Caterina Doglioni
Knowledge is Overrated: A zero-knowledge machine learning and cryptographic hashing-based framework for verifiable, low latency inference at the LHC
Nov 16, 2025Abstract:Low latency event-selection (trigger) algorithms are essential components of Large Hadron Collider (LHC) operation. Modern machine learning (ML) models have shown great offline performance as classifiers and could improve trigger performance, thereby improving downstream physics analyses. However, inference on such large models does not satisfy the $40\text{MHz}$ online latency constraint at the LHC. In this work, we propose \texttt{PHAZE}, a novel framework built on cryptographic techniques like hashing and zero-knowledge machine learning (zkML) to achieve low latency inference, via a certifiable, early-exit mechanism from an arbitrarily large baseline model. We lay the foundations for such a framework to achieve nanosecond-order latency and discuss its inherent advantages, such as built-in anomaly detection, within the scope of LHC triggers, as well as its potential to enable a dynamic low-level trigger in the future.
Strategic White Paper on AI Infrastructure for Particle, Nuclear, and Astroparticle Physics: Insights from JENA and EuCAIF
Mar 18, 2025



Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) is transforming scientific research, with deep learning methods playing a central role in data analysis, simulations, and signal detection across particle, nuclear, and astroparticle physics. Within the JENA communities-ECFA, NuPECC, and APPEC-and as part of the EuCAIF initiative, AI integration is advancing steadily. However, broader adoption remains constrained by challenges such as limited computational resources, a lack of expertise, and difficulties in transitioning from research and development (R&D) to production. This white paper provides a strategic roadmap, informed by a community survey, to address these barriers. It outlines critical infrastructure requirements, prioritizes training initiatives, and proposes funding strategies to scale AI capabilities across fundamental physics over the next five years.
Applications and Techniques for Fast Machine Learning in Science
Oct 25, 2021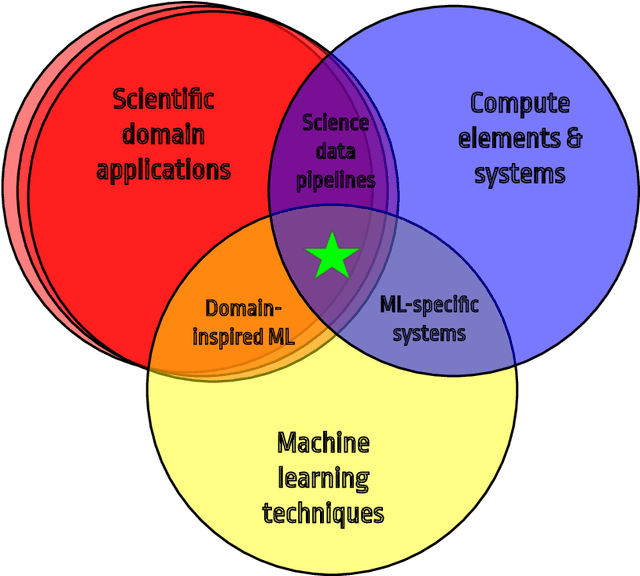
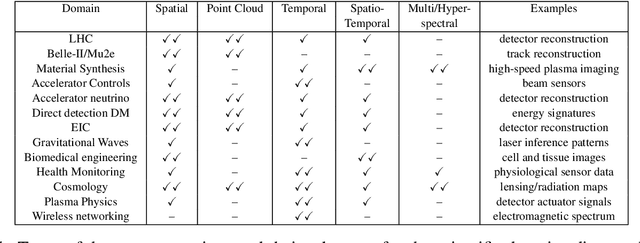
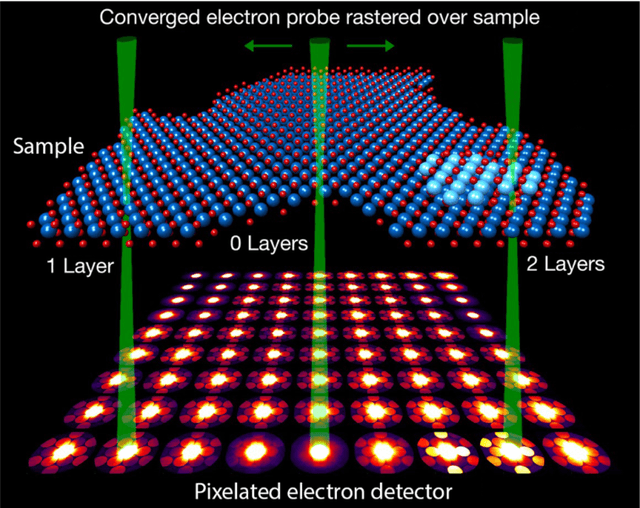
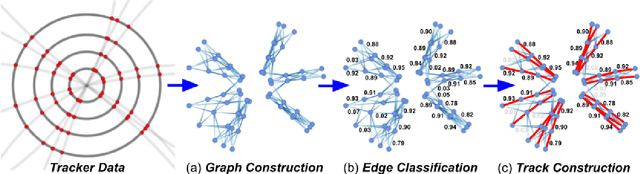
Abstract:In this community review report, we discuss applications and techniques for fast machine learning (ML) in science -- the concept of integrating power ML methods into the real-time experimental data processing loop to accelerate scientific discovery. The material for the report builds on two workshops held by the Fast ML for Science community and covers three main areas: applications for fast ML across a number of scientific domains; techniques for training and implementing performant and resource-efficient ML algorithms; and computing architectures, platforms, and technologies for deploying these algorithms. We also present overlapping challenges across the multiple scientific domains where common solutions can be found. This community report is intended to give plenty of examples and inspiration for scientific discovery through integrated and accelerated ML solutions. This is followed by a high-level overview and organization of technical advances, including an abundance of pointers to source material, which can enable these breakthroughs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge