Fangfang Xia
Division of Data Science and Learning, Argonne National Laboratory, Argonne, IL, USA, University of Chicago Consortium for Advanced Science and Engineering, University of Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA
Scaling Large Vision-Language Models for Enhanced Multimodal Comprehension In Biomedical Image Analysis
Jan 26, 2025Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated immense capabilities in understanding textual data and are increasingly being adopted to help researchers accelerate scientific discovery through knowledge extraction (information retrieval), knowledge distillation (summarizing key findings and methodologies into concise forms), and knowledge synthesis (aggregating information from multiple scientific sources to address complex queries, generate hypothesis and formulate experimental plans). However, scientific data often exists in both visual and textual modalities. Vision language models (VLMs) address this by incorporating a pretrained vision backbone for processing images and a cross-modal projector that adapts image tokens into the LLM dimensional space, thereby providing richer multimodal comprehension. Nevertheless, off-the-shelf VLMs show limited capabilities in handling domain-specific data and are prone to hallucinations. We developed intelligent assistants finetuned from LLaVA models to enhance multimodal understanding in low-dose radiation therapy (LDRT)-a benign approach used in the treatment of cancer-related illnesses. Using multilingual data from 42,673 articles, we devise complex reasoning and detailed description tasks for visual question answering (VQA) benchmarks. Our assistants, trained on 50,882 image-text pairs, demonstrate superior performance over base models as evaluated using LLM-as-a-judge approach, particularly in reducing hallucination and improving domain-specific comprehension.
Surgical tool classification and localization: results and methods from the MICCAI 2022 SurgToolLoc challenge
May 11, 2023



Abstract:The ability to automatically detect and track surgical instruments in endoscopic videos can enable transformational interventions. Assessing surgical performance and efficiency, identifying skilled tool use and choreography, and planning operational and logistical aspects of OR resources are just a few of the applications that could benefit. Unfortunately, obtaining the annotations needed to train machine learning models to identify and localize surgical tools is a difficult task. Annotating bounding boxes frame-by-frame is tedious and time-consuming, yet large amounts of data with a wide variety of surgical tools and surgeries must be captured for robust training. Moreover, ongoing annotator training is needed to stay up to date with surgical instrument innovation. In robotic-assisted surgery, however, potentially informative data like timestamps of instrument installation and removal can be programmatically harvested. The ability to rely on tool installation data alone would significantly reduce the workload to train robust tool-tracking models. With this motivation in mind we invited the surgical data science community to participate in the challenge, SurgToolLoc 2022. The goal was to leverage tool presence data as weak labels for machine learning models trained to detect tools and localize them in video frames with bounding boxes. We present the results of this challenge along with many of the team's efforts. We conclude by discussing these results in the broader context of machine learning and surgical data science. The training data used for this challenge consisting of 24,695 video clips with tool presence labels is also being released publicly and can be accessed at https://console.cloud.google.com/storage/browser/isi-surgtoolloc-2022.
Why is the winner the best?
Mar 30, 2023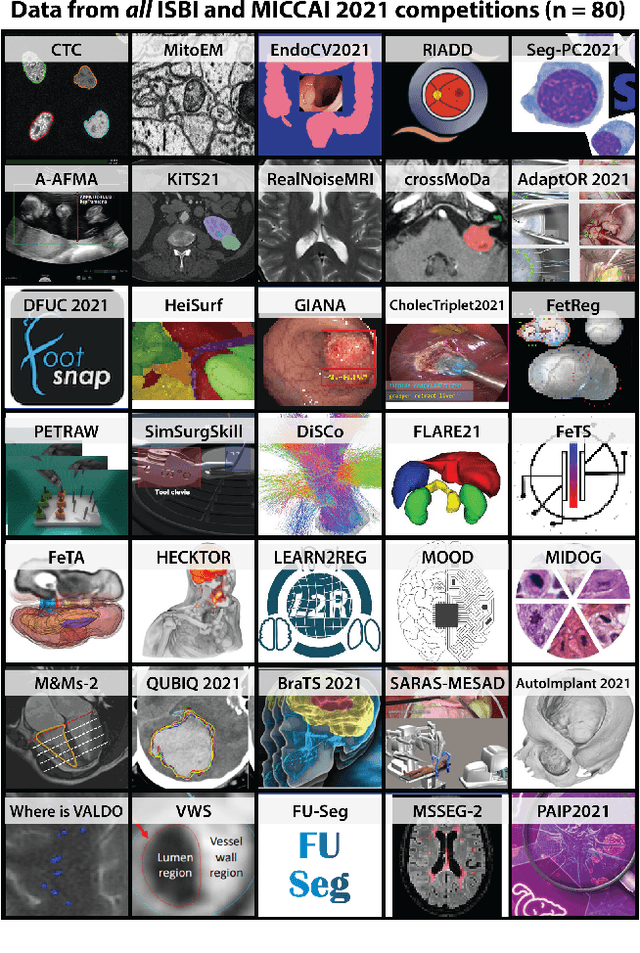
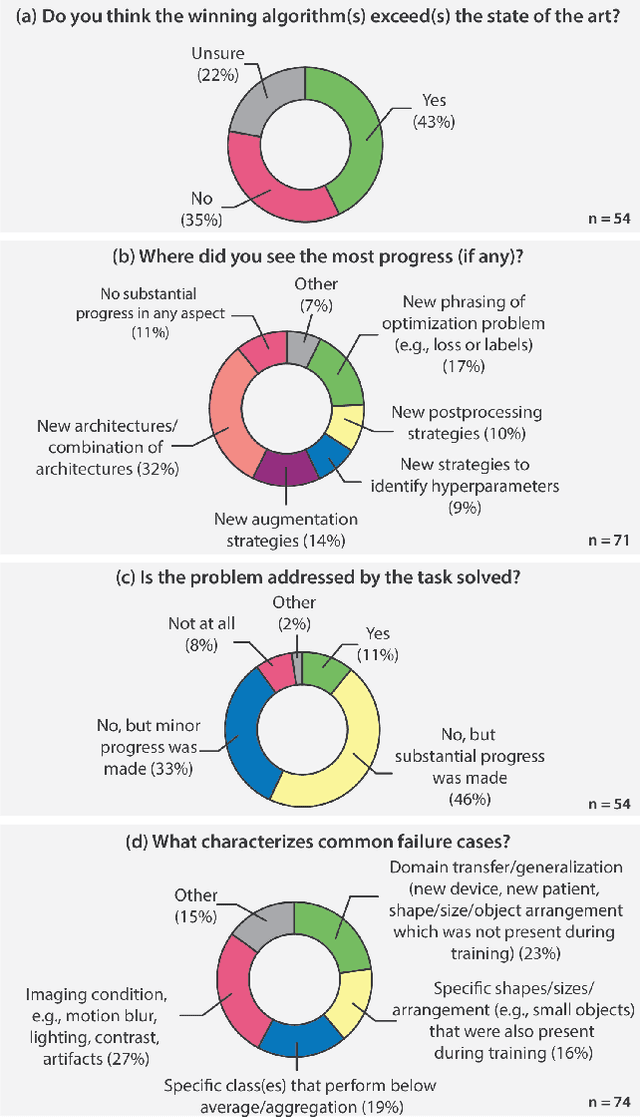
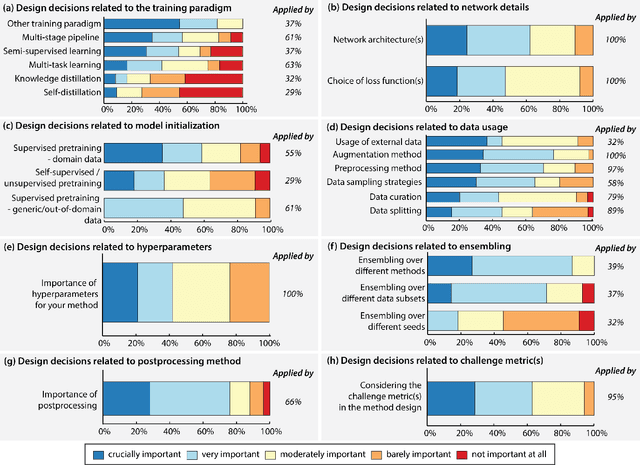
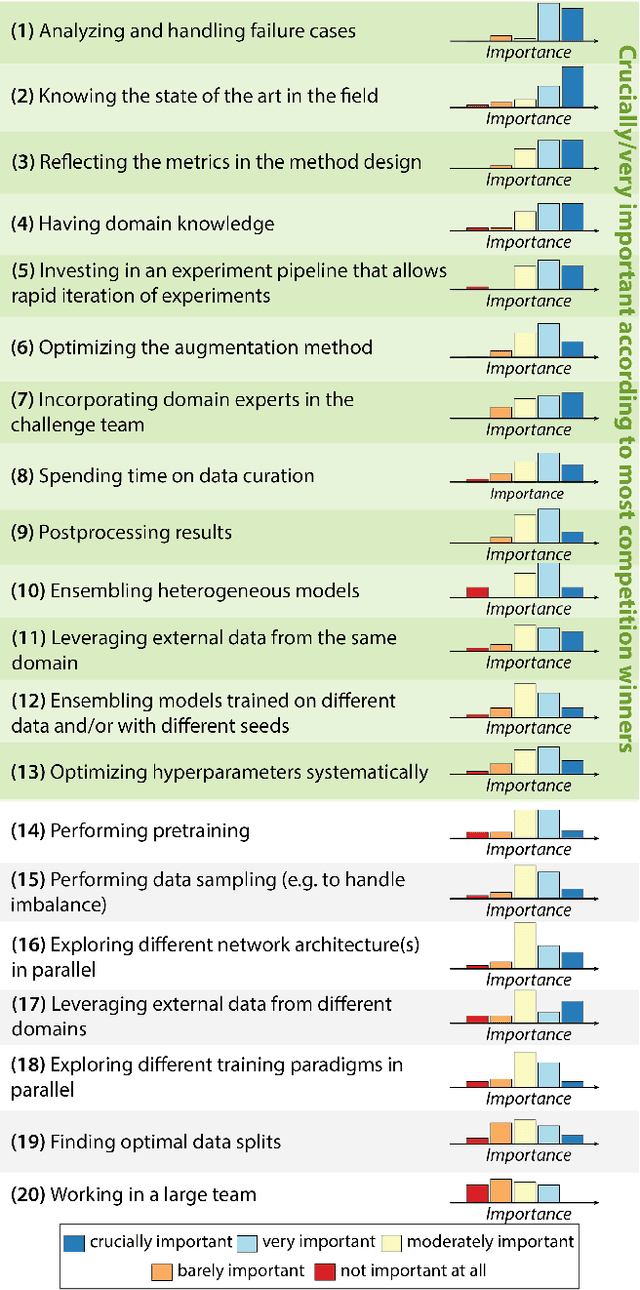
Abstract:International benchmarking competitions have become fundamental for the comparative performance assessment of image analysis methods. However, little attention has been given to investigating what can be learnt from these competitions. Do they really generate scientific progress? What are common and successful participation strategies? What makes a solution superior to a competing method? To address this gap in the literature, we performed a multi-center study with all 80 competitions that were conducted in the scope of IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021. Statistical analyses performed based on comprehensive descriptions of the submitted algorithms linked to their rank as well as the underlying participation strategies revealed common characteristics of winning solutions. These typically include the use of multi-task learning (63%) and/or multi-stage pipelines (61%), and a focus on augmentation (100%), image preprocessing (97%), data curation (79%), and postprocessing (66%). The "typical" lead of a winning team is a computer scientist with a doctoral degree, five years of experience in biomedical image analysis, and four years of experience in deep learning. Two core general development strategies stood out for highly-ranked teams: the reflection of the metrics in the method design and the focus on analyzing and handling failure cases. According to the organizers, 43% of the winning algorithms exceeded the state of the art but only 11% completely solved the respective domain problem. The insights of our study could help researchers (1) improve algorithm development strategies when approaching new problems, and (2) focus on open research questions revealed by this work.
Biomedical image analysis competitions: The state of current participation practice
Dec 16, 2022Abstract:The number of international benchmarking competitions is steadily increasing in various fields of machine learning (ML) research and practice. So far, however, little is known about the common practice as well as bottlenecks faced by the community in tackling the research questions posed. To shed light on the status quo of algorithm development in the specific field of biomedical imaging analysis, we designed an international survey that was issued to all participants of challenges conducted in conjunction with the IEEE ISBI 2021 and MICCAI 2021 conferences (80 competitions in total). The survey covered participants' expertise and working environments, their chosen strategies, as well as algorithm characteristics. A median of 72% challenge participants took part in the survey. According to our results, knowledge exchange was the primary incentive (70%) for participation, while the reception of prize money played only a minor role (16%). While a median of 80 working hours was spent on method development, a large portion of participants stated that they did not have enough time for method development (32%). 25% perceived the infrastructure to be a bottleneck. Overall, 94% of all solutions were deep learning-based. Of these, 84% were based on standard architectures. 43% of the respondents reported that the data samples (e.g., images) were too large to be processed at once. This was most commonly addressed by patch-based training (69%), downsampling (37%), and solving 3D analysis tasks as a series of 2D tasks. K-fold cross-validation on the training set was performed by only 37% of the participants and only 50% of the participants performed ensembling based on multiple identical models (61%) or heterogeneous models (39%). 48% of the respondents applied postprocessing steps.
Cost-Effective Online Contextual Model Selection
Jul 13, 2022

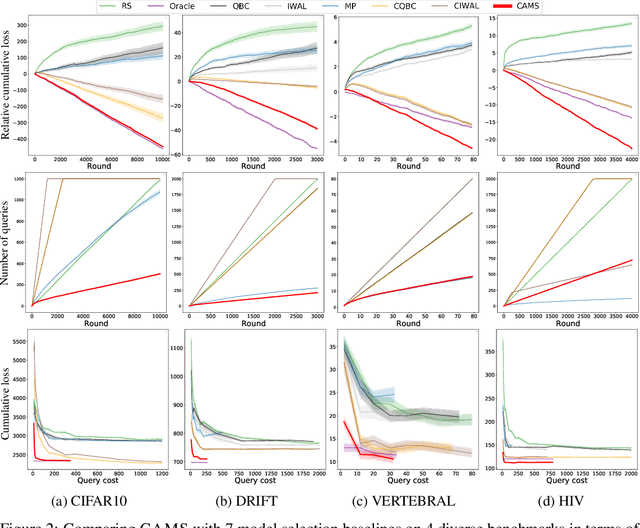
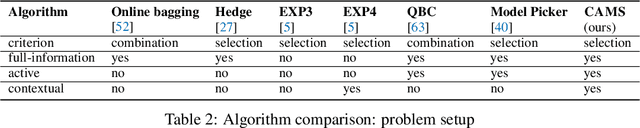
Abstract:How can we collect the most useful labels to learn a model selection policy, when presented with arbitrary heterogeneous data streams? In this paper, we formulate this task as an online contextual active model selection problem, where at each round the learner receives an unlabeled data point along with a context. The goal is to output the best model for any given context without obtaining an excessive amount of labels. In particular, we focus on the task of selecting pre-trained classifiers, and propose a contextual active model selection algorithm (CAMS), which relies on a novel uncertainty sampling query criterion defined on a given policy class for adaptive model selection. In comparison to prior art, our algorithm does not assume a globally optimal model. We provide rigorous theoretical analysis for the regret and query complexity under both adversarial and stochastic settings. Our experiments on several benchmark classification datasets demonstrate the algorithm's effectiveness in terms of both regret and query complexity. Notably, to achieve the same accuracy, CAMS incurs less than 10% of the label cost when compared to the best online model selection baselines on CIFAR10.
CholecTriplet2021: A benchmark challenge for surgical action triplet recognition
Apr 10, 2022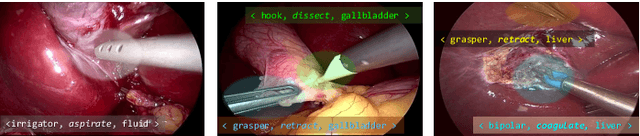
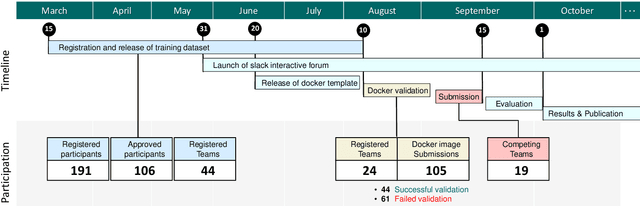
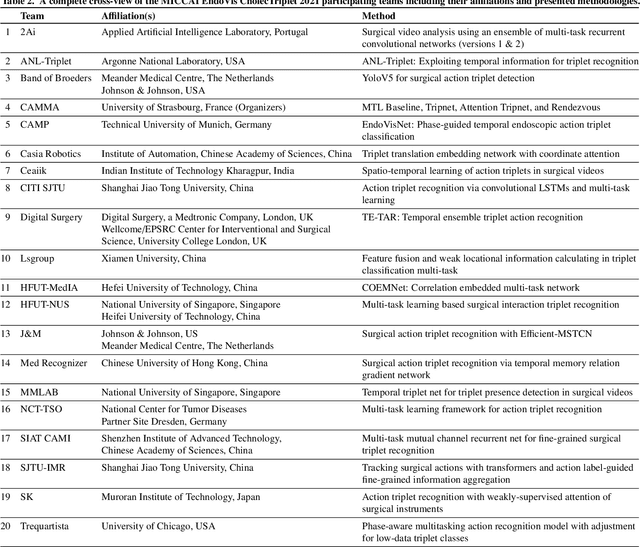
Abstract:Context-aware decision support in the operating room can foster surgical safety and efficiency by leveraging real-time feedback from surgical workflow analysis. Most existing works recognize surgical activities at a coarse-grained level, such as phases, steps or events, leaving out fine-grained interaction details about the surgical activity; yet those are needed for more helpful AI assistance in the operating room. Recognizing surgical actions as triplets of <instrument, verb, target> combination delivers comprehensive details about the activities taking place in surgical videos. This paper presents CholecTriplet2021: an endoscopic vision challenge organized at MICCAI 2021 for the recognition of surgical action triplets in laparoscopic videos. The challenge granted private access to the large-scale CholecT50 dataset, which is annotated with action triplet information. In this paper, we present the challenge setup and assessment of the state-of-the-art deep learning methods proposed by the participants during the challenge. A total of 4 baseline methods from the challenge organizers and 19 new deep learning algorithms by competing teams are presented to recognize surgical action triplets directly from surgical videos, achieving mean average precision (mAP) ranging from 4.2% to 38.1%. This study also analyzes the significance of the results obtained by the presented approaches, performs a thorough methodological comparison between them, in-depth result analysis, and proposes a novel ensemble method for enhanced recognition. Our analysis shows that surgical workflow analysis is not yet solved, and also highlights interesting directions for future research on fine-grained surgical activity recognition which is of utmost importance for the development of AI in surgery.
Neko: a Library for Exploring Neuromorphic Learning Rules
May 01, 2021



Abstract:The field of neuromorphic computing is in a period of active exploration. While many tools have been developed to simulate neuronal dynamics or convert deep networks to spiking models, general software libraries for learning rules remain underexplored. This is partly due to the diverse, challenging nature of efforts to design new learning rules, which range from encoding methods to gradient approximations, from population approaches that mimic the Bayesian brain to constrained learning algorithms deployed on memristor crossbars. To address this gap, we present Neko, a modular, extensible library with a focus on aiding the design of new learning algorithms. We demonstrate the utility of Neko in three exemplar cases: online local learning, probabilistic learning, and analog on-device learning. Our results show that Neko can replicate the state-of-the-art algorithms and, in one case, lead to significant outperformance in accuracy and speed. Further, it offers tools including gradient comparison that can help develop new algorithmic variants. Neko is an open source Python library that supports PyTorch and TensorFlow backends.
Pandemic Drugs at Pandemic Speed: Accelerating COVID-19 Drug Discovery with Hybrid Machine Learning- and Physics-based Simulations on High Performance Computers
Mar 04, 2021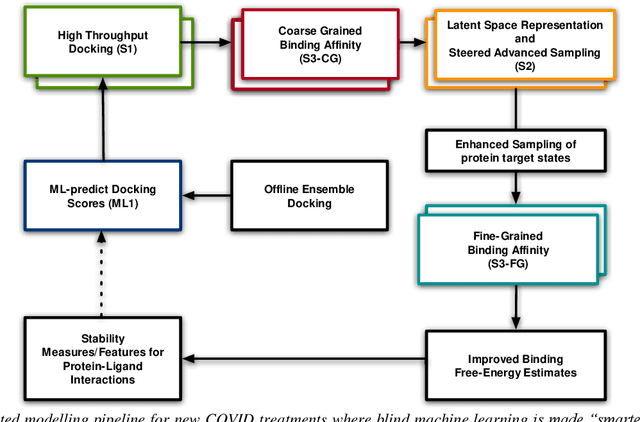
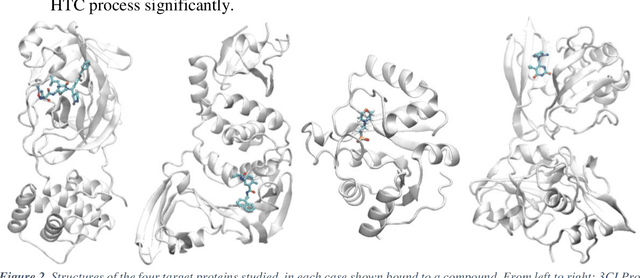
Abstract:The race to meet the challenges of the global pandemic has served as a reminder that the existing drug discovery process is expensive, inefficient and slow. There is a major bottleneck screening the vast number of potential small molecules to shortlist lead compounds for antiviral drug development. New opportunities to accelerate drug discovery lie at the interface between machine learning methods, in this case developed for linear accelerators, and physics-based methods. The two in silico methods, each have their own advantages and limitations which, interestingly, complement each other. Here, we present an innovative method that combines both approaches to accelerate drug discovery. The scale of the resulting workflow is such that it is dependent on high performance computing. We have demonstrated the applicability of this workflow on four COVID-19 target proteins and our ability to perform the required large-scale calculations to identify lead compounds on a variety of supercomputers.
Learning Curves for Drug Response Prediction in Cancer Cell Lines
Nov 25, 2020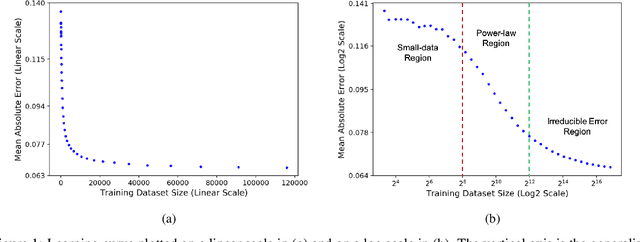
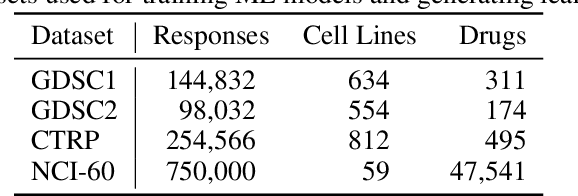
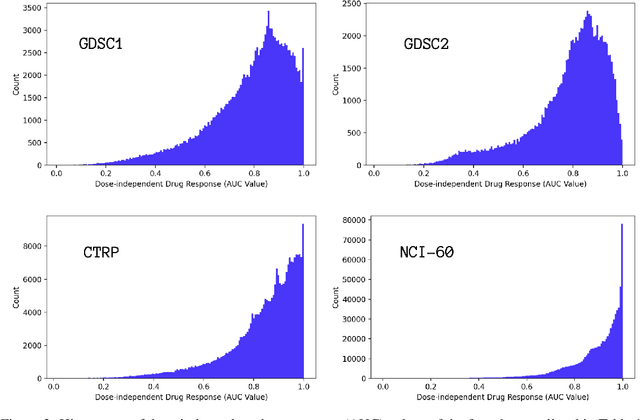
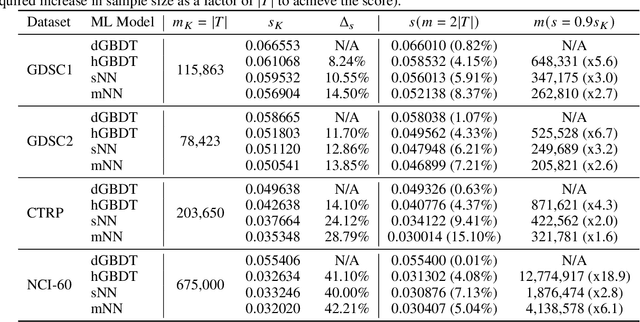
Abstract:Motivated by the size of cell line drug sensitivity data, researchers have been developing machine learning (ML) models for predicting drug response to advance cancer treatment. As drug sensitivity studies continue generating data, a common question is whether the proposed predictors can further improve the generalization performance with more training data. We utilize empirical learning curves for evaluating and comparing the data scaling properties of two neural networks (NNs) and two gradient boosting decision tree (GBDT) models trained on four drug screening datasets. The learning curves are accurately fitted to a power law model, providing a framework for assessing the data scaling behavior of these predictors. The curves demonstrate that no single model dominates in terms of prediction performance across all datasets and training sizes, suggesting that the shape of these curves depends on the unique model-dataset pair. The multi-input NN (mNN), in which gene expressions and molecular drug descriptors are input into separate subnetworks, outperforms a single-input NN (sNN), where the cell and drug features are concatenated for the input layer. In contrast, a GBDT with hyperparameter tuning exhibits superior performance as compared with both NNs at the lower range of training sizes for two of the datasets, whereas the mNN performs better at the higher range of training sizes. Moreover, the trajectory of the curves suggests that increasing the sample size is expected to further improve prediction scores of both NNs. These observations demonstrate the benefit of using learning curves to evaluate predictors, providing a broader perspective on the overall data scaling characteristics. The fitted power law curves provide a forward-looking performance metric and can serve as a co-design tool to guide experimental biologists and computational scientists in the design of future experiments.
Recurrent and Spiking Modeling of Sparse Surgical Kinematics
Jun 11, 2020



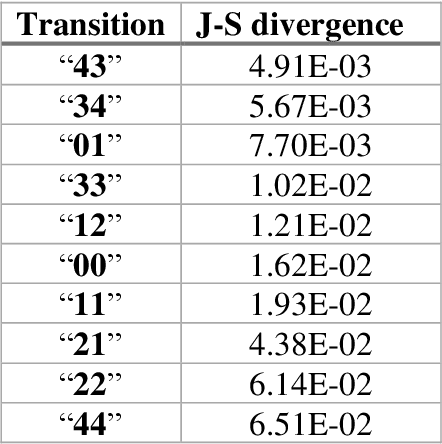
Abstract:Robot-assisted minimally invasive surgery is improving surgeon performance and patient outcomes. This innovation is also turning what has been a subjective practice into motion sequences that can be precisely measured. A growing number of studies have used machine learning to analyze video and kinematic data captured from surgical robots. In these studies, models are typically trained on benchmark datasets for representative surgical tasks to assess surgeon skill levels. While they have shown that novices and experts can be accurately classified, it is not clear whether machine learning can separate highly proficient surgeons from one another, especially without video data. In this study, we explore the possibility of using only kinematic data to predict surgeons of similar skill levels. We focus on a new dataset created from surgical exercises on a simulation device for skill training. A simple, efficient encoding scheme was devised to encode kinematic sequences so that they were amenable to edge learning. We report that it is possible to identify surgical fellows receiving near perfect scores in the simulation exercises based on their motion characteristics alone. Further, our model could be converted to a spiking neural network to train and infer on the Nengo simulation framework with no loss in accuracy. Overall, this study suggests that building neuromorphic models from sparse motion features may be a potentially useful strategy for identifying surgeons and gestures with chips deployed on robotic systems to offer adaptive assistance during surgery and training with additional latency and privacy benefits.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge