Sangwu Lee
Accessible, At-Home Detection of Parkinson's Disease via Multi-task Video Analysis
Jun 21, 2024Abstract:Limited access to neurological care leads to missed diagnoses of Parkinson's disease (PD), leaving many individuals unidentified and untreated. We trained a novel neural network-based fusion architecture to detect Parkinson's disease (PD) by analyzing features extracted from webcam recordings of three tasks: finger tapping, facial expression (smiling), and speech (uttering a sentence containing all letters of the alphabet). Additionally, the model incorporated Monte Carlo Dropout to improve prediction accuracy by considering uncertainties. The study participants (n = 845, 272 with PD) were randomly split into three sets: 60% for training, 20% for model selection (hyper-parameter tuning), and 20% for final performance evaluation. The dataset consists of 1102 sessions, each session containing videos of all three tasks. Our proposed model achieved significantly better accuracy, area under the ROC curve (AUROC), and sensitivity at non-inferior specificity compared to any single-task model. Withholding uncertain predictions further boosted the performance, achieving 88.0% (95% CI: 87.7% - 88.4%) accuracy, 93.0% (92.8% - 93.2%) AUROC, 79.3% (78.4% - 80.2%) sensitivity, and 92.6% (92.3% - 92.8%) specificity, at the expense of not being able to predict for 2.3% (2.0% - 2.6%) data. Further analysis suggests that the trained model does not exhibit any detectable bias across sex and ethnic subgroups and is most effective for individuals aged between 50 and 80. This accessible, low-cost approach requiring only an internet-enabled device with a webcam and microphone paves the way for convenient PD screening at home, particularly in regions with limited access to clinical specialists.
Hi5: 2D Hand Pose Estimation with Zero Human Annotation
Jun 05, 2024



Abstract:We propose a new large synthetic hand pose estimation dataset, Hi5, and a novel inexpensive method for collecting high-quality synthetic data that requires no human annotation or validation. Leveraging recent advancements in computer graphics, high-fidelity 3D hand models with diverse genders and skin colors, and dynamic environments and camera movements, our data synthesis pipeline allows precise control over data diversity and representation, ensuring robust and fair model training. We generate a dataset with 583,000 images with accurate pose annotation using a single consumer PC that closely represents real-world variability. Pose estimation models trained with Hi5 perform competitively on real-hand benchmarks while surpassing models trained with real data when tested on occlusions and perturbations. Our experiments show promising results for synthetic data as a viable solution for data representation problems in real datasets. Overall, this paper provides a promising new approach to synthetic data creation and annotation that can reduce costs and increase the diversity and quality of data for hand pose estimation.
Self-Imagine: Effective Unimodal Reasoning with Multimodal Models using Self-Imagination
Jan 16, 2024
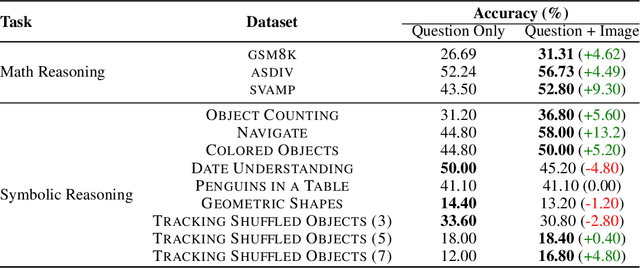


Abstract:The potential of Vision-Language Models (\textsc{vlm}s) often remains underutilized in handling complex text-based problems, particularly when these problems could benefit from visual representation. Resonating with humans' ability to solve complex text-based problems by (1) creating a visual diagram from the problem and (2) deducing what steps they need to take to solve it, we propose \textsc{Self-Imagine}. We leverage a single Vision-Language Model (\textsc{vlm}) to generate a structured representation of the question using HTML, then render the HTML as an image, and finally use the same \vlm to answer the question using both the question and the image. Our approach does not require any additional training data or training. We evaluate our approach in three mathematics tasks and nine general-purpose reasoning tasks using state-of-the-art \textsc{vlm}. Our approach boosts the performance of \textsc{vlm} on all math tasks (\gsm: +4.62\%; \asdiv: +4.49\%; \svamp: +9.30\%) and the majority of the general-purpose reasoning tasks by 0.4\% to 13.20\% while achieving comparable performance in other tasks. Code and data at https://github.com/snat1505027/self-imagine .
PARK: Parkinson's Analysis with Remote Kinetic-tasks
Nov 21, 2023

Abstract:We present a web-based framework to screen for Parkinson's disease (PD) by allowing users to perform neurological tests in their homes. Our web framework guides the users to complete three tasks involving speech, facial expression, and finger movements. The task videos are analyzed to classify whether the users show signs of PD. We present the results in an easy-to-understand manner, along with personalized resources to further access to treatment and care. Our framework is accessible by any major web browser, improving global access to neurological care.
Unmasking Parkinson's Disease with Smile: An AI-enabled Screening Framework
Aug 03, 2023



Abstract:Parkinson's disease (PD) diagnosis remains challenging due to lacking a reliable biomarker and limited access to clinical care. In this study, we present an analysis of the largest video dataset containing micro-expressions to screen for PD. We collected 3,871 videos from 1,059 unique participants, including 256 self-reported PD patients. The recordings are from diverse sources encompassing participants' homes across multiple countries, a clinic, and a PD care facility in the US. Leveraging facial landmarks and action units, we extracted features relevant to Hypomimia, a prominent symptom of PD characterized by reduced facial expressions. An ensemble of AI models trained on these features achieved an accuracy of 89.7% and an Area Under the Receiver Operating Characteristic (AUROC) of 89.3% while being free from detectable bias across population subgroups based on sex and ethnicity on held-out data. Further analysis reveals that features from the smiling videos alone lead to comparable performance, even on two external test sets the model has never seen during training, suggesting the potential for PD risk assessment from smiling selfie videos.
Using AI to Measure Parkinson's Disease Severity at Home
Apr 13, 2023Abstract:We present an artificial intelligence system to remotely assess the motor performance of individuals with Parkinson's disease (PD). Participants performed a motor task (i.e., tapping fingers) in front of a webcam, and data from 250 global participants were rated by three expert neurologists following the Movement Disorder Society Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS). The neurologists' ratings were highly reliable, with an intra-class correlation coefficient (ICC) of 0.88. We developed computer algorithms to obtain objective measurements that align with the MDS-UPDRS guideline and are strongly correlated with the neurologists' ratings. Our machine learning model trained on these measures outperformed an MDS-UPDRS certified rater, with a mean absolute error (MAE) of 0.59 compared to the rater's MAE of 0.79. However, the model performed slightly worse than the expert neurologists (0.53 MAE). The methodology can be replicated for similar motor tasks, providing the possibility of evaluating individuals with PD and other movement disorders remotely, objectively, and in areas with limited access to neurological care.
TextMI: Textualize Multimodal Information for Integrating Non-verbal Cues in Pre-trained Language Models
Mar 29, 2023Abstract:Pre-trained large language models have recently achieved ground-breaking performance in a wide variety of language understanding tasks. However, the same model can not be applied to multimodal behavior understanding tasks (e.g., video sentiment/humor detection) unless non-verbal features (e.g., acoustic and visual) can be integrated with language. Jointly modeling multiple modalities significantly increases the model complexity, and makes the training process data-hungry. While an enormous amount of text data is available via the web, collecting large-scale multimodal behavioral video datasets is extremely expensive, both in terms of time and money. In this paper, we investigate whether large language models alone can successfully incorporate non-verbal information when they are presented in textual form. We present a way to convert the acoustic and visual information into corresponding textual descriptions and concatenate them with the spoken text. We feed this augmented input to a pre-trained BERT model and fine-tune it on three downstream multimodal tasks: sentiment, humor, and sarcasm detection. Our approach, TextMI, significantly reduces model complexity, adds interpretability to the model's decision, and can be applied for a diverse set of tasks while achieving superior (multimodal sarcasm detection) or near SOTA (multimodal sentiment analysis and multimodal humor detection) performance. We propose TextMI as a general, competitive baseline for multimodal behavioral analysis tasks, particularly in a low-resource setting.
Detecting Parkinson's Disease from Speech-task in an accessible and interpretable manner
Sep 02, 2020



Abstract:Every nine minutes a person is diagnosed with Parkinson's Disease (PD) in the United States. However, studies have shown that between 25 and 80\% of individuals with Parkinson's Disease (PD) remain undiagnosed. An online, in the wild audio recording application has the potential to help screen for the disease if risk can be accurately assessed. In this paper, we collect data from 726 unique subjects (262 PD and 464 Non-PD) uttering the "quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog ...." to conduct automated PD assessment. We extracted both standard acoustic features and deep learning based embedding features from the speech data and trained several machine learning algorithms on them. Our models achieved 0.75 AUC by modeling the standard acoustic features through the XGBoost model. We also provide explanation behind our model's decision and show that it is focusing mostly on the widely used MFCC features and a subset of dysphonia features previously used for detecting PD from verbal phonation task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge