Alexandre Passos
UMass Amherst
PaLM 2 Technical Report
May 17, 2023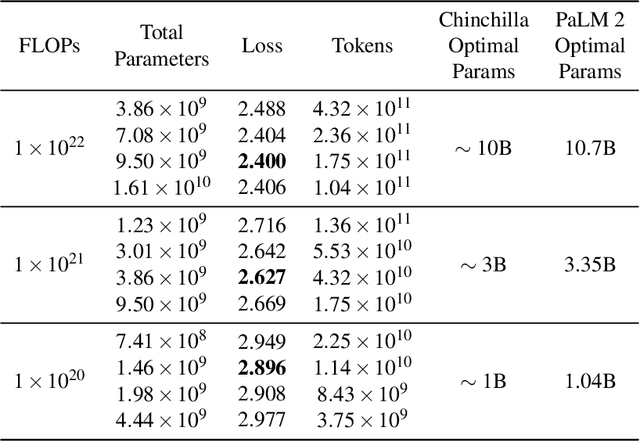

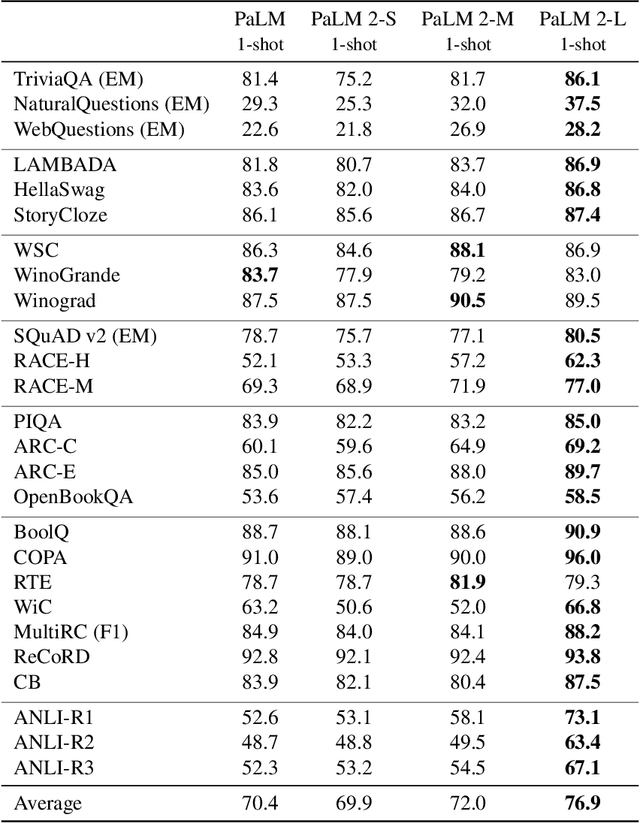

Abstract:We introduce PaLM 2, a new state-of-the-art language model that has better multilingual and reasoning capabilities and is more compute-efficient than its predecessor PaLM. PaLM 2 is a Transformer-based model trained using a mixture of objectives. Through extensive evaluations on English and multilingual language, and reasoning tasks, we demonstrate that PaLM 2 has significantly improved quality on downstream tasks across different model sizes, while simultaneously exhibiting faster and more efficient inference compared to PaLM. This improved efficiency enables broader deployment while also allowing the model to respond faster, for a more natural pace of interaction. PaLM 2 demonstrates robust reasoning capabilities exemplified by large improvements over PaLM on BIG-Bench and other reasoning tasks. PaLM 2 exhibits stable performance on a suite of responsible AI evaluations, and enables inference-time control over toxicity without additional overhead or impact on other capabilities. Overall, PaLM 2 achieves state-of-the-art performance across a diverse set of tasks and capabilities. When discussing the PaLM 2 family, it is important to distinguish between pre-trained models (of various sizes), fine-tuned variants of these models, and the user-facing products that use these models. In particular, user-facing products typically include additional pre- and post-processing steps. Additionally, the underlying models may evolve over time. Therefore, one should not expect the performance of user-facing products to exactly match the results reported in this report.
Scaling Up Models and Data with $\texttt{t5x}$ and $\texttt{seqio}$
Mar 31, 2022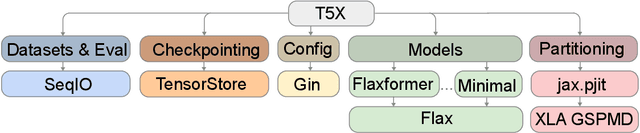
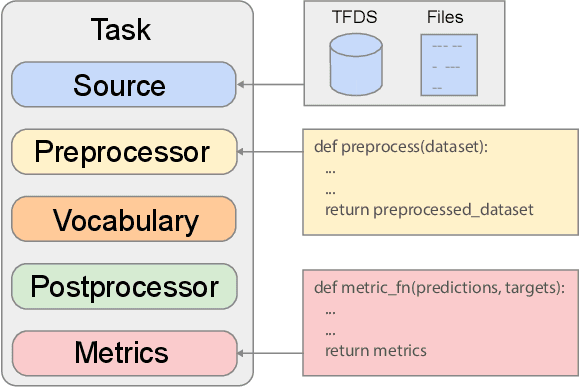
Abstract:Recent neural network-based language models have benefited greatly from scaling up the size of training datasets and the number of parameters in the models themselves. Scaling can be complicated due to various factors including the need to distribute computation on supercomputer clusters (e.g., TPUs), prevent bottlenecks when infeeding data, and ensure reproducible results. In this work, we present two software libraries that ease these issues: $\texttt{t5x}$ simplifies the process of building and training large language models at scale while maintaining ease of use, and $\texttt{seqio}$ provides a task-based API for simple creation of fast and reproducible training data and evaluation pipelines. These open-source libraries have been used to train models with hundreds of billions of parameters on datasets with multiple terabytes of training data. Along with the libraries, we release configurations and instructions for T5-like encoder-decoder models as well as GPT-like decoder-only architectures. $\texttt{t5x}$ and $\texttt{seqio}$ are open source and available at https://github.com/google-research/t5x and https://github.com/google/seqio, respectively.
FRUIT: Faithfully Reflecting Updated Information in Text
Dec 16, 2021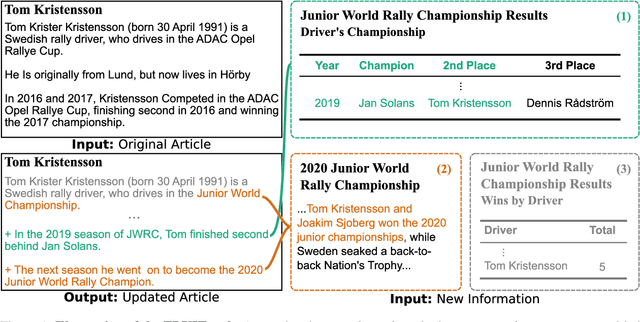
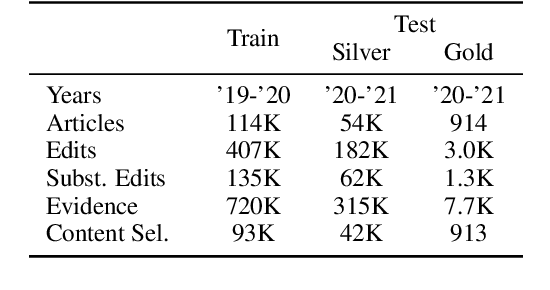


Abstract:Textual knowledge bases such as Wikipedia require considerable effort to keep up to date and consistent. While automated writing assistants could potentially ease this burden, the problem of suggesting edits grounded in external knowledge has been under-explored. In this paper, we introduce the novel generation task of *faithfully reflecting updated information in text*(FRUIT) where the goal is to update an existing article given new evidence. We release the FRUIT-WIKI dataset, a collection of over 170K distantly supervised data produced from pairs of Wikipedia snapshots, along with our data generation pipeline and a gold evaluation set of 914 instances whose edits are guaranteed to be supported by the evidence. We provide benchmark results for popular generation systems as well as EDIT5 -- a T5-based approach tailored to editing we introduce that establishes the state of the art. Our analysis shows that developing models that can update articles faithfully requires new capabilities for neural generation models, and opens doors to many new applications.
Faster Neural Network Training with Data Echoing
Jul 12, 2019



Abstract:In the twilight of Moore's law, GPUs and other specialized hardware accelerators have dramatically sped up neural network training. However, earlier stages of the training pipeline, such as disk I/O and data preprocessing, do not run on accelerators. As accelerators continue to improve, these earlier stages will increasingly become the bottleneck. In this paper, we introduce "data echoing," which reduces the total computation used by earlier pipeline stages and speeds up training whenever computation upstream from accelerators dominates the training time. Data echoing reuses (or "echoes") intermediate outputs from earlier pipeline stages in order to reclaim idle capacity. We investigate the behavior of different data echoing algorithms on various workloads, for various amounts of echoing, and for various batch sizes. We find that in all settings, at least one data echoing algorithm can match the baseline's predictive performance using less upstream computation. In some cases, data echoing can even compensate for a 4x slower input pipeline.
TensorFlow Eager: A Multi-Stage, Python-Embedded DSL for Machine Learning
Feb 27, 2019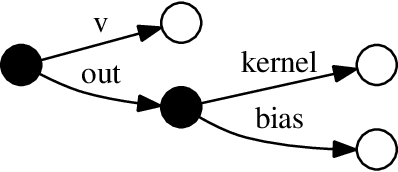
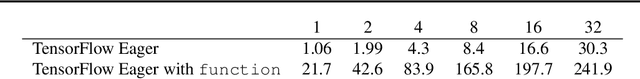
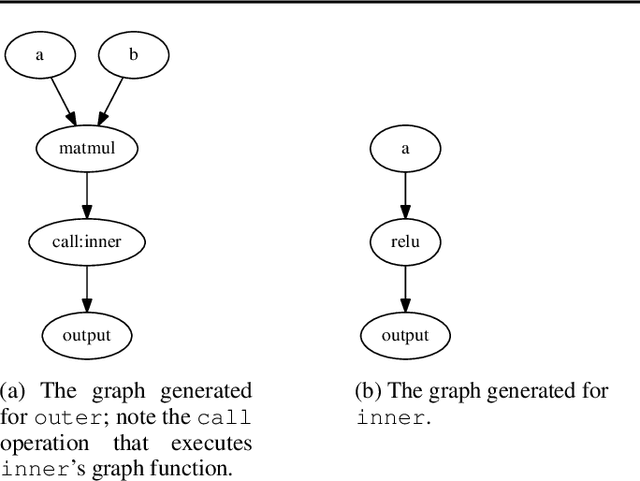
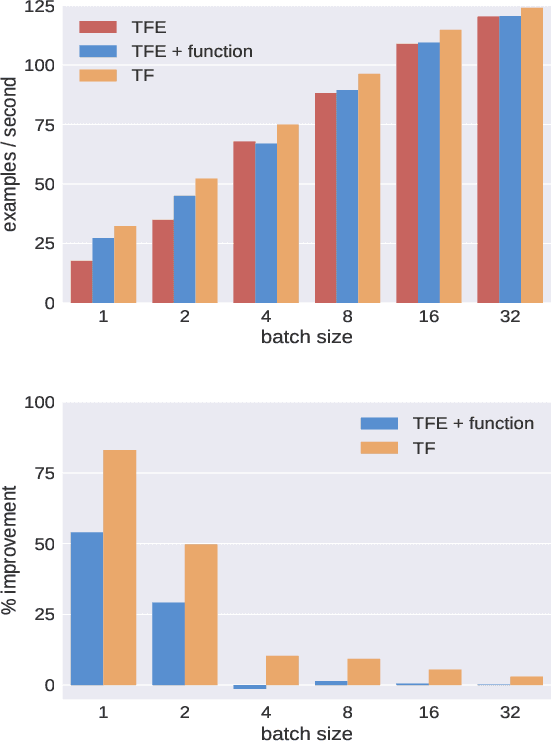
Abstract:TensorFlow Eager is a multi-stage, Python-embedded domain-specific language for hardware-accelerated machine learning, suitable for both interactive research and production. TensorFlow, which TensorFlow Eager extends, requires users to represent computations as dataflow graphs; this permits compiler optimizations and simplifies deployment but hinders rapid prototyping and run-time dynamism. TensorFlow Eager eliminates these usability costs without sacrificing the benefits furnished by graphs: It provides an imperative front-end to TensorFlow that executes operations immediately and a JIT tracer that translates Python functions composed of TensorFlow operations into executable dataflow graphs. TensorFlow Eager thus offers a multi-stage programming model that makes it easy to interpolate between imperative and staged execution in a single package.
Scikit-learn: Machine Learning in Python
Jun 05, 2018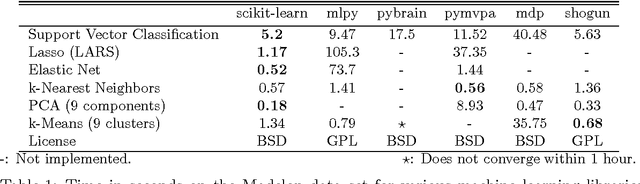
Abstract:Scikit-learn is a Python module integrating a wide range of state-of-the-art machine learning algorithms for medium-scale supervised and unsupervised problems. This package focuses on bringing machine learning to non-specialists using a general-purpose high-level language. Emphasis is put on ease of use, performance, documentation, and API consistency. It has minimal dependencies and is distributed under the simplified BSD license, encouraging its use in both academic and commercial settings. Source code, binaries, and documentation can be downloaded from http://scikit-learn.org.
* Update authors list and URLs
Large scale distributed neural network training through online distillation
Apr 09, 2018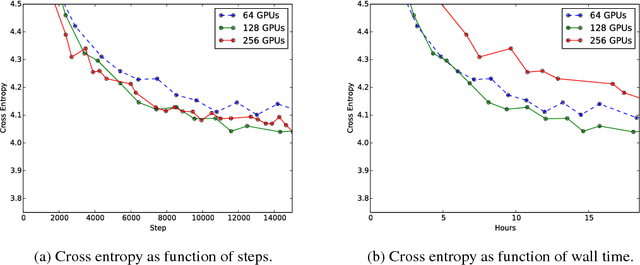

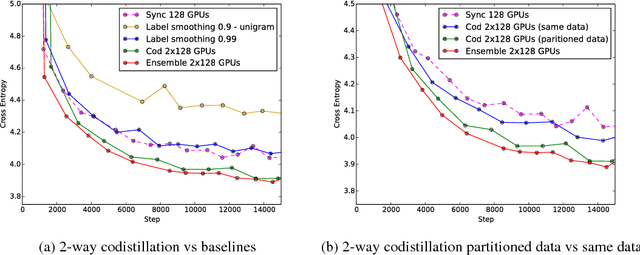
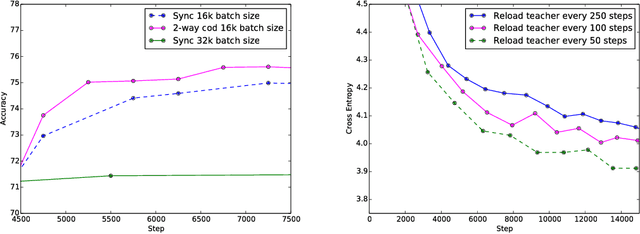
Abstract:Techniques such as ensembling and distillation promise model quality improvements when paired with almost any base model. However, due to increased test-time cost (for ensembles) and increased complexity of the training pipeline (for distillation), these techniques are challenging to use in industrial settings. In this paper we explore a variant of distillation which is relatively straightforward to use as it does not require a complicated multi-stage setup or many new hyperparameters. Our first claim is that online distillation enables us to use extra parallelism to fit very large datasets about twice as fast. Crucially, we can still speed up training even after we have already reached the point at which additional parallelism provides no benefit for synchronous or asynchronous stochastic gradient descent. Two neural networks trained on disjoint subsets of the data can share knowledge by encouraging each model to agree with the predictions the other model would have made. These predictions can come from a stale version of the other model so they can be safely computed using weights that only rarely get transmitted. Our second claim is that online distillation is a cost-effective way to make the exact predictions of a model dramatically more reproducible. We support our claims using experiments on the Criteo Display Ad Challenge dataset, ImageNet, and the largest to-date dataset used for neural language modeling, containing $6\times 10^{11}$ tokens and based on the Common Crawl repository of web data.
Efficient Non-parametric Estimation of Multiple Embeddings per Word in Vector Space
Apr 24, 2015



Abstract:There is rising interest in vector-space word embeddings and their use in NLP, especially given recent methods for their fast estimation at very large scale. Nearly all this work, however, assumes a single vector per word type ignoring polysemy and thus jeopardizing their usefulness for downstream tasks. We present an extension to the Skip-gram model that efficiently learns multiple embeddings per word type. It differs from recent related work by jointly performing word sense discrimination and embedding learning, by non-parametrically estimating the number of senses per word type, and by its efficiency and scalability. We present new state-of-the-art results in the word similarity in context task and demonstrate its scalability by training with one machine on a corpus of nearly 1 billion tokens in less than 6 hours.
Learning Soft Linear Constraints with Application to Citation Field Extraction
Oct 17, 2014



Abstract:Accurately segmenting a citation string into fields for authors, titles, etc. is a challenging task because the output typically obeys various global constraints. Previous work has shown that modeling soft constraints, where the model is encouraged, but not require to obey the constraints, can substantially improve segmentation performance. On the other hand, for imposing hard constraints, dual decomposition is a popular technique for efficient prediction given existing algorithms for unconstrained inference. We extend the technique to perform prediction subject to soft constraints. Moreover, with a technique for performing inference given soft constraints, it is easy to automatically generate large families of constraints and learn their costs with a simple convex optimization problem during training. This allows us to obtain substantial gains in accuracy on a new, challenging citation extraction dataset.
Lexicon Infused Phrase Embeddings for Named Entity Resolution
Apr 22, 2014



Abstract:Most state-of-the-art approaches for named-entity recognition (NER) use semi supervised information in the form of word clusters and lexicons. Recently neural network-based language models have been explored, as they as a byproduct generate highly informative vector representations for words, known as word embeddings. In this paper we present two contributions: a new form of learning word embeddings that can leverage information from relevant lexicons to improve the representations, and the first system to use neural word embeddings to achieve state-of-the-art results on named-entity recognition in both CoNLL and Ontonotes NER. Our system achieves an F1 score of 90.90 on the test set for CoNLL 2003---significantly better than any previous system trained on public data, and matching a system employing massive private industrial query-log data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge