Aijia Zhang
Interleaved Tool-Call Reasoning for Protein Function Understanding
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in large language models (LLMs) have highlighted the effectiveness of chain-of-thought reasoning in symbolic domains such as mathematics and programming. However, our study shows that directly transferring such text-based reasoning paradigms to protein function understanding is ineffective: reinforcement learning mainly amplifies superficial keyword patterns while failing to introduce new biological knowledge, resulting in limited generalization. We argue that protein function prediction is a knowledge-intensive scientific task that fundamentally relies on external biological priors and computational tools rather than purely internal reasoning. To address this gap, we propose PFUA, a tool-augmented protein reasoning agent that unifies problem decomposition, tool invocation, and grounded answer generation. Instead of relying on long unconstrained reasoning traces, PFUA integrates domain-specific tools to produce verifiable intermediate evidence. Experiments on four benchmarks demonstrate that PFUA consistently outperforms text-only reasoning models with an average performance improvement of 103%.
Distributionally Robust Deep Q-Learning
May 25, 2025Abstract:We propose a novel distributionally robust $Q$-learning algorithm for the non-tabular case accounting for continuous state spaces where the state transition of the underlying Markov decision process is subject to model uncertainty. The uncertainty is taken into account by considering the worst-case transition from a ball around a reference probability measure. To determine the optimal policy under the worst-case state transition, we solve the associated non-linear Bellman equation by dualising and regularising the Bellman operator with the Sinkhorn distance, which is then parameterized with deep neural networks. This approach allows us to modify the Deep Q-Network algorithm to optimise for the worst case state transition. We illustrate the tractability and effectiveness of our approach through several applications, including a portfolio optimisation task based on S\&{P}~500 data.
An Efficient Memory Module for Graph Few-Shot Class-Incremental Learning
Nov 11, 2024



Abstract:Incremental graph learning has gained significant attention for its ability to address the catastrophic forgetting problem in graph representation learning. However, traditional methods often rely on a large number of labels for node classification, which is impractical in real-world applications. This makes few-shot incremental learning on graphs a pressing need. Current methods typically require extensive training samples from meta-learning to build memory and perform intensive fine-tuning of GNN parameters, leading to high memory consumption and potential loss of previously learned knowledge. To tackle these challenges, we introduce Mecoin, an efficient method for building and maintaining memory. Mecoin employs Structured Memory Units to cache prototypes of learned categories, as well as Memory Construction Modules to update these prototypes for new categories through interactions between the nodes and the cached prototypes. Additionally, we have designed a Memory Representation Adaptation Module to store probabilities associated with each class prototype, reducing the need for parameter fine-tuning and lowering the forgetting rate. When a sample matches its corresponding class prototype, the relevant probabilities are retrieved from the MRaM. Knowledge is then distilled back into the GNN through a Graph Knowledge Distillation Module, preserving the model's memory. We analyze the effectiveness of Mecoin in terms of generalization error and explore the impact of different distillation strategies on model performance through experiments and VC-dimension analysis. Compared to other related works, Mecoin shows superior performance in accuracy and forgetting rate. Our code is publicly available on the https://github.com/Arvin0313/Mecoin-GFSCIL.git .
Beyond Isolation: Multi-Agent Synergy for Improving Knowledge Graph Construction
Dec 05, 2023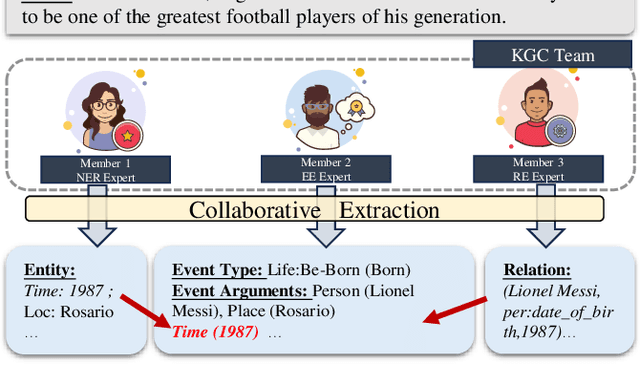
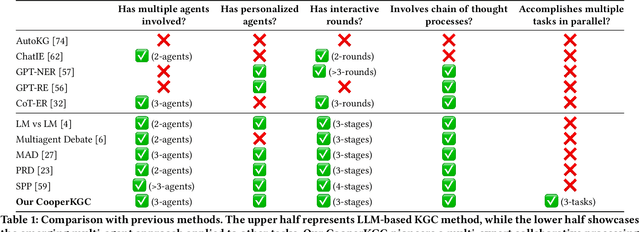

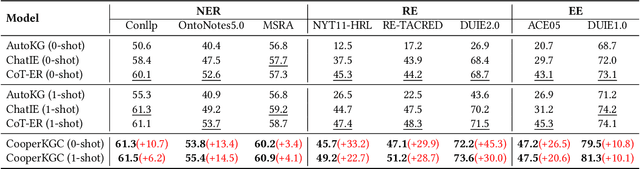
Abstract:Knowledge graph construction (KGC) is a multifaceted undertaking involving the extraction of entities, relations, and events. Traditionally, large language models (LLMs) have been viewed as solitary task-solving agents in this complex landscape. However, this paper challenges this paradigm by introducing a novel framework, CooperKGC. Departing from the conventional approach, CooperKGC establishes a collaborative processing network, assembling a KGC collaboration team capable of concurrently addressing entity, relation, and event extraction tasks. Our experiments unequivocally demonstrate that fostering collaboration and information interaction among diverse agents within CooperKGC yields superior results compared to individual cognitive processes operating in isolation. Importantly, our findings reveal that the collaboration facilitated by CooperKGC enhances knowledge selection, correction, and aggregation capabilities across multiple rounds of interactions.
Cognitive Mirage: A Review of Hallucinations in Large Language Models
Sep 13, 2023



Abstract:As large language models continue to develop in the field of AI, text generation systems are susceptible to a worrisome phenomenon known as hallucination. In this study, we summarize recent compelling insights into hallucinations in LLMs. We present a novel taxonomy of hallucinations from various text generation tasks, thus provide theoretical insights, detection methods and improvement approaches. Based on this, future research directions are proposed. Our contribution are threefold: (1) We provide a detailed and complete taxonomy for hallucinations appearing in text generation tasks; (2) We provide theoretical analyses of hallucinations in LLMs and provide existing detection and improvement methods; (3) We propose several research directions that can be developed in the future. As hallucinations garner significant attention from the community, we will maintain updates on relevant research progress.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge