Sebastian Bodenstedt
Institute for Anthropomatics and Robotics, Karlsruhe Institute of Technology, Karlsruhe
MoE-ACT: Improving Surgical Imitation Learning Policies through Supervised Mixture-of-Experts
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Imitation learning has achieved remarkable success in robotic manipulation, yet its application to surgical robotics remains challenging due to data scarcity, constrained workspaces, and the need for an exceptional level of safety and predictability. We present a supervised Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture designed for phase-structured surgical manipulation tasks, which can be added on top of any autonomous policy. Unlike prior surgical robot learning approaches that rely on multi-camera setups or thousands of demonstrations, we show that a lightweight action decoder policy like Action Chunking Transformer (ACT) can learn complex, long-horizon manipulation from less than 150 demonstrations using solely stereo endoscopic images, when equipped with our architecture. We evaluate our approach on the collaborative surgical task of bowel grasping and retraction, where a robot assistant interprets visual cues from a human surgeon, executes targeted grasping on deformable tissue, and performs sustained retraction. We benchmark our method against state-of-the-art Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models and the standard ACT baseline. Our results show that generalist VLAs fail to acquire the task entirely, even under standard in-distribution conditions. Furthermore, while standard ACT achieves moderate success in-distribution, adopting a supervised MoE architecture significantly boosts its performance, yielding higher success rates in-distribution and demonstrating superior robustness in out-of-distribution scenarios, including novel grasp locations, reduced illumination, and partial occlusions. Notably, it generalizes to unseen testing viewpoints and also transfers zero-shot to ex vivo porcine tissue without additional training, offering a promising pathway toward in vivo deployment. To support this, we present qualitative preliminary results of policy roll-outs during in vivo porcine surgery.
Federated Learning for Surgical Vision in Appendicitis Classification: Results of the FedSurg EndoVis 2024 Challenge
Oct 06, 2025Abstract:Purpose: The FedSurg challenge was designed to benchmark the state of the art in federated learning for surgical video classification. Its goal was to assess how well current methods generalize to unseen clinical centers and adapt through local fine-tuning while enabling collaborative model development without sharing patient data. Methods: Participants developed strategies to classify inflammation stages in appendicitis using a preliminary version of the multi-center Appendix300 video dataset. The challenge evaluated two tasks: generalization to an unseen center and center-specific adaptation after fine-tuning. Submitted approaches included foundation models with linear probing, metric learning with triplet loss, and various FL aggregation schemes (FedAvg, FedMedian, FedSAM). Performance was assessed using F1-score and Expected Cost, with ranking robustness evaluated via bootstrapping and statistical testing. Results: In the generalization task, performance across centers was limited. In the adaptation task, all teams improved after fine-tuning, though ranking stability was low. The ViViT-based submission achieved the strongest overall performance. The challenge highlighted limitations in generalization, sensitivity to class imbalance, and difficulties in hyperparameter tuning in decentralized training, while spatiotemporal modeling and context-aware preprocessing emerged as promising strategies. Conclusion: The FedSurg Challenge establishes the first benchmark for evaluating FL strategies in surgical video classification. Findings highlight the trade-off between local personalization and global robustness, and underscore the importance of architecture choice, preprocessing, and loss design. This benchmarking offers a reference point for future development of imbalance-aware, adaptive, and robust FL methods in clinical surgical AI.
Federated EndoViT: Pretraining Vision Transformers via Federated Learning on Endoscopic Image Collections
Apr 23, 2025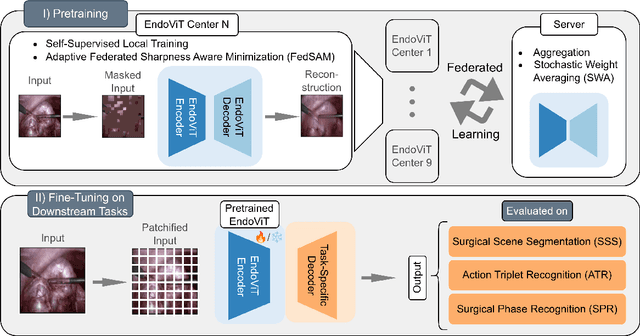
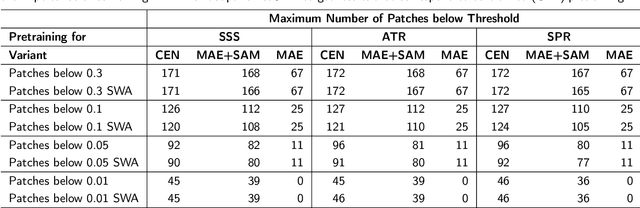
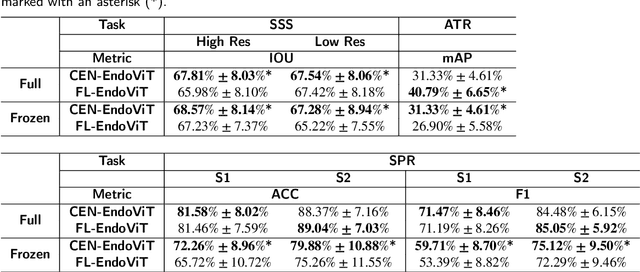
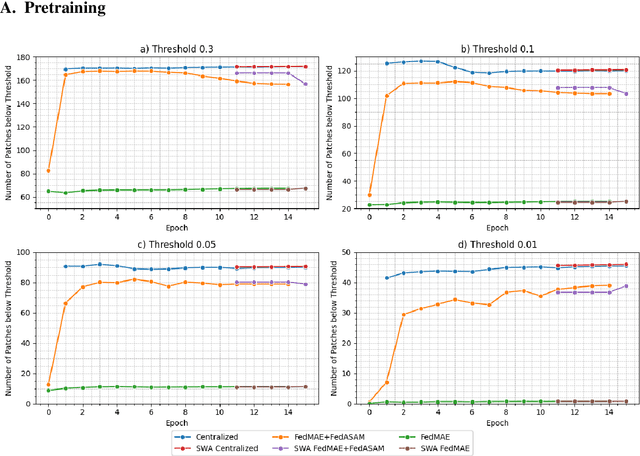
Abstract:Purpose: In this study, we investigate the training of foundation models using federated learning to address data-sharing limitations and enable collaborative model training without data transfer for minimally invasive surgery. Methods: Inspired by the EndoViT study, we adapt the Masked Autoencoder for federated learning, enhancing it with adaptive Sharpness-Aware Minimization (FedSAM) and Stochastic Weight Averaging (SWA). Our model is pretrained on the Endo700k dataset collection and later fine-tuned and evaluated for tasks such as Semantic Segmentation, Action Triplet Recognition, and Surgical Phase Recognition. Results: Our findings demonstrate that integrating adaptive FedSAM into the federated MAE approach improves pretraining, leading to a reduction in reconstruction loss per patch. The application of FL-EndoViT in surgical downstream tasks results in performance comparable to CEN-EndoViT. Furthermore, FL-EndoViT exhibits advantages over CEN-EndoViT in surgical scene segmentation when data is limited and in action triplet recognition when large datasets are used. Conclusion: These findings highlight the potential of federated learning for privacy-preserving training of surgical foundation models, offering a robust and generalizable solution for surgical data science. Effective collaboration requires adapting federated learning methods, such as the integration of FedSAM, which can accommodate the inherent data heterogeneity across institutions. In future, exploring FL in video-based models may enhance these capabilities by incorporating spatiotemporal dynamics crucial for real-world surgical environments.
One model to use them all: Training a segmentation model with complementary datasets
Feb 29, 2024Abstract:Understanding a surgical scene is crucial for computer-assisted surgery systems to provide any intelligent assistance functionality. One way of achieving this scene understanding is via scene segmentation, where every pixel of a frame is classified and therefore identifies the visible structures and tissues. Progress on fully segmenting surgical scenes has been made using machine learning. However, such models require large amounts of annotated training data, containing examples of all relevant object classes. Such fully annotated datasets are hard to create, as every pixel in a frame needs to be annotated by medical experts and, therefore, are rarely available. In this work, we propose a method to combine multiple partially annotated datasets, which provide complementary annotations, into one model, enabling better scene segmentation and the use of multiple readily available datasets. Our method aims to combine available data with complementary labels by leveraging mutual exclusive properties to maximize information. Specifically, we propose to use positive annotations of other classes as negative samples and to exclude background pixels of binary annotations, as we cannot tell if they contain a class not annotated but predicted by the model. We evaluate our method by training a DeepLabV3 on the publicly available Dresden Surgical Anatomy Dataset, which provides multiple subsets of binary segmented anatomical structures. Our approach successfully combines 6 classes into one model, increasing the overall Dice Score by 4.4% compared to an ensemble of models trained on the classes individually. By including information on multiple classes, we were able to reduce confusion between stomach and colon by 24%. Our results demonstrate the feasibility of training a model on multiple datasets. This paves the way for future work further alleviating the need for one large, fully segmented datasets.
SAR-RARP50: Segmentation of surgical instrumentation and Action Recognition on Robot-Assisted Radical Prostatectomy Challenge
Dec 31, 2023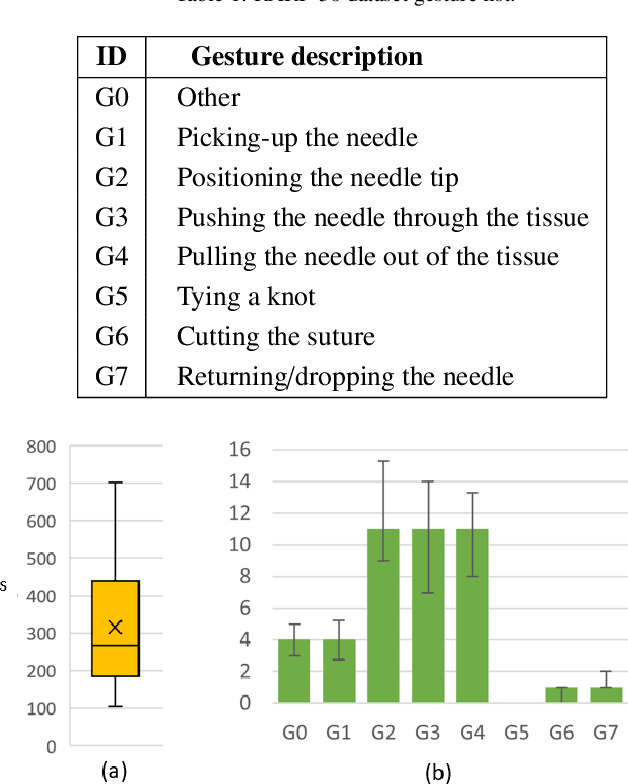
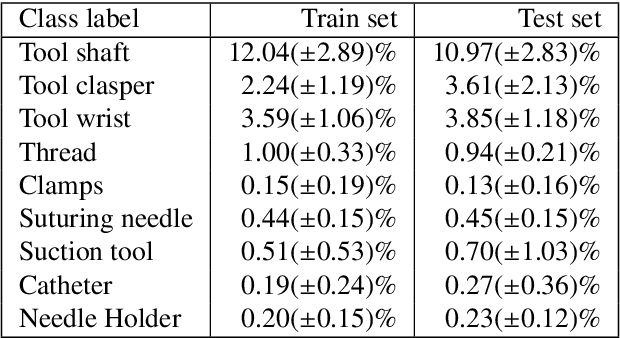
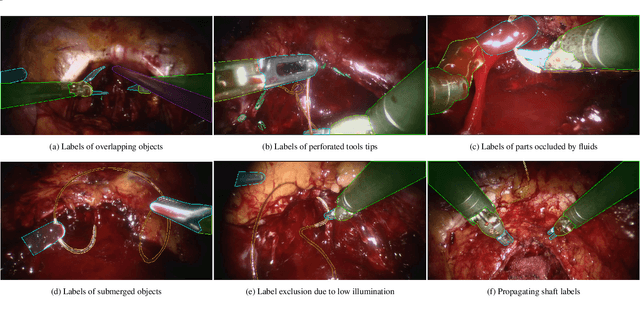
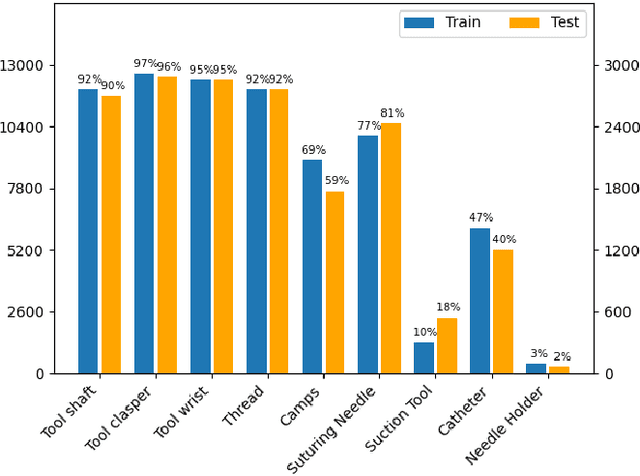
Abstract:Surgical tool segmentation and action recognition are fundamental building blocks in many computer-assisted intervention applications, ranging from surgical skills assessment to decision support systems. Nowadays, learning-based action recognition and segmentation approaches outperform classical methods, relying, however, on large, annotated datasets. Furthermore, action recognition and tool segmentation algorithms are often trained and make predictions in isolation from each other, without exploiting potential cross-task relationships. With the EndoVis 2022 SAR-RARP50 challenge, we release the first multimodal, publicly available, in-vivo, dataset for surgical action recognition and semantic instrumentation segmentation, containing 50 suturing video segments of Robotic Assisted Radical Prostatectomy (RARP). The aim of the challenge is twofold. First, to enable researchers to leverage the scale of the provided dataset and develop robust and highly accurate single-task action recognition and tool segmentation approaches in the surgical domain. Second, to further explore the potential of multitask-based learning approaches and determine their comparative advantage against their single-task counterparts. A total of 12 teams participated in the challenge, contributing 7 action recognition methods, 9 instrument segmentation techniques, and 4 multitask approaches that integrated both action recognition and instrument segmentation.
Graph data modelling for outcome prediction in oropharyngeal cancer patients
Oct 04, 2023



Abstract:Graph neural networks (GNNs) are becoming increasingly popular in the medical domain for the tasks of disease classification and outcome prediction. Since patient data is not readily available as a graph, most existing methods either manually define a patient graph, or learn a latent graph based on pairwise similarities between the patients. There are also hypergraph neural network (HGNN)-based methods that were introduced recently to exploit potential higher order associations between the patients by representing them as a hypergraph. In this work, we propose a patient hypergraph network (PHGN), which has been investigated in an inductive learning setup for binary outcome prediction in oropharyngeal cancer (OPC) patients using computed tomography (CT)-based radiomic features for the first time. Additionally, the proposed model was extended to perform time-to-event analyses, and compared with GNN and baseline linear models.
Non-rigid Point Cloud Registration for Middle Ear Diagnostics with Endoscopic Optical Coherence Tomography
Apr 26, 2023Abstract:Purpose: Middle ear infection is the most prevalent inflammatory disease, especially among the pediatric population. Current diagnostic methods are subjective and depend on visual cues from an otoscope, which is limited for otologists to identify pathology. To address this shortcoming, endoscopic optical coherence tomography (OCT) provides both morphological and functional in-vivo measurements of the middle ear. However, due to the shadow of prior structures, interpretation of OCT images is challenging and time-consuming. To facilitate fast diagnosis and measurement, improvement in the readability of OCT data is achieved by merging morphological knowledge from ex-vivo middle ear models with OCT volumetric data, so that OCT applications can be further promoted in daily clinical settings. Methods: We propose C2P-Net: a two-staged non-rigid registration pipeline for complete to partial point clouds, which are sampled from ex-vivo and in-vivo OCT models, respectively. To overcome the lack of labeled training data, a fast and effective generation pipeline in Blender3D is designed to simulate middle ear shapes and extract in-vivo noisy and partial point clouds. Results: We evaluate the performance of C2P-Net through experiments on both synthetic and real OCT datasets. The results demonstrate that C2P-Net is generalized to unseen middle ear point clouds and capable of handling realistic noise and incompleteness in synthetic and real OCT data. Conclusion: In this work, we aim to enable diagnosis of middle ear structures with the assistance of OCT images. We propose C2P-Net: a two-staged non-rigid registration pipeline for point clouds to support the interpretation of in-vivo noisy and partial OCT images for the first time. Code is available at: https://gitlab.com/nct\_tso\_public/c2p-net.
Why is the winner the best?
Mar 30, 2023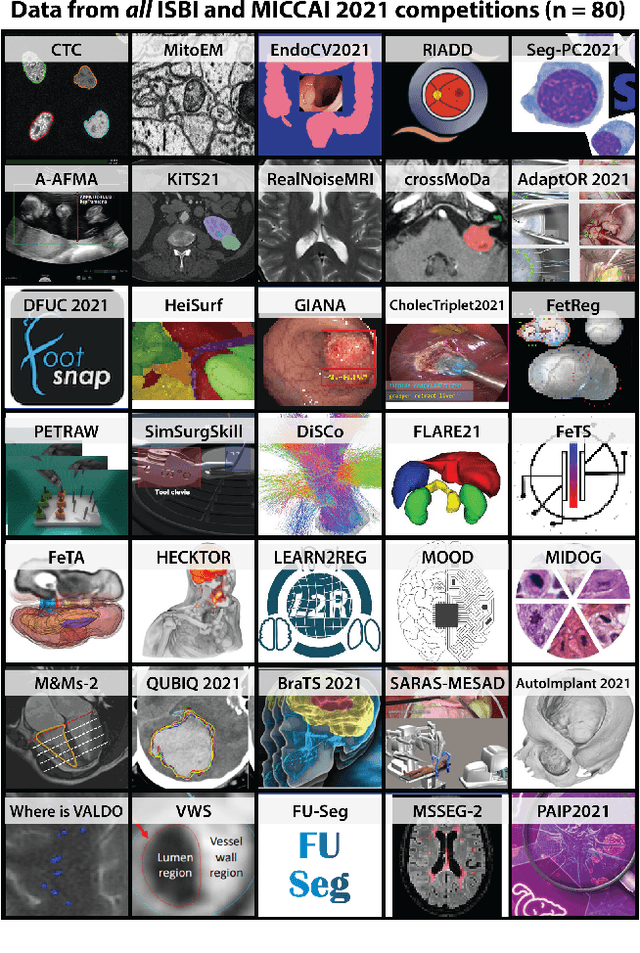
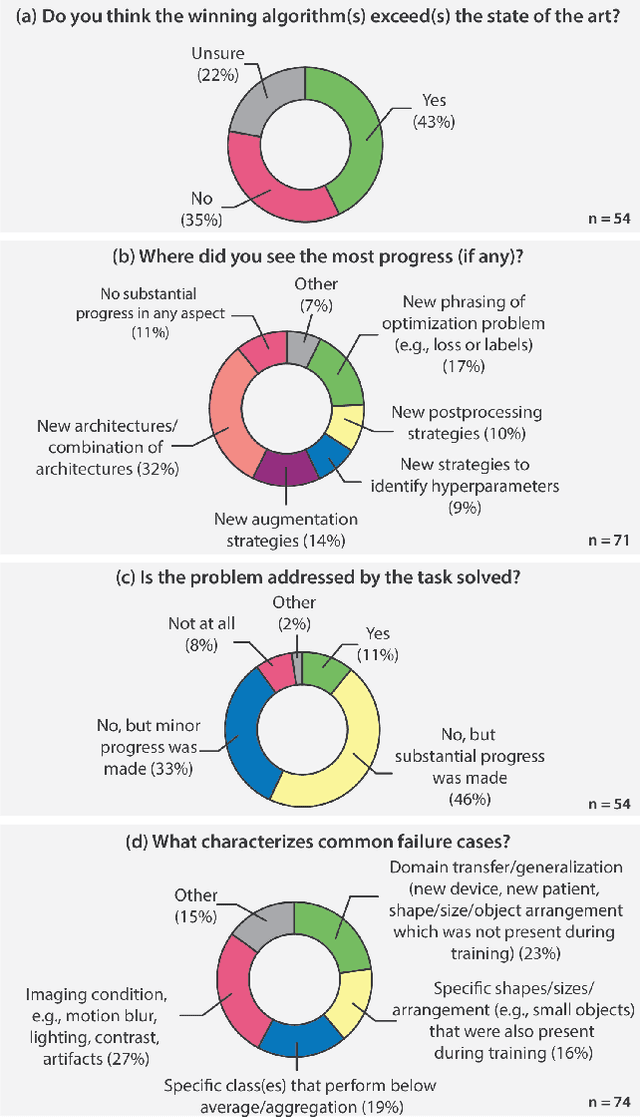
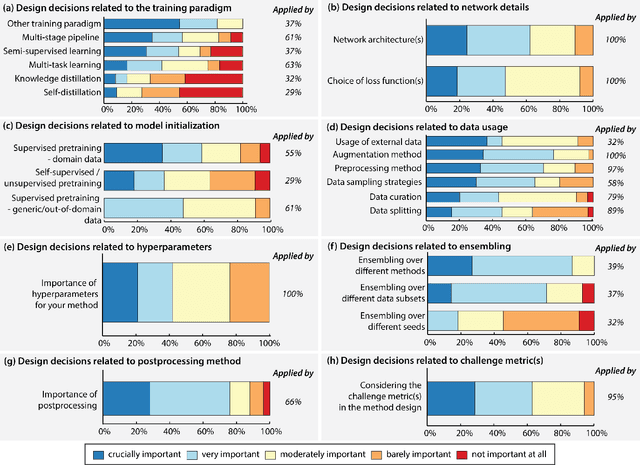
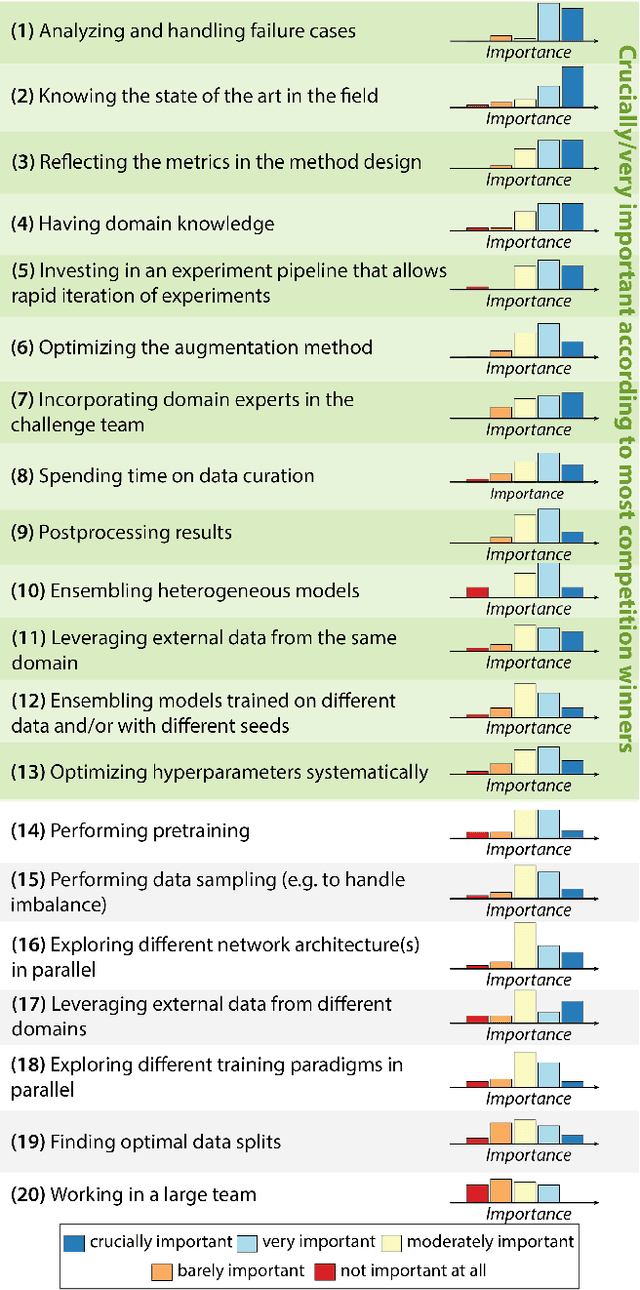
Abstract:International benchmarking competitions have become fundamental for the comparative performance assessment of image analysis methods. However, little attention has been given to investigating what can be learnt from these competitions. Do they really generate scientific progress? What are common and successful participation strategies? What makes a solution superior to a competing method? To address this gap in the literature, we performed a multi-center study with all 80 competitions that were conducted in the scope of IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021. Statistical analyses performed based on comprehensive descriptions of the submitted algorithms linked to their rank as well as the underlying participation strategies revealed common characteristics of winning solutions. These typically include the use of multi-task learning (63%) and/or multi-stage pipelines (61%), and a focus on augmentation (100%), image preprocessing (97%), data curation (79%), and postprocessing (66%). The "typical" lead of a winning team is a computer scientist with a doctoral degree, five years of experience in biomedical image analysis, and four years of experience in deep learning. Two core general development strategies stood out for highly-ranked teams: the reflection of the metrics in the method design and the focus on analyzing and handling failure cases. According to the organizers, 43% of the winning algorithms exceeded the state of the art but only 11% completely solved the respective domain problem. The insights of our study could help researchers (1) improve algorithm development strategies when approaching new problems, and (2) focus on open research questions revealed by this work.
Biomedical image analysis competitions: The state of current participation practice
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:The number of international benchmarking competitions is steadily increasing in various fields of machine learning (ML) research and practice. So far, however, little is known about the common practice as well as bottlenecks faced by the community in tackling the research questions posed. To shed light on the status quo of algorithm development in the specific field of biomedical imaging analysis, we designed an international survey that was issued to all participants of challenges conducted in conjunction with the IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021 conferences (80 competitions in total). The survey covered participants' expertise and working environments, their chosen strategies, as well as algorithm characteristics. A median of 72% challenge participants took part in the survey. According to our results, knowledge exchange was the primary incentive (70%) for participation, while the reception of prize money played only a minor role (16%). While a median of 80 working hours was spent on method development, a large portion of participants stated that they did not have enough time for method development (32%). 25% perceived the infrastructure to be a bottleneck. Overall, 94% of all solutions were deep learning-based. Of these, 84% were based on standard architectures. 43% of the respondents reported that the data samples (e.g., images) were too large to be processed at once. This was most commonly addressed by patch-based training (69%), downsampling (37%), and solving 3D analysis tasks as a series of 2D tasks. K-fold cross-validation on the training set was performed by only 37% of the participants and only 50% of the participants performed ensembling based on multiple identical models (61%) or heterogeneous models (39%). 48% of the respondents applied postprocessing steps.
CholecTriplet2021: A benchmark challenge for surgical action triplet recognition
Apr 10, 2022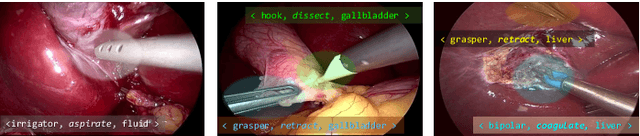
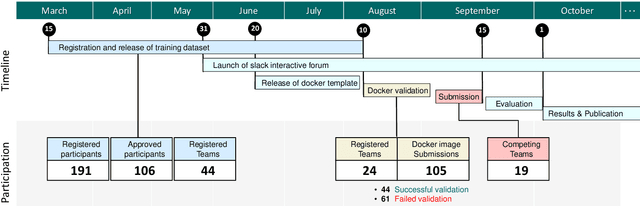
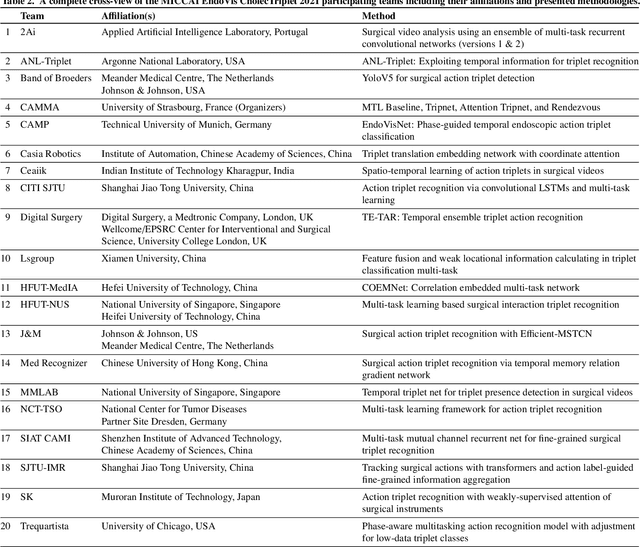
Abstract:Context-aware decision support in the operating room can foster surgical safety and efficiency by leveraging real-time feedback from surgical workflow analysis. Most existing works recognize surgical activities at a coarse-grained level, such as phases, steps or events, leaving out fine-grained interaction details about the surgical activity; yet those are needed for more helpful AI assistance in the operating room. Recognizing surgical actions as triplets of <instrument, verb, target> combination delivers comprehensive details about the activities taking place in surgical videos. This paper presents CholecTriplet2021: an endoscopic vision challenge organized at MICCAI 2021 for the recognition of surgical action triplets in laparoscopic videos. The challenge granted private access to the large-scale CholecT50 dataset, which is annotated with action triplet information. In this paper, we present the challenge setup and assessment of the state-of-the-art deep learning methods proposed by the participants during the challenge. A total of 4 baseline methods from the challenge organizers and 19 new deep learning algorithms by competing teams are presented to recognize surgical action triplets directly from surgical videos, achieving mean average precision (mAP) ranging from 4.2% to 38.1%. This study also analyzes the significance of the results obtained by the presented approaches, performs a thorough methodological comparison between them, in-depth result analysis, and proposes a novel ensemble method for enhanced recognition. Our analysis shows that surgical workflow analysis is not yet solved, and also highlights interesting directions for future research on fine-grained surgical activity recognition which is of utmost importance for the development of AI in surgery.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge