Kelvin Xu
Training Language Models on the Knowledge Graph: Insights on Hallucinations and Their Detectability
Aug 14, 2024



Abstract:While many capabilities of language models (LMs) improve with increased training budget, the influence of scale on hallucinations is not yet fully understood. Hallucinations come in many forms, and there is no universally accepted definition. We thus focus on studying only those hallucinations where a correct answer appears verbatim in the training set. To fully control the training data content, we construct a knowledge graph (KG)-based dataset, and use it to train a set of increasingly large LMs. We find that for a fixed dataset, larger and longer-trained LMs hallucinate less. However, hallucinating on $\leq5$% of the training data requires an order of magnitude larger model, and thus an order of magnitude more compute, than Hoffmann et al. (2022) reported was optimal. Given this costliness, we study how hallucination detectors depend on scale. While we see detector size improves performance on fixed LM's outputs, we find an inverse relationship between the scale of the LM and the detectability of its hallucinations.
Scaling LLM Test-Time Compute Optimally can be More Effective than Scaling Model Parameters
Aug 06, 2024



Abstract:Enabling LLMs to improve their outputs by using more test-time computation is a critical step towards building generally self-improving agents that can operate on open-ended natural language. In this paper, we study the scaling of inference-time computation in LLMs, with a focus on answering the question: if an LLM is allowed to use a fixed but non-trivial amount of inference-time compute, how much can it improve its performance on a challenging prompt? Answering this question has implications not only on the achievable performance of LLMs, but also on the future of LLM pretraining and how one should tradeoff inference-time and pre-training compute. Despite its importance, little research attempted to understand the scaling behaviors of various test-time inference methods. Moreover, current work largely provides negative results for a number of these strategies. In this work, we analyze two primary mechanisms to scale test-time computation: (1) searching against dense, process-based verifier reward models; and (2) updating the model's distribution over a response adaptively, given the prompt at test time. We find that in both cases, the effectiveness of different approaches to scaling test-time compute critically varies depending on the difficulty of the prompt. This observation motivates applying a "compute-optimal" scaling strategy, which acts to most effectively allocate test-time compute adaptively per prompt. Using this compute-optimal strategy, we can improve the efficiency of test-time compute scaling by more than 4x compared to a best-of-N baseline. Additionally, in a FLOPs-matched evaluation, we find that on problems where a smaller base model attains somewhat non-trivial success rates, test-time compute can be used to outperform a 14x larger model.
Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:In this report, we present the latest model of the Gemini family, Gemini 1.5 Pro, a highly compute-efficient multimodal mixture-of-experts model capable of recalling and reasoning over fine-grained information from millions of tokens of context, including multiple long documents and hours of video and audio. Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves near-perfect recall on long-context retrieval tasks across modalities, improves the state-of-the-art in long-document QA, long-video QA and long-context ASR, and matches or surpasses Gemini 1.0 Ultra's state-of-the-art performance across a broad set of benchmarks. Studying the limits of Gemini 1.5 Pro's long-context ability, we find continued improvement in next-token prediction and near-perfect retrieval (>99%) up to at least 10M tokens, a generational leap over existing models such as Claude 2.1 (200k) and GPT-4 Turbo (128k). Finally, we highlight surprising new capabilities of large language models at the frontier; when given a grammar manual for Kalamang, a language with fewer than 200 speakers worldwide, the model learns to translate English to Kalamang at a similar level to a person who learned from the same content.
Beyond Human Data: Scaling Self-Training for Problem-Solving with Language Models
Dec 22, 2023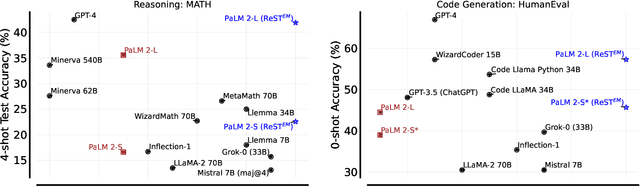
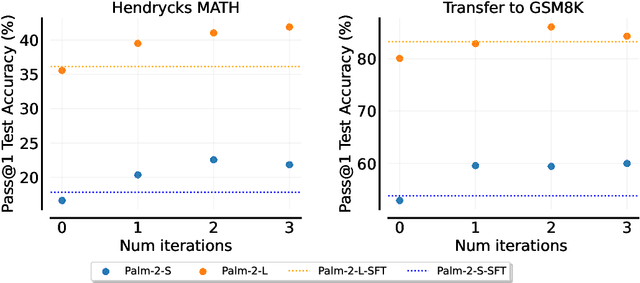
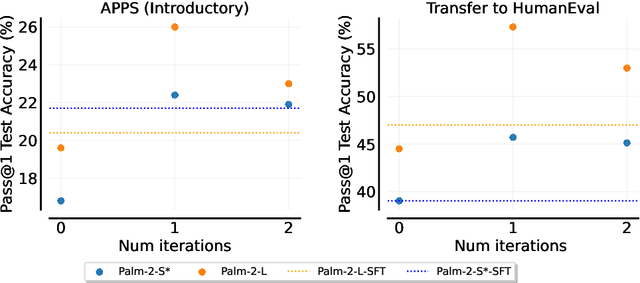
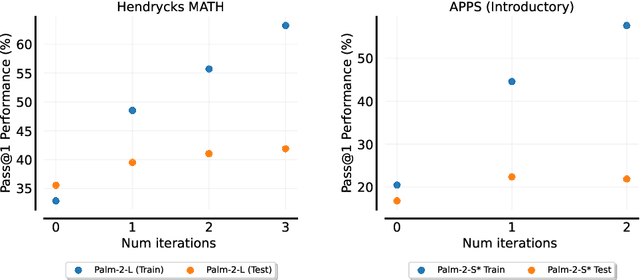
Abstract:Fine-tuning language models~(LMs) on human-generated data remains a prevalent practice. However, the performance of such models is often limited by the quantity and diversity of high-quality human data. In this paper, we explore whether we can go beyond human data on tasks where we have access to scalar feedback, for example, on math problems where one can verify correctness. To do so, we investigate a simple self-training method based on expectation-maximization, which we call ReST$^{EM}$, where we (1) generate samples from the model and filter them using binary feedback, (2) fine-tune the model on these samples, and (3) repeat this process a few times. Testing on advanced MATH reasoning and APPS coding benchmarks using PaLM-2 models, we find that ReST$^{EM}$ scales favorably with model size and significantly surpasses fine-tuning only on human data. Overall, our findings suggest self-training with feedback can substantially reduce dependence on human-generated data.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
LMRL Gym: Benchmarks for Multi-Turn Reinforcement Learning with Language Models
Nov 30, 2023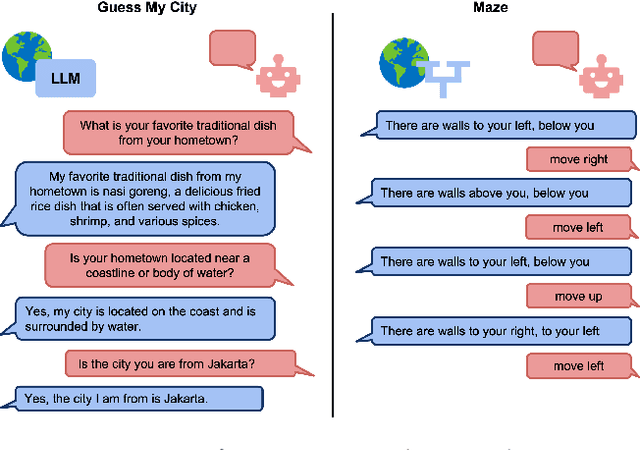
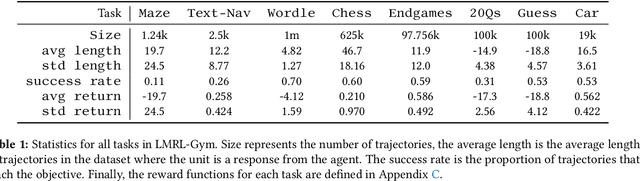
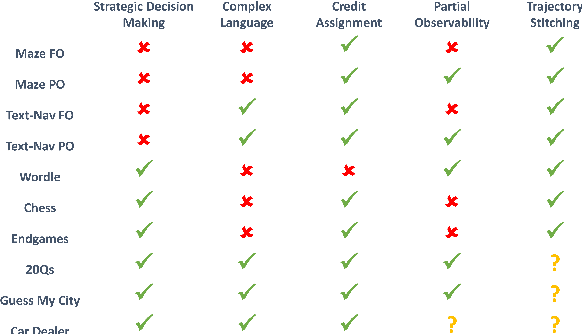
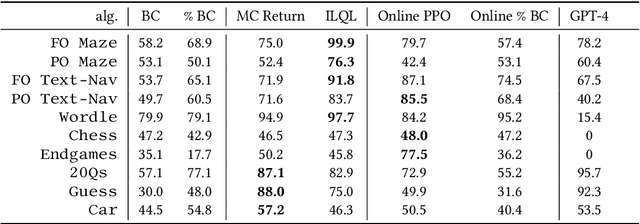
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) provide excellent text-generation capabilities, but standard prompting and generation methods generally do not lead to intentional or goal-directed agents and might necessitate considerable prompt tuning. This becomes particularly apparent in multi-turn conversations: even the best current LLMs rarely ask clarifying questions, engage in explicit information gathering, or take actions now that lead to better decisions after multiple turns. Reinforcement learning has the potential to leverage the powerful modeling capabilities of LLMs, as well as their internal representation of textual interactions, to create capable goal-directed language agents. This can enable intentional and temporally extended interactions, such as with humans, through coordinated persuasion and carefully crafted questions, or in goal-directed play through text games to bring about desired final outcomes. However, enabling this requires the community to develop stable and reliable reinforcement learning algorithms that can effectively train LLMs. Developing such algorithms requires tasks that can gauge progress on algorithm design, provide accessible and reproducible evaluations for multi-turn interactions, and cover a range of task properties and challenges in improving reinforcement learning algorithms. Our paper introduces the LMRL-Gym benchmark for evaluating multi-turn RL for LLMs, together with an open-source research framework containing a basic toolkit for getting started on multi-turn RL with offline value-based and policy-based RL methods. Our benchmark consists of 8 different language tasks, which require multiple rounds of language interaction and cover a range of tasks in open-ended dialogue and text games.
Frontier Language Models are not Robust to Adversarial Arithmetic, or "What do I need to say so you agree 2+2=5?
Nov 15, 2023



Abstract:We introduce and study the problem of adversarial arithmetic, which provides a simple yet challenging testbed for language model alignment. This problem is comprised of arithmetic questions posed in natural language, with an arbitrary adversarial string inserted before the question is complete. Even in the simple setting of 1-digit addition problems, it is easy to find adversarial prompts that make all tested models (including PaLM2, GPT4, Claude2) misbehave, and even to steer models to a particular wrong answer. We additionally provide a simple algorithm for finding successful attacks by querying those same models, which we name "prompt inversion rejection sampling" (PIRS). We finally show that models can be partially hardened against these attacks via reinforcement learning and via agentic constitutional loops. However, we were not able to make a language model fully robust against adversarial arithmetic attacks.
Small-scale proxies for large-scale Transformer training instabilities
Sep 25, 2023



Abstract:Teams that have trained large Transformer-based models have reported training instabilities at large scale that did not appear when training with the same hyperparameters at smaller scales. Although the causes of such instabilities are of scientific interest, the amount of resources required to reproduce them has made investigation difficult. In this work, we seek ways to reproduce and study training stability and instability at smaller scales. First, we focus on two sources of training instability described in previous work: the growth of logits in attention layers (Dehghani et al., 2023) and divergence of the output logits from the log probabilities (Chowdhery et al., 2022). By measuring the relationship between learning rate and loss across scales, we show that these instabilities also appear in small models when training at high learning rates, and that mitigations previously employed at large scales are equally effective in this regime. This prompts us to investigate the extent to which other known optimizer and model interventions influence the sensitivity of the final loss to changes in the learning rate. To this end, we study methods such as warm-up, weight decay, and the $\mu$Param (Yang et al., 2022), and combine techniques to train small models that achieve similar losses across orders of magnitude of learning rate variation. Finally, to conclude our exploration we study two cases where instabilities can be predicted before they emerge by examining the scaling behavior of model activation and gradient norms.
PaLM 2 Technical Report
May 17, 2023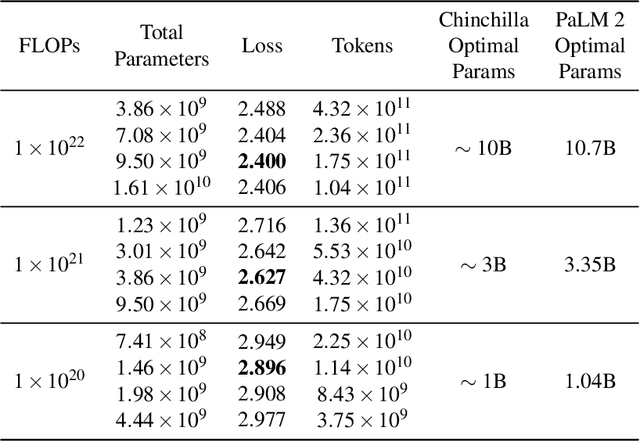

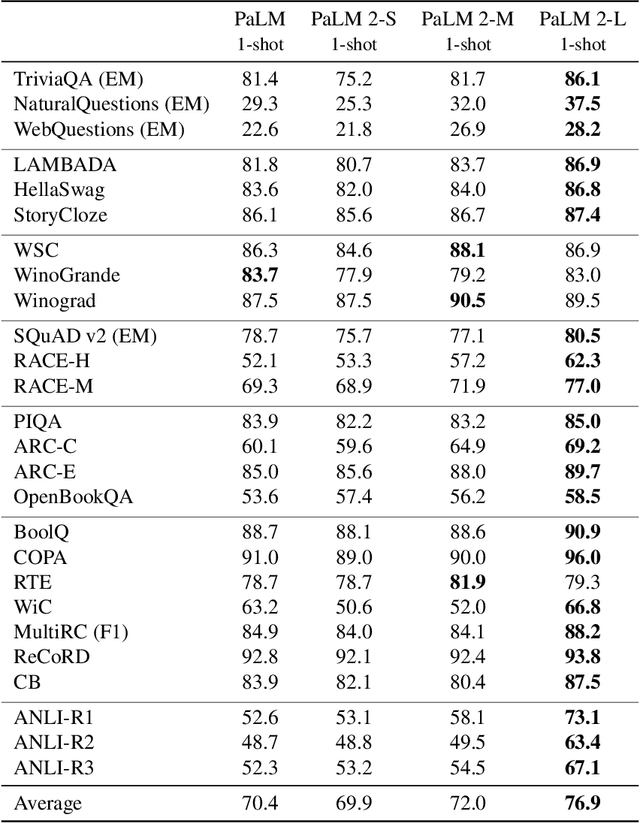

Abstract:We introduce PaLM 2, a new state-of-the-art language model that has better multilingual and reasoning capabilities and is more compute-efficient than its predecessor PaLM. PaLM 2 is a Transformer-based model trained using a mixture of objectives. Through extensive evaluations on English and multilingual language, and reasoning tasks, we demonstrate that PaLM 2 has significantly improved quality on downstream tasks across different model sizes, while simultaneously exhibiting faster and more efficient inference compared to PaLM. This improved efficiency enables broader deployment while also allowing the model to respond faster, for a more natural pace of interaction. PaLM 2 demonstrates robust reasoning capabilities exemplified by large improvements over PaLM on BIG-Bench and other reasoning tasks. PaLM 2 exhibits stable performance on a suite of responsible AI evaluations, and enables inference-time control over toxicity without additional overhead or impact on other capabilities. Overall, PaLM 2 achieves state-of-the-art performance across a diverse set of tasks and capabilities. When discussing the PaLM 2 family, it is important to distinguish between pre-trained models (of various sizes), fine-tuned variants of these models, and the user-facing products that use these models. In particular, user-facing products typically include additional pre- and post-processing steps. Additionally, the underlying models may evolve over time. Therefore, one should not expect the performance of user-facing products to exactly match the results reported in this report.
Dexterous Manipulation from Images: Autonomous Real-World RL via Substep Guidance
Dec 19, 2022



Abstract:Complex and contact-rich robotic manipulation tasks, particularly those that involve multi-fingered hands and underactuated object manipulation, present a significant challenge to any control method. Methods based on reinforcement learning offer an appealing choice for such settings, as they can enable robots to learn to delicately balance contact forces and dexterously reposition objects without strong modeling assumptions. However, running reinforcement learning on real-world dexterous manipulation systems often requires significant manual engineering. This negates the benefits of autonomous data collection and ease of use that reinforcement learning should in principle provide. In this paper, we describe a system for vision-based dexterous manipulation that provides a "programming-free" approach for users to define new tasks and enable robots with complex multi-fingered hands to learn to perform them through interaction. The core principle underlying our system is that, in a vision-based setting, users should be able to provide high-level intermediate supervision that circumvents challenges in teleoperation or kinesthetic teaching which allow a robot to not only learn a task efficiently but also to autonomously practice. Our system includes a framework for users to define a final task and intermediate sub-tasks with image examples, a reinforcement learning procedure that learns the task autonomously without interventions, and experimental results with a four-finger robotic hand learning multi-stage object manipulation tasks directly in the real world, without simulation, manual modeling, or reward engineering.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge