Xilin He
Segment Anyword: Mask Prompt Inversion for Open-Set Grounded Segmentation
May 23, 2025Abstract:Open-set image segmentation poses a significant challenge because existing methods often demand extensive training or fine-tuning and generally struggle to segment unified objects consistently across diverse text reference expressions. Motivated by this, we propose Segment Anyword, a novel training-free visual concept prompt learning approach for open-set language grounded segmentation that relies on token-level cross-attention maps from a frozen diffusion model to produce segmentation surrogates or mask prompts, which are then refined into targeted object masks. Initial prompts typically lack coherence and consistency as the complexity of the image-text increases, resulting in suboptimal mask fragments. To tackle this issue, we further introduce a novel linguistic-guided visual prompt regularization that binds and clusters visual prompts based on sentence dependency and syntactic structural information, enabling the extraction of robust, noise-tolerant mask prompts, and significant improvements in segmentation accuracy. The proposed approach is effective, generalizes across different open-set segmentation tasks, and achieves state-of-the-art results of 52.5 (+6.8 relative) mIoU on Pascal Context 59, 67.73 (+25.73 relative) cIoU on gRefCOCO, and 67.4 (+1.1 relative to fine-tuned methods) mIoU on GranDf, which is the most complex open-set grounded segmentation task in the field.
BOTM: Echocardiography Segmentation via Bi-directional Optimal Token Matching
May 23, 2025Abstract:Existed echocardiography segmentation methods often suffer from anatomical inconsistency challenge caused by shape variation, partial observation and region ambiguity with similar intensity across 2D echocardiographic sequences, resulting in false positive segmentation with anatomical defeated structures in challenging low signal-to-noise ratio conditions. To provide a strong anatomical guarantee across different echocardiographic frames, we propose a novel segmentation framework named BOTM (Bi-directional Optimal Token Matching) that performs echocardiography segmentation and optimal anatomy transportation simultaneously. Given paired echocardiographic images, BOTM learns to match two sets of discrete image tokens by finding optimal correspondences from a novel anatomical transportation perspective. We further extend the token matching into a bi-directional cross-transport attention proxy to regulate the preserved anatomical consistency within the cardiac cyclic deformation in temporal domain. Extensive experimental results show that BOTM can generate stable and accurate segmentation outcomes (e.g. -1.917 HD on CAMUS2H LV, +1.9% Dice on TED), and provide a better matching interpretation with anatomical consistency guarantee.
CA-Edit: Causality-Aware Condition Adapter for High-Fidelity Local Facial Attribute Editing
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:For efficient and high-fidelity local facial attribute editing, most existing editing methods either require additional fine-tuning for different editing effects or tend to affect beyond the editing regions. Alternatively, inpainting methods can edit the target image region while preserving external areas. However, current inpainting methods still suffer from the generation misalignment with facial attributes description and the loss of facial skin details. To address these challenges, (i) a novel data utilization strategy is introduced to construct datasets consisting of attribute-text-image triples from a data-driven perspective, (ii) a Causality-Aware Condition Adapter is proposed to enhance the contextual causality modeling of specific details, which encodes the skin details from the original image while preventing conflicts between these cues and textual conditions. In addition, a Skin Transition Frequency Guidance technique is introduced for the local modeling of contextual causality via sampling guidance driven by low-frequency alignment. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of our method in boosting both fidelity and editability for localized attribute editing. The code is available at https://github.com/connorxian/CA-Edit.
Towards Combating Frequency Simplicity-biased Learning for Domain Generalization
Oct 21, 2024Abstract:Domain generalization methods aim to learn transferable knowledge from source domains that can generalize well to unseen target domains. Recent studies show that neural networks frequently suffer from a simplicity-biased learning behavior which leads to over-reliance on specific frequency sets, namely as frequency shortcuts, instead of semantic information, resulting in poor generalization performance. Despite previous data augmentation techniques successfully enhancing generalization performances, they intend to apply more frequency shortcuts, thereby causing hallucinations of generalization improvement. In this paper, we aim to prevent such learning behavior of applying frequency shortcuts from a data-driven perspective. Given the theoretical justification of models' biased learning behavior on different spatial frequency components, which is based on the dataset frequency properties, we argue that the learning behavior on various frequency components could be manipulated by changing the dataset statistical structure in the Fourier domain. Intuitively, as frequency shortcuts are hidden in the dominant and highly dependent frequencies of dataset structure, dynamically perturbating the over-reliance frequency components could prevent the application of frequency shortcuts. To this end, we propose two effective data augmentation modules designed to collaboratively and adaptively adjust the frequency characteristic of the dataset, aiming to dynamically influence the learning behavior of the model and ultimately serving as a strategy to mitigate shortcut learning. Code is available at AdvFrequency (https://github.com/C0notSilly/AdvFrequency).
SynFER: Towards Boosting Facial Expression Recognition with Synthetic Data
Oct 13, 2024


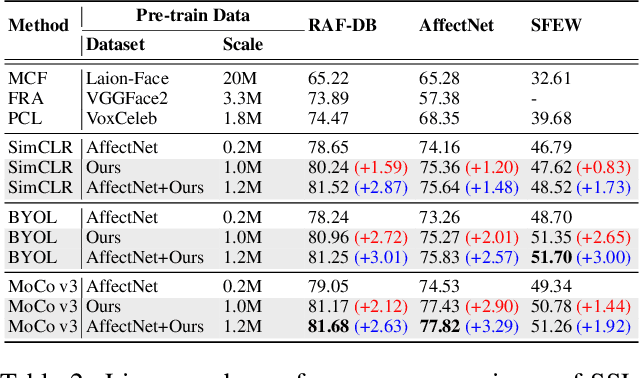
Abstract:Facial expression datasets remain limited in scale due to privacy concerns, the subjectivity of annotations, and the labor-intensive nature of data collection. This limitation poses a significant challenge for developing modern deep learning-based facial expression analysis models, particularly foundation models, that rely on large-scale data for optimal performance. To tackle the overarching and complex challenge, we introduce SynFER (Synthesis of Facial Expressions with Refined Control), a novel framework for synthesizing facial expression image data based on high-level textual descriptions as well as more fine-grained and precise control through facial action units. To ensure the quality and reliability of the synthetic data, we propose a semantic guidance technique to steer the generation process and a pseudo-label generator to help rectify the facial expression labels for the synthetic images. To demonstrate the generation fidelity and the effectiveness of the synthetic data from SynFER, we conduct extensive experiments on representation learning using both synthetic data and real-world data. Experiment results validate the efficacy of the proposed approach and the synthetic data. Notably, our approach achieves a 67.23% classification accuracy on AffectNet when training solely with synthetic data equivalent to the AffectNet training set size, which increases to 69.84% when scaling up to five times the original size. Our code will be made publicly available.
Domain-Guided Weight Modulation for Semi-Supervised Domain Generalization
Sep 04, 2024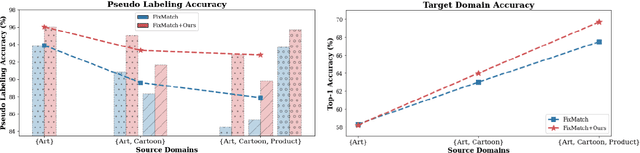
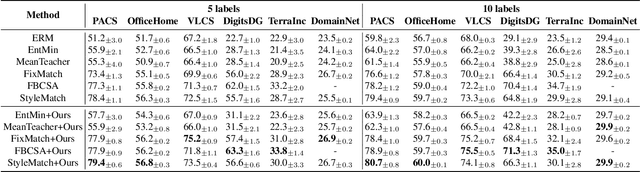
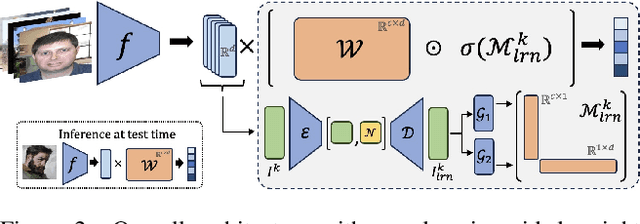

Abstract:Unarguably, deep learning models capable of generalizing to unseen domain data while leveraging a few labels are of great practical significance due to low developmental costs. In search of this endeavor, we study the challenging problem of semi-supervised domain generalization (SSDG), where the goal is to learn a domain-generalizable model while using only a small fraction of labeled data and a relatively large fraction of unlabeled data. Domain generalization (DG) methods show subpar performance under the SSDG setting, whereas semi-supervised learning (SSL) methods demonstrate relatively better performance, however, they are considerably poor compared to the fully-supervised DG methods. Towards handling this new, but challenging problem of SSDG, we propose a novel method that can facilitate the generation of accurate pseudo-labels under various domain shifts. This is accomplished by retaining the domain-level specialism in the classifier during training corresponding to each source domain. Specifically, we first create domain-level information vectors on the fly which are then utilized to learn a domain-aware mask for modulating the classifier's weights. We provide a mathematical interpretation for the effect of this modulation procedure on both pseudo-labeling and model training. Our method is plug-and-play and can be readily applied to different SSL baselines for SSDG. Extensive experiments on six challenging datasets in two different SSDG settings show that our method provides visible gains over the various strong SSL-based SSDG baselines.
Boosting Adversarial Transferability across Model Genus by Deformation-Constrained Warping
Feb 06, 2024Abstract:Adversarial examples generated by a surrogate model typically exhibit limited transferability to unknown target systems. To address this problem, many transferability enhancement approaches (e.g., input transformation and model augmentation) have been proposed. However, they show poor performances in attacking systems having different model genera from the surrogate model. In this paper, we propose a novel and generic attacking strategy, called Deformation-Constrained Warping Attack (DeCoWA), that can be effectively applied to cross model genus attack. Specifically, DeCoWA firstly augments input examples via an elastic deformation, namely Deformation-Constrained Warping (DeCoW), to obtain rich local details of the augmented input. To avoid severe distortion of global semantics led by random deformation, DeCoW further constrains the strength and direction of the warping transformation by a novel adaptive control strategy. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the transferable examples crafted by our DeCoWA on CNN surrogates can significantly hinder the performance of Transformers (and vice versa) on various tasks, including image classification, video action recognition, and audio recognition. Code is made available at https://github.com/LinQinLiang/DeCoWA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge