Haoyu Jiang
Helios: A Foundational Language Model for Smart Energy Knowledge Reasoning and Application
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:In the global drive toward carbon neutrality, deeply coordinated smart energy systems underpin industrial transformation. However, the interdisciplinary, fragmented, and fast-evolving expertise in this domain prevents general-purpose LLMs, which lack domain knowledge and physical-constraint awareness, from delivering precise engineering-aligned inference and generation. To address these challenges, we introduce Helios, a large language model tailored to the smart energy domain, together with a comprehensive suite of resources to advance LLM research in this field. Specifically, we develop Enersys, a multi-agent collaborative framework for end-to-end dataset construction, through which we produce: (1) a smart energy knowledge base, EnerBase, to enrich the model's foundational expertise; (2) an instruction fine-tuning dataset, EnerInstruct, to strengthen performance on domain-specific downstream tasks; and (3) an RLHF dataset, EnerReinforce, to align the model with human preferences and industry standards. Leveraging these resources, Helios undergoes large-scale pretraining, SFT, and RLHF. We also release EnerBench, a benchmark for evaluating LLMs in smart energy scenarios, and demonstrate that our approach significantly enhances domain knowledge mastery, task execution accuracy, and alignment with human preferences.
HyperLoad: A Cross-Modality Enhanced Large Language Model-Based Framework for Green Data Center Cooling Load Prediction
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:The rapid growth of artificial intelligence is exponentially escalating computational demand, inflating data center energy use and carbon emissions, and spurring rapid deployment of green data centers to relieve resource and environmental stress. Achieving sub-minute orchestration of renewables, storage, and loads, while minimizing PUE and lifecycle carbon intensity, hinges on accurate load forecasting. However, existing methods struggle to address small-sample scenarios caused by cold start, load distortion, multi-source data fragmentation, and distribution shifts in green data centers. We introduce HyperLoad, a cross-modality framework that exploits pre-trained large language models (LLMs) to overcome data scarcity. In the Cross-Modality Knowledge Alignment phase, textual priors and time-series data are mapped to a common latent space, maximizing the utility of prior knowledge. In the Multi-Scale Feature Modeling phase, domain-aligned priors are injected through adaptive prefix-tuning, enabling rapid scenario adaptation, while an Enhanced Global Interaction Attention mechanism captures cross-device temporal dependencies. The public DCData dataset is released for benchmarking. Under both data sufficient and data scarce settings, HyperLoad consistently surpasses state-of-the-art (SOTA) baselines, demonstrating its practicality for sustainable green data center management.
Data Fusion for BS-UE Cooperative MIMO-OFDM ISAC
Sep 16, 2025Abstract:Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) is a promising technique for expanding the functionalities of wireless networks with enhanced spectral efficiency. The 3rd Generation Partnership Project (3GPP) has defined six basic sensing operation modes in wireless networks. To further enhance the sensing capability of wireless networks, this paper proposes a new sensing operation mode, i.e., the base station (BS) and user equipment (UE) cooperative sensing. Specifically, after decoding the communication data, the UE further processes the received signal to extract the target sensing information. We propose an efficient algorithm for fusing the sensing results obtained by the BS and UE, by exploiting the geometric relationship among BS, UE and targets as well as the expected sensing quality in the BS monostatic and BS-UE bistatic sensing. The results show that the proposed data fusion method for cooperative sensing can effectively improve the position and velocity estimation accuracy of multiple targets, and provide a new approach on the expansion of the sensing pattern.
Simulation-based Inference via Langevin Dynamics with Score Matching
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Simulation-based inference (SBI) enables Bayesian analysis when the likelihood is intractable but model simulations are available. Recent advances in statistics and machine learning, including Approximate Bayesian Computation and deep generative models, have expanded the applicability of SBI, yet these methods often face challenges in moderate to high-dimensional parameter spaces. Motivated by the success of gradient-based Monte Carlo methods in Bayesian sampling, we propose a novel SBI method that integrates score matching with Langevin dynamics to explore complex posterior landscapes more efficiently in such settings. Our approach introduces tailored score-matching procedures for SBI, including a localization scheme that reduces simulation costs and an architectural regularization that embeds the statistical structure of log-likelihood scores to improve score-matching accuracy. We provide theoretical analysis of the method and illustrate its practical benefits on benchmark tasks and on more challenging problems in moderate to high dimensions, where it performs favorably compared to existing approaches.
Ray Antenna Array Achieves Uniform Angular Resolution Cost-Effectively for Low-Altitude UAV Swarm ISAC
May 15, 2025Abstract:Ray antenna array (RAA) is a novel multi-antenna architecture comprising massive low-cost antenna elements and a few radio-frequency (RF) chains. The antenna elements are arranged in a novel ray-like structure, where each ray corresponds to a simple uniform linear array (sULA) with deliberately designed orientation and all its antenna elements are directly connected. By further designing a ray selection network (RSN), appropriate sULAs are selected to connect to the RF chains for further baseband processing. RAA has three appealing advantages: (i) dramatically reduced hardware cost since no phase shifters are needed; (ii) enhanced beamforming gain as antenna elements with higher directivity can be used; (iii) uniform angular resolution across all signal directions. Such benefits make RAA especially appealing for integrated sensing and communication (ISAC), particularly for low-altitude unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) swarm ISAC, where high-mobility aerial targets may easily move away from the boresight of conventional antenna arrays, causing severe communication and sensing performance degradation. Therefore, this paper studies RAA-based ISAC for low-altitude UAV swarm systems. First, we establish an input-output mathematical model for RAA-based UAV ISAC and rigorously show that RAA achieves uniform angular resolution for all directions. Besides, we design the RAA orientation and RSN. Furthermore, RAA-based ISAC with orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) for UAV swarm is studied, and efficient algorithm is proposed for sensing target parameter estimation. Extensive simulation results demonstrate the significant performance improvement by RAA system over the conventional antenna arrays, in terms of sensing angular resolution and communication spectral efficiency, highlighting the great potential of the novel RAA system to meet the growing demands of low-altitude UAV ISAC.
UCDR-Adapter: Exploring Adaptation of Pre-Trained Vision-Language Models for Universal Cross-Domain Retrieval
Dec 14, 2024



Abstract:Universal Cross-Domain Retrieval (UCDR) retrieves relevant images from unseen domains and classes without semantic labels, ensuring robust generalization. Existing methods commonly employ prompt tuning with pre-trained vision-language models but are inherently limited by static prompts, reducing adaptability. We propose UCDR-Adapter, which enhances pre-trained models with adapters and dynamic prompt generation through a two-phase training strategy. First, Source Adapter Learning integrates class semantics with domain-specific visual knowledge using a Learnable Textual Semantic Template and optimizes Class and Domain Prompts via momentum updates and dual loss functions for robust alignment. Second, Target Prompt Generation creates dynamic prompts by attending to masked source prompts, enabling seamless adaptation to unseen domains and classes. Unlike prior approaches, UCDR-Adapter dynamically adapts to evolving data distributions, enhancing both flexibility and generalization. During inference, only the image branch and generated prompts are used, eliminating reliance on textual inputs for highly efficient retrieval. Extensive benchmark experiments show that UCDR-Adapter consistently outperforms ProS in most cases and other state-of-the-art methods on UCDR, U(c)CDR, and U(d)CDR settings.
CredID: Credible Multi-Bit Watermark for Large Language Models Identification
Dec 04, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are widely used in complex natural language processing tasks but raise privacy and security concerns due to the lack of identity recognition. This paper proposes a multi-party credible watermarking framework (CredID) involving a trusted third party (TTP) and multiple LLM vendors to address these issues. In the watermark embedding stage, vendors request a seed from the TTP to generate watermarked text without sending the user's prompt. In the extraction stage, the TTP coordinates each vendor to extract and verify the watermark from the text. This provides a credible watermarking scheme while preserving vendor privacy. Furthermore, current watermarking algorithms struggle with text quality, information capacity, and robustness, making it challenging to meet the diverse identification needs of LLMs. Thus, we propose a novel multi-bit watermarking algorithm and an open-source toolkit to facilitate research. Experiments show our CredID enhances watermark credibility and efficiency without compromising text quality. Additionally, we successfully utilized this framework to achieve highly accurate identification among multiple LLM vendors.
Building Intelligence Identification System via Large Language Model Watermarking: A Survey and Beyond
Jul 15, 2024



Abstract:Large Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly integrated into diverse industries, posing substantial security risks due to unauthorized replication and misuse. To mitigate these concerns, robust identification mechanisms are widely acknowledged as an effective strategy. Identification systems for LLMs now rely heavily on watermarking technology to manage and protect intellectual property and ensure data security. However, previous studies have primarily concentrated on the basic principles of algorithms and lacked a comprehensive analysis of watermarking theory and practice from the perspective of intelligent identification. To bridge this gap, firstly, we explore how a robust identity recognition system can be effectively implemented and managed within LLMs by various participants using watermarking technology. Secondly, we propose a mathematical framework based on mutual information theory, which systematizes the identification process to achieve more precise and customized watermarking. Additionally, we present a comprehensive evaluation of performance metrics for LLM watermarking, reflecting participant preferences and advancing discussions on its identification applications. Lastly, we outline the existing challenges in current watermarking technologies and theoretical frameworks, and provide directional guidance to address these challenges. Our systematic classification and detailed exposition aim to enhance the comparison and evaluation of various methods, fostering further research and development toward a transparent, secure, and equitable LLM ecosystem.
Magnitude-based Neuron Pruning for Backdoor Defens
May 28, 2024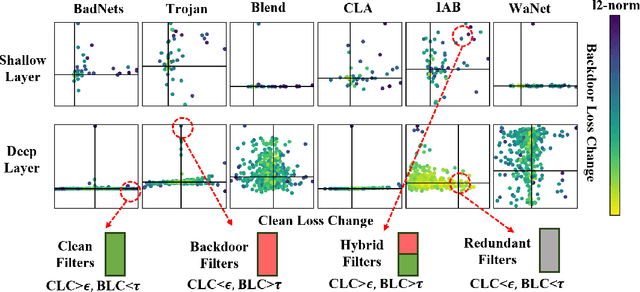
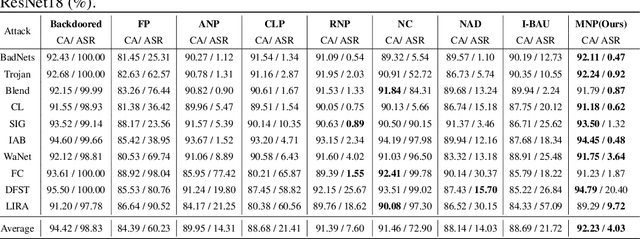
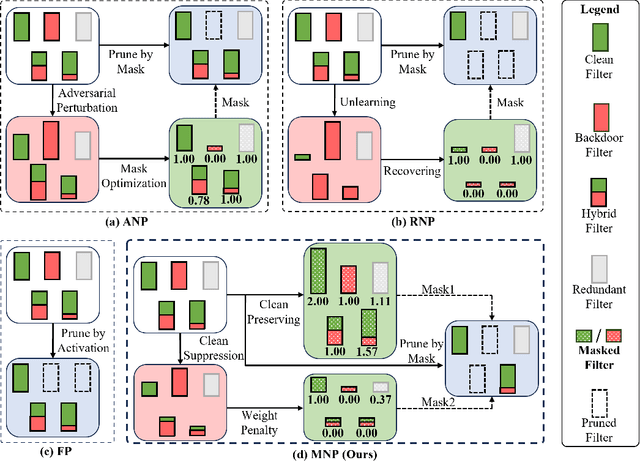
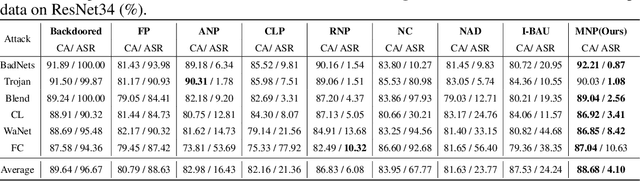
Abstract:Deep Neural Networks (DNNs) are known to be vulnerable to backdoor attacks, posing concerning threats to their reliable deployment. Recent research reveals that backdoors can be erased from infected DNNs by pruning a specific group of neurons, while how to effectively identify and remove these backdoor-associated neurons remains an open challenge. In this paper, we investigate the correlation between backdoor behavior and neuron magnitude, and find that backdoor neurons deviate from the magnitude-saliency correlation of the model. The deviation inspires us to propose a Magnitude-based Neuron Pruning (MNP) method to detect and prune backdoor neurons. Specifically, MNP uses three magnitude-guided objective functions to manipulate the magnitude-saliency correlation of backdoor neurons, thus achieving the purpose of exposing backdoor behavior, eliminating backdoor neurons and preserving clean neurons, respectively. Experiments show our pruning strategy achieves state-of-the-art backdoor defense performance against a variety of backdoor attacks with a limited amount of clean data, demonstrating the crucial role of magnitude for guiding backdoor defenses.
OCGEC: One-class Graph Embedding Classification for DNN Backdoor Detection
Dec 04, 2023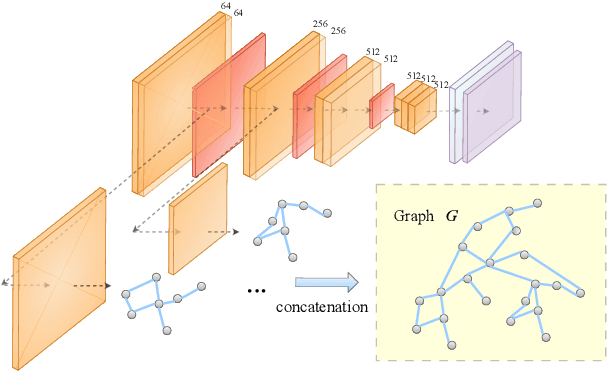
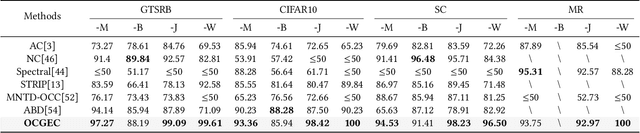
Abstract:Deep neural networks (DNNs) have been found vulnerable to backdoor attacks, raising security concerns about their deployment in mission-critical applications. There are various approaches to detect backdoor attacks, however they all make certain assumptions about the target attack to be detected and require equal and huge numbers of clean and backdoor samples for training, which renders these detection methods quite limiting in real-world circumstances. This study proposes a novel one-class classification framework called One-class Graph Embedding Classification (OCGEC) that uses GNNs for model-level backdoor detection with only a little amount of clean data. First, we train thousands of tiny models as raw datasets from a small number of clean datasets. Following that, we design a ingenious model-to-graph method for converting the model's structural details and weight features into graph data. We then pre-train a generative self-supervised graph autoencoder (GAE) to better learn the features of benign models in order to detect backdoor models without knowing the attack strategy. After that, we dynamically combine the GAE and one-class classifier optimization goals to form classification boundaries that distinguish backdoor models from benign models. Our OCGEC combines the powerful representation capabilities of graph neural networks with the utility of one-class classification techniques in the field of anomaly detection. In comparison to other baselines, it achieves AUC scores of more than 98% on a number of tasks, which far exceeds existing methods for detection even when they rely on a huge number of positive and negative samples. Our pioneering application of graphic scenarios for generic backdoor detection can provide new insights that can be used to improve other backdoor defense tasks. Code is available at https://github.com/jhy549/OCGEC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge