Biqing Qi
MARTI-MARS$^2$: Scaling Multi-Agent Self-Search via Reinforcement Learning for Code Generation
Feb 08, 2026Abstract:While the complex reasoning capability of Large Language Models (LLMs) has attracted significant attention, single-agent systems often encounter inherent performance ceilings in complex tasks such as code generation. Multi-agent collaboration offers a promising avenue to transcend these boundaries. However, existing frameworks typically rely on prompt-based test-time interactions or multi-role configurations trained with homogeneous parameters, limiting error correction capabilities and strategic diversity. In this paper, we propose a Multi-Agent Reinforced Training and Inference Framework with Self-Search Scaling (MARTI-MARS2), which integrates policy learning with multi-agent tree search by formulating the multi-agent collaborative exploration process as a dynamic and learnable environment. By allowing agents to iteratively explore and refine within the environment, the framework facilitates evolution from parameter-sharing homogeneous multi-role training to heterogeneous multi-agent training, breaking through single-agent capability limits. We also introduce an efficient inference strategy MARTI-MARS2-T+ to fully exploit the scaling potential of multi-agent collaboration at test time. We conduct extensive experiments across varied model scales (8B, 14B, and 32B) on challenging code generation benchmarks. Utilizing two collaborating 32B models, MARTI-MARS2 achieves 77.7%, outperforming strong baselines like GPT-5.1. Furthermore, MARTI-MARS2 reveals a novel scaling law: shifting from single-agent to homogeneous multi-role and ultimately to heterogeneous multi-agent paradigms progressively yields higher RL performance ceilings, robust TTS capabilities, and greater policy diversity, suggesting that policy diversity is critical for scaling intelligence via multi-agent reinforcement learning.
LLMRouterBench: A Massive Benchmark and Unified Framework for LLM Routing
Jan 12, 2026Abstract:Large language model (LLM) routing assigns each query to the most suitable model from an ensemble. We introduce LLMRouterBench, a large-scale benchmark and unified framework for LLM routing. It comprises over 400K instances from 21 datasets and 33 models. Moreover, it provides comprehensive metrics for both performance-oriented routing and performance-cost trade-off routing, and integrates 10 representative routing baselines. Using LLMRouterBench, we systematically re-evaluate the field. While confirming strong model complementarity-the central premise of LLM routing-we find that many routing methods exhibit similar performance under unified evaluation, and several recent approaches, including commercial routers, fail to reliably outperform a simple baseline. Meanwhile, a substantial gap remains to the Oracle, driven primarily by persistent model-recall failures. We further show that backbone embedding models have limited impact, that larger ensembles exhibit diminishing returns compared to careful model curation, and that the benchmark also enables latency-aware analysis. All code and data are available at https://github.com/ynulihao/LLMRouterBench.
D2Pruner: Debiased Importance and Structural Diversity for MLLM Token Pruning
Dec 22, 2025



Abstract:Processing long visual token sequences poses a significant computational burden on Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs). While token pruning offers a path to acceleration, we find that current methods, while adequate for general understanding, catastrophically fail on fine-grained localization tasks. We attribute this failure to the inherent flaws of the two prevailing strategies: importance-based methods suffer from a strong positional bias, an inherent model artifact that distracts from semantic content, while diversity-based methods exhibit structural blindness, disregarding the user's prompt and spatial redundancy. To address this, we introduce D2Pruner, a framework that rectifies these issues by uniquely combining debiased importance with a structural pruning mechanism. Our method first secures a core set of the most critical tokens as pivots based on a debiased attention score. It then performs a Maximal Independent Set (MIS) selection on the remaining tokens, which are modeled on a hybrid graph where edges signify spatial proximity and semantic similarity. This process iteratively preserves the most important and available token while removing its neighbors, ensuring that the supplementary tokens are chosen to maximize importance and diversity. Extensive experiments demonstrate that D2Pruner has exceptional efficiency and fidelity. Applied to LLaVA-1.5-7B for general understanding tasks, it reduces FLOPs by 74.2\% while retaining 99.2\% of its original performance. Furthermore, in challenging localization benchmarks with InternVL-2.5-8B, it maintains 85.7\% performance at a 90\% token reduction rate, marking a significant advancement with up to 63. 53\% improvement over existing methods.
SDAR-VL: Stable and Efficient Block-wise Diffusion for Vision-Language Understanding
Dec 16, 2025



Abstract:Block-wise discrete diffusion offers an attractive balance between parallel generation and causal dependency modeling, making it a promising backbone for vision-language modeling. However, its practical adoption has been limited by high training cost, slow convergence, and instability, which have so far kept it behind strong autoregressive (AR) baselines. We present \textbf{SDAR-VL}, the first systematic application of block-wise discrete diffusion to large-scale vision-language understanding (VLU), together with an \emph{integrated framework for efficient and stable training}. This framework unifies three components: (1) \textbf{Asynchronous Block-wise Noise Scheduling} to diversify supervision within each batch; (2) \textbf{Effective Mask Ratio Scaling} for unbiased loss normalization under stochastic masking; and (3) a \textbf{Progressive Beta Noise Curriculum} that increases effective mask coverage while preserving corruption diversity. Experiments on 21 single-image, multi-image, and video benchmarks show that SDAR-VL consistently improves \emph{training efficiency}, \emph{convergence stability}, and \emph{task performance} over conventional block diffusion. On this evaluation suite, SDAR-VL sets a new state of the art among diffusion-based vision-language models and, under matched settings, matches or surpasses strong AR baselines such as LLaVA-OneVision as well as the global diffusion baseline LLaDA-V, establishing block-wise diffusion as a practical backbone for VLU.
AsyncVLA: Asynchronous Flow Matching for Vision-Language-Action Models
Nov 18, 2025



Abstract:Vision-language-action (VLA) models have recently emerged as a powerful paradigm for building generalist robots. However, traditional VLA models that generate actions through flow matching (FM) typically rely on rigid and uniform time schedules, i.e., synchronous FM (SFM). Without action context awareness and asynchronous self-correction, SFM becomes unstable in long-horizon tasks, where a single action error can cascade into failure. In this work, we propose asynchronous flow matching VLA (AsyncVLA), a novel framework that introduces temporal flexibility in asynchronous FM (AFM) and enables self-correction in action generation. AsyncVLA breaks from the vanilla SFM in VLA models by generating the action tokens in a non-uniform time schedule with action context awareness. Besides, our method introduces the confidence rater to extract confidence of the initially generated actions, enabling the model to selectively refine inaccurate action tokens before execution. Moreover, we propose a unified training procedure for SFM and AFM that endows a single model with both modes, improving KV-cache utilization. Extensive experiments on robotic manipulation benchmarks demonstrate that AsyncVLA is data-efficient and exhibits self-correction ability. AsyncVLA achieves state-of-the-art results across general embodied evaluations due to its asynchronous generation in AFM. Our code is available at https://github.com/YuhuaJiang2002/AsyncVLA.
PDAC: Efficient Coreset Selection for Continual Learning via Probability Density Awareness
Nov 12, 2025Abstract:Rehearsal-based Continual Learning (CL) maintains a limited memory buffer to store replay samples for knowledge retention, making these approaches heavily reliant on the quality of the stored samples. Current Rehearsal-based CL methods typically construct the memory buffer by selecting a representative subset (referred to as coresets), aiming to approximate the training efficacy of the full dataset with minimal storage overhead. However, mainstream Coreset Selection (CS) methods generally formulate the CS problem as a bi-level optimization problem that relies on numerous inner and outer iterations to solve, leading to substantial computational cost thus limiting their practical efficiency. In this paper, we aim to provide a more efficient selection logic and scheme for coreset construction. To this end, we first analyze the Mean Squared Error (MSE) between the buffer-trained model and the Bayes-optimal model through the perspective of localized error decomposition to investigate the contribution of samples from different regions to MSE suppression. Further theoretical and experimental analyses demonstrate that samples with high probability density play a dominant role in error suppression. Inspired by this, we propose the Probability Density-Aware Coreset (PDAC) method. PDAC leverages the Projected Gaussian Mixture (PGM) model to estimate each sample's joint density, enabling efficient density-prioritized buffer selection. Finally, we introduce the streaming Expectation Maximization (EM) algorithm to enhance the adaptability of PGM parameters to streaming data, yielding Streaming PDAC (SPDAC) for streaming scenarios. Extensive comparative experiments show that our methods outperforms other baselines across various CL settings while ensuring favorable efficiency.
Nirvana: A Specialized Generalist Model With Task-Aware Memory Mechanism
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Specialized Generalist Models (SGMs) aim to preserve broad capabilities while achieving expert-level performance in target domains. However, traditional LLM structures including Transformer, Linear Attention, and hybrid models do not employ specialized memory mechanism guided by task information. In this paper, we present Nirvana, an SGM with specialized memory mechanism, linear time complexity, and test-time task information extraction. Besides, we propose the Task-Aware Memory Trigger ($\textit{Trigger}$) that flexibly adjusts memory mechanism based on the current task's requirements. In Trigger, each incoming sample is treated as a self-supervised fine-tuning task, enabling Nirvana to adapt its task-related parameters on the fly to domain shifts. We also design the Specialized Memory Updater ($\textit{Updater}$) that dynamically memorizes the context guided by Trigger. We conduct experiments on both general language tasks and specialized medical tasks. On a variety of natural language modeling benchmarks, Nirvana achieves competitive or superior results compared to the existing LLM structures. To prove the effectiveness of Trigger on specialized tasks, we test Nirvana's performance on a challenging medical task, i.e., Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). We post-train frozen Nirvana backbone with lightweight codecs on paired electromagnetic signals and MRI images. Despite the frozen Nirvana backbone, Trigger guides the model to adapt to the MRI domain with the change of task-related parameters. Nirvana achieves higher-quality MRI reconstruction compared to conventional MRI models as well as the models with traditional LLMs' backbone, and can also generate accurate preliminary clinical reports accordingly.
ScaleCUA: Scaling Open-Source Computer Use Agents with Cross-Platform Data
Sep 18, 2025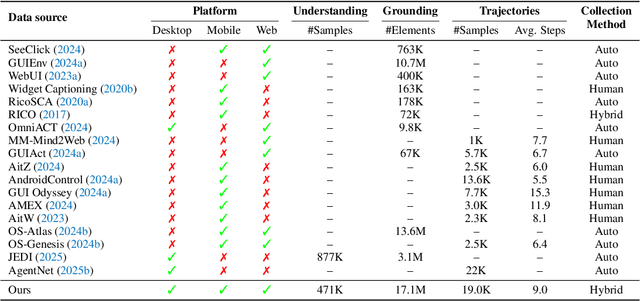
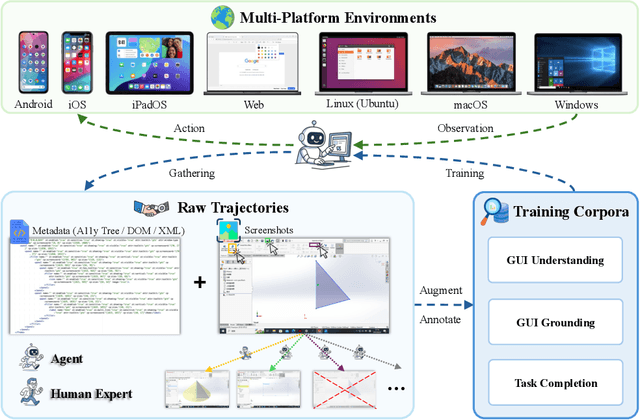
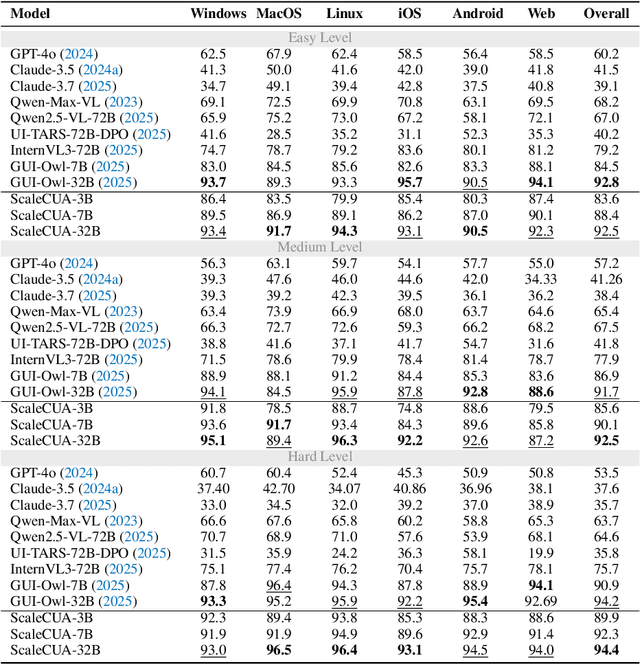
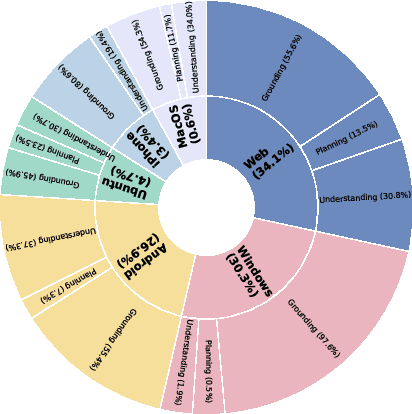
Abstract:Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have enabled computer use agents (CUAs) that operate GUIs autonomously, showing great potential, yet progress is limited by the lack of large-scale, open-source computer use data and foundation models. In this work, we introduce ScaleCUA, a step toward scaling open-source CUAs. It offers a large-scale dataset spanning 6 operating systems and 3 task domains, built via a closed-loop pipeline uniting automated agents with human experts. Trained on this scaled-up data, ScaleCUA can operate seamlessly across platforms. Specifically, it delivers strong gains over baselines (+26.6 on WebArena-Lite-v2, +10.7 on ScreenSpot-Pro) and sets new state-of-the-art results (94.4% on MMBench-GUI L1-Hard, 60.6% on OSWorld-G, 47.4% on WebArena-Lite-v2). These findings underscore the power of data-driven scaling for general-purpose computer use agents. We will release data, models, and code to advance future research: https://github.com/OpenGVLab/ScaleCUA.
A Survey of Reinforcement Learning for Large Reasoning Models
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we survey recent advances in Reinforcement Learning (RL) for reasoning with Large Language Models (LLMs). RL has achieved remarkable success in advancing the frontier of LLM capabilities, particularly in addressing complex logical tasks such as mathematics and coding. As a result, RL has emerged as a foundational methodology for transforming LLMs into LRMs. With the rapid progress of the field, further scaling of RL for LRMs now faces foundational challenges not only in computational resources but also in algorithm design, training data, and infrastructure. To this end, it is timely to revisit the development of this domain, reassess its trajectory, and explore strategies to enhance the scalability of RL toward Artificial SuperIntelligence (ASI). In particular, we examine research applying RL to LLMs and LRMs for reasoning abilities, especially since the release of DeepSeek-R1, including foundational components, core problems, training resources, and downstream applications, to identify future opportunities and directions for this rapidly evolving area. We hope this review will promote future research on RL for broader reasoning models. Github: https://github.com/TsinghuaC3I/Awesome-RL-for-LRMs
InternVL3.5: Advancing Open-Source Multimodal Models in Versatility, Reasoning, and Efficiency
Aug 25, 2025



Abstract:We introduce InternVL 3.5, a new family of open-source multimodal models that significantly advances versatility, reasoning capability, and inference efficiency along the InternVL series. A key innovation is the Cascade Reinforcement Learning (Cascade RL) framework, which enhances reasoning through a two-stage process: offline RL for stable convergence and online RL for refined alignment. This coarse-to-fine training strategy leads to substantial improvements on downstream reasoning tasks, e.g., MMMU and MathVista. To optimize efficiency, we propose a Visual Resolution Router (ViR) that dynamically adjusts the resolution of visual tokens without compromising performance. Coupled with ViR, our Decoupled Vision-Language Deployment (DvD) strategy separates the vision encoder and language model across different GPUs, effectively balancing computational load. These contributions collectively enable InternVL3.5 to achieve up to a +16.0\% gain in overall reasoning performance and a 4.05$\times$ inference speedup compared to its predecessor, i.e., InternVL3. In addition, InternVL3.5 supports novel capabilities such as GUI interaction and embodied agency. Notably, our largest model, i.e., InternVL3.5-241B-A28B, attains state-of-the-art results among open-source MLLMs across general multimodal, reasoning, text, and agentic tasks -- narrowing the performance gap with leading commercial models like GPT-5. All models and code are publicly released.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge