Aman Madaan
In-Context Principle Learning from Mistakes
Feb 09, 2024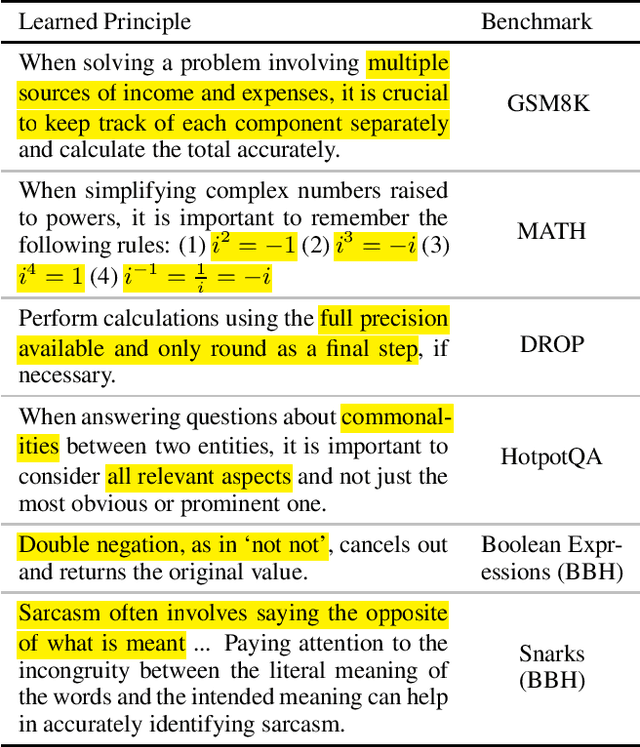
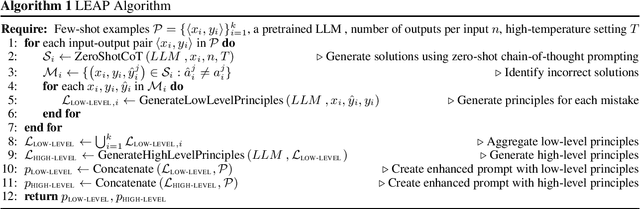
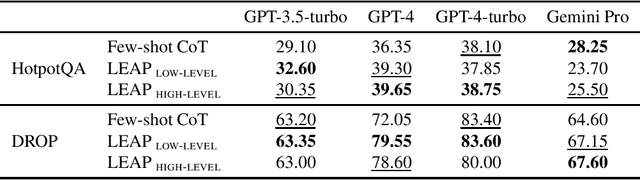
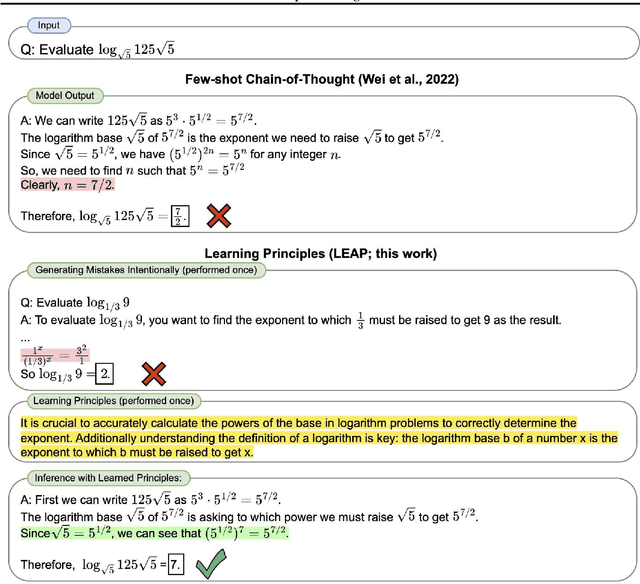
Abstract:In-context learning (ICL, also known as few-shot prompting) has been the standard method of adapting LLMs to downstream tasks, by learning from a few input-output examples. Nonetheless, all ICL-based approaches only learn from correct input-output pairs. In this paper, we revisit this paradigm, by learning more from the few given input-output examples. We introduce Learning Principles (LEAP): First, we intentionally induce the model to make mistakes on these few examples; then we reflect on these mistakes, and learn explicit task-specific "principles" from them, which help solve similar problems and avoid common mistakes; finally, we prompt the model to answer unseen test questions using the original few-shot examples and these learned general principles. We evaluate LEAP on a wide range of benchmarks, including multi-hop question answering (Hotpot QA), textual QA (DROP), Big-Bench Hard reasoning, and math problems (GSM8K and MATH); in all these benchmarks, LEAP improves the strongest available LLMs such as GPT-3.5-turbo, GPT-4, GPT-4 turbo and Claude-2.1. For example, LEAP improves over the standard few-shot prompting using GPT-4 by 7.5% in DROP, and by 3.3% in HotpotQA. Importantly, LEAP does not require any more input or examples than the standard few-shot prompting settings.
Self-Imagine: Effective Unimodal Reasoning with Multimodal Models using Self-Imagination
Jan 16, 2024
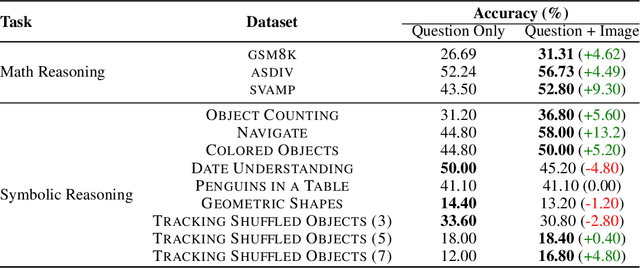


Abstract:The potential of Vision-Language Models (\textsc{vlm}s) often remains underutilized in handling complex text-based problems, particularly when these problems could benefit from visual representation. Resonating with humans' ability to solve complex text-based problems by (1) creating a visual diagram from the problem and (2) deducing what steps they need to take to solve it, we propose \textsc{Self-Imagine}. We leverage a single Vision-Language Model (\textsc{vlm}) to generate a structured representation of the question using HTML, then render the HTML as an image, and finally use the same \vlm to answer the question using both the question and the image. Our approach does not require any additional training data or training. We evaluate our approach in three mathematics tasks and nine general-purpose reasoning tasks using state-of-the-art \textsc{vlm}. Our approach boosts the performance of \textsc{vlm} on all math tasks (\gsm: +4.62\%; \asdiv: +4.49\%; \svamp: +9.30\%) and the majority of the general-purpose reasoning tasks by 0.4\% to 13.20\% while achieving comparable performance in other tasks. Code and data at https://github.com/snat1505027/self-imagine .
Program-Aided Reasoners Know What They Know
Nov 16, 2023Abstract:Prior work shows that program-aided reasoning, in which large language models (LLMs) are combined with programs written in programming languages such as Python, can significantly improve accuracy on various reasoning tasks. However, while accuracy is essential, it is also important for such reasoners to "know what they know", which can be quantified through the calibration of the model. In this paper, we compare the calibration of Program Aided Language Models (PAL) and text-based Chain-of-thought (COT) prompting techniques over 5 datasets and 2 model types: LLaMA models and OpenAI models. Our results indicate that PAL leads to improved calibration in 75% of the instances. Our analysis uncovers that prompting styles that produce lesser diversity in generations also have more calibrated results, and thus we also experiment with inducing lower generation diversity using temperature scaling and find that for certain temperatures, PAL is not only more accurate but is also more calibrated than COT. Overall, we demonstrate that, in the majority of cases, program-aided reasoners better know what they know than text-based counterparts.
AutoMix: Automatically Mixing Language Models
Oct 19, 2023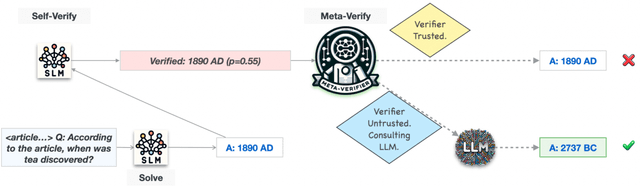
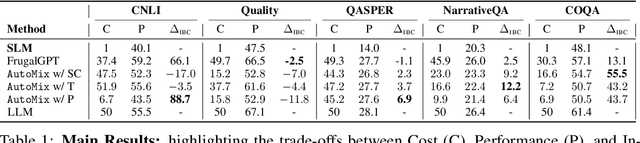
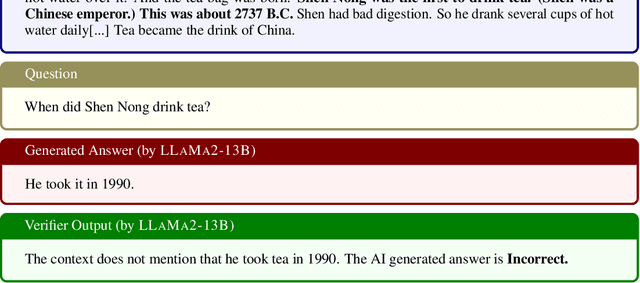

Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are now available in various sizes and configurations from cloud API providers. While this diversity offers a broad spectrum of choices, effectively leveraging the options to optimize computational cost and performance remains challenging. In this work, we present AutoMix, an approach that strategically routes queries to larger LMs, based on the approximate correctness of outputs from a smaller LM. Central to AutoMix is a few-shot self-verification mechanism, which estimates the reliability of its own outputs without requiring training. Given that verifications can be noisy, we employ a meta verifier in AutoMix to refine the accuracy of these assessments. Our experiments using LLAMA2-13/70B, on five context-grounded reasoning datasets demonstrate that AutoMix surpasses established baselines, improving the incremental benefit per cost by up to 89%. Our code and data are available at https://github.com/automix-llm/automix.
How FaR Are Large Language Models From Agents with Theory-of-Mind?
Oct 04, 2023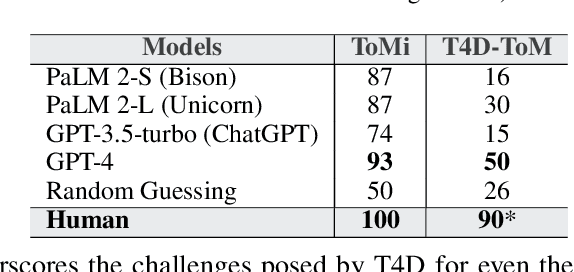

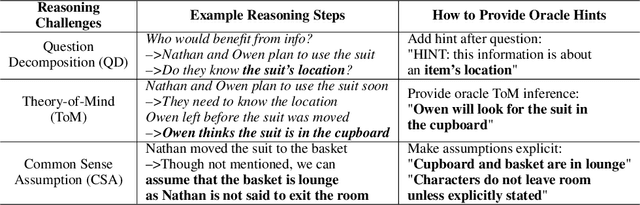
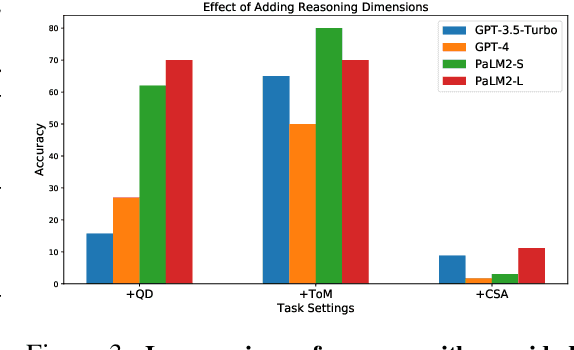
Abstract:"Thinking is for Doing." Humans can infer other people's mental states from observations--an ability called Theory-of-Mind (ToM)--and subsequently act pragmatically on those inferences. Existing question answering benchmarks such as ToMi ask models questions to make inferences about beliefs of characters in a story, but do not test whether models can then use these inferences to guide their actions. We propose a new evaluation paradigm for large language models (LLMs): Thinking for Doing (T4D), which requires models to connect inferences about others' mental states to actions in social scenarios. Experiments on T4D demonstrate that LLMs such as GPT-4 and PaLM 2 seemingly excel at tracking characters' beliefs in stories, but they struggle to translate this capability into strategic action. Our analysis reveals the core challenge for LLMs lies in identifying the implicit inferences about mental states without being explicitly asked about as in ToMi, that lead to choosing the correct action in T4D. To bridge this gap, we introduce a zero-shot prompting framework, Foresee and Reflect (FaR), which provides a reasoning structure that encourages LLMs to anticipate future challenges and reason about potential actions. FaR boosts GPT-4's performance from 50% to 71% on T4D, outperforming other prompting methods such as Chain-of-Thought and Self-Ask. Moreover, FaR generalizes to diverse out-of-distribution story structures and scenarios that also require ToM inferences to choose an action, consistently outperforming other methods including few-shot in-context learning.
Let's Sample Step by Step: Adaptive-Consistency for Efficient Reasoning with LLMs
May 19, 2023



Abstract:A popular approach for improving the correctness of output from large language models (LLMs) is Self-Consistency - poll the LLM multiple times and output the most frequent solution. Existing Self-Consistency techniques always draw a constant number of samples per question, where a better approach will be to non-uniformly distribute the available budget based on the amount of agreement in the samples drawn so far. In response, we introduce Adaptive-Consistency, a cost-efficient, model-agnostic technique that dynamically adjusts the number of samples per question using a lightweight stopping criterion. Our experiments over 13 datasets and two LLMs demonstrate that Adaptive-Consistency reduces sample budget by up to 6.0 times with an average accuracy drop of less than 0.1%.
RL4F: Generating Natural Language Feedback with Reinforcement Learning for Repairing Model Outputs
May 15, 2023



Abstract:Despite their unprecedented success, even the largest language models make mistakes. Similar to how humans learn and improve using feedback, previous work proposed providing language models with natural language feedback to guide them in repairing their outputs. Because human-generated critiques are expensive to obtain, researchers have devised learned critique generators in lieu of human critics while assuming one can train downstream models to utilize generated feedback. However, this approach does not apply to black-box or limited access models such as ChatGPT, as they cannot be fine-tuned. Moreover, in the era of large general-purpose language agents, fine-tuning is neither computationally nor spatially efficient as it results in multiple copies of the network. In this work, we introduce RL4F (Reinforcement Learning for Feedback), a multi-agent collaborative framework where the critique generator is trained to maximize end-task performance of GPT-3, a fixed model more than 200 times its size. RL4F produces critiques that help GPT-3 revise its outputs. We study three datasets for action planning, summarization and alphabetization and show improvements (~5% on average) in multiple text similarity metrics over strong baselines across all three tasks.
Bridging the Gap: A Survey on Integrating Feedback for Natural Language Generation
May 01, 2023


Abstract:Many recent advances in natural language generation have been fueled by training large language models on internet-scale data. However, this paradigm can lead to models that generate toxic, inaccurate, and unhelpful content, and automatic evaluation metrics often fail to identify these behaviors. As models become more capable, human feedback is an invaluable signal for evaluating and improving models. This survey aims to provide an overview of the recent research that has leveraged human feedback to improve natural language generation. First, we introduce an encompassing formalization of feedback, and identify and organize existing research into a taxonomy following this formalization. Next, we discuss how feedback can be described by its format and objective, and cover the two approaches proposed to use feedback (either for training or decoding): directly using the feedback or training feedback models. We also discuss existing datasets for human-feedback data collection, and concerns surrounding feedback collection. Finally, we provide an overview of the nascent field of AI feedback, which exploits large language models to make judgments based on a set of principles and minimize the need for human intervention.
Self-Refine: Iterative Refinement with Self-Feedback
Mar 30, 2023



Abstract:Like people, LLMs do not always generate the best text for a given generation problem on their first try (e.g., summaries, answers, explanations). Just as people then refine their text, we introduce SELF-REFINE, a framework for similarly improving initial outputs from LLMs through iterative feedback and refinement. The main idea is to generate an output using an LLM, then allow the same model to provide multi-aspect feedback for its own output; finally, the same model refines its previously generated output given its own feedback. Unlike earlier work, our iterative refinement framework does not require supervised training data or reinforcement learning, and works with a single LLM. We experiment with 7 diverse tasks, ranging from review rewriting to math reasoning, demonstrating that our approach outperforms direct generation. In all tasks, outputs generated with SELF-REFINE are preferred by humans and by automated metrics over those generated directly with GPT-3.5 and GPT-4, improving on average by absolute 20% across tasks.
Learning Performance-Improving Code Edits
Feb 21, 2023Abstract:The waning of Moore's Law has shifted the focus of the tech industry towards alternative methods for continued performance gains. While optimizing compilers are a standard tool to help increase program efficiency, programmers continue to shoulder much responsibility in crafting and refactoring code with better performance characteristics. In this paper, we investigate the ability of large language models (LLMs) to suggest functionally correct, performance improving code edits. We hypothesize that language models can suggest such edits in ways that would be impractical for static analysis alone. We investigate these questions by curating a large-scale dataset of Performance-Improving Edits, PIE. PIE contains trajectories of programs, where a programmer begins with an initial, slower version and iteratively makes changes to improve the program's performance. We use PIE to evaluate and improve the capacity of large language models. Specifically, use examples from PIE to fine-tune multiple variants of CODEGEN, a billion-scale Transformer-decoder model. Additionally, we use examples from PIE to prompt OpenAI's CODEX using a few-shot prompting. By leveraging PIE, we find that both CODEX and CODEGEN can generate performance-improving edits, with speedups of more than 2.5x for over 25% of the programs, for C++ and Python, even after the C++ programs were compiled using the O3 optimization level. Crucially, we show that PIE allows CODEGEN, an open-sourced and 10x smaller model than CODEX, to match the performance of CODEX on this challenging task. Overall, this work opens new doors for creating systems and methods that can help programmers write efficient code.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge