Yuxiang Lin
Emotion-LLaMAv2 and MMEVerse: A New Framework and Benchmark for Multimodal Emotion Understanding
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:Understanding human emotions from multimodal signals poses a significant challenge in affective computing and human-robot interaction. While multimodal large language models (MLLMs) have excelled in general vision-language tasks, their capabilities in emotional reasoning remain limited. The field currently suffers from a scarcity of large-scale datasets with high-quality, descriptive emotion annotations and lacks standardized benchmarks for evaluation. Our preliminary framework, Emotion-LLaMA, pioneered instruction-tuned multimodal learning for emotion reasoning but was restricted by explicit face detectors, implicit fusion strategies, and low-quality training data with limited scale. To address these limitations, we present Emotion-LLaMAv2 and the MMEVerse benchmark, establishing an end-to-end pipeline together with a standardized evaluation setting for emotion recognition and reasoning. Emotion-LLaMAv2 introduces three key advances. First, an end-to-end multiview encoder eliminates external face detection and captures nuanced emotional cues via richer spatial and temporal multiview tokens. Second, a Conv Attention pre-fusion module is designed to enable simultaneous local and global multimodal feature interactions external to the LLM backbone. Third, a perception-to-cognition curriculum instruction tuning scheme within the LLaMA2 backbone unifies emotion recognition and free-form emotion reasoning. To support large-scale training and reproducible evaluation, MMEVerse aggregates twelve publicly available emotion datasets, including IEMOCAP, MELD, DFEW, and MAFW, into a unified multimodal instruction format. The data are re-annotated via a multi-agent pipeline involving Qwen2 Audio, Qwen2.5 VL, and GPT 4o, producing 130k training clips and 36k testing clips across 18 evaluation benchmarks.
Do LLM Agents Know How to Ground, Recover, and Assess? A Benchmark for Epistemic Competence in Information-Seeking Agents
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Recent work has explored training Large Language Model (LLM) search agents with reinforcement learning (RL) for open-domain question answering (QA). However, most evaluations focus solely on final answer accuracy, overlooking how these agents reason with and act on external evidence. We introduce SeekBench, the first benchmark for evaluating the \textit{epistemic competence} of LLM search agents through step-level analysis of their response traces. SeekBench comprises 190 expert-annotated traces with over 1,800 response steps generated by LLM search agents, each enriched with evidence annotations for granular analysis of whether agents (1) generate reasoning steps grounded in observed evidence, (2) adaptively reformulate searches to recover from low-quality results, and (3) have proper calibration to correctly assess whether the current evidence is sufficient for providing an answer.
Why We Feel: Breaking Boundaries in Emotional Reasoning with Multimodal Large Language Models
Apr 10, 2025Abstract:Most existing emotion analysis emphasizes which emotion arises (e.g., happy, sad, angry) but neglects the deeper why. We propose Emotion Interpretation (EI), focusing on causal factors-whether explicit (e.g., observable objects, interpersonal interactions) or implicit (e.g., cultural context, off-screen events)-that drive emotional responses. Unlike traditional emotion recognition, EI tasks require reasoning about triggers instead of mere labeling. To facilitate EI research, we present EIBench, a large-scale benchmark encompassing 1,615 basic EI samples and 50 complex EI samples featuring multifaceted emotions. Each instance demands rationale-based explanations rather than straightforward categorization. We further propose a Coarse-to-Fine Self-Ask (CFSA) annotation pipeline, which guides Vision-Language Models (VLLMs) through iterative question-answer rounds to yield high-quality labels at scale. Extensive evaluations on open-source and proprietary large language models under four experimental settings reveal consistent performance gaps-especially for more intricate scenarios-underscoring EI's potential to enrich empathetic, context-aware AI applications. Our benchmark and methods are publicly available at: https://github.com/Lum1104/EIBench, offering a foundation for advanced multimodal causal analysis and next-generation affective computing.
ST-Align: A Multimodal Foundation Model for Image-Gene Alignment in Spatial Transcriptomics
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:Spatial transcriptomics (ST) provides high-resolution pathological images and whole-transcriptomic expression profiles at individual spots across whole-slide scales. This setting makes it an ideal data source to develop multimodal foundation models. Although recent studies attempted to fine-tune visual encoders with trainable gene encoders based on spot-level, the absence of a wider slide perspective and spatial intrinsic relationships limits their ability to capture ST-specific insights effectively. Here, we introduce ST-Align, the first foundation model designed for ST that deeply aligns image-gene pairs by incorporating spatial context, effectively bridging pathological imaging with genomic features. We design a novel pretraining framework with a three-target alignment strategy for ST-Align, enabling (1) multi-scale alignment across image-gene pairs, capturing both spot- and niche-level contexts for a comprehensive perspective, and (2) cross-level alignment of multimodal insights, connecting localized cellular characteristics and broader tissue architecture. Additionally, ST-Align employs specialized encoders tailored to distinct ST contexts, followed by an Attention-Based Fusion Network (ABFN) for enhanced multimodal fusion, effectively merging domain-shared knowledge with ST-specific insights from both pathological and genomic data. We pre-trained ST-Align on 1.3 million spot-niche pairs and evaluated its performance through two downstream tasks across six datasets, demonstrating superior zero-shot and few-shot capabilities. ST-Align highlights the potential for reducing the cost of ST and providing valuable insights into the distinction of critical compositions within human tissue.
FlexEdit: Marrying Free-Shape Masks to VLLM for Flexible Image Editing
Aug 22, 2024



Abstract:Combining Vision Large Language Models (VLLMs) with diffusion models offers a powerful method for executing image editing tasks based on human language instructions. However, language instructions alone often fall short in accurately conveying user requirements, particularly when users want to add, replace elements in specific areas of an image. Luckily, masks can effectively indicate the exact locations or elements to be edited, while they require users to precisely draw the shapes at the desired locations, which is highly user-unfriendly. To address this, we propose FlexEdit, an end-to-end image editing method that leverages both free-shape masks and language instructions for Flexible Editing. Our approach employs a VLLM in comprehending the image content, mask, and user instructions. Additionally, we introduce the Mask Enhance Adapter (MEA) that fuses the embeddings of the VLLM with the image data, ensuring a seamless integration of mask information and model output embeddings. Furthermore, we construct FSMI-Edit, a benchmark specifically tailored for free-shape mask, including 8 types of free-shape mask. Extensive experiments show that our method achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance in LLM-based image editing, and our simple prompting technique stands out in its effectiveness. The code and data can be found at https://github.com/A-new-b/flex_edit.
Emotion-LLaMA: Multimodal Emotion Recognition and Reasoning with Instruction Tuning
Jun 17, 2024



Abstract:Accurate emotion perception is crucial for various applications, including human-computer interaction, education, and counseling. However, traditional single-modality approaches often fail to capture the complexity of real-world emotional expressions, which are inherently multimodal. Moreover, existing Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) face challenges in integrating audio and recognizing subtle facial micro-expressions. To address this, we introduce the MERR dataset, containing 28,618 coarse-grained and 4,487 fine-grained annotated samples across diverse emotional categories. This dataset enables models to learn from varied scenarios and generalize to real-world applications. Furthermore, we propose Emotion-LLaMA, a model that seamlessly integrates audio, visual, and textual inputs through emotion-specific encoders. By aligning features into a shared space and employing a modified LLaMA model with instruction tuning, Emotion-LLaMA significantly enhances both emotional recognition and reasoning capabilities. Extensive evaluations show Emotion-LLaMA outperforms other MLLMs, achieving top scores in Clue Overlap (7.83) and Label Overlap (6.25) on EMER, an F1 score of 0.9036 on MER2023 challenge, and the highest UAR (45.59) and WAR (59.37) in zero-shot evaluations on DFEW dataset.
SurvMamba: State Space Model with Multi-grained Multi-modal Interaction for Survival Prediction
Apr 11, 2024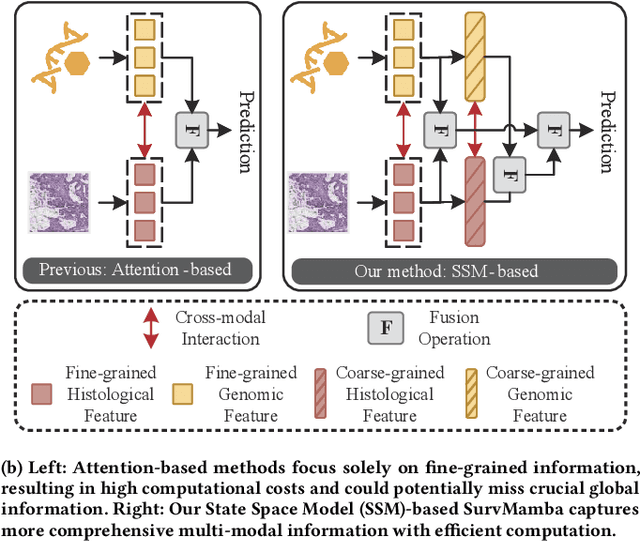
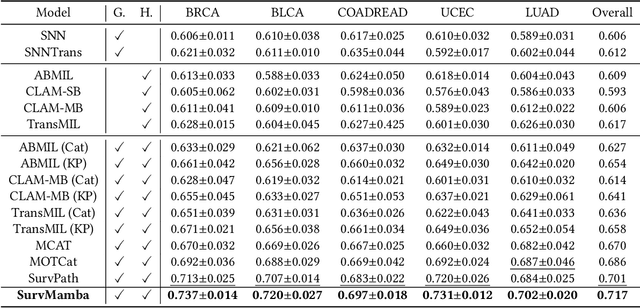
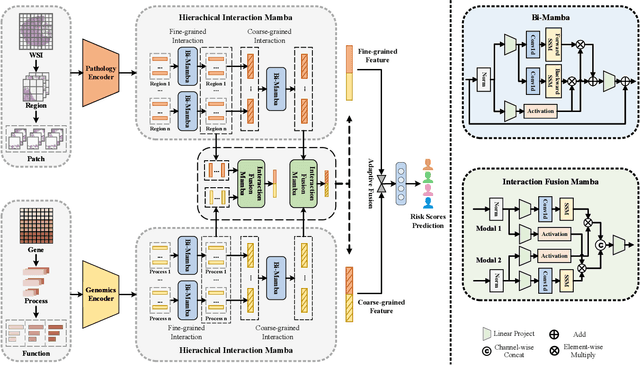
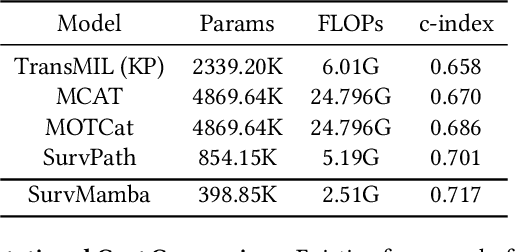
Abstract:Multi-modal learning that combines pathological images with genomic data has significantly enhanced the accuracy of survival prediction. Nevertheless, existing methods have not fully utilized the inherent hierarchical structure within both whole slide images (WSIs) and transcriptomic data, from which better intra-modal representations and inter-modal integration could be derived. Moreover, many existing studies attempt to improve multi-modal representations through attention mechanisms, which inevitably lead to high complexity when processing high-dimensional WSIs and transcriptomic data. Recently, a structured state space model named Mamba emerged as a promising approach for its superior performance in modeling long sequences with low complexity. In this study, we propose Mamba with multi-grained multi-modal interaction (SurvMamba) for survival prediction. SurvMamba is implemented with a Hierarchical Interaction Mamba (HIM) module that facilitates efficient intra-modal interactions at different granularities, thereby capturing more detailed local features as well as rich global representations. In addition, an Interaction Fusion Mamba (IFM) module is used for cascaded inter-modal interactive fusion, yielding more comprehensive features for survival prediction. Comprehensive evaluations on five TCGA datasets demonstrate that SurvMamba outperforms other existing methods in terms of performance and computational cost.
MIPS at SemEval-2024 Task 3: Multimodal Emotion-Cause Pair Extraction in Conversations with Multimodal Language Models
Apr 11, 2024



Abstract:This paper presents our winning submission to Subtask 2 of SemEval 2024 Task 3 on multimodal emotion cause analysis in conversations. We propose a novel Multimodal Emotion Recognition and Multimodal Emotion Cause Extraction (MER-MCE) framework that integrates text, audio, and visual modalities using specialized emotion encoders. Our approach sets itself apart from top-performing teams by leveraging modality-specific features for enhanced emotion understanding and causality inference. Experimental evaluation demonstrates the advantages of our multimodal approach, with our submission achieving a competitive weighted F1 score of 0.3435, ranking third with a margin of only 0.0339 behind the 1st team and 0.0025 behind the 2nd team. Project: https://github.com/MIPS-COLT/MER-MCE.git
Invisible Gas Detection: An RGB-Thermal Cross Attention Network and A New Benchmark
Mar 26, 2024



Abstract:The widespread use of various chemical gases in industrial processes necessitates effective measures to prevent their leakage during transportation and storage, given their high toxicity. Thermal infrared-based computer vision detection techniques provide a straightforward approach to identify gas leakage areas. However, the development of high-quality algorithms has been challenging due to the low texture in thermal images and the lack of open-source datasets. In this paper, we present the RGB-Thermal Cross Attention Network (RT-CAN), which employs an RGB-assisted two-stream network architecture to integrate texture information from RGB images and gas area information from thermal images. Additionally, to facilitate the research of invisible gas detection, we introduce Gas-DB, an extensive open-source gas detection database including about 1.3K well-annotated RGB-thermal images with eight variant collection scenes. Experimental results demonstrate that our method successfully leverages the advantages of both modalities, achieving state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance among RGB-thermal methods, surpassing single-stream SOTA models in terms of accuracy, Intersection of Union (IoU), and F2 metrics by 4.86%, 5.65%, and 4.88%, respectively. The code and data will be made available soon.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge