Xianhui Lin
AnimateAnywhere: Rouse the Background in Human Image Animation
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Human image animation aims to generate human videos of given characters and backgrounds that adhere to the desired pose sequence. However, existing methods focus more on human actions while neglecting the generation of background, which typically leads to static results or inharmonious movements. The community has explored camera pose-guided animation tasks, yet preparing the camera trajectory is impractical for most entertainment applications and ordinary users. As a remedy, we present an AnimateAnywhere framework, rousing the background in human image animation without requirements on camera trajectories. In particular, based on our key insight that the movement of the human body often reflects the motion of the background, we introduce a background motion learner (BML) to learn background motions from human pose sequences. To encourage the model to learn more accurate cross-frame correspondences, we further deploy an epipolar constraint on the 3D attention map. Specifically, the mask used to suppress geometrically unreasonable attention is carefully constructed by combining an epipolar mask and the current 3D attention map. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our AnimateAnywhere effectively learns the background motion from human pose sequences, achieving state-of-the-art performance in generating human animation results with vivid and realistic backgrounds. The source code and model will be available at https://github.com/liuxiaoyu1104/AnimateAnywhere.
MetaDesigner: Advancing Artistic Typography through AI-Driven, User-Centric, and Multilingual WordArt Synthesis
Jun 28, 2024
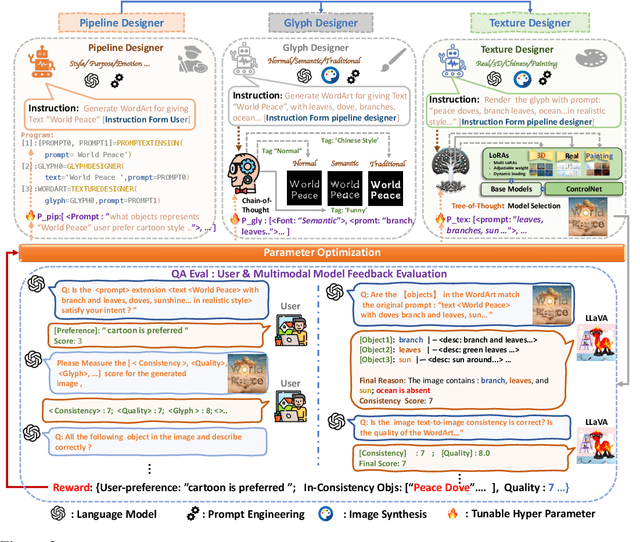
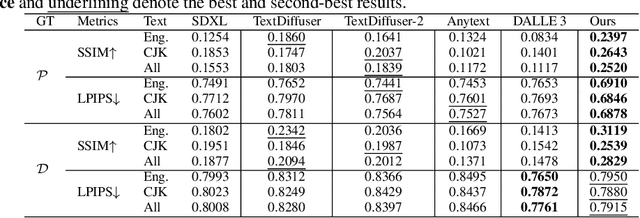
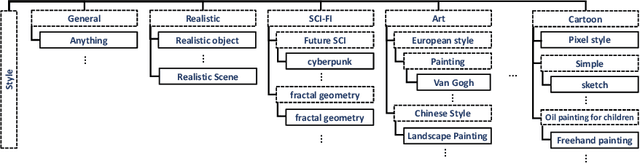
Abstract:MetaDesigner revolutionizes artistic typography synthesis by leveraging the strengths of Large Language Models (LLMs) to drive a design paradigm centered around user engagement. At the core of this framework lies a multi-agent system comprising the Pipeline, Glyph, and Texture agents, which collectively enable the creation of customized WordArt, ranging from semantic enhancements to the imposition of complex textures. MetaDesigner incorporates a comprehensive feedback mechanism that harnesses insights from multimodal models and user evaluations to refine and enhance the design process iteratively. Through this feedback loop, the system adeptly tunes hyperparameters to align with user-defined stylistic and thematic preferences, generating WordArt that not only meets but exceeds user expectations of visual appeal and contextual relevance. Empirical validations highlight MetaDesigner's capability to effectively serve diverse WordArt applications, consistently producing aesthetically appealing and context-sensitive results.
SmartControl: Enhancing ControlNet for Handling Rough Visual Conditions
Apr 09, 2024Abstract:Human visual imagination usually begins with analogies or rough sketches. For example, given an image with a girl playing guitar before a building, one may analogously imagine how it seems like if Iron Man playing guitar before Pyramid in Egypt. Nonetheless, visual condition may not be precisely aligned with the imaginary result indicated by text prompt, and existing layout-controllable text-to-image (T2I) generation models is prone to producing degraded generated results with obvious artifacts. To address this issue, we present a novel T2I generation method dubbed SmartControl, which is designed to modify the rough visual conditions for adapting to text prompt. The key idea of our SmartControl is to relax the visual condition on the areas that are conflicted with text prompts. In specific, a Control Scale Predictor (CSP) is designed to identify the conflict regions and predict the local control scales, while a dataset with text prompts and rough visual conditions is constructed for training CSP. It is worth noting that, even with a limited number (e.g., 1,000~2,000) of training samples, our SmartControl can generalize well to unseen objects. Extensive experiments on four typical visual condition types clearly show the efficacy of our SmartControl against state-of-the-arts. Source code, pre-trained models, and datasets are available at https://github.com/liuxiaoyu1104/SmartControl.
VideoElevator: Elevating Video Generation Quality with Versatile Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models (T2I) have demonstrated unprecedented capabilities in creating realistic and aesthetic images. On the contrary, text-to-video diffusion models (T2V) still lag far behind in frame quality and text alignment, owing to insufficient quality and quantity of training videos. In this paper, we introduce VideoElevator, a training-free and plug-and-play method, which elevates the performance of T2V using superior capabilities of T2I. Different from conventional T2V sampling (i.e., temporal and spatial modeling), VideoElevator explicitly decomposes each sampling step into temporal motion refining and spatial quality elevating. Specifically, temporal motion refining uses encapsulated T2V to enhance temporal consistency, followed by inverting to the noise distribution required by T2I. Then, spatial quality elevating harnesses inflated T2I to directly predict less noisy latent, adding more photo-realistic details. We have conducted experiments in extensive prompts under the combination of various T2V and T2I. The results show that VideoElevator not only improves the performance of T2V baselines with foundational T2I, but also facilitates stylistic video synthesis with personalized T2I. Our code is available at https://github.com/YBYBZhang/VideoElevator.
WordArt Designer API: User-Driven Artistic Typography Synthesis with Large Language Models on ModelScope
Jan 12, 2024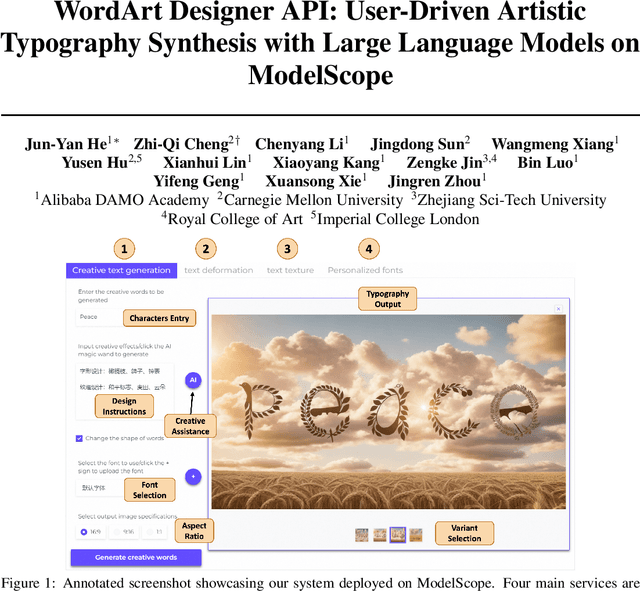
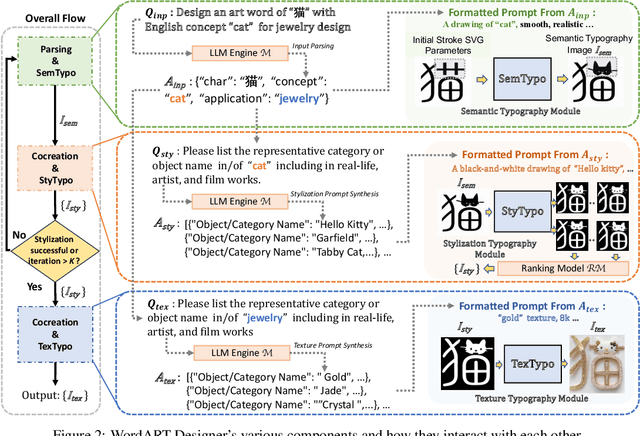

Abstract:This paper introduces the WordArt Designer API, a novel framework for user-driven artistic typography synthesis utilizing Large Language Models (LLMs) on ModelScope. We address the challenge of simplifying artistic typography for non-professionals by offering a dynamic, adaptive, and computationally efficient alternative to traditional rigid templates. Our approach leverages the power of LLMs to understand and interpret user input, facilitating a more intuitive design process. We demonstrate through various case studies how users can articulate their aesthetic preferences and functional requirements, which the system then translates into unique and creative typographic designs. Our evaluations indicate significant improvements in user satisfaction, design flexibility, and creative expression over existing systems. The WordArt Designer API not only democratizes the art of typography but also opens up new possibilities for personalized digital communication and design.
DreaMoving: A Human Video Generation Framework based on Diffusion Models
Dec 11, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we present DreaMoving, a diffusion-based controllable video generation framework to produce high-quality customized human videos. Specifically, given target identity and posture sequences, DreaMoving can generate a video of the target identity moving or dancing anywhere driven by the posture sequences. To this end, we propose a Video ControlNet for motion-controlling and a Content Guider for identity preserving. The proposed model is easy to use and can be adapted to most stylized diffusion models to generate diverse results. The project page is available at https://dreamoving.github.io/dreamoving
WordArt Designer: User-Driven Artistic Typography Synthesis using Large Language Models
Oct 20, 2023



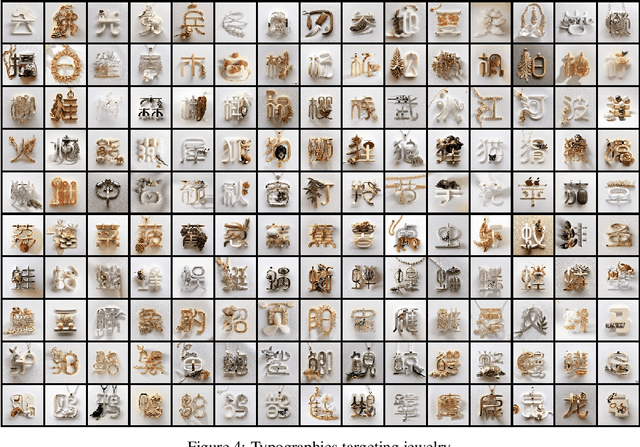
Abstract:This paper introduces "WordArt Designer", a user-driven framework for artistic typography synthesis, relying on Large Language Models (LLM). The system incorporates four key modules: the "LLM Engine", "SemTypo", "StyTypo", and "TexTypo" modules. 1) The "LLM Engine", empowered by LLM (e.g., GPT-3.5-turbo), interprets user inputs and generates actionable prompts for the other modules, thereby transforming abstract concepts into tangible designs. 2) The "SemTypo module" optimizes font designs using semantic concepts, striking a balance between artistic transformation and readability. 3) Building on the semantic layout provided by the "SemTypo module", the "StyTypo module" creates smooth, refined images. 4) The "TexTypo module" further enhances the design's aesthetics through texture rendering, enabling the generation of inventive textured fonts. Notably, "WordArt Designer" highlights the fusion of generative AI with artistic typography. Experience its capabilities on ModelScope: https://www.modelscope.cn/studios/WordArt/WordArt.
VQ-Font: Few-Shot Font Generation with Structure-Aware Enhancement and Quantization
Aug 27, 2023



Abstract:Few-shot font generation is challenging, as it needs to capture the fine-grained stroke styles from a limited set of reference glyphs, and then transfer to other characters, which are expected to have similar styles. However, due to the diversity and complexity of Chinese font styles, the synthesized glyphs of existing methods usually exhibit visible artifacts, such as missing details and distorted strokes. In this paper, we propose a VQGAN-based framework (i.e., VQ-Font) to enhance glyph fidelity through token prior refinement and structure-aware enhancement. Specifically, we pre-train a VQGAN to encapsulate font token prior within a codebook. Subsequently, VQ-Font refines the synthesized glyphs with the codebook to eliminate the domain gap between synthesized and real-world strokes. Furthermore, our VQ-Font leverages the inherent design of Chinese characters, where structure components such as radicals and character components are combined in specific arrangements, to recalibrate fine-grained styles based on references. This process improves the matching and fusion of styles at the structure level. Both modules collaborate to enhance the fidelity of the generated fonts. Experiments on a collected font dataset show that our VQ-Font outperforms the competing methods both quantitatively and qualitatively, especially in generating challenging styles.
From Face to Natural Image: Learning Real Degradation for Blind Image Super-Resolution
Oct 03, 2022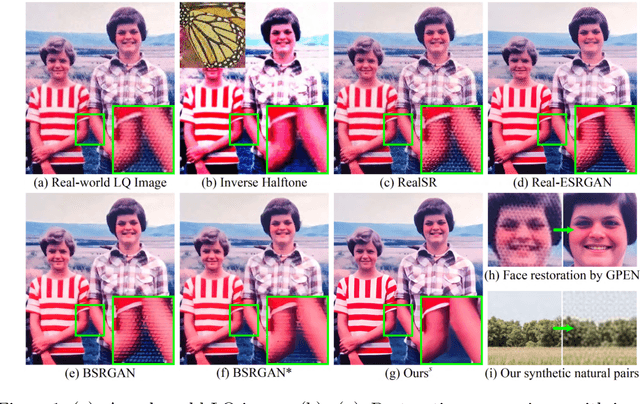
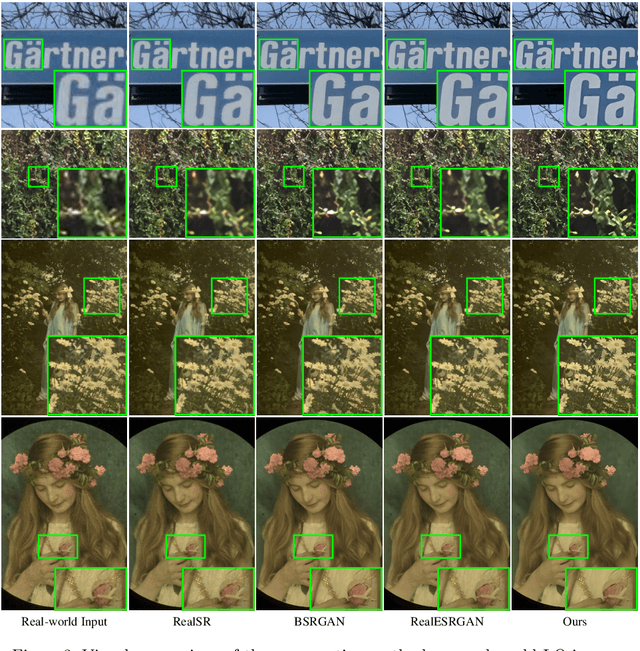
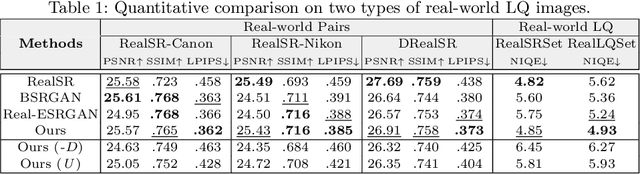
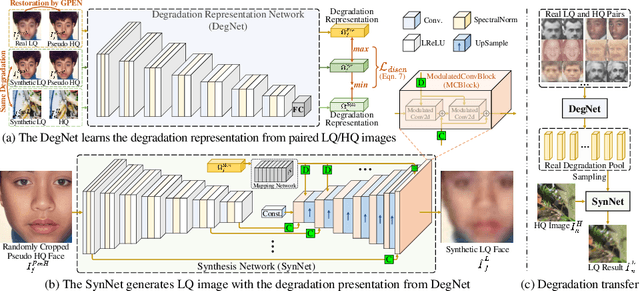

Abstract:Designing proper training pairs is critical for super-resolving the real-world low-quality (LQ) images, yet suffers from the difficulties in either acquiring paired ground-truth HQ images or synthesizing photo-realistic degraded observations. Recent works mainly circumvent this by simulating the degradation with handcrafted or estimated degradation parameters. However, existing synthetic degradation models are incapable to model complicated real degradation types, resulting in limited improvement on these scenarios, \eg, old photos. Notably, face images, which have the same degradation process with the natural images, can be robustly restored with photo-realistic textures by exploiting their specific structure priors. In this work, we use these real-world LQ face images and their restored HQ counterparts to model the complex real degradation (namely ReDegNet), and then transfer it to HQ natural images to synthesize their realistic LQ ones. Specifically, we take these paired HQ and LQ face images as inputs to explicitly predict the degradation-aware and content-independent representations, which control the degraded image generation. Subsequently, we transfer these real degradation representations from face to natural images to synthesize the degraded LQ natural images. Experiments show that our ReDegNet can well learn the real degradation process from face images, and the restoration network trained with our synthetic pairs performs favorably against SOTAs. More importantly, our method provides a new manner to handle the unsynthesizable real-world scenarios by learning their degradation representations through face images within them, which can be used for specifically fine-tuning. The source code is available at https://github.com/csxmli2016/ReDegNet.
Progressive Semantic-Aware Style Transformation for Blind Face Restoration
Sep 18, 2020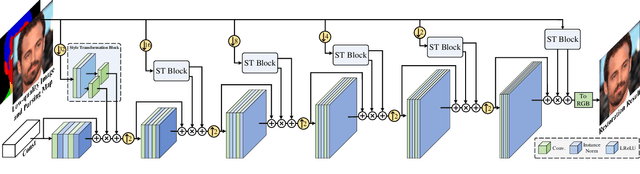
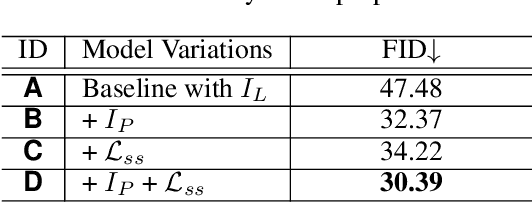


Abstract:Face restoration is important in face image processing, and has been widely studied in recent years. However, previous works often fail to generate plausible high quality (HQ) results for real-world low quality (LQ) face images. In this paper, we propose a new progressive semantic-aware style transformation framework, named PSFR-GAN, for face restoration. Specifically, instead of using an encoder-decoder framework as previous methods, we formulate the restoration of LQ face images as a multi-scale progressive restoration procedure through semantic-aware style transformation. Given a pair of LQ face image and its corresponding parsing map, we first generate a multi-scale pyramid of the inputs, and then progressively modulate different scale features from coarse-to-fine in a semantic-aware style transfer way. Compared with previous networks, the proposed PSFR-GAN makes full use of the semantic (parsing maps) and pixel (LQ images) space information from different scales of input pairs. In addition, we further introduce a semantic aware style loss which calculates the feature style loss for each semantic region individually to improve the details of face textures. Finally, we pretrain a face parsing network which can generate decent parsing maps from real-world LQ face images. Experiment results show that our model trained with synthetic data can not only produce more realistic high-resolution results for synthetic LQ inputs and but also generalize better to natural LQ face images compared with state-of-the-art methods. Codes are available at https://github.com/chaofengc/PSFRGAN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge