Rongshan Yu
AFD-INSTRUCTION: A Comprehensive Antibody Instruction Dataset with Functional Annotations for LLM-Based Understanding and Design
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have significantly advanced protein representation learning. However, their capacity to interpret and design antibodies through natural language remains limited. To address this challenge, we present AFD-Instruction, the first large-scale instruction dataset with functional annotations tailored to antibodies. This dataset encompasses two key components: antibody understanding, which infers functional attributes directly from sequences, and antibody design, which enables de novo sequence generation under functional constraints. These components provide explicit sequence-function alignment and support antibody design guided by natural language instructions. Extensive instruction-tuning experiments on general-purpose LLMs demonstrate that AFD-Instruction consistently improves performance across diverse antibody-related tasks. By linking antibody sequences with textual descriptions of function, AFD-Instruction establishes a new foundation for advancing antibody modeling and accelerating therapeutic discovery.
ST-Align: A Multimodal Foundation Model for Image-Gene Alignment in Spatial Transcriptomics
Nov 25, 2024



Abstract:Spatial transcriptomics (ST) provides high-resolution pathological images and whole-transcriptomic expression profiles at individual spots across whole-slide scales. This setting makes it an ideal data source to develop multimodal foundation models. Although recent studies attempted to fine-tune visual encoders with trainable gene encoders based on spot-level, the absence of a wider slide perspective and spatial intrinsic relationships limits their ability to capture ST-specific insights effectively. Here, we introduce ST-Align, the first foundation model designed for ST that deeply aligns image-gene pairs by incorporating spatial context, effectively bridging pathological imaging with genomic features. We design a novel pretraining framework with a three-target alignment strategy for ST-Align, enabling (1) multi-scale alignment across image-gene pairs, capturing both spot- and niche-level contexts for a comprehensive perspective, and (2) cross-level alignment of multimodal insights, connecting localized cellular characteristics and broader tissue architecture. Additionally, ST-Align employs specialized encoders tailored to distinct ST contexts, followed by an Attention-Based Fusion Network (ABFN) for enhanced multimodal fusion, effectively merging domain-shared knowledge with ST-specific insights from both pathological and genomic data. We pre-trained ST-Align on 1.3 million spot-niche pairs and evaluated its performance through two downstream tasks across six datasets, demonstrating superior zero-shot and few-shot capabilities. ST-Align highlights the potential for reducing the cost of ST and providing valuable insights into the distinction of critical compositions within human tissue.
SlideChat: A Large Vision-Language Assistant for Whole-Slide Pathology Image Understanding
Oct 15, 2024



Abstract:Despite the progress made by multimodal large language models (MLLMs) in computational pathology, they remain limited by a predominant focus on patch-level analysis, missing essential contextual information at the whole-slide level. The lack of large-scale instruction datasets and the gigapixel scale of whole slide images (WSIs) pose significant developmental challenges. In this paper, we present SlideChat, the first vision-language assistant capable of understanding gigapixel whole-slide images, exhibiting excellent multimodal conversational capability and response complex instruction across diverse pathology scenarios. To support its development, we created SlideInstruction, the largest instruction-following dataset for WSIs consisting of 4.2K WSI captions and 176K VQA pairs with multiple categories. Furthermore, we propose SlideBench, a multimodal benchmark that incorporates captioning and VQA tasks to assess SlideChat's capabilities in varied clinical settings such as microscopy, diagnosis. Compared to both general and specialized MLLMs, SlideChat exhibits exceptional capabilities achieving state-of-the-art performance on 18 of 22 tasks. For example, it achieved an overall accuracy of 81.17% on SlideBench-VQA (TCGA), and 54.15% on SlideBench-VQA (BCNB). We will fully release SlideChat, SlideInstruction and SlideBench as open-source resources to facilitate research and development in computational pathology.
FedSAC: Dynamic Submodel Allocation for Collaborative Fairness in Federated Learning
May 28, 2024



Abstract:Collaborative fairness stands as an essential element in federated learning to encourage client participation by equitably distributing rewards based on individual contributions. Existing methods primarily focus on adjusting gradient allocations among clients to achieve collaborative fairness. However, they frequently overlook crucial factors such as maintaining consistency across local models and catering to the diverse requirements of high-contributing clients. This oversight inevitably decreases both fairness and model accuracy in practice. To address these issues, we propose FedSAC, a novel Federated learning framework with dynamic Submodel Allocation for Collaborative fairness, backed by a theoretical convergence guarantee. First, we present the concept of "bounded collaborative fairness (BCF)", which ensures fairness by tailoring rewards to individual clients based on their contributions. Second, to implement the BCF, we design a submodel allocation module with a theoretical guarantee of fairness. This module incentivizes high-contributing clients with high-performance submodels containing a diverse range of crucial neurons, thereby preserving consistency across local models. Third, we further develop a dynamic aggregation module to adaptively aggregate submodels, ensuring the equitable treatment of low-frequency neurons and consequently enhancing overall model accuracy. Extensive experiments conducted on three public benchmarks demonstrate that FedSAC outperforms all baseline methods in both fairness and model accuracy. We see this work as a significant step towards incentivizing broader client participation in federated learning. The source code is available at https://github.com/wangzihuixmu/FedSAC.
SurvMamba: State Space Model with Multi-grained Multi-modal Interaction for Survival Prediction
Apr 11, 2024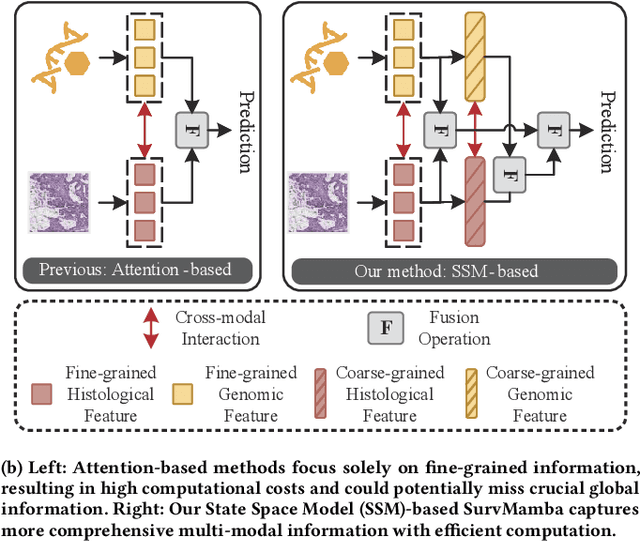
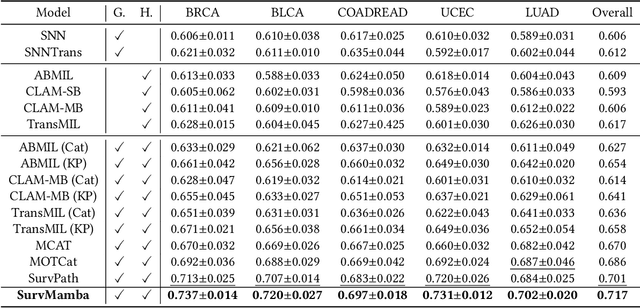
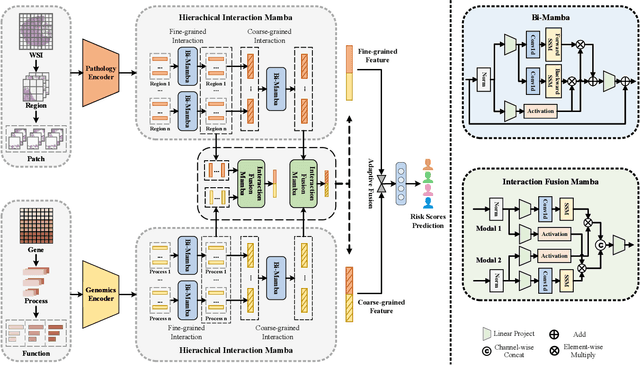
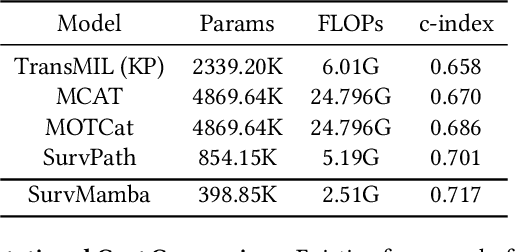
Abstract:Multi-modal learning that combines pathological images with genomic data has significantly enhanced the accuracy of survival prediction. Nevertheless, existing methods have not fully utilized the inherent hierarchical structure within both whole slide images (WSIs) and transcriptomic data, from which better intra-modal representations and inter-modal integration could be derived. Moreover, many existing studies attempt to improve multi-modal representations through attention mechanisms, which inevitably lead to high complexity when processing high-dimensional WSIs and transcriptomic data. Recently, a structured state space model named Mamba emerged as a promising approach for its superior performance in modeling long sequences with low complexity. In this study, we propose Mamba with multi-grained multi-modal interaction (SurvMamba) for survival prediction. SurvMamba is implemented with a Hierarchical Interaction Mamba (HIM) module that facilitates efficient intra-modal interactions at different granularities, thereby capturing more detailed local features as well as rich global representations. In addition, an Interaction Fusion Mamba (IFM) module is used for cascaded inter-modal interactive fusion, yielding more comprehensive features for survival prediction. Comprehensive evaluations on five TCGA datasets demonstrate that SurvMamba outperforms other existing methods in terms of performance and computational cost.
Generalizable Whole Slide Image Classification with Fine-Grained Visual-Semantic Interaction
Feb 29, 2024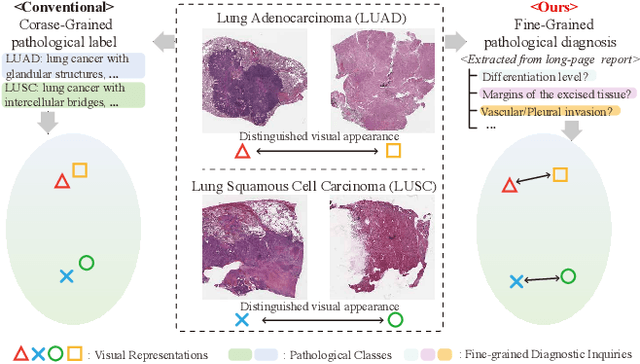

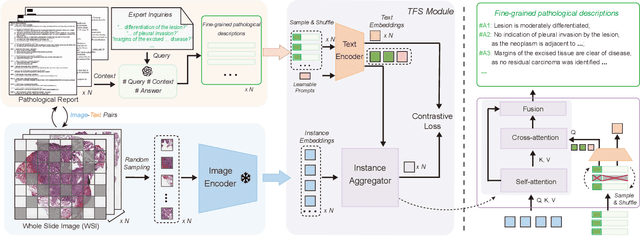
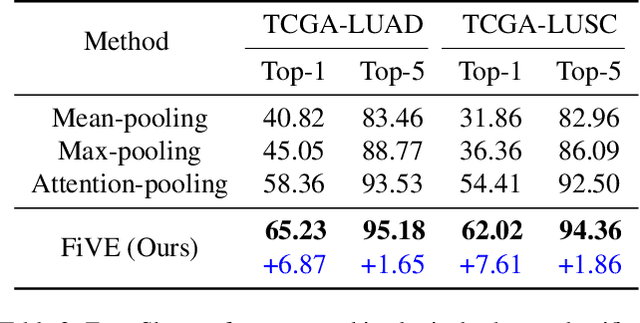
Abstract:Whole Slide Image (WSI) classification is often formulated as a Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) problem. Recently, Vision-Language Models (VLMs) have demonstrated remarkable performance in WSI classification. However, existing methods leverage coarse-grained pathogenetic descriptions for visual representation supervision, which are insufficient to capture the complex visual appearance of pathogenetic images, hindering the generalizability of models on diverse downstream tasks. Additionally, processing high-resolution WSIs can be computationally expensive. In this paper, we propose a novel "Fine-grained Visual-Semantic Interaction" (FiVE) framework for WSI classification. It is designed to enhance the model's generalizability by leveraging the interplay between localized visual patterns and fine-grained pathological semantics. Specifically, with meticulously designed queries, we start by utilizing a large language model to extract fine-grained pathological descriptions from various non-standardized raw reports. The output descriptions are then reconstructed into fine-grained labels used for training. By introducing a Task-specific Fine-grained Semantics (TFS) module, we enable prompts to capture crucial visual information in WSIs, which enhances representation learning and augments generalization capabilities significantly. Furthermore, given that pathological visual patterns are redundantly distributed across tissue slices, we sample a subset of visual instances during training. Our method demonstrates robust generalizability and strong transferability, dominantly outperforming the counterparts on the TCGA Lung Cancer dataset with at least 9.19% higher accuracy in few-shot experiments.
Federated Learning with Fair Averaging
May 17, 2021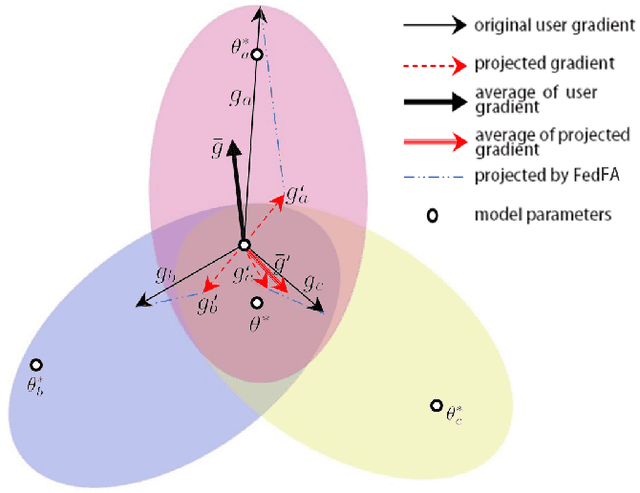
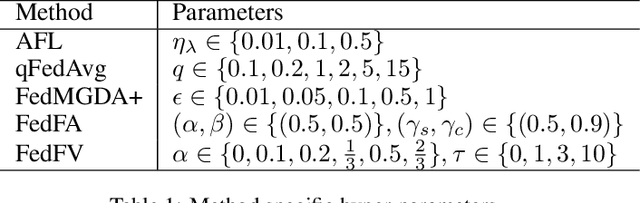
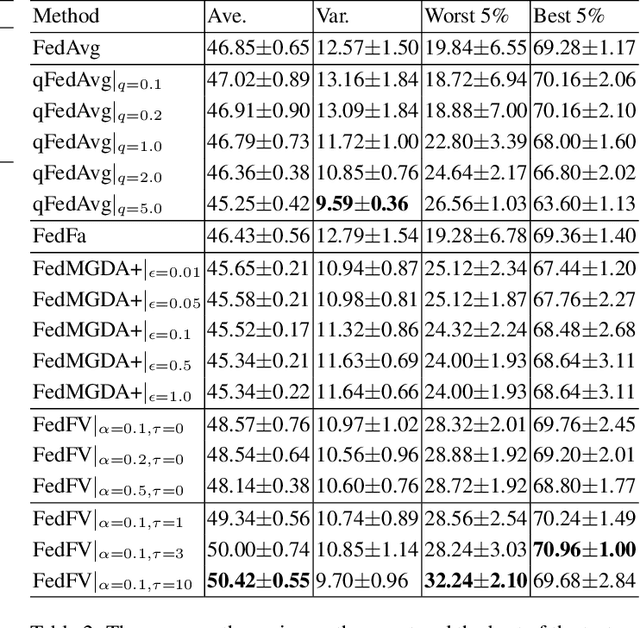
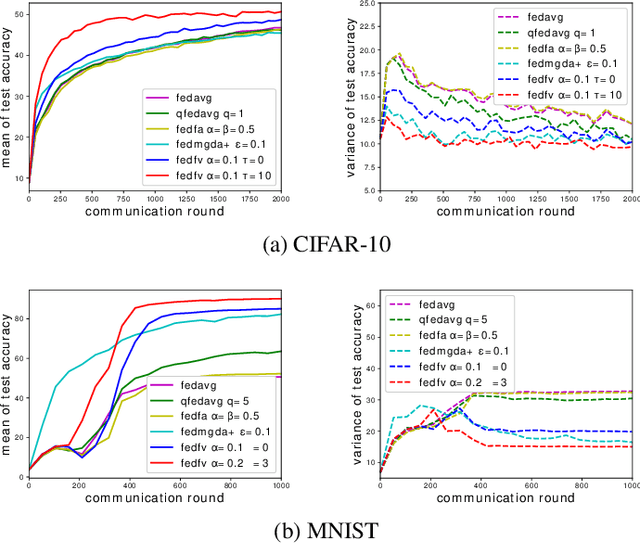
Abstract:Fairness has emerged as a critical problem in federated learning (FL). In this work, we identify a cause of unfairness in FL -- \emph{conflicting} gradients with large differences in the magnitudes. To address this issue, we propose the federated fair averaging (FedFV) algorithm to mitigate potential conflicts among clients before averaging their gradients. We first use the cosine similarity to detect gradient conflicts, and then iteratively eliminate such conflicts by modifying both the direction and the magnitude of the gradients. We further show the theoretical foundation of FedFV to mitigate the issue conflicting gradients and converge to Pareto stationary solutions. Extensive experiments on a suite of federated datasets confirm that FedFV compares favorably against state-of-the-art methods in terms of fairness, accuracy and efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge