Daniele Bonacorsi
Strategic White Paper on AI Infrastructure for Particle, Nuclear, and Astroparticle Physics: Insights from JENA and EuCAIF
Mar 18, 2025



Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming scientific research, with deep learning methods playing a central role in data analysis, simulations, and signal detection across particle, nuclear, and astroparticle physics. Within the JENA communities-ECFA, NuPECC, and APPEC-and as part of the EuCAIF initiative, AI integration is advancing steadily. However, broader adoption remains constrained by challenges such as limited computational resources, a lack of expertise, and difficulties in transitioning from research and development (R&D) to production. This white paper provides a strategic roadmap, informed by a community survey, to address these barriers. It outlines critical infrastructure requirements, prioritizes training initiatives, and proposes funding strategies to scale AI capabilities across fundamental physics over the next five years.
Improving Parametric Neural Networks for High-Energy Physics (and Beyond)
Feb 08, 2022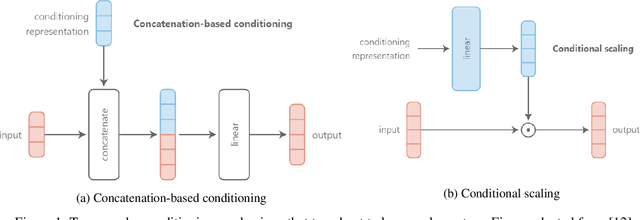
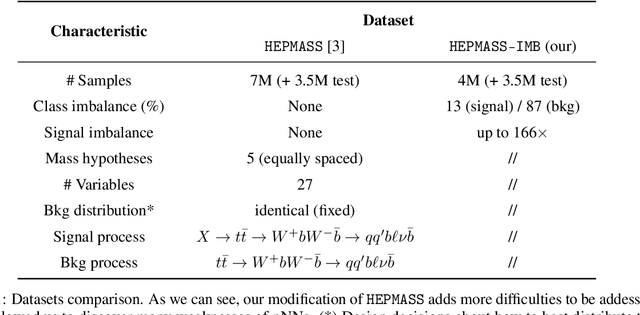
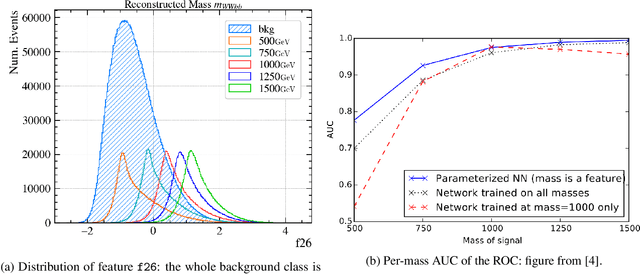
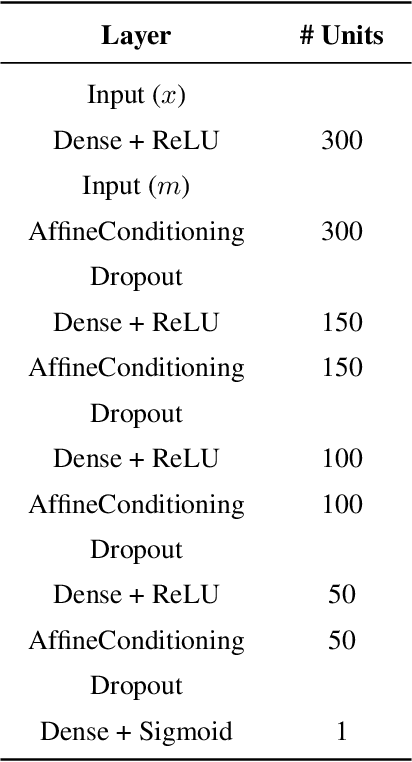
Abstract:Signal-background classification is a central problem in High-Energy Physics, that plays a major role for the discovery of new fundamental particles. A recent method -- the Parametric Neural Network (pNN) -- leverages multiple signal mass hypotheses as an additional input feature to effectively replace a whole set of individual classifier, each providing (in principle) the best response for a single mass hypothesis. In this work we aim at deepening the understanding of pNNs in light of real-world usage. We discovered several peculiarities of parametric networks, providing intuition, metrics, and guidelines to them. We further propose an alternative parametrization scheme, resulting in a new parametrized neural network architecture: the AffinePNN; along with many other generally applicable improvements. Finally, we extensively evaluate our models on the HEPMASS dataset, along its imbalanced version (called HEPMASS-IMB) we provide here for the first time to further validate our approach. Provided results are in terms of the impact of the proposed design decisions, classification performance, and interpolation capability as well.
Collection and harmonization of system logs and prototypal Analytics services with the Elastic (ELK) suite at the INFN-CNAF computing centre
May 13, 2021



Abstract:The distributed Grid infrastructure for High Energy Physics experiments at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) in Geneva comprises a set of computing centres, spread all over the world, as part of the Worldwide LHC Computing Grid (WLCG). In Italy, the Tier-1 functionalities are served by the INFN-CNAF data center, which provides also computing and storage resources to more than twenty non-LHC experiments. For this reason, a high amount of logs are collected each day from various sources, which are highly heterogeneous and difficult to harmonize. In this contribution, a working implementation of a system that collects, parses and displays the log information from CNAF data sources and the investigation of a Machine Learning based predictive maintenance system, is presented.
* Submitted to proceedings of International Symposium on Grids & Clouds 2019 (ISGC2019)
Real-Time Anomaly Detection in Data Centers for Log-based Predictive Maintenance using an Evolving Fuzzy-Rule-Based Approach
Apr 25, 2020



Abstract:Detection of anomalous behaviors in data centers is crucial to predictive maintenance and data safety. With data centers, we mean any computer network that allows users to transmit and exchange data and information. In particular, we focus on the Tier-1 data center of the Italian Institute for Nuclear Physics (INFN), which supports the high-energy physics experiments at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) in Geneva. The center provides resources and services needed for data processing, storage, analysis, and distribution. Log records in the data center is a stochastic and non-stationary phenomenon in nature. We propose a real-time approach to monitor and classify log records based on sliding time windows, and a time-varying evolving fuzzy-rule-based classification model. The most frequent log pattern according to a control chart is taken as the normal system status. We extract attributes from time windows to gradually develop and update an evolving Gaussian Fuzzy Classifier (eGFC) on the fly. The real-time anomaly monitoring system has to provide encouraging results in terms of accuracy, compactness, and real-time operation.
Machine Learning in High Energy Physics Community White Paper
Jul 08, 2018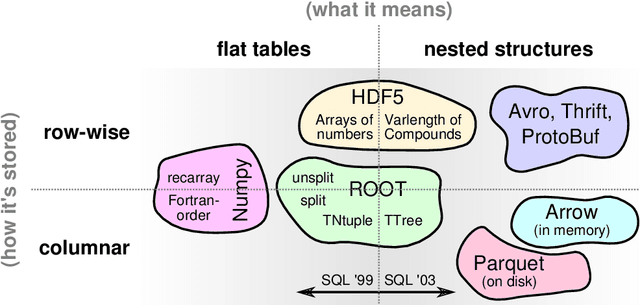
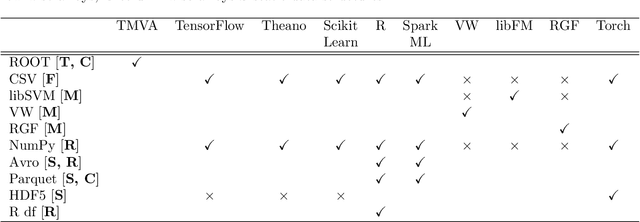
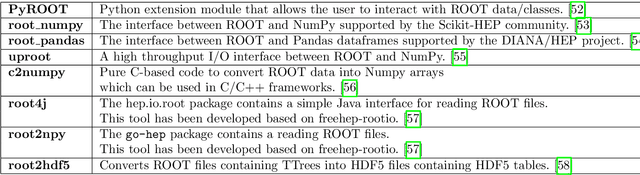
Abstract:Machine learning is an important research area in particle physics, beginning with applications to high-level physics analysis in the 1990s and 2000s, followed by an explosion of applications in particle and event identification and reconstruction in the 2010s. In this document we discuss promising future research and development areas in machine learning in particle physics with a roadmap for their implementation, software and hardware resource requirements, collaborative initiatives with the data science community, academia and industry, and training the particle physics community in data science. The main objective of the document is to connect and motivate these areas of research and development with the physics drivers of the High-Luminosity Large Hadron Collider and future neutrino experiments and identify the resource needs for their implementation. Additionally we identify areas where collaboration with external communities will be of great benefit.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge