Gregory Holste
CXR-LT 2024: A MICCAI challenge on long-tailed, multi-label, and zero-shot disease classification from chest X-ray
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:The CXR-LT series is a community-driven initiative designed to enhance lung disease classification using chest X-rays (CXR). It tackles challenges in open long-tailed lung disease classification and enhances the measurability of state-of-the-art techniques. The first event, CXR-LT 2023, aimed to achieve these goals by providing high-quality benchmark CXR data for model development and conducting comprehensive evaluations to identify ongoing issues impacting lung disease classification performance. Building on the success of CXR-LT 2023, the CXR-LT 2024 expands the dataset to 377,110 chest X-rays (CXRs) and 45 disease labels, including 19 new rare disease findings. It also introduces a new focus on zero-shot learning to address limitations identified in the previous event. Specifically, CXR-LT 2024 features three tasks: (i) long-tailed classification on a large, noisy test set, (ii) long-tailed classification on a manually annotated "gold standard" subset, and (iii) zero-shot generalization to five previously unseen disease findings. This paper provides an overview of CXR-LT 2024, detailing the data curation process and consolidating state-of-the-art solutions, including the use of multimodal models for rare disease detection, advanced generative approaches to handle noisy labels, and zero-shot learning strategies for unseen diseases. Additionally, the expanded dataset enhances disease coverage to better represent real-world clinical settings, offering a valuable resource for future research. By synthesizing the insights and innovations of participating teams, we aim to advance the development of clinically realistic and generalizable diagnostic models for chest radiography.
Harnessing the power of longitudinal medical imaging for eye disease prognosis using Transformer-based sequence modeling
May 14, 2024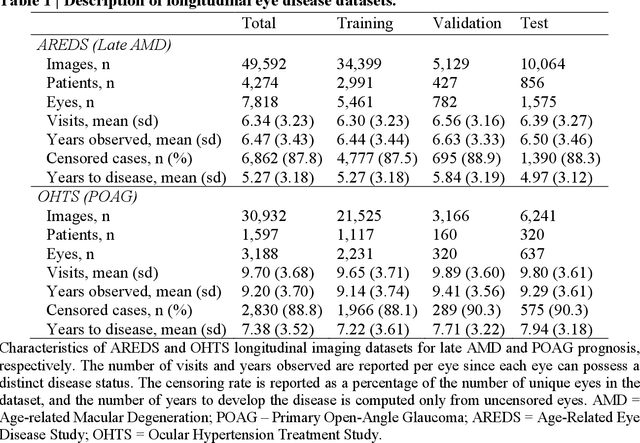
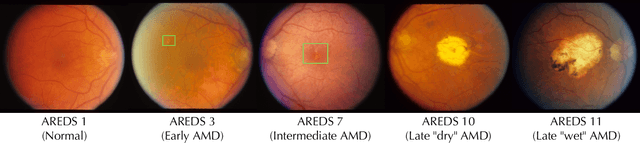
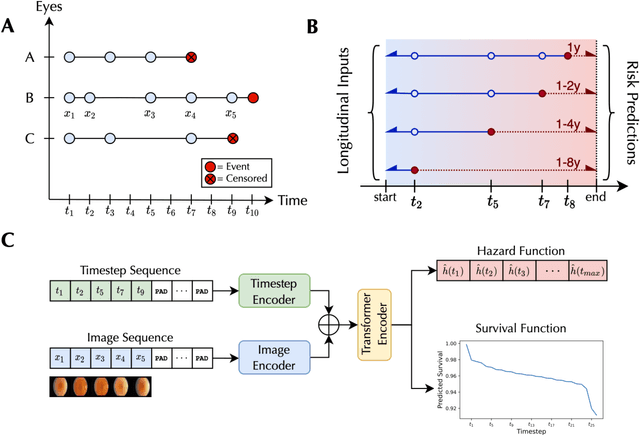
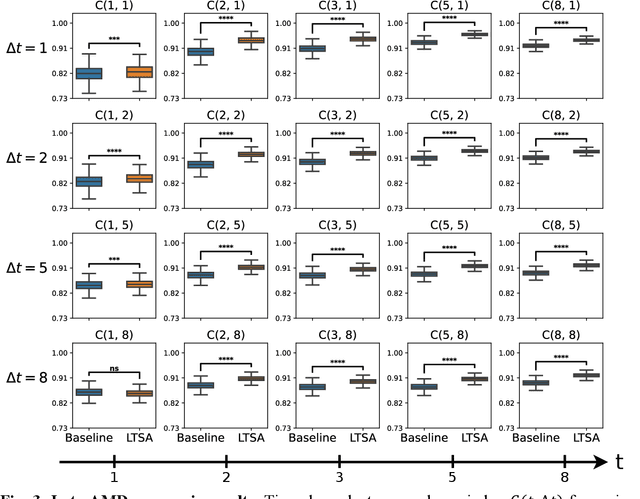
Abstract:Deep learning has enabled breakthroughs in automated diagnosis from medical imaging, with many successful applications in ophthalmology. However, standard medical image classification approaches only assess disease presence at the time of acquisition, neglecting the common clinical setting of longitudinal imaging. For slow, progressive eye diseases like age-related macular degeneration (AMD) and primary open-angle glaucoma (POAG), patients undergo repeated imaging over time to track disease progression and forecasting the future risk of developing disease is critical to properly plan treatment. Our proposed Longitudinal Transformer for Survival Analysis (LTSA) enables dynamic disease prognosis from longitudinal medical imaging, modeling the time to disease from sequences of fundus photography images captured over long, irregular time periods. Using longitudinal imaging data from the Age-Related Eye Disease Study (AREDS) and Ocular Hypertension Treatment Study (OHTS), LTSA significantly outperformed a single-image baseline in 19/20 head-to-head comparisons on late AMD prognosis and 18/20 comparisons on POAG prognosis. A temporal attention analysis also suggested that, while the most recent image is typically the most influential, prior imaging still provides additional prognostic value.
Deep Rib Fracture Instance Segmentation and Classification from CT on the RibFrac Challenge
Feb 14, 2024Abstract:Rib fractures are a common and potentially severe injury that can be challenging and labor-intensive to detect in CT scans. While there have been efforts to address this field, the lack of large-scale annotated datasets and evaluation benchmarks has hindered the development and validation of deep learning algorithms. To address this issue, the RibFrac Challenge was introduced, providing a benchmark dataset of over 5,000 rib fractures from 660 CT scans, with voxel-level instance mask annotations and diagnosis labels for four clinical categories (buckle, nondisplaced, displaced, or segmental). The challenge includes two tracks: a detection (instance segmentation) track evaluated by an FROC-style metric and a classification track evaluated by an F1-style metric. During the MICCAI 2020 challenge period, 243 results were evaluated, and seven teams were invited to participate in the challenge summary. The analysis revealed that several top rib fracture detection solutions achieved performance comparable or even better than human experts. Nevertheless, the current rib fracture classification solutions are hardly clinically applicable, which can be an interesting area in the future. As an active benchmark and research resource, the data and online evaluation of the RibFrac Challenge are available at the challenge website. As an independent contribution, we have also extended our previous internal baseline by incorporating recent advancements in large-scale pretrained networks and point-based rib segmentation techniques. The resulting FracNet+ demonstrates competitive performance in rib fracture detection, which lays a foundation for further research and development in AI-assisted rib fracture detection and diagnosis.
Improving Fairness of Automated Chest X-ray Diagnosis by Contrastive Learning
Jan 25, 2024Abstract:Purpose: Limited studies exploring concrete methods or approaches to tackle and enhance model fairness in the radiology domain. Our proposed AI model utilizes supervised contrastive learning to minimize bias in CXR diagnosis. Materials and Methods: In this retrospective study, we evaluated our proposed method on two datasets: the Medical Imaging and Data Resource Center (MIDRC) dataset with 77,887 CXR images from 27,796 patients collected as of April 20, 2023 for COVID-19 diagnosis, and the NIH Chest X-ray (NIH-CXR) dataset with 112,120 CXR images from 30,805 patients collected between 1992 and 2015. In the NIH-CXR dataset, thoracic abnormalities include atelectasis, cardiomegaly, effusion, infiltration, mass, nodule, pneumonia, pneumothorax, consolidation, edema, emphysema, fibrosis, pleural thickening, or hernia. Our proposed method utilizes supervised contrastive learning with carefully selected positive and negative samples to generate fair image embeddings, which are fine-tuned for subsequent tasks to reduce bias in chest X-ray (CXR) diagnosis. We evaluated the methods using the marginal AUC difference ($\delta$ mAUC). Results: The proposed model showed a significant decrease in bias across all subgroups when compared to the baseline models, as evidenced by a paired T-test (p<0.0001). The $\delta$ mAUC obtained by our method were 0.0116 (95\% CI, 0.0110-0.0123), 0.2102 (95% CI, 0.2087-0.2118), and 0.1000 (95\% CI, 0.0988-0.1011) for sex, race, and age on MIDRC, and 0.0090 (95\% CI, 0.0082-0.0097) for sex and 0.0512 (95% CI, 0.0512-0.0532) for age on NIH-CXR, respectively. Conclusion: Employing supervised contrastive learning can mitigate bias in CXR diagnosis, addressing concerns of fairness and reliability in deep learning-based diagnostic methods.
Towards long-tailed, multi-label disease classification from chest X-ray: Overview of the CXR-LT challenge
Oct 24, 2023



Abstract:Many real-world image recognition problems, such as diagnostic medical imaging exams, are "long-tailed" $\unicode{x2013}$ there are a few common findings followed by many more relatively rare conditions. In chest radiography, diagnosis is both a long-tailed and multi-label problem, as patients often present with multiple findings simultaneously. While researchers have begun to study the problem of long-tailed learning in medical image recognition, few have studied the interaction of label imbalance and label co-occurrence posed by long-tailed, multi-label disease classification. To engage with the research community on this emerging topic, we conducted an open challenge, CXR-LT, on long-tailed, multi-label thorax disease classification from chest X-rays (CXRs). We publicly release a large-scale benchmark dataset of over 350,000 CXRs, each labeled with at least one of 26 clinical findings following a long-tailed distribution. We synthesize common themes of top-performing solutions, providing practical recommendations for long-tailed, multi-label medical image classification. Finally, we use these insights to propose a path forward involving vision-language foundation models for few- and zero-shot disease classification.
How Does Pruning Impact Long-Tailed Multi-Label Medical Image Classifiers?
Aug 17, 2023Abstract:Pruning has emerged as a powerful technique for compressing deep neural networks, reducing memory usage and inference time without significantly affecting overall performance. However, the nuanced ways in which pruning impacts model behavior are not well understood, particularly for long-tailed, multi-label datasets commonly found in clinical settings. This knowledge gap could have dangerous implications when deploying a pruned model for diagnosis, where unexpected model behavior could impact patient well-being. To fill this gap, we perform the first analysis of pruning's effect on neural networks trained to diagnose thorax diseases from chest X-rays (CXRs). On two large CXR datasets, we examine which diseases are most affected by pruning and characterize class "forgettability" based on disease frequency and co-occurrence behavior. Further, we identify individual CXRs where uncompressed and heavily pruned models disagree, known as pruning-identified exemplars (PIEs), and conduct a human reader study to evaluate their unifying qualities. We find that radiologists perceive PIEs as having more label noise, lower image quality, and higher diagnosis difficulty. This work represents a first step toward understanding the impact of pruning on model behavior in deep long-tailed, multi-label medical image classification. All code, model weights, and data access instructions can be found at https://github.com/VITA-Group/PruneCXR.
Improved Multimodal Fusion for Small Datasets with Auxiliary Supervision
Apr 01, 2023Abstract:Prostate cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related death in men worldwide. Like many cancers, diagnosis involves expert integration of heterogeneous patient information such as imaging, clinical risk factors, and more. For this reason, there have been many recent efforts toward deep multimodal fusion of image and non-image data for clinical decision tasks. Many of these studies propose methods to fuse learned features from each patient modality, providing significant downstream improvements with techniques like cross-modal attention gating, Kronecker product fusion, orthogonality regularization, and more. While these enhanced fusion operations can improve upon feature concatenation, they often come with an extremely high learning capacity, meaning they are likely to overfit when applied even to small or low-dimensional datasets. Rather than designing a highly expressive fusion operation, we propose three simple methods for improved multimodal fusion with small datasets that aid optimization by generating auxiliary sources of supervision during training: extra supervision, clinical prediction, and dense fusion. We validate the proposed approaches on prostate cancer diagnosis from paired histopathology imaging and tabular clinical features. The proposed methods are straightforward to implement and can be applied to any classification task with paired image and non-image data.
Long-Tailed Classification of Thorax Diseases on Chest X-Ray: A New Benchmark Study
Aug 29, 2022

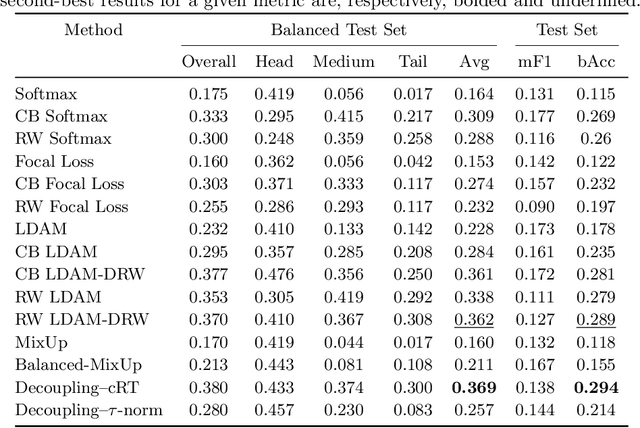

Abstract:Imaging exams, such as chest radiography, will yield a small set of common findings and a much larger set of uncommon findings. While a trained radiologist can learn the visual presentation of rare conditions by studying a few representative examples, teaching a machine to learn from such a "long-tailed" distribution is much more difficult, as standard methods would be easily biased toward the most frequent classes. In this paper, we present a comprehensive benchmark study of the long-tailed learning problem in the specific domain of thorax diseases on chest X-rays. We focus on learning from naturally distributed chest X-ray data, optimizing classification accuracy over not only the common "head" classes, but also the rare yet critical "tail" classes. To accomplish this, we introduce a challenging new long-tailed chest X-ray benchmark to facilitate research on developing long-tailed learning methods for medical image classification. The benchmark consists of two chest X-ray datasets for 19- and 20-way thorax disease classification, containing classes with as many as 53,000 and as few as 7 labeled training images. We evaluate both standard and state-of-the-art long-tailed learning methods on this new benchmark, analyzing which aspects of these methods are most beneficial for long-tailed medical image classification and summarizing insights for future algorithm design. The datasets, trained models, and code are available at https://github.com/VITA-Group/LongTailCXR.
Self-Supervised Learning of Echocardiogram Videos Enables Data-Efficient Clinical Diagnosis
Jul 23, 2022



Abstract:Given the difficulty of obtaining high-quality labels for medical image recognition tasks, there is a need for deep learning techniques that can be adequately fine-tuned on small labeled data sets. Recent advances in self-supervised learning techniques have shown that such an in-domain representation learning approach can provide a strong initialization for supervised fine-tuning, proving much more data-efficient than standard transfer learning from a supervised pretraining task. However, these applications are not adapted to applications to medical diagnostics captured in a video format. With this progress in mind, we developed a self-supervised learning approach catered to echocardiogram videos with the goal of learning strong representations for downstream fine-tuning on the task of diagnosing aortic stenosis (AS), a common and dangerous disease of the aortic valve. When fine-tuned on 1% of the training data, our best self-supervised learning model achieves 0.818 AUC (95% CI: 0.794, 0.840), while the standard transfer learning approach reaches 0.644 AUC (95% CI: 0.610, 0.677). We also find that our self-supervised model attends more closely to the aortic valve when predicting severe AS as demonstrated by saliency map visualizations.
Radiomics-Guided Global-Local Transformer for Weakly Supervised Pathology Localization in Chest X-Rays
Jul 14, 2022



Abstract:Before the recent success of deep learning methods for automated medical image analysis, practitioners used handcrafted radiomic features to quantitatively describe local patches of medical images. However, extracting discriminative radiomic features relies on accurate pathology localization, which is difficult to acquire in real-world settings. Despite advances in disease classification and localization from chest X-rays, many approaches fail to incorporate clinically-informed domain knowledge. For these reasons, we propose a Radiomics-Guided Transformer (RGT) that fuses \textit{global} image information with \textit{local} knowledge-guided radiomics information to provide accurate cardiopulmonary pathology localization and classification \textit{without any bounding box annotations}. RGT consists of an image Transformer branch, a radiomics Transformer branch, and fusion layers that aggregate image and radiomic information. Using the learned self-attention of its image branch, RGT extracts a bounding box for which to compute radiomic features, which are further processed by the radiomics branch; learned image and radiomic features are then fused and mutually interact via cross-attention layers. Thus, RGT utilizes a novel end-to-end feedback loop that can bootstrap accurate pathology localization only using image-level disease labels. Experiments on the NIH ChestXRay dataset demonstrate that RGT outperforms prior works in weakly supervised disease localization (by an average margin of 3.6\% over various intersection-over-union thresholds) and classification (by 1.1\% in average area under the receiver operating characteristic curve). We publicly release our codes and pre-trained models at \url{https://github.com/VITA-Group/chext}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge