Gamaleldin Elsayed
Training Language Models on the Knowledge Graph: Insights on Hallucinations and Their Detectability
Aug 14, 2024



Abstract:While many capabilities of language models (LMs) improve with increased training budget, the influence of scale on hallucinations is not yet fully understood. Hallucinations come in many forms, and there is no universally accepted definition. We thus focus on studying only those hallucinations where a correct answer appears verbatim in the training set. To fully control the training data content, we construct a knowledge graph (KG)-based dataset, and use it to train a set of increasingly large LMs. We find that for a fixed dataset, larger and longer-trained LMs hallucinate less. However, hallucinating on $\leq5$% of the training data requires an order of magnitude larger model, and thus an order of magnitude more compute, than Hoffmann et al. (2022) reported was optimal. Given this costliness, we study how hallucination detectors depend on scale. While we see detector size improves performance on fixed LM's outputs, we find an inverse relationship between the scale of the LM and the detectability of its hallucinations.
Gemini 1.5: Unlocking multimodal understanding across millions of tokens of context
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:In this report, we present the latest model of the Gemini family, Gemini 1.5 Pro, a highly compute-efficient multimodal mixture-of-experts model capable of recalling and reasoning over fine-grained information from millions of tokens of context, including multiple long documents and hours of video and audio. Gemini 1.5 Pro achieves near-perfect recall on long-context retrieval tasks across modalities, improves the state-of-the-art in long-document QA, long-video QA and long-context ASR, and matches or surpasses Gemini 1.0 Ultra's state-of-the-art performance across a broad set of benchmarks. Studying the limits of Gemini 1.5 Pro's long-context ability, we find continued improvement in next-token prediction and near-perfect retrieval (>99%) up to at least 10M tokens, a generational leap over existing models such as Claude 2.1 (200k) and GPT-4 Turbo (128k). Finally, we highlight surprising new capabilities of large language models at the frontier; when given a grammar manual for Kalamang, a language with fewer than 200 speakers worldwide, the model learns to translate English to Kalamang at a similar level to a person who learned from the same content.
Beyond Human Data: Scaling Self-Training for Problem-Solving with Language Models
Dec 22, 2023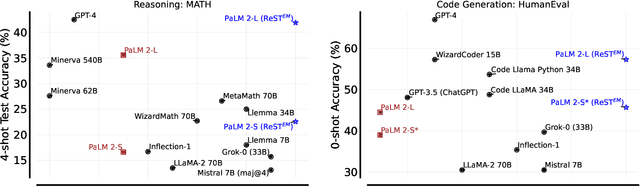
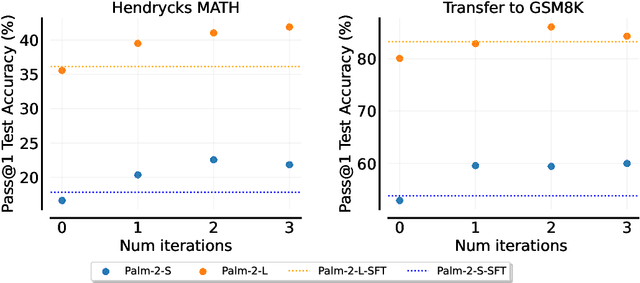
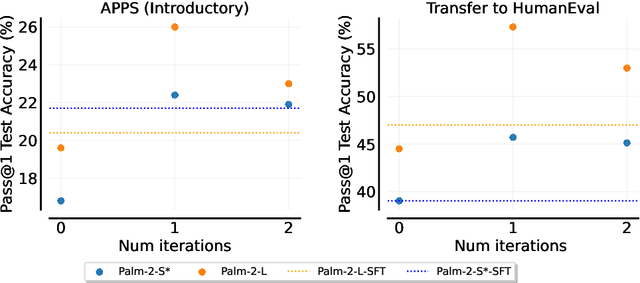
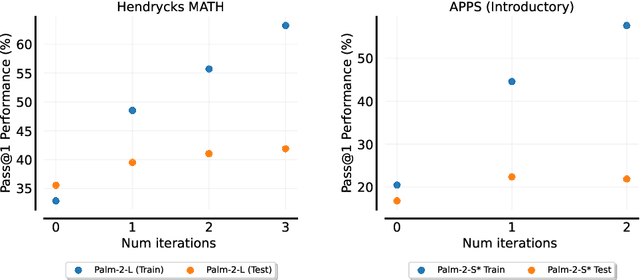
Abstract:Fine-tuning language models~(LMs) on human-generated data remains a prevalent practice. However, the performance of such models is often limited by the quantity and diversity of high-quality human data. In this paper, we explore whether we can go beyond human data on tasks where we have access to scalar feedback, for example, on math problems where one can verify correctness. To do so, we investigate a simple self-training method based on expectation-maximization, which we call ReST$^{EM}$, where we (1) generate samples from the model and filter them using binary feedback, (2) fine-tune the model on these samples, and (3) repeat this process a few times. Testing on advanced MATH reasoning and APPS coding benchmarks using PaLM-2 models, we find that ReST$^{EM}$ scales favorably with model size and significantly surpasses fine-tuning only on human data. Overall, our findings suggest self-training with feedback can substantially reduce dependence on human-generated data.
Gemini: A Family of Highly Capable Multimodal Models
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:This report introduces a new family of multimodal models, Gemini, that exhibit remarkable capabilities across image, audio, video, and text understanding. The Gemini family consists of Ultra, Pro, and Nano sizes, suitable for applications ranging from complex reasoning tasks to on-device memory-constrained use-cases. Evaluation on a broad range of benchmarks shows that our most-capable Gemini Ultra model advances the state of the art in 30 of 32 of these benchmarks - notably being the first model to achieve human-expert performance on the well-studied exam benchmark MMLU, and improving the state of the art in every one of the 20 multimodal benchmarks we examined. We believe that the new capabilities of Gemini models in cross-modal reasoning and language understanding will enable a wide variety of use cases and we discuss our approach toward deploying them responsibly to users.
Affective Visual Dialog: A Large-Scale Benchmark for Emotional Reasoning Based on Visually Grounded Conversations
Sep 12, 2023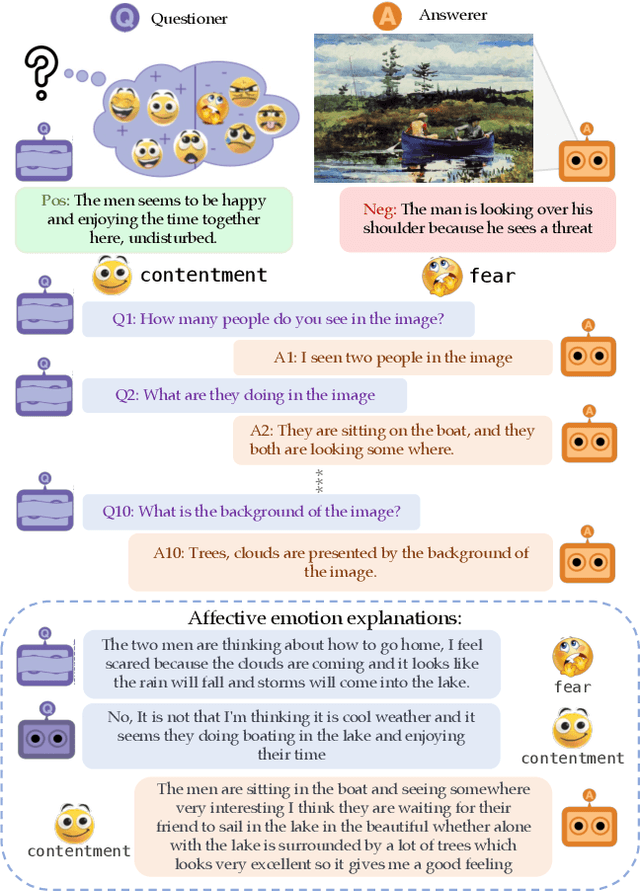
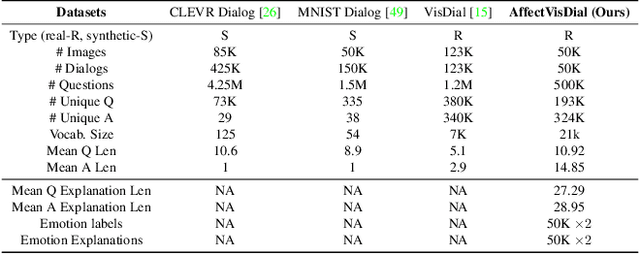

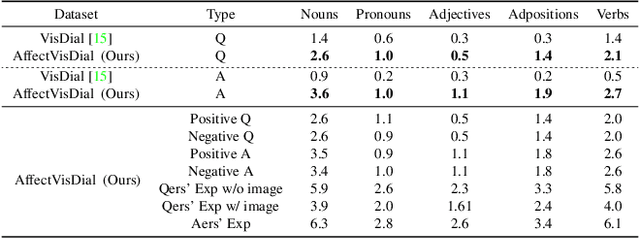
Abstract:We introduce Affective Visual Dialog, an emotion explanation and reasoning task as a testbed for research on understanding the formation of emotions in visually grounded conversations. The task involves three skills: (1) Dialog-based Question Answering (2) Dialog-based Emotion Prediction and (3) Affective emotion explanation generation based on the dialog. Our key contribution is the collection of a large-scale dataset, dubbed AffectVisDial, consisting of 50K 10-turn visually grounded dialogs as well as concluding emotion attributions and dialog-informed textual emotion explanations, resulting in a total of 27,180 working hours. We explain our design decisions in collecting the dataset and introduce the questioner and answerer tasks that are associated with the participants in the conversation. We train and demonstrate solid Affective Visual Dialog baselines adapted from state-of-the-art models. Remarkably, the responses generated by our models show promising emotional reasoning abilities in response to visually grounded conversations. Our project page is available at https://affective-visual-dialog.github.io.
RSN: Range Sparse Net for Efficient, Accurate LiDAR 3D Object Detection
Jun 25, 2021



Abstract:The detection of 3D objects from LiDAR data is a critical component in most autonomous driving systems. Safe, high speed driving needs larger detection ranges, which are enabled by new LiDARs. These larger detection ranges require more efficient and accurate detection models. Towards this goal, we propose Range Sparse Net (RSN), a simple, efficient, and accurate 3D object detector in order to tackle real time 3D object detection in this extended detection regime. RSN predicts foreground points from range images and applies sparse convolutions on the selected foreground points to detect objects. The lightweight 2D convolutions on dense range images results in significantly fewer selected foreground points, thus enabling the later sparse convolutions in RSN to efficiently operate. Combining features from the range image further enhance detection accuracy. RSN runs at more than 60 frames per second on a 150m x 150m detection region on Waymo Open Dataset (WOD) while being more accurate than previously published detectors. As of 11/2020, RSN is ranked first in the WOD leaderboard based on the APH/LEVEL 1 metrics for LiDAR-based pedestrian and vehicle detection, while being several times faster than alternatives.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge