Facial Inpainting
Facial inpainting is the process of reconstructing missing regions on a person's face in images.
Papers and Code
JUST-DUB-IT: Video Dubbing via Joint Audio-Visual Diffusion
Jan 29, 2026Audio-Visual Foundation Models, which are pretrained to jointly generate sound and visual content, have recently shown an unprecedented ability to model multi-modal generation and editing, opening new opportunities for downstream tasks. Among these tasks, video dubbing could greatly benefit from such priors, yet most existing solutions still rely on complex, task-specific pipelines that struggle in real-world settings. In this work, we introduce a single-model approach that adapts a foundational audio-video diffusion model for video-to-video dubbing via a lightweight LoRA. The LoRA enables the model to condition on an input audio-video while jointly generating translated audio and synchronized facial motion. To train this LoRA, we leverage the generative model itself to synthesize paired multilingual videos of the same speaker. Specifically, we generate multilingual videos with language switches within a single clip, and then inpaint the face and audio in each half to match the language of the other half. By leveraging the rich generative prior of the audio-visual model, our approach preserves speaker identity and lip synchronization while remaining robust to complex motion and real-world dynamics. We demonstrate that our approach produces high-quality dubbed videos with improved visual fidelity, lip synchronization, and robustness compared to existing dubbing pipelines.
Now You See Me, Now You Don't: A Unified Framework for Expression Consistent Anonymization in Talking Head Videos
Jan 14, 2026Face video anonymization is aimed at privacy preservation while allowing for the analysis of videos in a number of computer vision downstream tasks such as expression recognition, people tracking, and action recognition. We propose here a novel unified framework referred to as Anon-NET, streamlined to de-identify facial videos, while preserving age, gender, race, pose, and expression of the original video. Specifically, we inpaint faces by a diffusion-based generative model guided by high-level attribute recognition and motion-aware expression transfer. We then animate deidentified faces by video-driven animation, which accepts the de-identified face and the original video as input. Extensive experiments on the datasets VoxCeleb2, CelebV-HQ, and HDTF, which include diverse facial dynamics, demonstrate the effectiveness of AnonNET in obfuscating identity while retaining visual realism and temporal consistency. The code of AnonNet will be publicly released.
SyncAnyone: Implicit Disentanglement via Progressive Self-Correction for Lip-Syncing in the wild
Dec 25, 2025High-quality AI-powered video dubbing demands precise audio-lip synchronization, high-fidelity visual generation, and faithful preservation of identity and background. Most existing methods rely on a mask-based training strategy, where the mouth region is masked in talking-head videos, and the model learns to synthesize lip movements from corrupted inputs and target audios. While this facilitates lip-sync accuracy, it disrupts spatiotemporal context, impairing performance on dynamic facial motions and causing instability in facial structure and background consistency. To overcome this limitation, we propose SyncAnyone, a novel two-stage learning framework that achieves accurate motion modeling and high visual fidelity simultaneously. In Stage 1, we train a diffusion-based video transformer for masked mouth inpainting, leveraging its strong spatiotemporal modeling to generate accurate, audio-driven lip movements. However, due to input corruption, minor artifacts may arise in the surrounding facial regions and the background. In Stage 2, we develop a mask-free tuning pipeline to address mask-induced artifacts. Specifically, on the basis of the Stage 1 model, we develop a data generation pipeline that creates pseudo-paired training samples by synthesizing lip-synced videos from the source video and random sampled audio. We further tune the stage 2 model on this synthetic data, achieving precise lip editing and better background consistency. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art results in visual quality, temporal coherence, and identity preservation under in-the wild lip-syncing scenarios.
BLANKET: Anonymizing Faces in Infant Video Recordings
Dec 17, 2025



Ensuring the ethical use of video data involving human subjects, particularly infants, requires robust anonymization methods. We propose BLANKET (Baby-face Landmark-preserving ANonymization with Keypoint dEtection consisTency), a novel approach designed to anonymize infant faces in video recordings while preserving essential facial attributes. Our method comprises two stages. First, a new random face, compatible with the original identity, is generated via inpainting using a diffusion model. Second, the new identity is seamlessly incorporated into each video frame through temporally consistent face swapping with authentic expression transfer. The method is evaluated on a dataset of short video recordings of babies and is compared to the popular anonymization method, DeepPrivacy2. Key metrics assessed include the level of de-identification, preservation of facial attributes, impact on human pose estimation (as an example of a downstream task), and presence of artifacts. Both methods alter the identity, and our method outperforms DeepPrivacy2 in all other respects. The code is available as an easy-to-use anonymization demo at https://github.com/ctu-vras/blanket-infant-face-anonym.
* Project website: https://github.com/ctu-vras/blanket-infant-face-anonym
DirectSwap: Mask-Free Cross-Identity Training and Benchmarking for Expression-Consistent Video Head Swapping
Dec 10, 2025
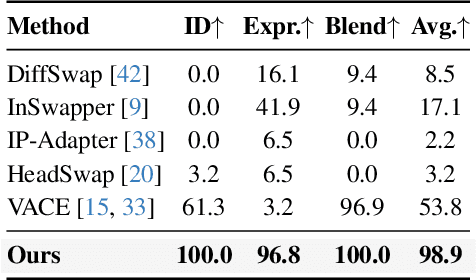
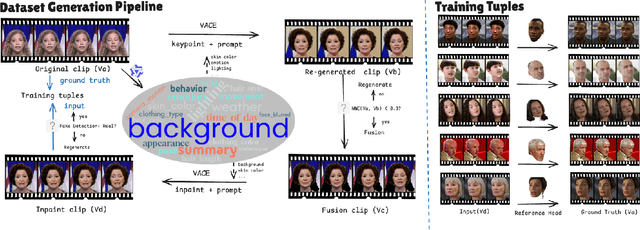
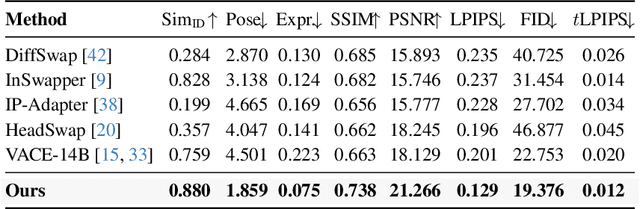
Video head swapping aims to replace the entire head of a video subject, including facial identity, head shape, and hairstyle, with that of a reference image, while preserving the target body, background, and motion dynamics. Due to the lack of ground-truth paired swapping data, prior methods typically train on cross-frame pairs of the same person within a video and rely on mask-based inpainting to mitigate identity leakage. Beyond potential boundary artifacts, this paradigm struggles to recover essential cues occluded by the mask, such as facial pose, expressions, and motion dynamics. To address these issues, we prompt a video editing model to synthesize new heads for existing videos as fake swapping inputs, while maintaining frame-synchronized facial poses and expressions. This yields HeadSwapBench, the first cross-identity paired dataset for video head swapping, which supports both training (\TrainNum{} videos) and benchmarking (\TestNum{} videos) with genuine outputs. Leveraging this paired supervision, we propose DirectSwap, a mask-free, direct video head-swapping framework that extends an image U-Net into a video diffusion model with a motion module and conditioning inputs. Furthermore, we introduce the Motion- and Expression-Aware Reconstruction (MEAR) loss, which reweights the diffusion loss per pixel using frame-difference magnitudes and facial-landmark proximity, thereby enhancing cross-frame coherence in motion and expressions. Extensive experiments demonstrate that DirectSwap achieves state-of-the-art visual quality, identity fidelity, and motion and expression consistency across diverse in-the-wild video scenes. We will release the source code and the HeadSwapBench dataset to facilitate future research.
AvatarTex: High-Fidelity Facial Texture Reconstruction from Single-Image Stylized Avatars
Nov 10, 2025We present AvatarTex, a high-fidelity facial texture reconstruction framework capable of generating both stylized and photorealistic textures from a single image. Existing methods struggle with stylized avatars due to the lack of diverse multi-style datasets and challenges in maintaining geometric consistency in non-standard textures. To address these limitations, AvatarTex introduces a novel three-stage diffusion-to-GAN pipeline. Our key insight is that while diffusion models excel at generating diversified textures, they lack explicit UV constraints, whereas GANs provide a well-structured latent space that ensures style and topology consistency. By integrating these strengths, AvatarTex achieves high-quality topology-aligned texture synthesis with both artistic and geometric coherence. Specifically, our three-stage pipeline first completes missing texture regions via diffusion-based inpainting, refines style and structure consistency using GAN-based latent optimization, and enhances fine details through diffusion-based repainting. To address the need for a stylized texture dataset, we introduce TexHub, a high-resolution collection of 20,000 multi-style UV textures with precise UV-aligned layouts. By leveraging TexHub and our structured diffusion-to-GAN pipeline, AvatarTex establishes a new state-of-the-art in multi-style facial texture reconstruction. TexHub will be released upon publication to facilitate future research in this field.
Controllable Localized Face Anonymization Via Diffusion Inpainting
Sep 18, 2025



The growing use of portrait images in computer vision highlights the need to protect personal identities. At the same time, anonymized images must remain useful for downstream computer vision tasks. In this work, we propose a unified framework that leverages the inpainting ability of latent diffusion models to generate realistic anonymized images. Unlike prior approaches, we have complete control over the anonymization process by designing an adaptive attribute-guidance module that applies gradient correction during the reverse denoising process, aligning the facial attributes of the generated image with those of the synthesized target image. Our framework also supports localized anonymization, allowing users to specify which facial regions are left unchanged. Extensive experiments conducted on the public CelebA-HQ and FFHQ datasets show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art approaches while requiring no additional model training. The source code is available on our page.
Geometry-Aware Video Inpainting for Joint Headset Occlusion Removal and Face Reconstruction in Social XR
Aug 17, 2025Head-mounted displays (HMDs) are essential for experiencing extended reality (XR) environments and observing virtual content. However, they obscure the upper part of the user's face, complicating external video recording and significantly impacting social XR applications such as teleconferencing, where facial expressions and eye gaze details are crucial for creating an immersive experience. This study introduces a geometry-aware learning-based framework to jointly remove HMD occlusions and reconstruct complete 3D facial geometry from RGB frames captured from a single viewpoint. The method integrates a GAN-based video inpainting network, guided by dense facial landmarks and a single occlusion-free reference frame, to restore missing facial regions while preserving identity. Subsequently, a SynergyNet-based module regresses 3D Morphable Model (3DMM) parameters from the inpainted frames, enabling accurate 3D face reconstruction. Dense landmark optimization is incorporated throughout the pipeline to improve both the inpainting quality and the fidelity of the recovered geometry. Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed framework can successfully remove HMDs from RGB facial videos while maintaining facial identity and realism, producing photorealistic 3D face geometry outputs. Ablation studies further show that the framework remains robust across different landmark densities, with only minor quality degradation under sparse landmark configurations.
DicFace: Dirichlet-Constrained Variational Codebook Learning for Temporally Coherent Video Face Restoration
Jun 16, 2025



Video face restoration faces a critical challenge in maintaining temporal consistency while recovering fine facial details from degraded inputs. This paper presents a novel approach that extends Vector-Quantized Variational Autoencoders (VQ-VAEs), pretrained on static high-quality portraits, into a video restoration framework through variational latent space modeling. Our key innovation lies in reformulating discrete codebook representations as Dirichlet-distributed continuous variables, enabling probabilistic transitions between facial features across frames. A spatio-temporal Transformer architecture jointly models inter-frame dependencies and predicts latent distributions, while a Laplacian-constrained reconstruction loss combined with perceptual (LPIPS) regularization enhances both pixel accuracy and visual quality. Comprehensive evaluations on blind face restoration, video inpainting, and facial colorization tasks demonstrate state-of-the-art performance. This work establishes an effective paradigm for adapting intensive image priors, pretrained on high-quality images, to video restoration while addressing the critical challenge of flicker artifacts. The source code has been open-sourced and is available at https://github.com/fudan-generative-vision/DicFace.
OmniSync: Towards Universal Lip Synchronization via Diffusion Transformers
May 27, 2025Lip synchronization is the task of aligning a speaker's lip movements in video with corresponding speech audio, and it is essential for creating realistic, expressive video content. However, existing methods often rely on reference frames and masked-frame inpainting, which limit their robustness to identity consistency, pose variations, facial occlusions, and stylized content. In addition, since audio signals provide weaker conditioning than visual cues, lip shape leakage from the original video will affect lip sync quality. In this paper, we present OmniSync, a universal lip synchronization framework for diverse visual scenarios. Our approach introduces a mask-free training paradigm using Diffusion Transformer models for direct frame editing without explicit masks, enabling unlimited-duration inference while maintaining natural facial dynamics and preserving character identity. During inference, we propose a flow-matching-based progressive noise initialization to ensure pose and identity consistency, while allowing precise mouth-region editing. To address the weak conditioning signal of audio, we develop a Dynamic Spatiotemporal Classifier-Free Guidance (DS-CFG) mechanism that adaptively adjusts guidance strength over time and space. We also establish the AIGC-LipSync Benchmark, the first evaluation suite for lip synchronization in diverse AI-generated videos. Extensive experiments demonstrate that OmniSync significantly outperforms prior methods in both visual quality and lip sync accuracy, achieving superior results in both real-world and AI-generated videos.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge