Prakhar Gupta
GS
Revisiting In-Context Learning with Long Context Language Models
Dec 22, 2024



Abstract:In-Context Learning (ICL) is a technique by which language models make predictions based on examples provided in their input context. Previously, their context window size imposed a limit on the number of examples that can be shown, making example selection techniques crucial for identifying the maximally effective set of examples. However, the recent advent of Long Context Language Models (LCLMs) has significantly increased the number of examples that can be included in context, raising an important question of whether ICL performance in a many-shot regime is still sensitive to the method of sample selection. To answer this, we revisit these approaches in the context of LCLMs through extensive experiments on 18 datasets spanning 4 tasks. Surprisingly, we observe that sophisticated example selection techniques do not yield significant improvements over a simple random sample selection method. Instead, we find that the advent of LCLMs has fundamentally shifted the challenge of ICL from that of selecting the most effective examples to that of collecting sufficient examples to fill the context window. Specifically, in certain datasets, including all available examples does not fully utilize the context window; however, by augmenting the examples in context with a simple data augmentation approach, we substantially improve ICL performance by 5%.
Reinforcement Learning Compensated Model Predictive Control for Off-road Driving on Unknown Deformable Terrain
Aug 17, 2024Abstract:This study presents an Actor-Critic reinforcement learning Compensated Model Predictive Controller (AC2MPC) designed for high-speed, off-road autonomous driving on deformable terrains. Addressing the difficulty of modeling unknown tire-terrain interaction and ensuring real-time control feasibility and performance, this framework integrates deep reinforcement learning with a model predictive controller to manage unmodeled nonlinear dynamics. We evaluate the controller framework over constant and varying velocity profiles using high-fidelity simulator Project Chrono. Our findings demonstrate that our controller statistically outperforms standalone model-based and learning-based controllers over three unknown terrains that represent sandy deformable track, sandy and rocky track and cohesive clay-like deformable soil track. Despite varied and previously unseen terrain characteristics, this framework generalized well enough to track longitudinal reference speeds with the least error. Furthermore, this framework required significantly less training data compared to purely learning based controller, converging in fewer steps while delivering better performance. Even when under-trained, this controller outperformed the standalone controllers, highlighting its potential for safer and more efficient real-world deployment.
Leveraging Machine-Generated Rationales to Facilitate Social Meaning Detection in Conversations
Jun 27, 2024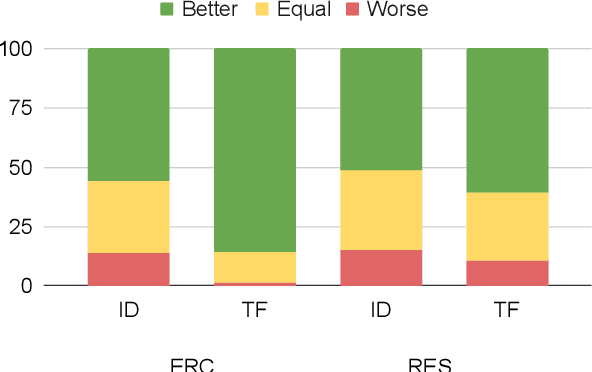
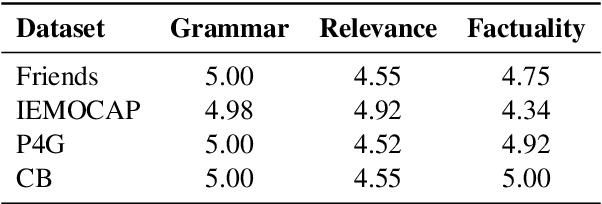
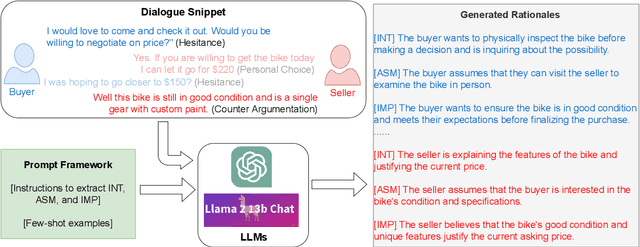
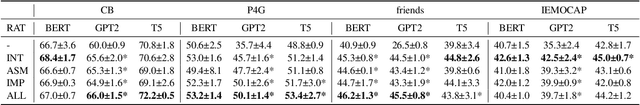
Abstract:We present a generalizable classification approach that leverages Large Language Models (LLMs) to facilitate the detection of implicitly encoded social meaning in conversations. We design a multi-faceted prompt to extract a textual explanation of the reasoning that connects visible cues to underlying social meanings. These extracted explanations or rationales serve as augmentations to the conversational text to facilitate dialogue understanding and transfer. Our empirical results over 2,340 experimental settings demonstrate the significant positive impact of adding these rationales. Our findings hold true for in-domain classification, zero-shot, and few-shot domain transfer for two different social meaning detection tasks, each spanning two different corpora.
GenAudit: Fixing Factual Errors in Language Model Outputs with Evidence
Feb 19, 2024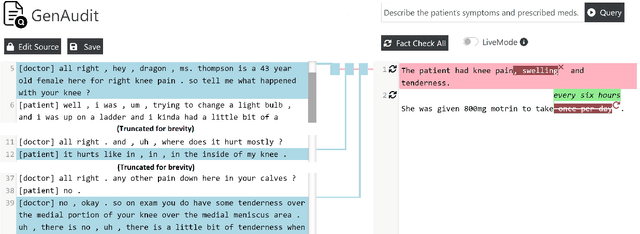


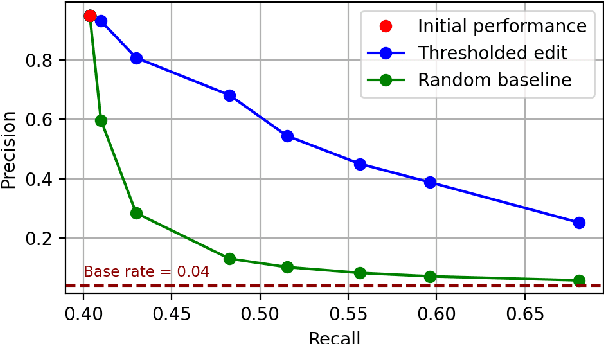
Abstract:LLMs can generate factually incorrect statements even when provided access to reference documents. Such errors can be dangerous in high-stakes applications (e.g., document-grounded QA for healthcare or finance). We present GenAudit -- a tool intended to assist fact-checking LLM responses for document-grounded tasks. GenAudit suggests edits to the LLM response by revising or removing claims that are not supported by the reference document, and also presents evidence from the reference for facts that do appear to have support. We train models to execute these tasks, and design an interactive interface to present suggested edits and evidence to users. Comprehensive evaluation by human raters shows that GenAudit can detect errors in 8 different LLM outputs when summarizing documents from diverse domains. To ensure that most errors are flagged by the system, we propose a method that can increase the error recall while minimizing impact on precision. We will release our tool (GenAudit) and fact-checking model for public use.
USB: A Unified Summarization Benchmark Across Tasks and Domains
May 23, 2023Abstract:An abundance of datasets exist for training and evaluating models on the task of summary generation.However, these datasets are often derived heuristically, and lack sufficient annotations to support research into all aspects of summarization, such as evidence extraction and controllable summarization. We introduce a benchmark comprising 8 tasks that require multi-dimensional understanding of summarization, e.g., surfacing evidence for a summary, assessing its correctness, and gauging its relevance to different topics. We compare various methods on this benchmark and discover that on multiple tasks, moderately-sized fine-tuned models consistently outperform much larger few-shot prompted language models. For factuality related tasks, we also evaluate existing heuristics to create training data and find that training on them performs worse than training on $20\times$ less human-labeled data. Our benchmark consists of data from 6 different domains, allowing us to study cross-domain performance of trained models. We find that for some tasks, the amount of training data matters more than the domain where it comes from, while for other tasks training specifically on data from the target domain, even if limited, is more beneficial. Our work fulfills the need for a well-annotated summarization benchmark with diverse tasks, and provides useful insights about the impact of the quality, size and domain of training data.
Self-Refine: Iterative Refinement with Self-Feedback
Mar 30, 2023



Abstract:Like people, LLMs do not always generate the best text for a given generation problem on their first try (e.g., summaries, answers, explanations). Just as people then refine their text, we introduce SELF-REFINE, a framework for similarly improving initial outputs from LLMs through iterative feedback and refinement. The main idea is to generate an output using an LLM, then allow the same model to provide multi-aspect feedback for its own output; finally, the same model refines its previously generated output given its own feedback. Unlike earlier work, our iterative refinement framework does not require supervised training data or reinforcement learning, and works with a single LLM. We experiment with 7 diverse tasks, ranging from review rewriting to math reasoning, demonstrating that our approach outperforms direct generation. In all tasks, outputs generated with SELF-REFINE are preferred by humans and by automated metrics over those generated directly with GPT-3.5 and GPT-4, improving on average by absolute 20% across tasks.
Using In-Context Learning to Improve Dialogue Safety
Feb 02, 2023



Abstract:While large neural-based conversational models have become increasingly proficient as dialogue agents, recent work has highlighted safety issues with these systems. For example, these systems can be goaded into generating toxic content, which often perpetuates social biases or stereotypes. We investigate a retrieval-based framework for reducing bias and toxicity in responses generated from neural-based chatbots. It uses in-context learning to steer a model towards safer generations. Concretely, to generate a response to an unsafe dialogue context, we retrieve demonstrations of safe model responses to similar dialogue contexts. We find our proposed approach performs competitively with strong baselines which use fine-tuning. For instance, using automatic evaluation, we find our best fine-tuned baseline only generates safe responses to unsafe dialogue contexts from DiaSafety 2.92% more than our approach. Finally, we also propose a straightforward re-ranking procedure which can further improve response safeness.
Understanding the Effectiveness of Very Large Language Models on Dialog Evaluation
Jan 27, 2023



Abstract:Language models have steadily increased in size over the past few years. They achieve a high level of performance on various natural language processing (NLP) tasks such as question answering and summarization. Large language models (LLMs) have been used for generation and can now output human-like text. Due to this, there are other downstream tasks in the realm of dialog that can now harness the LLMs' language understanding capabilities. Dialog evaluation is one task that this paper will explore. It concentrates on prompting with LLMs: BLOOM, OPT, GPT-3, Flan-T5, InstructDial and TNLGv2. The paper shows that the choice of datasets used for training a model contributes to how well it performs on a task as well as on how the prompt should be structured. Specifically, the more diverse and relevant the group of datasets that a model is trained on, the better dialog evaluation performs. This paper also investigates how the number of examples in the prompt and the type of example selection used affect the model's performance.
DialGuide: Aligning Dialogue Model Behavior with Developer Guidelines
Dec 20, 2022Abstract:Dialogue models are able to generate coherent and fluent responses, but they can still be challenging to control and may produce non-engaging, unsafe results. This unpredictability diminishes user trust and can hinder the use of the models in the real world. To address this, we introduce DialGuide, a novel framework for controlling dialogue model behavior using natural language rules, or guidelines. These guidelines provide information about the context they are applicable to and what should be included in the response, allowing the models to generate responses that are more closely aligned with the developer's expectations and intent. We evaluate DialGuide on three tasks in open-domain dialogue response generation: guideline selection, response generation, and response entailment verification. Our dataset contains 10,737 positive and 15,467 negative dialogue context-response-guideline triplets across two domains - chit-chat and safety. We provide baseline models for the tasks and benchmark their performance. We also demonstrate that DialGuide is effective in the dialogue safety domain, producing safe and engaging responses that follow developer guidelines.
Improving Zero and Few-shot Generalization in Dialogue through Instruction Tuning
May 25, 2022
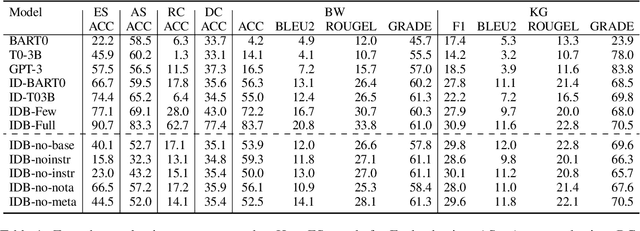
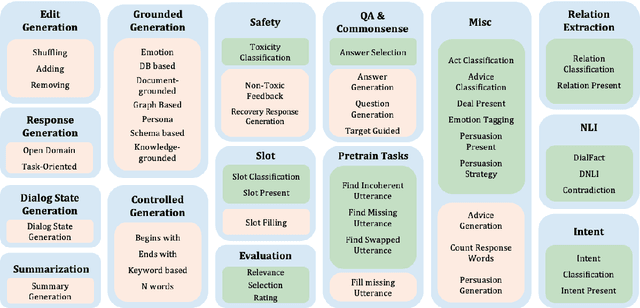
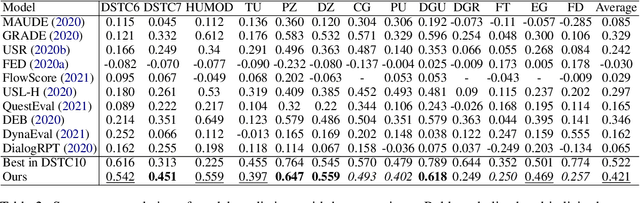
Abstract:Instruction tuning is an emergent paradigm in NLP wherein natural language instructions are leveraged with language models to induce zero-shot performance on unseen tasks. Instructions have been shown to enable good performance on unseen tasks and datasets in both large and small language models. Dialogue is an especially interesting area to explore instruction tuning because dialogue systems perform multiple kinds of tasks related to language (e.g., natural language understanding and generation, domain-specific interaction), yet instruction tuning has not been systematically explored for dialogue-related tasks. We introduce InstructDial, an instruction tuning framework for dialogue, which consists of a repository of 48 diverse dialogue tasks in a unified text-to-text format created from 59 openly available dialogue datasets. Next, we explore cross-task generalization ability on models tuned on InstructDial across diverse dialogue tasks. Our analysis reveals that InstructDial enables good zero-shot performance on unseen datasets and tasks such as dialogue evaluation and intent detection, and even better performance in a few-shot setting. To ensure that models adhere to instructions, we introduce novel meta-tasks. We establish benchmark zero-shot and few-shot performance of models trained using the proposed framework on multiple dialogue tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge