Javier Duarte
UC San Diego
Machine Learning on Heterogeneous, Edge, and Quantum Hardware for Particle Physics (ML-HEQUPP)
Feb 24, 2026Abstract:The next generation of particle physics experiments will face a new era of challenges in data acquisition, due to unprecedented data rates and volumes along with extreme environments and operational constraints. Harnessing this data for scientific discovery demands real-time inference and decision-making, intelligent data reduction, and efficient processing architectures beyond current capabilities. Crucial to the success of this experimental paradigm are several emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) and silicon microelectronics, and the advent of quantum algorithms and processing. Their intersection includes areas of research such as low-power and low-latency devices for edge computing, heterogeneous accelerator systems, reconfigurable hardware, novel codesign and synthesis strategies, readout for cryogenic or high-radiation environments, and analog computing. This white paper presents a community-driven vision to identify and prioritize research and development opportunities in hardware-based ML systems and corresponding physics applications, contributing towards a successful transition to the new data frontier of fundamental science.
Surrogate Neural Architecture Codesign Package (SNAC-Pack)
Dec 17, 2025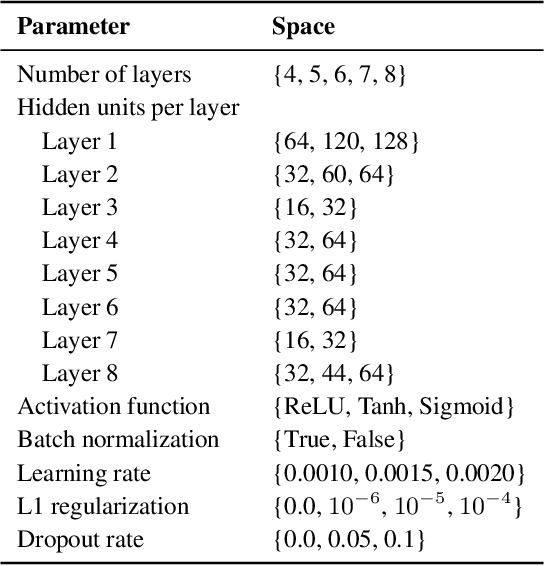
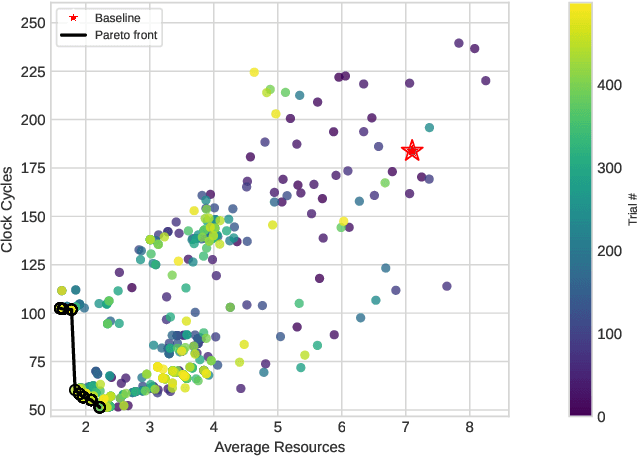
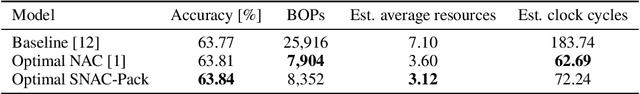
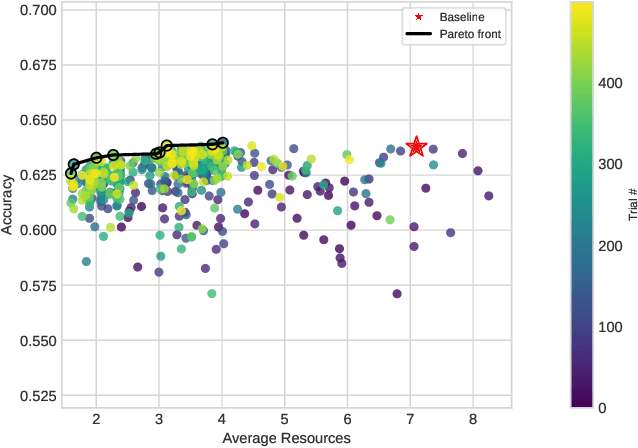
Abstract:Neural Architecture Search is a powerful approach for automating model design, but existing methods struggle to accurately optimize for real hardware performance, often relying on proxy metrics such as bit operations. We present Surrogate Neural Architecture Codesign Package (SNAC-Pack), an integrated framework that automates the discovery and optimization of neural networks focusing on FPGA deployment. SNAC-Pack combines Neural Architecture Codesign's multi-stage search capabilities with the Resource Utilization and Latency Estimator, enabling multi-objective optimization across accuracy, FPGA resource utilization, and latency without requiring time-intensive synthesis for each candidate model. We demonstrate SNAC-Pack on a high energy physics jet classification task, achieving 63.84% accuracy with resource estimation. When synthesized on a Xilinx Virtex UltraScale+ VU13P FPGA, the SNAC-Pack model matches baseline accuracy while maintaining comparable resource utilization to models optimized using traditional BOPs metrics. This work demonstrates the potential of hardware-aware neural architecture search for resource-constrained deployments and provides an open-source framework for automating the design of efficient FPGA-accelerated models.
wa-hls4ml: A Benchmark and Surrogate Models for hls4ml Resource and Latency Estimation
Nov 06, 2025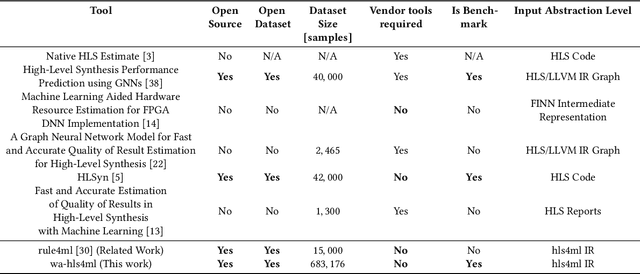
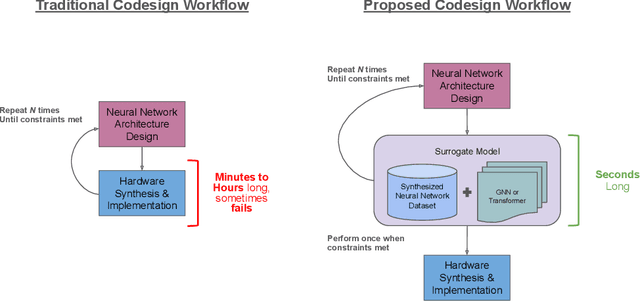
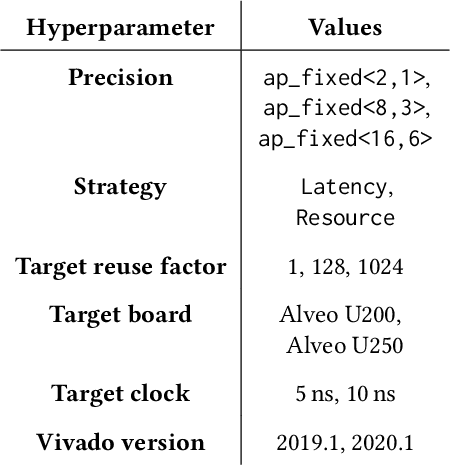
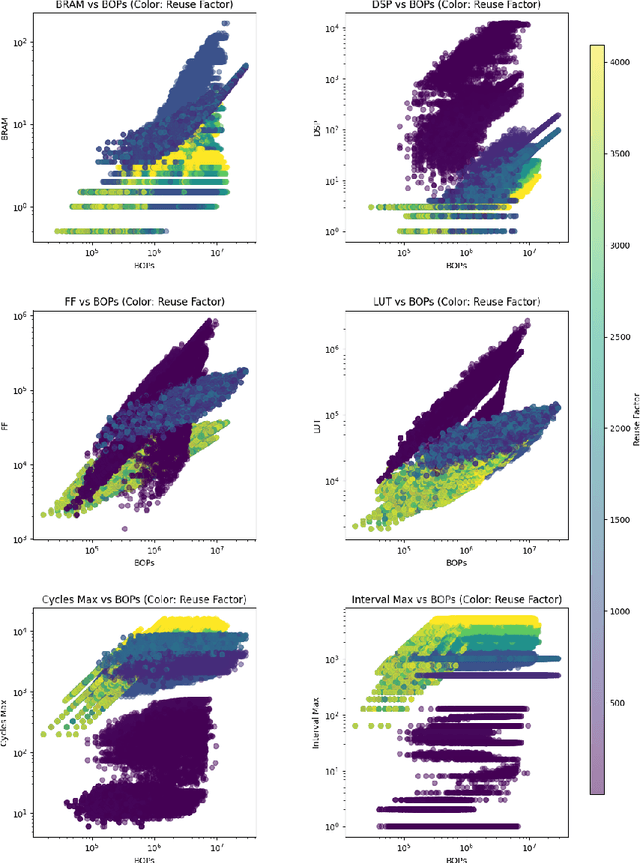
Abstract:As machine learning (ML) is increasingly implemented in hardware to address real-time challenges in scientific applications, the development of advanced toolchains has significantly reduced the time required to iterate on various designs. These advancements have solved major obstacles, but also exposed new challenges. For example, processes that were not previously considered bottlenecks, such as hardware synthesis, are becoming limiting factors in the rapid iteration of designs. To mitigate these emerging constraints, multiple efforts have been undertaken to develop an ML-based surrogate model that estimates resource usage of ML accelerator architectures. We introduce wa-hls4ml, a benchmark for ML accelerator resource and latency estimation, and its corresponding initial dataset of over 680,000 fully connected and convolutional neural networks, all synthesized using hls4ml and targeting Xilinx FPGAs. The benchmark evaluates the performance of resource and latency predictors against several common ML model architectures, primarily originating from scientific domains, as exemplar models, and the average performance across a subset of the dataset. Additionally, we introduce GNN- and transformer-based surrogate models that predict latency and resources for ML accelerators. We present the architecture and performance of the models and find that the models generally predict latency and resources for the 75% percentile within several percent of the synthesized resources on the synthetic test dataset.
RINO: Renormalization Group Invariance with No Labels
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:A common challenge with supervised machine learning (ML) in high energy physics (HEP) is the reliance on simulations for labeled data, which can often mismodel the underlying collision or detector response. To help mitigate this problem of domain shift, we propose RINO (Renormalization Group Invariance with No Labels), a self-supervised learning approach that can instead pretrain models directly on collision data, learning embeddings invariant to renormalization group flow scales. In this work, we pretrain a transformer-based model on jets originating from quantum chromodynamic (QCD) interactions from the JetClass dataset, emulating real QCD-dominated experimental data, and then finetune on the JetNet dataset -- emulating simulations -- for the task of identifying jets originating from top quark decays. RINO demonstrates improved generalization from the JetNet training data to JetClass data compared to supervised training on JetNet from scratch, demonstrating the potential for RINO pretraining on real collision data followed by fine-tuning on small, high-quality MC datasets, to improve the robustness of ML models in HEP.
Building Machine Learning Challenges for Anomaly Detection in Science
Mar 03, 2025



Abstract:Scientific discoveries are often made by finding a pattern or object that was not predicted by the known rules of science. Oftentimes, these anomalous events or objects that do not conform to the norms are an indication that the rules of science governing the data are incomplete, and something new needs to be present to explain these unexpected outliers. The challenge of finding anomalies can be confounding since it requires codifying a complete knowledge of the known scientific behaviors and then projecting these known behaviors on the data to look for deviations. When utilizing machine learning, this presents a particular challenge since we require that the model not only understands scientific data perfectly but also recognizes when the data is inconsistent and out of the scope of its trained behavior. In this paper, we present three datasets aimed at developing machine learning-based anomaly detection for disparate scientific domains covering astrophysics, genomics, and polar science. We present the different datasets along with a scheme to make machine learning challenges around the three datasets findable, accessible, interoperable, and reusable (FAIR). Furthermore, we present an approach that generalizes to future machine learning challenges, enabling the possibility of large, more compute-intensive challenges that can ultimately lead to scientific discovery.
Neural Architecture Codesign for Fast Physics Applications
Jan 09, 2025



Abstract:We develop a pipeline to streamline neural architecture codesign for physics applications to reduce the need for ML expertise when designing models for novel tasks. Our method employs neural architecture search and network compression in a two-stage approach to discover hardware efficient models. This approach consists of a global search stage that explores a wide range of architectures while considering hardware constraints, followed by a local search stage that fine-tunes and compresses the most promising candidates. We exceed performance on various tasks and show further speedup through model compression techniques such as quantization-aware-training and neural network pruning. We synthesize the optimal models to high level synthesis code for FPGA deployment with the hls4ml library. Additionally, our hierarchical search space provides greater flexibility in optimization, which can easily extend to other tasks and domains. We demonstrate this with two case studies: Bragg peak finding in materials science and jet classification in high energy physics, achieving models with improved accuracy, smaller latencies, or reduced resource utilization relative to the baseline models.
Learning Symmetry-Independent Jet Representations via Jet-Based Joint Embedding Predictive Architecture
Dec 05, 2024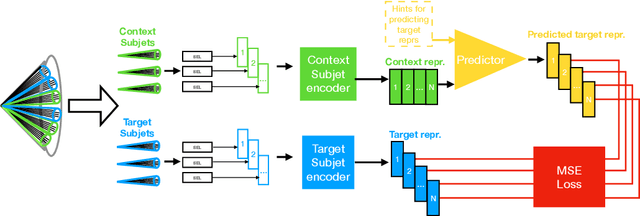
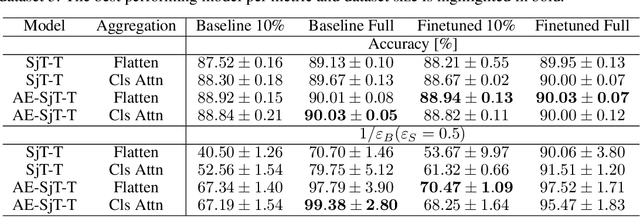
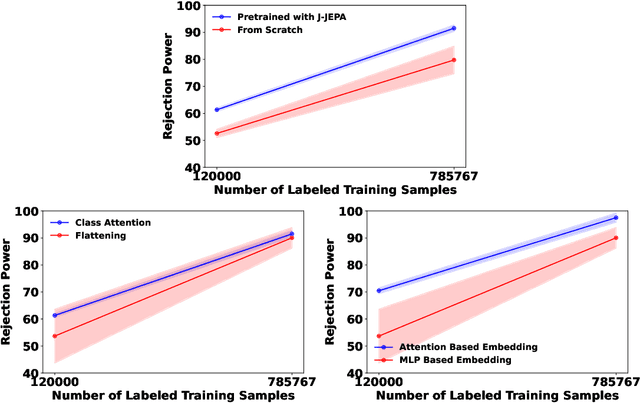
Abstract:In high energy physics, self-supervised learning (SSL) methods have the potential to aid in the creation of machine learning models without the need for labeled datasets for a variety of tasks, including those related to jets -- narrow sprays of particles produced by quarks and gluons in high energy particle collisions. This study introduces an approach to learning jet representations without hand-crafted augmentations using a jet-based joint embedding predictive architecture (J-JEPA), which aims to predict various physical targets from an informative context. As our method does not require hand-crafted augmentation like other common SSL techniques, J-JEPA avoids introducing biases that could harm downstream tasks. Since different tasks generally require invariance under different augmentations, this training without hand-crafted augmentation enables versatile applications, offering a pathway toward a cross-task foundation model. We finetune the representations learned by J-JEPA for jet tagging and benchmark them against task-specific representations.
Reconstruction of boosted and resolved multi-Higgs-boson events with symmetry-preserving attention networks
Dec 05, 2024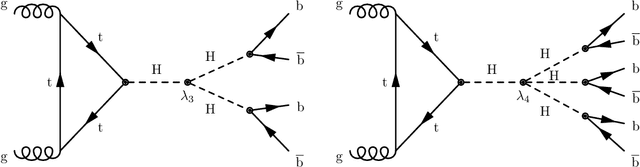
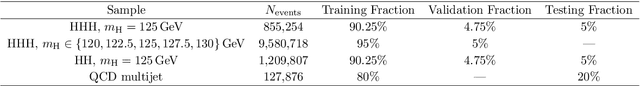


Abstract:The production of multiple Higgs bosons at the CERN LHC provides a direct way to measure the trilinear and quartic Higgs self-interaction strengths as well as potential access to beyond the standard model effects that can enhance production at large transverse momentum $p_{\mathrm{T}}$. The largest event fraction arises from the fully hadronic final state in which every Higgs boson decays to a bottom quark-antiquark pair ($b\bar{b}$). This introduces a combinatorial challenge known as the \emph{jet assignment problem}: assigning jets to sets representing Higgs boson candidates. Symmetry-preserving attention networks (SPA-Nets) have been been developed to address this challenge. However, the complexity of jet assignment increases when simultaneously considering both $H\rightarrow b\bar{b}$ reconstruction possibilities, i.e., two "resolved" small-radius jets each containing a shower initiated by a $b$-quark or one "boosted" large-radius jet containing a merged shower initiated by a $b\bar{b}$ pair. The latter improves the reconstruction efficiency at high $p_{\mathrm{T}}$. In this work, we introduce a generalization to the SPA-Net approach to simultaneously consider both boosted and resolved reconstruction possibilities and unambiguously interpret an event as "fully resolved'', "fully boosted", or in between. We report the performance of baseline methods, the original SPA-Net approach, and our generalized version on nonresonant $HH$ and $HHH$ production at the LHC. Considering both boosted and resolved topologies, our SPA-Net approach increases the Higgs boson reconstruction purity by 57--62\% and the efficiency by 23--38\% compared to the baseline method depending on the final state.
Interpreting Transformers for Jet Tagging
Dec 04, 2024Abstract:Machine learning (ML) algorithms, particularly attention-based transformer models, have become indispensable for analyzing the vast data generated by particle physics experiments like ATLAS and CMS at the CERN LHC. Particle Transformer (ParT), a state-of-the-art model, leverages particle-level attention to improve jet-tagging tasks, which are critical for identifying particles resulting from proton collisions. This study focuses on interpreting ParT by analyzing attention heat maps and particle-pair correlations on the $\eta$-$\phi$ plane, revealing a binary attention pattern where each particle attends to at most one other particle. At the same time, we observe that ParT shows varying focus on important particles and subjets depending on decay, indicating that the model learns traditional jet substructure observables. These insights enhance our understanding of the model's internal workings and learning process, offering potential avenues for improving the efficiency of transformer architectures in future high-energy physics applications.
SymbolFit: Automatic Parametric Modeling with Symbolic Regression
Nov 15, 2024



Abstract:We introduce SymbolFit, a framework that automates parametric modeling by using symbolic regression to perform a machine-search for functions that fit the data, while simultaneously providing uncertainty estimates in a single run. Traditionally, constructing a parametric model to accurately describe binned data has been a manual and iterative process, requiring an adequate functional form to be determined before the fit can be performed. The main challenge arises when the appropriate functional forms cannot be derived from first principles, especially when there is no underlying true closed-form function for the distribution. In this work, we address this problem by utilizing symbolic regression, a machine learning technique that explores a vast space of candidate functions without needing a predefined functional form, treating the functional form itself as a trainable parameter. Our approach is demonstrated in data analysis applications in high-energy physics experiments at the CERN Large Hadron Collider (LHC). We demonstrate its effectiveness and efficiency using five real proton-proton collision datasets from new physics searches at the LHC, namely the background modeling in resonance searches for high-mass dijet, trijet, paired-dijet, diphoton, and dimuon events. We also validate the framework using several toy datasets with one and more variables.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge