Afroz Mohiuddin
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Scaling Up Models and Data with $\texttt{t5x}$ and $\texttt{seqio}$
Mar 31, 2022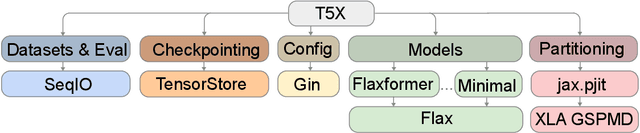
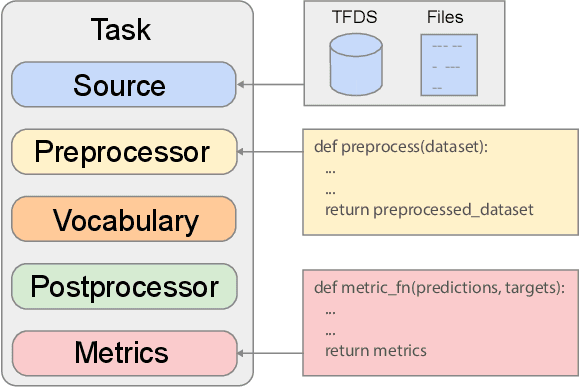
Abstract:Recent neural network-based language models have benefited greatly from scaling up the size of training datasets and the number of parameters in the models themselves. Scaling can be complicated due to various factors including the need to distribute computation on supercomputer clusters (e.g., TPUs), prevent bottlenecks when infeeding data, and ensure reproducible results. In this work, we present two software libraries that ease these issues: $\texttt{t5x}$ simplifies the process of building and training large language models at scale while maintaining ease of use, and $\texttt{seqio}$ provides a task-based API for simple creation of fast and reproducible training data and evaluation pipelines. These open-source libraries have been used to train models with hundreds of billions of parameters on datasets with multiple terabytes of training data. Along with the libraries, we release configurations and instructions for T5-like encoder-decoder models as well as GPT-like decoder-only architectures. $\texttt{t5x}$ and $\texttt{seqio}$ are open source and available at https://github.com/google-research/t5x and https://github.com/google/seqio, respectively.
Sparse is Enough in Scaling Transformers
Nov 24, 2021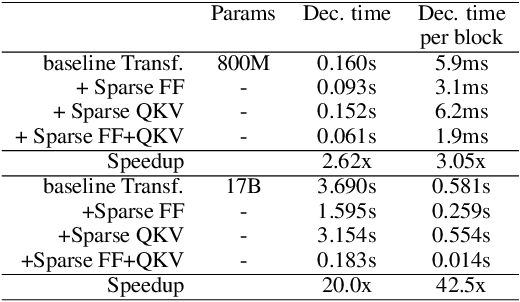
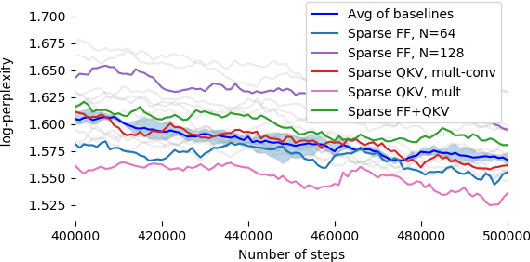
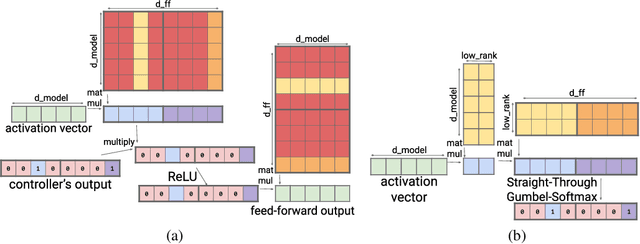
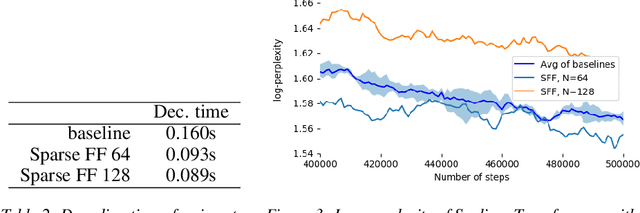
Abstract:Large Transformer models yield impressive results on many tasks, but are expensive to train, or even fine-tune, and so slow at decoding that their use and study becomes out of reach. We address this problem by leveraging sparsity. We study sparse variants for all layers in the Transformer and propose Scaling Transformers, a family of next generation Transformer models that use sparse layers to scale efficiently and perform unbatched decoding much faster than the standard Transformer as we scale up the model size. Surprisingly, the sparse layers are enough to obtain the same perplexity as the standard Transformer with the same number of parameters. We also integrate with prior sparsity approaches to attention and enable fast inference on long sequences even with limited memory. This results in performance competitive to the state-of-the-art on long text summarization.
Q-Value Weighted Regression: Reinforcement Learning with Limited Data
Feb 12, 2021
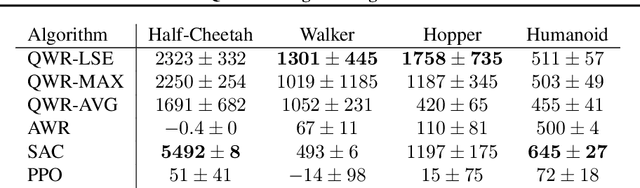
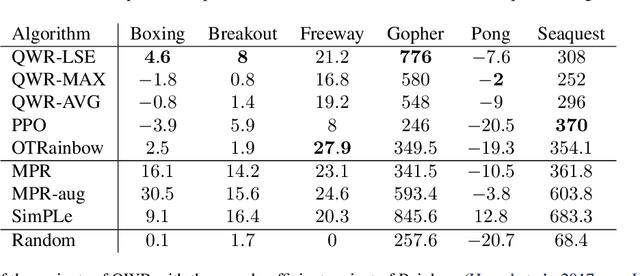
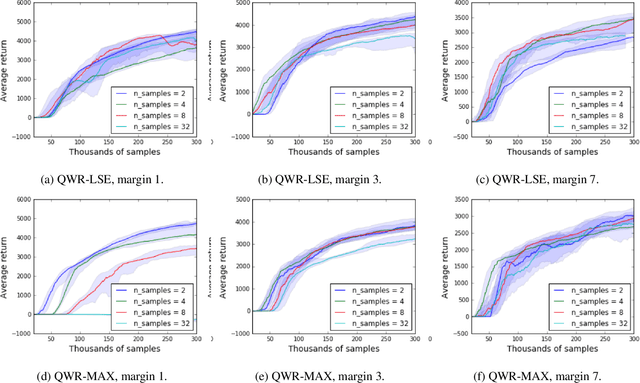
Abstract:Sample efficiency and performance in the offline setting have emerged as significant challenges of deep reinforcement learning. We introduce Q-Value Weighted Regression (QWR), a simple RL algorithm that excels in these aspects. QWR is an extension of Advantage Weighted Regression (AWR), an off-policy actor-critic algorithm that performs very well on continuous control tasks, also in the offline setting, but has low sample efficiency and struggles with high-dimensional observation spaces. We perform an analysis of AWR that explains its shortcomings and use these insights to motivate QWR. We show experimentally that QWR matches the state-of-the-art algorithms both on tasks with continuous and discrete actions. In particular, QWR yields results on par with SAC on the MuJoCo suite and - with the same set of hyperparameters - yields results on par with a highly tuned Rainbow implementation on a set of Atari games. We also verify that QWR performs well in the offline RL setting.
Rethinking Attention with Performers
Sep 30, 2020
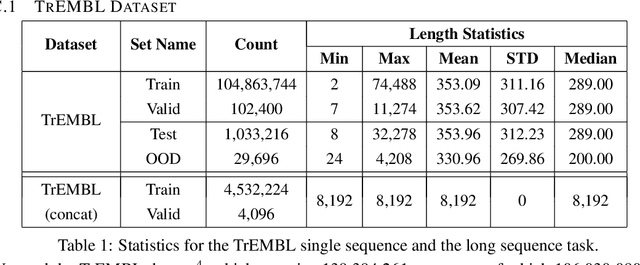

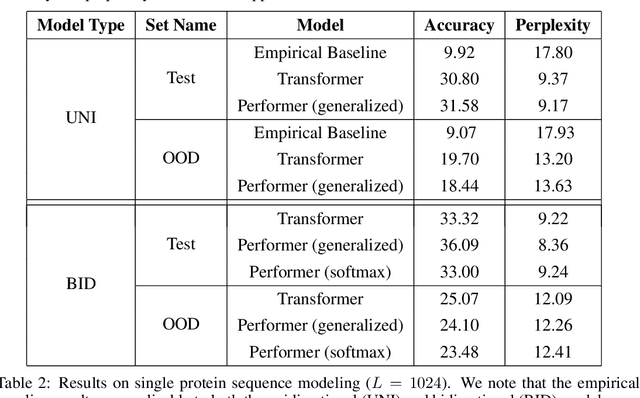
Abstract:We introduce Performers, Transformer architectures which can estimate regular (softmax) full-rank-attention Transformers with provable accuracy, but using only linear (as opposed to quadratic) space and time complexity, without relying on any priors such as sparsity or low-rankness. To approximate softmax attention-kernels, Performers use a novel Fast Attention Via positive Orthogonal Random features approach (FAVOR+), which may be of independent interest for scalable kernel methods. FAVOR+ can be also used to efficiently model kernelizable attention mechanisms beyond softmax. This representational power is crucial to accurately compare softmax with other kernels for the first time on large-scale tasks, beyond the reach of regular Transformers, and investigate optimal attention-kernels. Performers are linear architectures fully compatible with regular Transformers and with strong theoretical guarantees: unbiased or nearly-unbiased estimation of the attention matrix, uniform convergence and low estimation variance. We tested Performers on a rich set of tasks stretching from pixel-prediction through text models to protein sequence modeling. We demonstrate competitive results with other examined efficient sparse and dense attention methods, showcasing effectiveness of the novel attention-learning paradigm leveraged by Performers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge