Adam Aurisano
University of Cincinnati
Submanifold Sparse Convolutional Networks for Automated 3D Segmentation of Kidneys and Kidney Tumours in Computed Tomography
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:The accurate delineation of tumours in radiological images like Computed Tomography is a very specialised and time-consuming task, and currently a bottleneck preventing quantitative analyses to be performed routinely in the clinical setting. For this reason, developing methods for the automated segmentation of tumours in medical imaging is of the utmost importance and has driven significant efforts in recent years. However, challenges regarding the impracticality of 3D scans, given the large amount of voxels to be analysed, usually requires the downsampling of such images or using patches thereof when applying traditional convolutional neural networks. To overcome this problem, in this paper we propose a new methodology that uses, divided into two stages, voxel sparsification and submanifold sparse convolutional networks. This method allows segmentations to be performed with high-resolution inputs and a native 3D model architecture, obtaining state-of-the-art accuracies while significantly reducing the computational resources needed in terms of GPU memory and time. We studied the deployment of this methodology in the context of Computed Tomography images of renal cancer patients from the KiTS23 challenge, and our method achieved results competitive with the challenge winners, with Dice similarity coefficients of 95.8% for kidneys + masses, 85.7% for tumours + cysts, and 80.3% for tumours alone. Crucially, our method also offers significant computational improvements, achieving up to a 60% reduction in inference time and up to a 75\% reduction in VRAM usage compared to an equivalent dense architecture, across both CPU and various GPU cards tested.
NuGraph2: A Graph Neural Network for Neutrino Physics Event Reconstruction
Mar 18, 2024



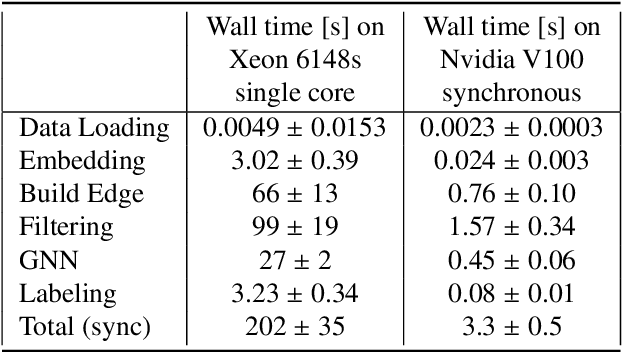
Abstract:Liquid Argon Time Projection Chamber (LArTPC) detector technology offers a wealth of high-resolution information on particle interactions, and leveraging that information to its full potential requires sophisticated automated reconstruction techniques. This article describes NuGraph2, a Graph Neural Network (GNN) for low-level reconstruction of simulated neutrino interactions in a LArTPC detector. Simulated neutrino interactions in the MicroBooNE detector geometry are described as heterogeneous graphs, with energy depositions on each detector plane forming nodes on planar subgraphs. The network utilizes a multi-head attention message-passing mechanism to perform background filtering and semantic labelling on these graph nodes, identifying those associated with the primary physics interaction with 98.0\% efficiency and labelling them according to particle type with 94.9\% efficiency. The network operates directly on detector observables across multiple 2D representations, but utilizes a 3D-context-aware mechanism to encourage consistency between these representations. Model inference takes 0.12 s/event on a CPU, and 0.005 s/event batched on a GPU. This architecture is designed to be a general-purpose solution for particle reconstruction in neutrino physics, with the potential for deployment across a broad range of detector technologies, and offers a core convolution engine that can be leveraged for a variety of tasks beyond the two described in this article.
Automated Segmentation of Computed Tomography Images with Submanifold Sparse Convolutional Networks
Dec 06, 2022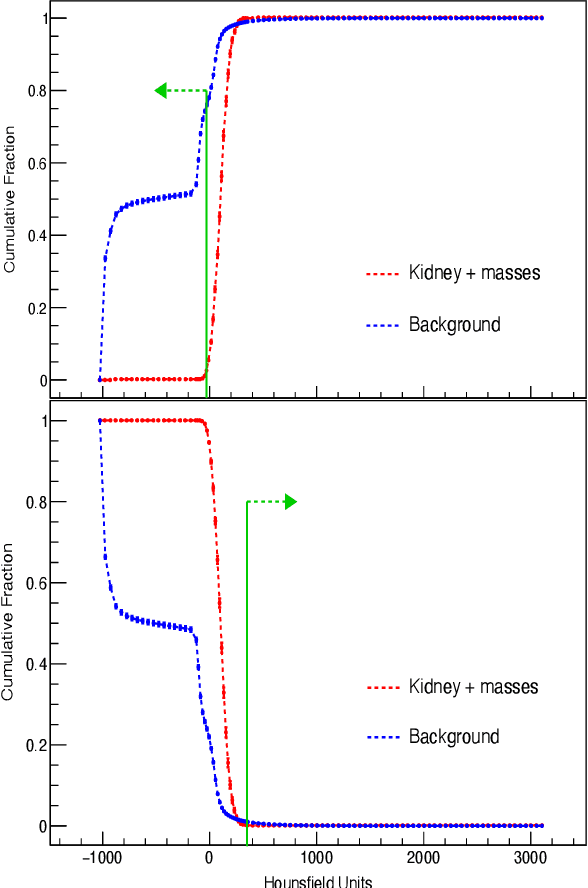
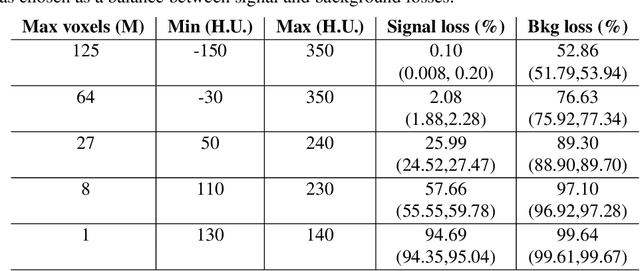
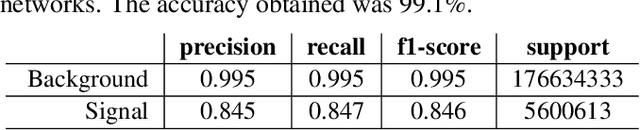
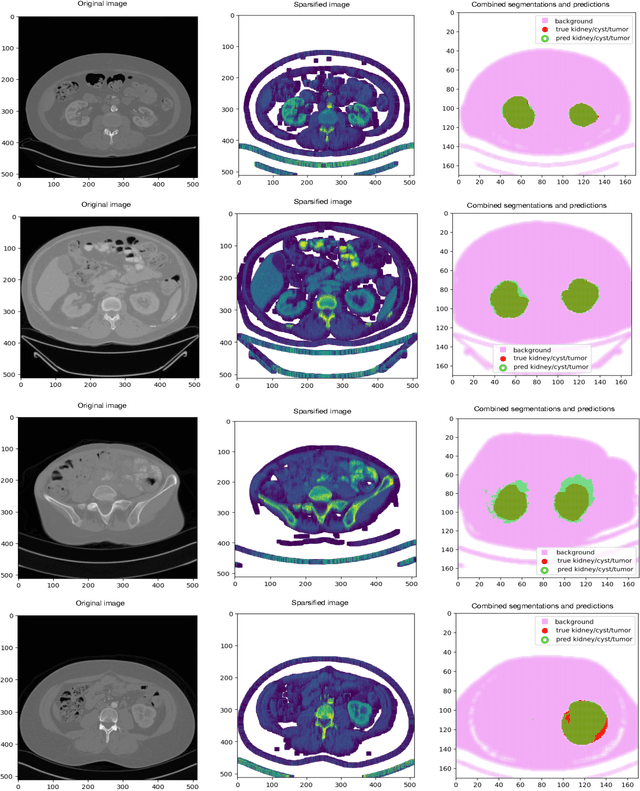
Abstract:Quantitative cancer image analysis relies on the accurate delineation of tumours, a very specialised and time-consuming task. For this reason, methods for automated segmentation of tumours in medical imaging have been extensively developed in recent years, being Computed Tomography one of the most popular imaging modalities explored. However, the large amount of 3D voxels in a typical scan is prohibitive for the entire volume to be analysed at once in conventional hardware. To overcome this issue, the processes of downsampling and/or resampling are generally implemented when using traditional convolutional neural networks in medical imaging. In this paper, we propose a new methodology that introduces a process of sparsification of the input images and submanifold sparse convolutional networks as an alternative to downsampling. As a proof of concept, we applied this new methodology to Computed Tomography images of renal cancer patients, obtaining performances of segmentations of kidneys and tumours competitive with previous methods (~84.6% Dice similarity coefficient), while achieving a significant improvement in computation time (2-3 min per training epoch).
Physics and Computing Performance of the Exa.TrkX TrackML Pipeline
Mar 11, 2021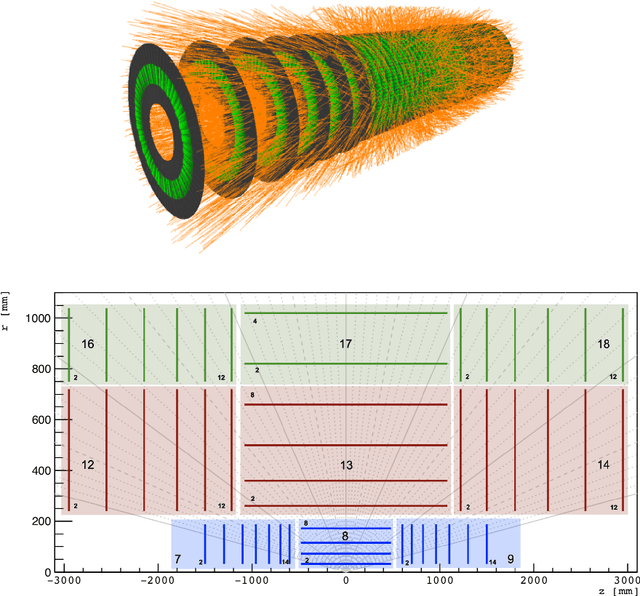
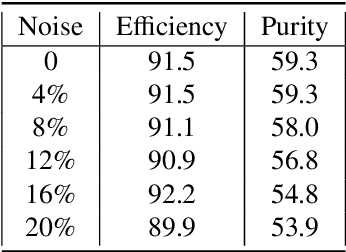
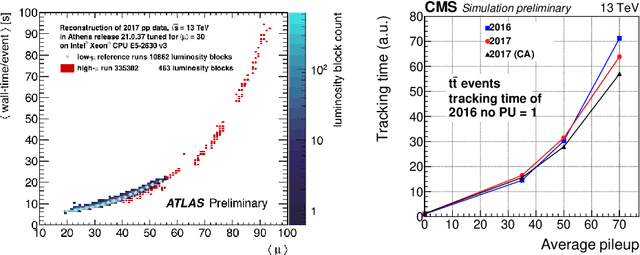
Abstract:The Exa.TrkX project has applied geometric learning concepts such as metric learning and graph neural networks to HEP particle tracking. The Exa.TrkX tracking pipeline clusters detector measurements to form track candidates and filters them. The pipeline, originally developed using the TrackML dataset (a simulation of an LHC-like tracking detector), has been demonstrated on various detectors, including the DUNE LArTPC and the CMS High-Granularity Calorimeter. This paper documents new developments needed to study the physics and computing performance of the Exa.TrkX pipeline on the full TrackML dataset, a first step towards validating the pipeline using ATLAS and CMS data. The pipeline achieves tracking efficiency and purity similar to production tracking algorithms. Crucially for future HEP applications, the pipeline benefits significantly from GPU acceleration, and its computational requirements scale close to linearly with the number of particles in the event.
Track Seeding and Labelling with Embedded-space Graph Neural Networks
Jun 30, 2020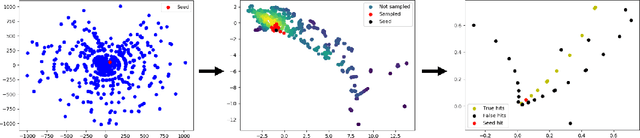
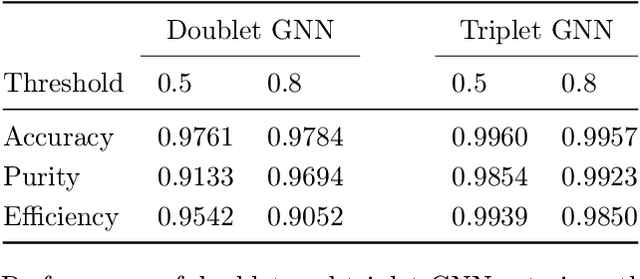
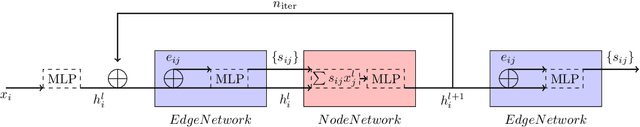
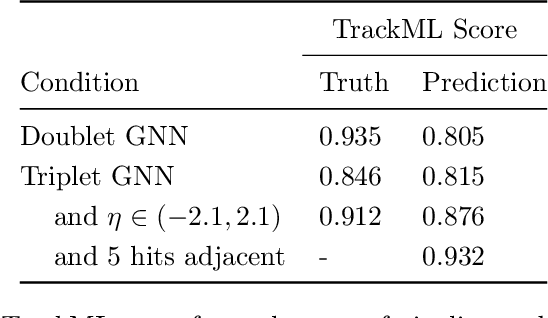
Abstract:To address the unprecedented scale of HL-LHC data, the Exa.TrkX project is investigating a variety of machine learning approaches to particle track reconstruction. The most promising of these solutions, graph neural networks (GNN), process the event as a graph that connects track measurements (detector hits corresponding to nodes) with candidate line segments between the hits (corresponding to edges). Detector information can be associated with nodes and edges, enabling a GNN to propagate the embedded parameters around the graph and predict node-, edge- and graph-level observables. Previously, message-passing GNNs have shown success in predicting doublet likelihood, and we here report updates on the state-of-the-art architectures for this task. In addition, the Exa.TrkX project has investigated innovations in both graph construction, and embedded representations, in an effort to achieve fully learned end-to-end track finding. Hence, we present a suite of extensions to the original model, with encouraging results for hitgraph classification. In addition, we explore increased performance by constructing graphs from learned representations which contain non-linear metric structure, allowing for efficient clustering and neighborhood queries of data points. We demonstrate how this framework fits in with both traditional clustering pipelines, and GNN approaches. The embedded graphs feed into high-accuracy doublet and triplet classifiers, or can be used as an end-to-end track classifier by clustering in an embedded space. A set of post-processing methods improve performance with knowledge of the detector physics. Finally, we present numerical results on the TrackML particle tracking challenge dataset, where our framework shows favorable results in both seeding and track finding.
Machine Learning in High Energy Physics Community White Paper
Jul 08, 2018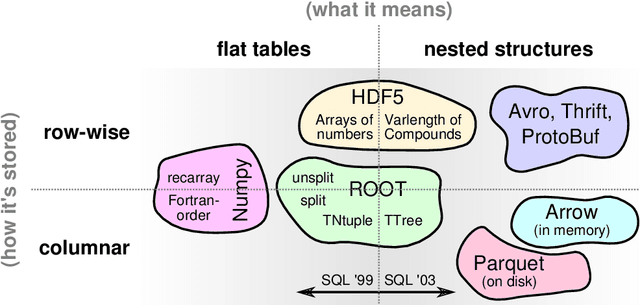
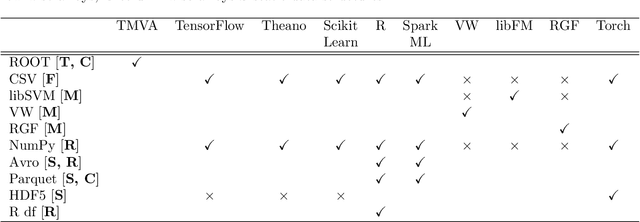
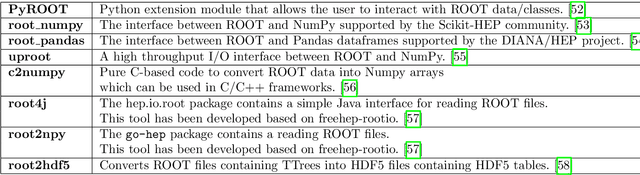
Abstract:Machine learning is an important research area in particle physics, beginning with applications to high-level physics analysis in the 1990s and 2000s, followed by an explosion of applications in particle and event identification and reconstruction in the 2010s. In this document we discuss promising future research and development areas in machine learning in particle physics with a roadmap for their implementation, software and hardware resource requirements, collaborative initiatives with the data science community, academia and industry, and training the particle physics community in data science. The main objective of the document is to connect and motivate these areas of research and development with the physics drivers of the High-Luminosity Large Hadron Collider and future neutrino experiments and identify the resource needs for their implementation. Additionally we identify areas where collaboration with external communities will be of great benefit.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge