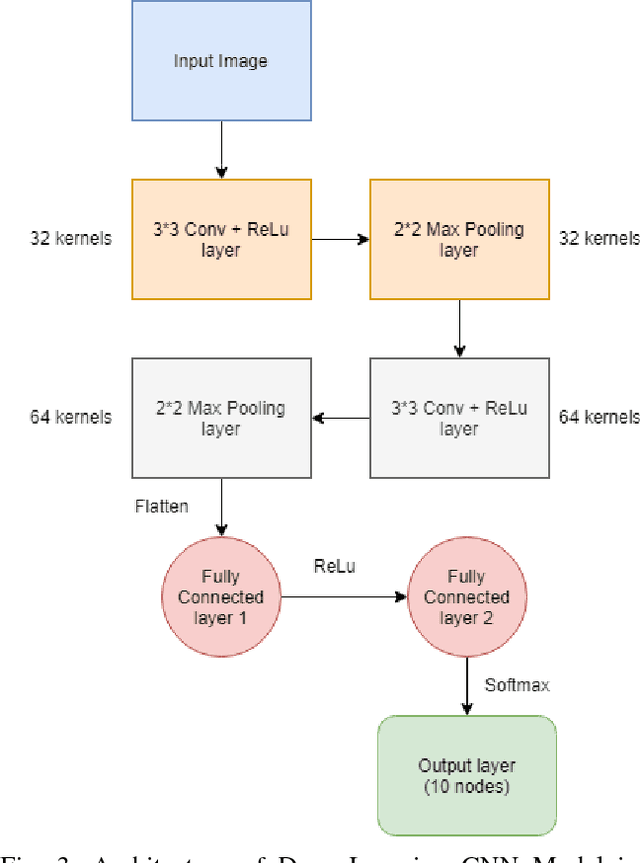
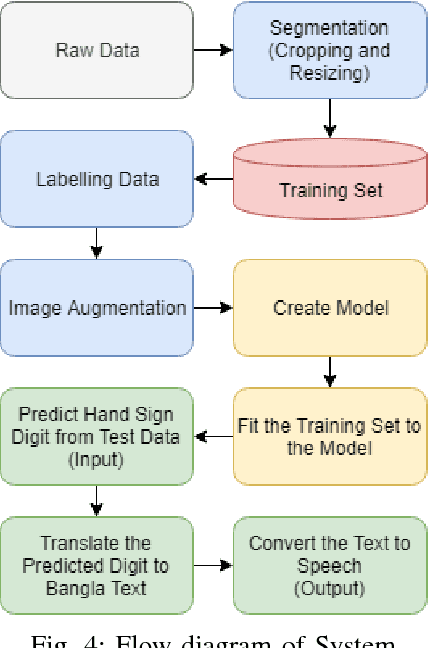
Abstract:Recent advancements in the field of computer vision with the help of deep neural networks have led us to explore and develop many existing challenges that were once unattended due to the lack of necessary technologies. Hand Sign/Gesture Recognition is one of the significant areas where the deep neural network is making a substantial impact. In the last few years, a large number of researches has been conducted to recognize hand signs and hand gestures, which we aim to extend to our mother-tongue, Bangla (also known as Bengali). The primary goal of our work is to make an automated tool to aid the people who are unable to speak. We developed a system that automatically detects hand sign based digits and speaks out the result in Bangla language. According to the report of the World Health Organization (WHO), 15% of people in the world live with some kind of disabilities. Among them, individuals with communication impairment such as speech disabilities experience substantial barrier in social interaction. The proposed system can be invaluable to mitigate such a barrier. The core of the system is built with a deep learning model which is based on convolutional neural networks (CNN). The model classifies hand sign based digits with 92% accuracy over validation data which ensures it a highly trustworthy system. Upon classification of the digits, the resulting output is fed to the text to speech engine and the translator unit eventually which generates audio output in Bangla language. A web application to demonstrate our tool is available at http://bit.ly/signdigits2banglaspeech.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge