Rick L. Stevens
Division of Data Science and Learning, Argonne National Laboratory, Lemont, IL, USA, Department of Computer Science, The University of Chicago, Chicago, IL, USA
Scalable Agentic Reasoning for Designing Biologics Targeting Intrinsically Disordered Proteins
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:Intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs) represent crucial therapeutic targets due to their significant role in disease -- approximately 80\% of cancer-related proteins contain long disordered regions -- but their lack of stable secondary/tertiary structures makes them "undruggable". While recent computational advances, such as diffusion models, can design high-affinity IDP binders, translating these to practical drug discovery requires autonomous systems capable of reasoning across complex conformational ensembles and orchestrating diverse computational tools at scale.To address this challenge, we designed and implemented StructBioReasoner, a scalable multi-agent system for designing biologics that can be used to target IDPs. StructBioReasoner employs a novel tournament-based reasoning framework where specialized agents compete to generate and refine therapeutic hypotheses, naturally distributing computational load for efficient exploration of the vast design space. Agents integrate domain knowledge with access to literature synthesis, AI-structure prediction, molecular simulations, and stability analysis, coordinating their execution on HPC infrastructure via an extensible federated agentic middleware, Academy. We benchmark StructBioReasoner across Der f 21 and NMNAT-2 and demonstrate that over 50\% of 787 designed and validated candidates for Der f 21 outperformed the human-designed reference binders from literature, in terms of improved binding free energy. For the more challenging NMNAT-2 protein, we identified three binding modes from 97,066 binders, including the well-studied NMNAT2:p53 interface. Thus, StructBioReasoner lays the groundwork for agentic reasoning systems for IDP therapeutic discovery on Exascale platforms.
Benchmarking community drug response prediction models: datasets, models, tools, and metrics for cross-dataset generalization analysis
Mar 18, 2025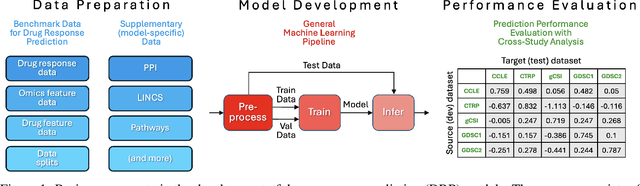
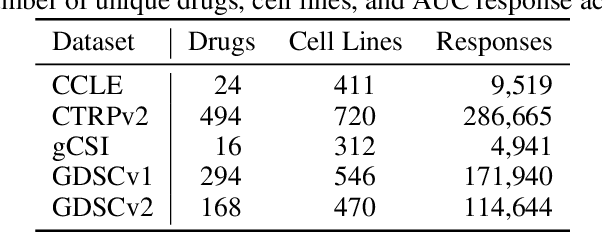
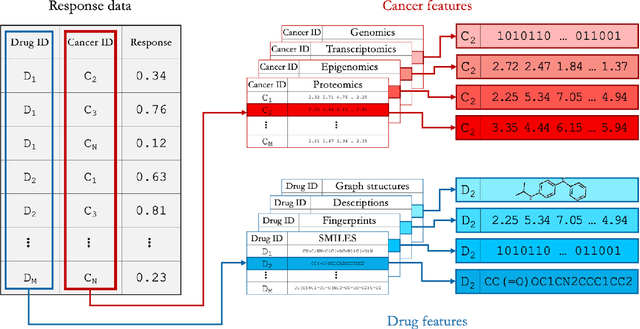

Abstract:Deep learning (DL) and machine learning (ML) models have shown promise in drug response prediction (DRP), yet their ability to generalize across datasets remains an open question, raising concerns about their real-world applicability. Due to the lack of standardized benchmarking approaches, model evaluations and comparisons often rely on inconsistent datasets and evaluation criteria, making it difficult to assess true predictive capabilities. In this work, we introduce a benchmarking framework for evaluating cross-dataset prediction generalization in DRP models. Our framework incorporates five publicly available drug screening datasets, six standardized DRP models, and a scalable workflow for systematic evaluation. To assess model generalization, we introduce a set of evaluation metrics that quantify both absolute performance (e.g., predictive accuracy across datasets) and relative performance (e.g., performance drop compared to within-dataset results), enabling a more comprehensive assessment of model transferability. Our results reveal substantial performance drops when models are tested on unseen datasets, underscoring the importance of rigorous generalization assessments. While several models demonstrate relatively strong cross-dataset generalization, no single model consistently outperforms across all datasets. Furthermore, we identify CTRPv2 as the most effective source dataset for training, yielding higher generalization scores across target datasets. By sharing this standardized evaluation framework with the community, our study aims to establish a rigorous foundation for model comparison, and accelerate the development of robust DRP models for real-world applications.
Entropy-Reinforced Planning with Large Language Models for Drug Discovery
Jun 11, 2024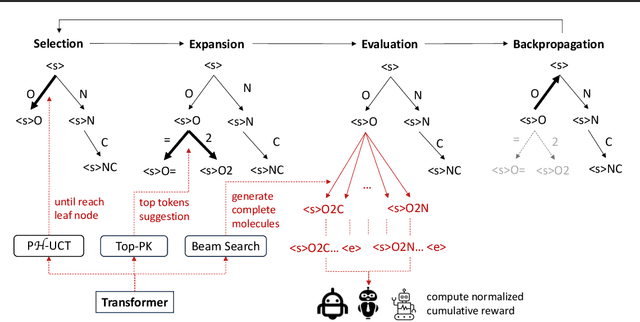
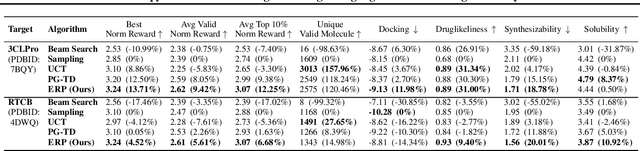
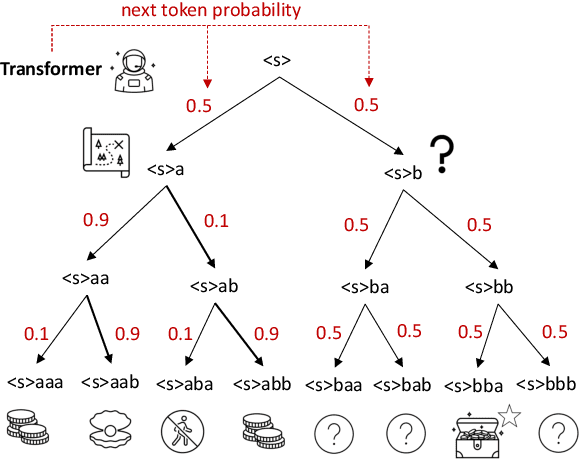
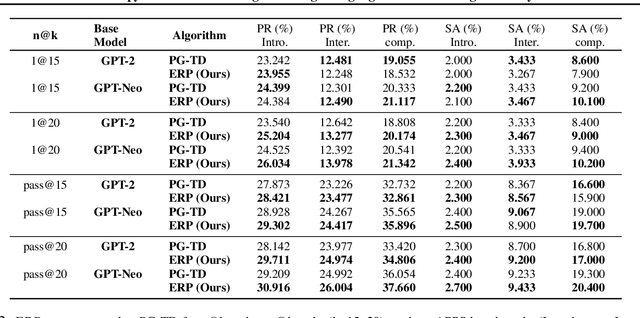
Abstract:The objective of drug discovery is to identify chemical compounds that possess specific pharmaceutical properties toward a binding target. Existing large language models (LLMS) can achieve high token matching scores in terms of likelihood for molecule generation. However, relying solely on LLM decoding often results in the generation of molecules that are either invalid due to a single misused token, or suboptimal due to unbalanced exploration and exploitation as a consequence of the LLMs prior experience. Here we propose ERP, Entropy-Reinforced Planning for Transformer Decoding, which employs an entropy-reinforced planning algorithm to enhance the Transformer decoding process and strike a balance between exploitation and exploration. ERP aims to achieve improvements in multiple properties compared to direct sampling from the Transformer. We evaluated ERP on the SARS-CoV-2 virus (3CLPro) and human cancer cell target protein (RTCB) benchmarks and demonstrated that, in both benchmarks, ERP consistently outperforms the current state-of-the-art algorithm by 1-5 percent, and baselines by 5-10 percent, respectively. Moreover, such improvement is robust across Transformer models trained with different objectives. Finally, to further illustrate the capabilities of ERP, we tested our algorithm on three code generation benchmarks and outperformed the current state-of-the-art approach as well. Our code is publicly available at: https://github.com/xuefeng-cs/ERP.
Blending Imitation and Reinforcement Learning for Robust Policy Improvement
Oct 04, 2023



Abstract:While reinforcement learning (RL) has shown promising performance, its sample complexity continues to be a substantial hurdle, restricting its broader application across a variety of domains. Imitation learning (IL) utilizes oracles to improve sample efficiency, yet it is often constrained by the quality of the oracles deployed. which actively interleaves between IL and RL based on an online estimate of their performance. RPI draws on the strengths of IL, using oracle queries to facilitate exploration, an aspect that is notably challenging in sparse-reward RL, particularly during the early stages of learning. As learning unfolds, RPI gradually transitions to RL, effectively treating the learned policy as an improved oracle. This algorithm is capable of learning from and improving upon a diverse set of black-box oracles. Integral to RPI are Robust Active Policy Selection (RAPS) and Robust Policy Gradient (RPG), both of which reason over whether to perform state-wise imitation from the oracles or learn from its own value function when the learner's performance surpasses that of the oracles in a specific state. Empirical evaluations and theoretical analysis validate that RPI excels in comparison to existing state-of-the-art methodologies, demonstrating superior performance across various benchmark domains.
Transferable Graph Neural Fingerprint Models for Quick Response to Future Bio-Threats
Jul 17, 2023



Abstract:Fast screening of drug molecules based on the ligand binding affinity is an important step in the drug discovery pipeline. Graph neural fingerprint is a promising method for developing molecular docking surrogates with high throughput and great fidelity. In this study, we built a COVID-19 drug docking dataset of about 300,000 drug candidates on 23 coronavirus protein targets. With this dataset, we trained graph neural fingerprint docking models for high-throughput virtual COVID-19 drug screening. The graph neural fingerprint models yield high prediction accuracy on docking scores with the mean squared error lower than $0.21$ kcal/mol for most of the docking targets, showing significant improvement over conventional circular fingerprint methods. To make the neural fingerprints transferable for unknown targets, we also propose a transferable graph neural fingerprint method trained on multiple targets. With comparable accuracy to target-specific graph neural fingerprint models, the transferable model exhibits superb training and data efficiency. We highlight that the impact of this study extends beyond COVID-19 dataset, as our approach for fast virtual ligand screening can be easily adapted and integrated into a general machine learning-accelerated pipeline to battle future bio-threats.
Deep learning methods for drug response prediction in cancer: predominant and emerging trends
Nov 18, 2022Abstract:Cancer claims millions of lives yearly worldwide. While many therapies have been made available in recent years, by in large cancer remains unsolved. Exploiting computational predictive models to study and treat cancer holds great promise in improving drug development and personalized design of treatment plans, ultimately suppressing tumors, alleviating suffering, and prolonging lives of patients. A wave of recent papers demonstrates promising results in predicting cancer response to drug treatments while utilizing deep learning methods. These papers investigate diverse data representations, neural network architectures, learning methodologies, and evaluations schemes. However, deciphering promising predominant and emerging trends is difficult due to the variety of explored methods and lack of standardized framework for comparing drug response prediction models. To obtain a comprehensive landscape of deep learning methods, we conducted an extensive search and analysis of deep learning models that predict the response to single drug treatments. A total of 60 deep learning-based models have been curated and summary plots were generated. Based on the analysis, observable patterns and prevalence of methods have been revealed. This review allows to better understand the current state of the field and identify major challenges and promising solution paths.
Cost-Effective Online Contextual Model Selection
Jul 13, 2022

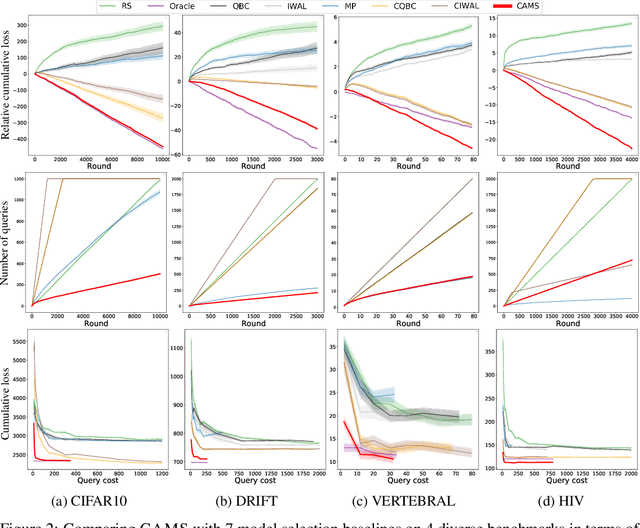
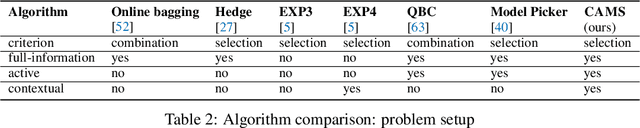
Abstract:How can we collect the most useful labels to learn a model selection policy, when presented with arbitrary heterogeneous data streams? In this paper, we formulate this task as an online contextual active model selection problem, where at each round the learner receives an unlabeled data point along with a context. The goal is to output the best model for any given context without obtaining an excessive amount of labels. In particular, we focus on the task of selecting pre-trained classifiers, and propose a contextual active model selection algorithm (CAMS), which relies on a novel uncertainty sampling query criterion defined on a given policy class for adaptive model selection. In comparison to prior art, our algorithm does not assume a globally optimal model. We provide rigorous theoretical analysis for the regret and query complexity under both adversarial and stochastic settings. Our experiments on several benchmark classification datasets demonstrate the algorithm's effectiveness in terms of both regret and query complexity. Notably, to achieve the same accuracy, CAMS incurs less than 10% of the label cost when compared to the best online model selection baselines on CIFAR10.
Spatial Graph Attention and Curiosity-driven Policy for Antiviral Drug Discovery
Jun 20, 2021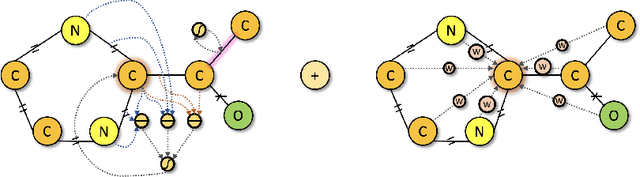
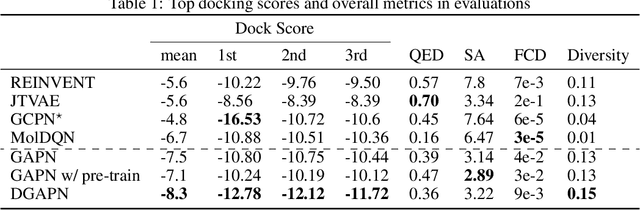
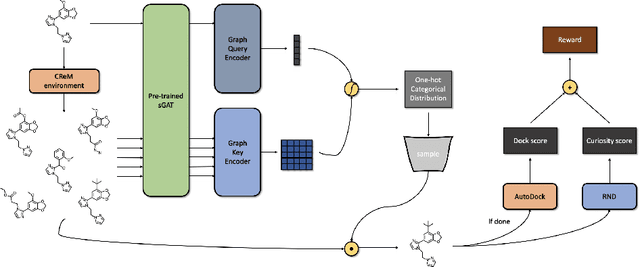
Abstract:We developed Distilled Graph Attention Policy Networks (DGAPNs), a curiosity-driven reinforcement learning model to generate novel graph-structured chemical representations that optimize user-defined objectives by efficiently navigating a physically constrained domain. The framework is examined on the task of generating molecules that are designed to bind, noncovalently, to functional sites of SARS-CoV-2 proteins. We present a spatial Graph Attention Network (sGAT) that leverages self-attention over both node and edge attributes as well as encoding spatial structure -- this capability is of considerable interest in areas such as molecular and synthetic biology and drug discovery. An attentional policy network is then introduced to learn decision rules for a dynamic, fragment-based chemical environment, and state-of-the-art policy gradient techniques are employed to train the network with enhanced stability. Exploration is efficiently encouraged by incorporating innovation reward bonuses learned and proposed by random network distillation. In experiments, our framework achieved outstanding results compared to state-of-the-art algorithms, while increasing the diversity of proposed molecules and reducing the complexity of paths to chemical synthesis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge