Jun-Yan He
Emotion-LLaMAv2 and MMEVerse: A New Framework and Benchmark for Multimodal Emotion Understanding
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Understanding human emotions from multimodal signals poses a significant challenge in affective computing and human-robot interaction. While multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have excelled in general vision-language tasks, their capabilities in emotional reasoning remain limited. The field currently suffers from a scarcity of large-scale datasets with high-quality, descriptive emotion annotations and lacks standardized benchmarks for evaluation. Our preliminary framework, Emotion-LLaMA, pioneered instruction-tuned multimodal learning for emotion reasoning but was restricted by explicit face detectors, implicit fusion strategies, and low-quality training data with limited scale. To address these limitations, we present Emotion-LLaMAv2 and the MMEVerse benchmark, establishing an end-to-end pipeline together with a standardized evaluation setting for emotion recognition and reasoning. Emotion-LLaMAv2 introduces three key advances. First, an end-to-end multiview encoder eliminates external face detection and captures nuanced emotional cues via richer spatial and temporal multiview tokens. Second, a Conv Attention pre-fusion module is designed to enable simultaneous local and global multimodal feature interactions external to the LLM backbone. Third, a perception-to-cognition curriculum instruction tuning scheme within the LLaMA2 backbone unifies emotion recognition and free-form emotion reasoning. To support large-scale training and reproducible evaluation, MMEVerse aggregates twelve publicly available emotion datasets, including IEMOCAP, MELD, DFEW, and MAFW, into a unified multimodal instruction format. The data are re-annotated via a multi-agent pipeline involving Qwen2 Audio, Qwen2.5 VL, and GPT 4o, producing 130k training clips and 36k testing clips across 18 evaluation benchmarks.
LongCat-Image Technical Report
Dec 08, 2025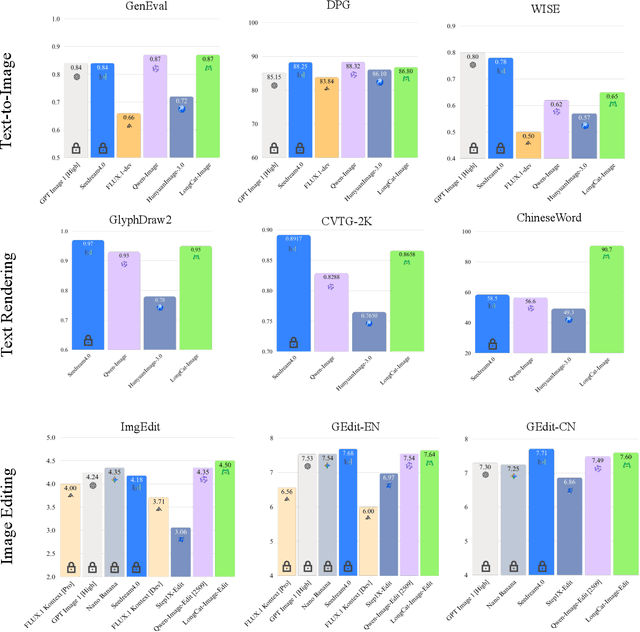

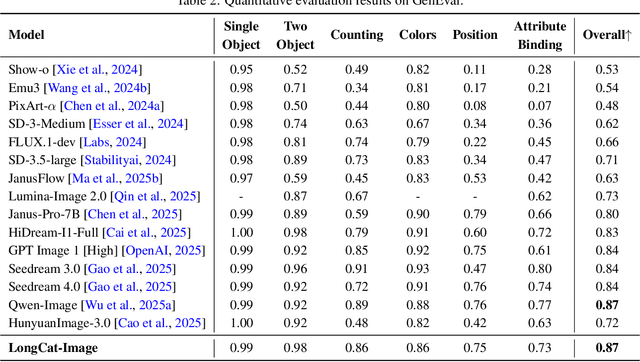
Abstract:We introduce LongCat-Image, a pioneering open-source and bilingual (Chinese-English) foundation model for image generation, designed to address core challenges in multilingual text rendering, photorealism, deployment efficiency, and developer accessibility prevalent in current leading models. 1) We achieve this through rigorous data curation strategies across the pre-training, mid-training, and SFT stages, complemented by the coordinated use of curated reward models during the RL phase. This strategy establishes the model as a new state-of-the-art (SOTA), delivering superior text-rendering capabilities and remarkable photorealism, and significantly enhancing aesthetic quality. 2) Notably, it sets a new industry standard for Chinese character rendering. By supporting even complex and rare characters, it outperforms both major open-source and commercial solutions in coverage, while also achieving superior accuracy. 3) The model achieves remarkable efficiency through its compact design. With a core diffusion model of only 6B parameters, it is significantly smaller than the nearly 20B or larger Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures common in the field. This ensures minimal VRAM usage and rapid inference, significantly reducing deployment costs. Beyond generation, LongCat-Image also excels in image editing, achieving SOTA results on standard benchmarks with superior editing consistency compared to other open-source works. 4) To fully empower the community, we have established the most comprehensive open-source ecosystem to date. We are releasing not only multiple model versions for text-to-image and image editing, including checkpoints after mid-training and post-training stages, but also the entire toolchain of training procedure. We believe that the openness of LongCat-Image will provide robust support for developers and researchers, pushing the frontiers of visual content creation.
Why We Feel: Breaking Boundaries in Emotional Reasoning with Multimodal Large Language Models
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Most existing emotion analysis emphasizes which emotion arises (e.g., happy, sad, angry) but neglects the deeper why. We propose Emotion Interpretation (EI), focusing on causal factors-whether explicit (e.g., observable objects, interpersonal interactions) or implicit (e.g., cultural context, off-screen events)-that drive emotional responses. Unlike traditional emotion recognition, EI tasks require reasoning about triggers instead of mere labeling. To facilitate EI research, we present EIBench, a large-scale benchmark encompassing 1,615 basic EI samples and 50 complex EI samples featuring multifaceted emotions. Each instance demands rationale-based explanations rather than straightforward categorization. We further propose a Coarse-to-Fine Self-Ask (CFSA) annotation pipeline, which guides Vision-Language Models (VLLMs) through iterative question-answer rounds to yield high-quality labels at scale. Extensive evaluations on open-source and proprietary large language models under four experimental settings reveal consistent performance gaps-especially for more intricate scenarios-underscoring EI's potential to enrich empathetic, context-aware AI applications. Our benchmark and methods are publicly available at: https://github.com/Lum1104/EIBench, offering a foundation for advanced multimodal causal analysis and next-generation affective computing.
UCDR-Adapter: Exploring Adaptation of Pre-Trained Vision-Language Models for Universal Cross-Domain Retrieval
Dec 14, 2024



Abstract:Universal Cross-Domain Retrieval (UCDR) retrieves relevant images from unseen domains and classes without semantic labels, ensuring robust generalization. Existing methods commonly employ prompt tuning with pre-trained vision-language models but are inherently limited by static prompts, reducing adaptability. We propose UCDR-Adapter, which enhances pre-trained models with adapters and dynamic prompt generation through a two-phase training strategy. First, Source Adapter Learning integrates class semantics with domain-specific visual knowledge using a Learnable Textual Semantic Template and optimizes Class and Domain Prompts via momentum updates and dual loss functions for robust alignment. Second, Target Prompt Generation creates dynamic prompts by attending to masked source prompts, enabling seamless adaptation to unseen domains and classes. Unlike prior approaches, UCDR-Adapter dynamically adapts to evolving data distributions, enhancing both flexibility and generalization. During inference, only the image branch and generated prompts are used, eliminating reliance on textual inputs for highly efficient retrieval. Extensive benchmark experiments show that UCDR-Adapter consistently outperforms ProS in most cases and other state-of-the-art methods on UCDR, U(c)CDR, and U(d)CDR settings.
GLDesigner: Leveraging Multi-Modal LLMs as Designer for Enhanced Aesthetic Text Glyph Layouts
Nov 18, 2024

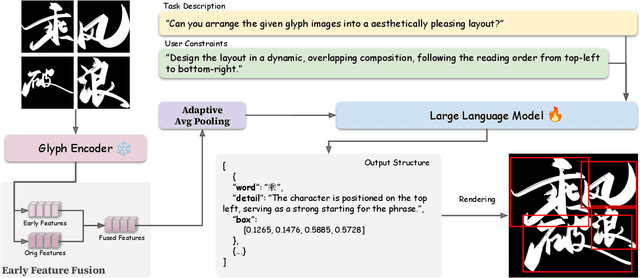
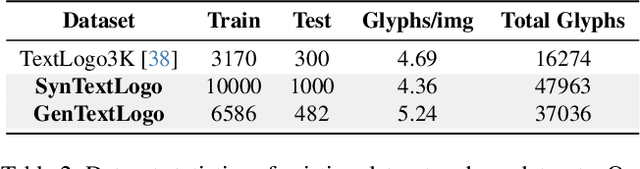
Abstract:Text logo design heavily relies on the creativity and expertise of professional designers, in which arranging element layouts is one of the most important procedures. However, few attention has been paid to this specific task which needs to take precise textural details and user constraints into consideration, but only on the broader tasks such as document/poster layout generation. In this paper, we propose a VLM-based framework that generates content-aware text logo layouts by integrating multi-modal inputs with user constraints, supporting a more flexible and stable layout design in real-world applications. We introduce two model techniques to reduce the computation for processing multiple glyph images simultaneously, while does not face performance degradation. To support instruction-tuning of out model, we construct two extensive text logo datasets, which are 5x more larger than the existing public dataset. Except for the geometric annotations (e.g. text masks and character recognition), we also compliment with comprehensive layout descriptions in natural language format, for more effective training to have reasoning ability when dealing with complex layouts and custom user constraints. Experimental studies demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed model and datasets, when comparing with previous methods in various benchmarks to evaluate geometric aesthetics and human preferences. The code and datasets will be publicly available.
POPoS: Improving Efficient and Robust Facial Landmark Detection with Parallel Optimal Position Search
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:Achieving a balance between accuracy and efficiency is a critical challenge in facial landmark detection (FLD). This paper introduces the Parallel Optimal Position Search (POPoS), a high-precision encoding-decoding framework designed to address the fundamental limitations of traditional FLD methods. POPoS employs three key innovations: (1) Pseudo-range multilateration is utilized to correct heatmap errors, enhancing the precision of landmark localization. By integrating multiple anchor points, this approach minimizes the impact of individual heatmap inaccuracies, leading to robust overall positioning. (2) To improve the pseudo-range accuracy of selected anchor points, a new loss function, named multilateration anchor loss, is proposed. This loss function effectively enhances the accuracy of the distance map, mitigates the risk of local optima, and ensures optimal solutions. (3) A single-step parallel computation algorithm is introduced, significantly enhancing computational efficiency and reducing processing time. Comprehensive evaluations across five benchmark datasets demonstrate that POPoS consistently outperforms existing methods, particularly excelling in low-resolution scenarios with minimal computational overhead. These features establish POPoS as a highly efficient and accurate tool for FLD, with broad applicability in real-world scenarios. The code is available at https://github.com/teslatasy/PoPoS
MetaDesigner: Advancing Artistic Typography through AI-Driven, User-Centric, and Multilingual WordArt Synthesis
Jun 28, 2024
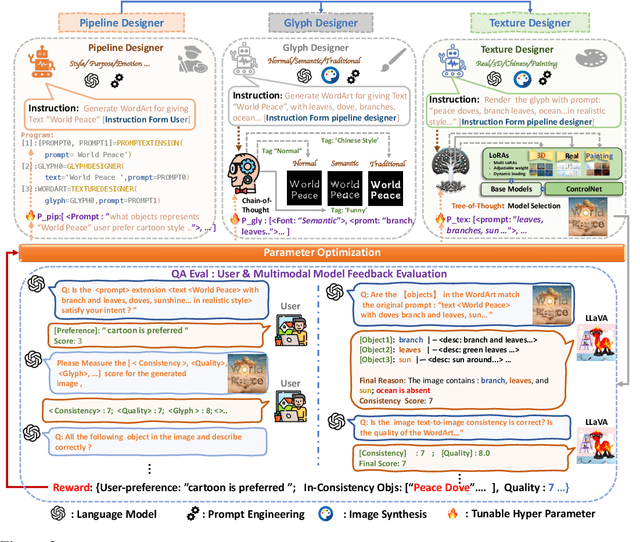
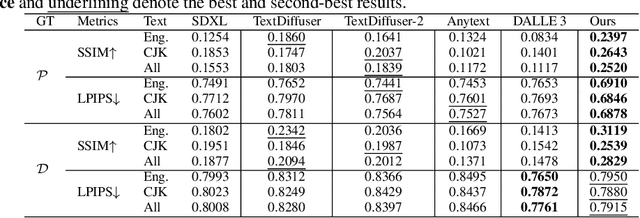
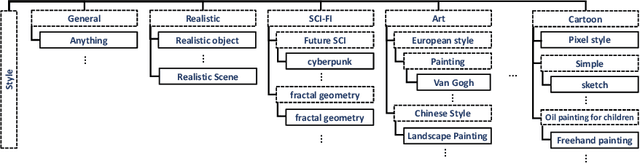
Abstract:MetaDesigner revolutionizes artistic typography synthesis by leveraging the strengths of Large Language Models (LLMs) to drive a design paradigm centered around user engagement. At the core of this framework lies a multi-agent system comprising the Pipeline, Glyph, and Texture agents, which collectively enable the creation of customized WordArt, ranging from semantic enhancements to the imposition of complex textures. MetaDesigner incorporates a comprehensive feedback mechanism that harnesses insights from multimodal models and user evaluations to refine and enhance the design process iteratively. Through this feedback loop, the system adeptly tunes hyperparameters to align with user-defined stylistic and thematic preferences, generating WordArt that not only meets but exceeds user expectations of visual appeal and contextual relevance. Empirical validations highlight MetaDesigner's capability to effectively serve diverse WordArt applications, consistently producing aesthetically appealing and context-sensitive results.
Human-Aware Vision-and-Language Navigation: Bridging Simulation to Reality with Dynamic Human Interactions
Jun 27, 2024



Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN) aims to develop embodied agents that navigate based on human instructions. However, current VLN frameworks often rely on static environments and optimal expert supervision, limiting their real-world applicability. To address this, we introduce Human-Aware Vision-and-Language Navigation (HA-VLN), extending traditional VLN by incorporating dynamic human activities and relaxing key assumptions. We propose the Human-Aware 3D (HA3D) simulator, which combines dynamic human activities with the Matterport3D dataset, and the Human-Aware Room-to-Room (HA-R2R) dataset, extending R2R with human activity descriptions. To tackle HA-VLN challenges, we present the Expert-Supervised Cross-Modal (VLN-CM) and Non-Expert-Supervised Decision Transformer (VLN-DT) agents, utilizing cross-modal fusion and diverse training strategies for effective navigation in dynamic human environments. A comprehensive evaluation, including metrics considering human activities, and systematic analysis of HA-VLN's unique challenges, underscores the need for further research to enhance HA-VLN agents' real-world robustness and adaptability. Ultimately, this work provides benchmarks and insights for future research on embodied AI and Sim2Real transfer, paving the way for more realistic and applicable VLN systems in human-populated environments.
Emotion-LLaMA: Multimodal Emotion Recognition and Reasoning with Instruction Tuning
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Accurate emotion perception is crucial for various applications, including human-computer interaction, education, and counseling. However, traditional single-modality approaches often fail to capture the complexity of real-world emotional expressions, which are inherently multimodal. Moreover, existing Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) face challenges in integrating audio and recognizing subtle facial micro-expressions. To address this, we introduce the MERR dataset, containing 28,618 coarse-grained and 4,487 fine-grained annotated samples across diverse emotional categories. This dataset enables models to learn from varied scenarios and generalize to real-world applications. Furthermore, we propose Emotion-LLaMA, a model that seamlessly integrates audio, visual, and textual inputs through emotion-specific encoders. By aligning features into a shared space and employing a modified LLaMA model with instruction tuning, Emotion-LLaMA significantly enhances both emotional recognition and reasoning capabilities. Extensive evaluations show Emotion-LLaMA outperforms other MLLMs, achieving top scores in Clue Overlap (7.83) and Label Overlap (6.25) on EMER, an F1 score of 0.9036 on MER2023 challenge, and the highest UAR (45.59) and WAR (59.37) in zero-shot evaluations on DFEW dataset.
MM-TTS: A Unified Framework for Multimodal, Prompt-Induced Emotional Text-to-Speech Synthesis
Apr 29, 2024



Abstract:Emotional Text-to-Speech (E-TTS) synthesis has gained significant attention in recent years due to its potential to enhance human-computer interaction. However, current E-TTS approaches often struggle to capture the complexity of human emotions, primarily relying on oversimplified emotional labels or single-modality inputs. To address these limitations, we propose the Multimodal Emotional Text-to-Speech System (MM-TTS), a unified framework that leverages emotional cues from multiple modalities to generate highly expressive and emotionally resonant speech. MM-TTS consists of two key components: (1) the Emotion Prompt Alignment Module (EP-Align), which employs contrastive learning to align emotional features across text, audio, and visual modalities, ensuring a coherent fusion of multimodal information; and (2) the Emotion Embedding-Induced TTS (EMI-TTS), which integrates the aligned emotional embeddings with state-of-the-art TTS models to synthesize speech that accurately reflects the intended emotions. Extensive evaluations across diverse datasets demonstrate the superior performance of MM-TTS compared to traditional E-TTS models. Objective metrics, including Word Error Rate (WER) and Character Error Rate (CER), show significant improvements on ESD dataset, with MM-TTS achieving scores of 7.35% and 3.07%, respectively. Subjective assessments further validate that MM-TTS generates speech with emotional fidelity and naturalness comparable to human speech. Our code and pre-trained models are publicly available at https://anonymous.4open.science/r/MMTTS-D214
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge