Yiran Wang
Natural Language-Driven Global Mapping of Martian Landforms
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:Planetary surfaces are typically analyzed using high-level semantic concepts in natural language, yet vast orbital image archives remain organized at the pixel level. This mismatch limits scalable, open-ended exploration of planetary surfaces. Here we present MarScope, a planetary-scale vision-language framework enabling natural language-driven, label-free mapping of Martian landforms. MarScope aligns planetary images and text in a shared semantic space, trained on over 200,000 curated image-text pairs. This framework transforms global geomorphic mapping on Mars by replacing pre-defined classifications with flexible semantic retrieval, enabling arbitrary user queries across the entire planet in 5 seconds with F1 scores up to 0.978. Applications further show that it extends beyond morphological classification to facilitate process-oriented analysis and similarity-based geomorphological mapping at a planetary scale. MarScope establishes a new paradigm where natural language serves as a direct interface for scientific discovery over massive geospatial datasets.
Klear: Unified Multi-Task Audio-Video Joint Generation
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Audio-video joint generation has progressed rapidly, yet substantial challenges still remain. Non-commercial approaches still suffer audio-visual asynchrony, poor lip-speech alignment, and unimodal degradation, which can be stemmed from weak audio-visual correspondence modeling, limited generalization, and scarce high-quality dense-caption data. To address these issues, we introduce Klear and delve into three axes--model architecture, training strategy, and data curation. Architecturally, we adopt a single-tower design with unified DiT blocks and an Omni-Full Attention mechanism, achieving tight audio-visual alignment and strong scalability. Training-wise, we adopt a progressive multitask regime--random modality masking to joint optimization across tasks, and a multistage curriculum, yielding robust representations, strengthening A-V aligned world knowledge, and preventing unimodal collapse. For datasets, we present the first large-scale audio-video dataset with dense captions, and introduce a novel automated data-construction pipeline which annotates and filters millions of diverse, high-quality, strictly aligned audio-video-caption triplets. Building on this, Klear scales to large datasets, delivering high-fidelity, semantically and temporally aligned, instruction-following generation in both joint and unimodal settings while generalizing robustly to out-of-distribution scenarios. Across tasks, it substantially outperforms prior methods by a large margin and achieves performance comparable to Veo 3, offering a unified, scalable path toward next-generation audio-video synthesis.
MacVQA: Adaptive Memory Allocation and Global Noise Filtering for Continual Visual Question Answering
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Visual Question Answering (VQA) requires models to reason over multimodal information, combining visual and textual data. With the development of continual learning, significant progress has been made in retaining knowledge and adapting to new information in the VQA domain. However, current methods often struggle with balancing knowledge retention, adaptation, and robust feature representation. To address these challenges, we propose a novel framework with adaptive memory allocation and global noise filtering called MacVQA for visual question answering. MacVQA fuses visual and question information while filtering noise to ensure robust representations, and employs prototype-based memory allocation to optimize feature quality and memory usage. These designs enable MacVQA to balance knowledge acquisition, retention, and compositional generalization in continual VQA learning. Experiments on ten continual VQA tasks show that MacVQA outperforms existing baselines, achieving 43.38% average accuracy and 2.32% average forgetting on standard tasks, and 42.53% average accuracy and 3.60% average forgetting on novel composition tasks.
SafeMo: Linguistically Grounded Unlearning for Trustworthy Text-to-Motion Generation
Jan 02, 2026Abstract:Text-to-motion (T2M) generation with diffusion backbones achieves strong realism and alignment. Safety concerns in T2M methods have been raised in recent years; existing methods replace discrete VQ-VAE codebook entries to steer the model away from unsafe behaviors. However, discrete codebook replacement-based methods have two critical flaws: firstly, replacing codebook entries which are reused by benign prompts leads to drifts on everyday tasks, degrading the model's benign performance; secondly, discrete token-based methods introduce quantization and smoothness loss, resulting in artifacts and jerky transitions. Moreover, existing text-to-motion datasets naturally contain unsafe intents and corresponding motions, making them unsuitable for safety-driven machine learning. To address these challenges, we propose SafeMo, a trustworthy motion generative framework integrating Minimal Motion Unlearning (MMU), a two-stage machine unlearning strategy, enabling safe human motion generation in continuous space, preserving continuous kinematics without codebook loss and delivering strong safety-utility trade-offs compared to current baselines. Additionally, we present the first safe text-to-motion dataset SafeMoVAE-29K integrating rewritten safe text prompts and continuous refined motion for trustworthy human motion unlearning. Built upon DiP, SafeMo efficiently generates safe human motions with natural transitions. Experiments demonstrate effective unlearning performance of SafeMo by showing strengthened forgetting on unsafe prompts, reaching 2.5x and 14.4x higher forget-set FID on HumanML3D and Motion-X respectively, compared to the previous SOTA human motion unlearning method LCR, with benign performance on safe prompts being better or comparable. Code: https://github.com/AIGeeksGroup/SafeMo. Website: https://aigeeksgroup.github.io/SafeMo.
HY-Motion 1.0: Scaling Flow Matching Models for Text-To-Motion Generation
Dec 29, 2025Abstract:We present HY-Motion 1.0, a series of state-of-the-art, large-scale, motion generation models capable of generating 3D human motions from textual descriptions. HY-Motion 1.0 represents the first successful attempt to scale up Diffusion Transformer (DiT)-based flow matching models to the billion-parameter scale within the motion generation domain, delivering instruction-following capabilities that significantly outperform current open-source benchmarks. Uniquely, we introduce a comprehensive, full-stage training paradigm -- including large-scale pretraining on over 3,000 hours of motion data, high-quality fine-tuning on 400 hours of curated data, and reinforcement learning from both human feedback and reward models -- to ensure precise alignment with the text instruction and high motion quality. This framework is supported by our meticulous data processing pipeline, which performs rigorous motion cleaning and captioning. Consequently, our model achieves the most extensive coverage, spanning over 200 motion categories across 6 major classes. We release HY-Motion 1.0 to the open-source community to foster future research and accelerate the transition of 3D human motion generation models towards commercial maturity.
Terahertz Signal Coverage Enhancement in Hall Scenarios Based on Single-Hop and Dual-Hop Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Terahertz (THz) communication offers ultra-high data rates and has emerged as a promising technology for future wireless networks. However, the inherently high free-space path loss of THz waves significantly limits the coverage range of THz communication systems. Therefore, extending the effective coverage area is a key challenge for the practical deployment of THz networks. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RIS), which can dynamically manipulate electromagnetic wave propagation, provide a solution to enhance THz coverage. To investigate multi-RIS deployment scenarios, this work integrates an antenna array-based RIS model into the ray-tracing simulation platform. Using an indoor hall as a representative case study, the enhancement effects of single-hop and dual-hop RIS configurations on indoor signal coverage are evaluated under various deployment schemes. The developed framework offers valuable insights and design references for optimizing RIS-assisted indoor THz communication and coverage estimation.
Medical Referring Image Segmentation via Next-Token Mask Prediction
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Medical Referring Image Segmentation (MRIS) involves segmenting target regions in medical images based on natural language descriptions. While achieving promising results, recent approaches usually involve complex design of multimodal fusion or multi-stage decoders. In this work, we propose NTP-MRISeg, a novel framework that reformulates MRIS as an autoregressive next-token prediction task over a unified multimodal sequence of tokenized image, text, and mask representations. This formulation streamlines model design by eliminating the need for modality-specific fusion and external segmentation models, supports a unified architecture for end-to-end training. It also enables the use of pretrained tokenizers from emerging large-scale multimodal models, enhancing generalization and adaptability. More importantly, to address challenges under this formulation-such as exposure bias, long-tail token distributions, and fine-grained lesion edges-we propose three novel strategies: (1) a Next-k Token Prediction (NkTP) scheme to reduce cumulative prediction errors, (2) Token-level Contrastive Learning (TCL) to enhance boundary sensitivity and mitigate long-tail distribution effects, and (3) a memory-based Hard Error Token (HET) optimization strategy that emphasizes difficult tokens during training. Extensive experiments on the QaTa-COV19 and MosMedData+ datasets demonstrate that NTP-MRISeg achieves new state-of-the-art performance, offering a streamlined and effective alternative to traditional MRIS pipelines.
Kling-Foley: Multimodal Diffusion Transformer for High-Quality Video-to-Audio Generation
Jun 24, 2025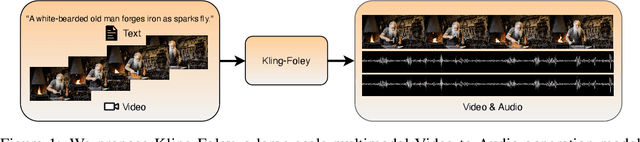
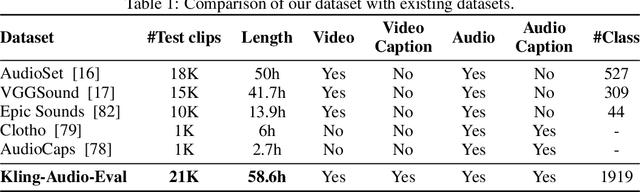
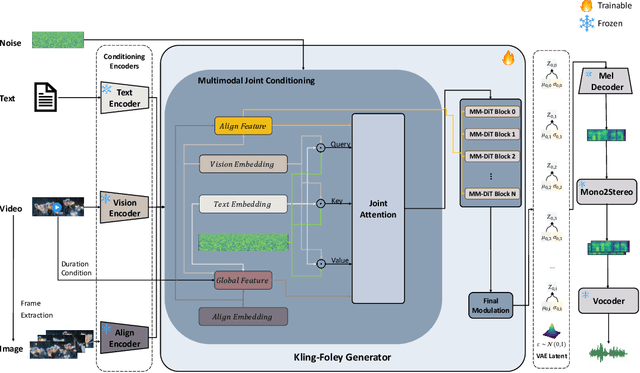
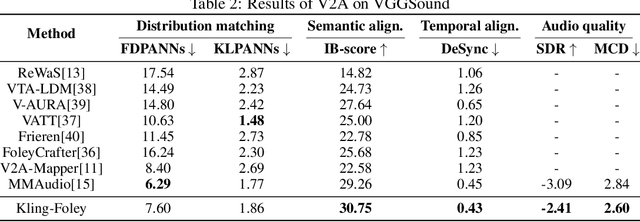
Abstract:We propose Kling-Foley, a large-scale multimodal Video-to-Audio generation model that synthesizes high-quality audio synchronized with video content. In Kling-Foley, we introduce multimodal diffusion transformers to model the interactions between video, audio, and text modalities, and combine it with a visual semantic representation module and an audio-visual synchronization module to enhance alignment capabilities. Specifically, these modules align video conditions with latent audio elements at the frame level, thereby improving semantic alignment and audio-visual synchronization. Together with text conditions, this integrated approach enables precise generation of video-matching sound effects. In addition, we propose a universal latent audio codec that can achieve high-quality modeling in various scenarios such as sound effects, speech, singing, and music. We employ a stereo rendering method that imbues synthesized audio with a spatial presence. At the same time, in order to make up for the incomplete types and annotations of the open-source benchmark, we also open-source an industrial-level benchmark Kling-Audio-Eval. Our experiments show that Kling-Foley trained with the flow matching objective achieves new audio-visual SOTA performance among public models in terms of distribution matching, semantic alignment, temporal alignment and audio quality.
Latent Tensor Factorization with Nonlinear PID Control for Missing Data Recovery in Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:Non-Intrusive Load Monitoring (NILM) has emerged as a key smart grid technology, identifying electrical device and providing detailed energy consumption data for precise demand response management. Nevertheless, NILM data suffers from missing values due to inescapable factors like sensor failure, leading to inaccuracies in non-intrusive load monitoring. A stochastic gradient descent (SGD)-based latent factorization of tensors model has proven to be effective in estimating missing data, however, it updates a latent factor solely based on the current stochastic gradient, without considering past information, which leads to slow convergence of anLFT model. To address this issue, this paper proposes a Nonlinear Proportional-integral-derivative (PID)-Incorporated Latent factorization of tensors (NPIL) model with two-fold ideas: a) rebuilding the instant learning error according to the principle of a nonlinear PID controller, thus, the past update information is efficiently incorporated into the learning scheme, and b) implementing gain parameter adaptation by utilizing particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm, hence, the model computational efficiency is effectively improved. Experimental results on real-world NILM datasets demonstrate that the proposed NPIL model surpasses state-of-the-art models in convergence rate and accuracy when predicting the missing NILM data.
TacoDepth: Towards Efficient Radar-Camera Depth Estimation with One-stage Fusion
Apr 16, 2025



Abstract:Radar-Camera depth estimation aims to predict dense and accurate metric depth by fusing input images and Radar data. Model efficiency is crucial for this task in pursuit of real-time processing on autonomous vehicles and robotic platforms. However, due to the sparsity of Radar returns, the prevailing methods adopt multi-stage frameworks with intermediate quasi-dense depth, which are time-consuming and not robust. To address these challenges, we propose TacoDepth, an efficient and accurate Radar-Camera depth estimation model with one-stage fusion. Specifically, the graph-based Radar structure extractor and the pyramid-based Radar fusion module are designed to capture and integrate the graph structures of Radar point clouds, delivering superior model efficiency and robustness without relying on the intermediate depth results. Moreover, TacoDepth can be flexible for different inference modes, providing a better balance of speed and accuracy. Extensive experiments are conducted to demonstrate the efficacy of our method. Compared with the previous state-of-the-art approach, TacoDepth improves depth accuracy and processing speed by 12.8% and 91.8%. Our work provides a new perspective on efficient Radar-Camera depth estimation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge