Nicholas Choma
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Spatial Graph Attention and Curiosity-driven Policy for Antiviral Drug Discovery
Jun 20, 2021
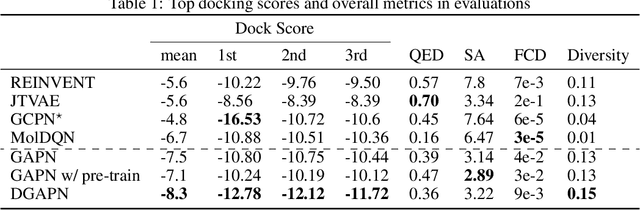
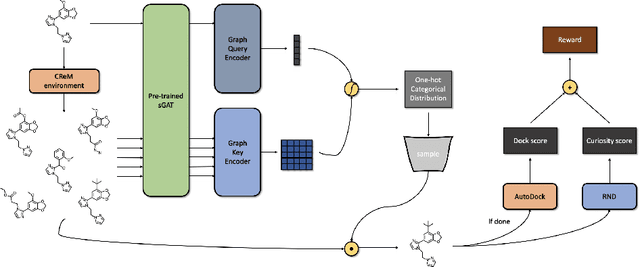
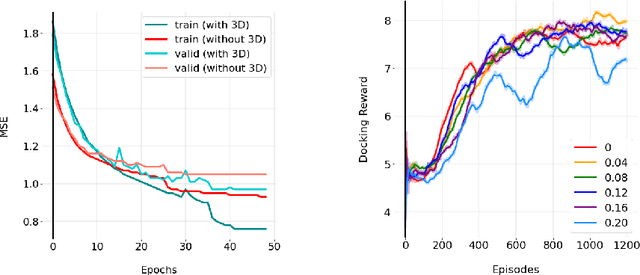
Abstract:We developed Distilled Graph Attention Policy Networks (DGAPNs), a curiosity-driven reinforcement learning model to generate novel graph-structured chemical representations that optimize user-defined objectives by efficiently navigating a physically constrained domain. The framework is examined on the task of generating molecules that are designed to bind, noncovalently, to functional sites of SARS-CoV-2 proteins. We present a spatial Graph Attention Network (sGAT) that leverages self-attention over both node and edge attributes as well as encoding spatial structure -- this capability is of considerable interest in areas such as molecular and synthetic biology and drug discovery. An attentional policy network is then introduced to learn decision rules for a dynamic, fragment-based chemical environment, and state-of-the-art policy gradient techniques are employed to train the network with enhanced stability. Exploration is efficiently encouraged by incorporating innovation reward bonuses learned and proposed by random network distillation. In experiments, our framework achieved outstanding results compared to state-of-the-art algorithms, while increasing the diversity of proposed molecules and reducing the complexity of paths to chemical synthesis.
Physics and Computing Performance of the Exa.TrkX TrackML Pipeline
Mar 11, 2021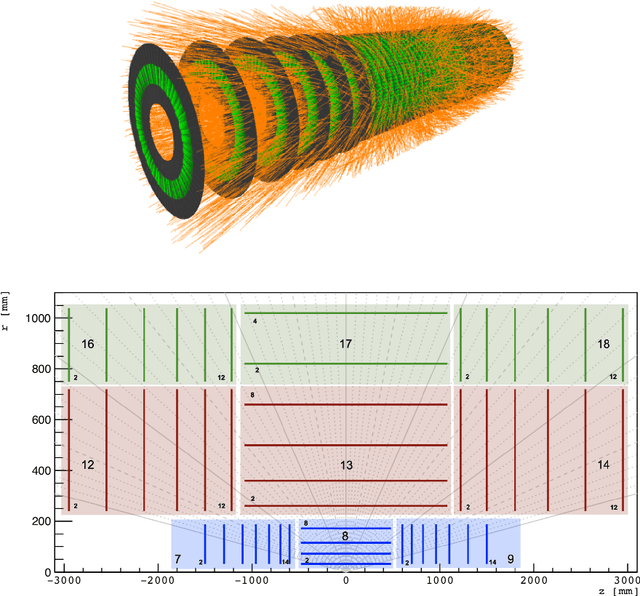
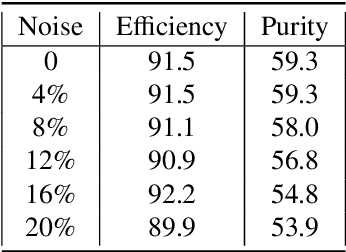
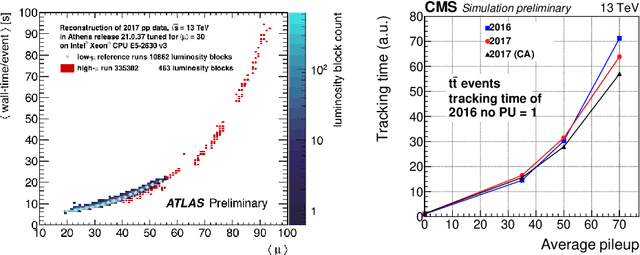
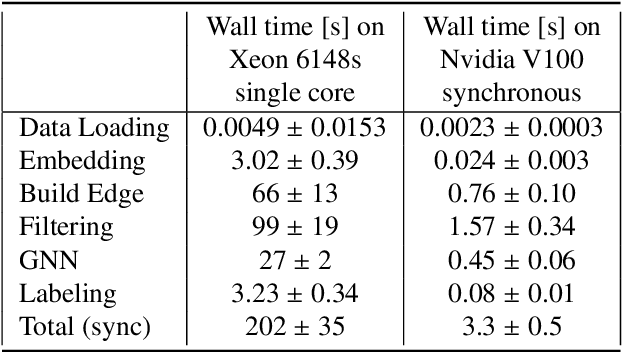
Abstract:The Exa.TrkX project has applied geometric learning concepts such as metric learning and graph neural networks to HEP particle tracking. The Exa.TrkX tracking pipeline clusters detector measurements to form track candidates and filters them. The pipeline, originally developed using the TrackML dataset (a simulation of an LHC-like tracking detector), has been demonstrated on various detectors, including the DUNE LArTPC and the CMS High-Granularity Calorimeter. This paper documents new developments needed to study the physics and computing performance of the Exa.TrkX pipeline on the full TrackML dataset, a first step towards validating the pipeline using ATLAS and CMS data. The pipeline achieves tracking efficiency and purity similar to production tracking algorithms. Crucially for future HEP applications, the pipeline benefits significantly from GPU acceleration, and its computational requirements scale close to linearly with the number of particles in the event.
Track Seeding and Labelling with Embedded-space Graph Neural Networks
Jun 30, 2020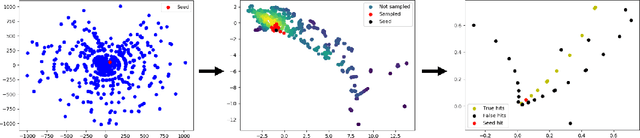
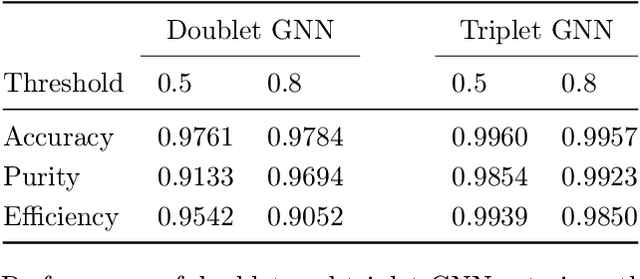
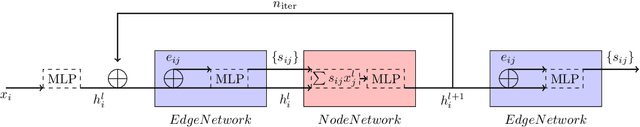
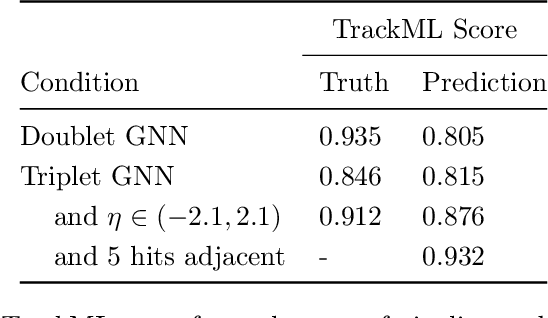
Abstract:To address the unprecedented scale of HL-LHC data, the Exa.TrkX project is investigating a variety of machine learning approaches to particle track reconstruction. The most promising of these solutions, graph neural networks (GNN), process the event as a graph that connects track measurements (detector hits corresponding to nodes) with candidate line segments between the hits (corresponding to edges). Detector information can be associated with nodes and edges, enabling a GNN to propagate the embedded parameters around the graph and predict node-, edge- and graph-level observables. Previously, message-passing GNNs have shown success in predicting doublet likelihood, and we here report updates on the state-of-the-art architectures for this task. In addition, the Exa.TrkX project has investigated innovations in both graph construction, and embedded representations, in an effort to achieve fully learned end-to-end track finding. Hence, we present a suite of extensions to the original model, with encouraging results for hitgraph classification. In addition, we explore increased performance by constructing graphs from learned representations which contain non-linear metric structure, allowing for efficient clustering and neighborhood queries of data points. We demonstrate how this framework fits in with both traditional clustering pipelines, and GNN approaches. The embedded graphs feed into high-accuracy doublet and triplet classifiers, or can be used as an end-to-end track classifier by clustering in an embedded space. A set of post-processing methods improve performance with knowledge of the detector physics. Finally, we present numerical results on the TrackML particle tracking challenge dataset, where our framework shows favorable results in both seeding and track finding.
Graph Neural Networks for IceCube Signal Classification
Sep 17, 2018
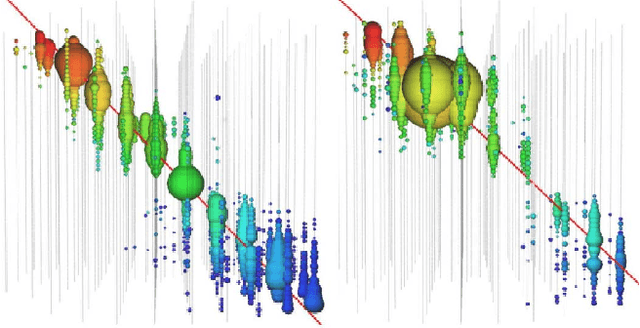

Abstract:Tasks involving the analysis of geometric (graph- and manifold-structured) data have recently gained prominence in the machine learning community, giving birth to a rapidly developing field of geometric deep learning. In this work, we leverage graph neural networks to improve signal detection in the IceCube neutrino observatory. The IceCube detector array is modeled as a graph, where vertices are sensors and edges are a learned function of the sensors' spatial coordinates. As only a subset of IceCube's sensors is active during a given observation, we note the adaptive nature of our GNN, wherein computation is restricted to the input signal support. We demonstrate the effectiveness of our GNN architecture on a task classifying IceCube events, where it outperforms both a traditional physics-based method as well as classical 3D convolution neural networks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge