Wayne Luk
Dynamic Expert Sharing: Decoupling Memory from Parallelism in Mixture-of-Experts Diffusion LLMs
Jan 31, 2026Abstract:Among parallel decoding paradigms, diffusion large language models (dLLMs) have emerged as a promising candidate that balances generation quality and throughput. However, their integration with Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architectures is constrained by an expert explosion: as the number of tokens generated in parallel increases, the number of distinct experts activated grows nearly linearly. This results in substantial memory traffic that pushes inference into a memory-bound regime, negating the efficiency gains of both MoE and parallel decoding. To address this challenge, we propose Dynamic Expert Sharing (DES), a novel technique that shifts MoE optimization from token-centric pruning and conventional expert skipping methods to sequence-level coreset selection. To maximize expert reuse, DES identifies a compact, high-utility set of experts to satisfy the requirements of an entire parallel decoding block. We introduce two innovative selection strategies: (1) Intra-Sequence Sharing (DES-Seq), which adapts optimal allocation to the sequence level, and (2) Saliency-Aware Voting (DES-Vote), a novel mechanism that allows tokens to collectively elect a coreset based on aggregated router weights. Extensive experiments on MoE dLLMs demonstrate that DES reduces unique expert activations by over 55% and latency by up to 38%, while retaining 99% of vanilla accuracy, effectively decoupling memory overhead from the degree of parallelism.
JetFormer: A Scalable and Efficient Transformer for Jet Tagging from Offline Analysis to FPGA Triggers
Jan 23, 2026Abstract:We present JetFormer, a versatile and scalable encoder-only Transformer architecture for particle jet tagging at the Large Hadron Collider (LHC). Unlike prior approaches that are often tailored to specific deployment regimes, JetFormer is designed to operate effectively across the full spectrum of jet tagging scenarios, from high-accuracy offline analysis to ultra-low-latency online triggering. The model processes variable-length sets of particle features without relying on input of explicit pairwise interactions, yet achieves competitive or superior performance compared to state-of-the-art methods. On the large-scale JetClass dataset, a large-scale JetFormer matches the accuracy of the interaction-rich ParT model (within 0.7%) while using 37.4% fewer FLOPs, demonstrating its computational efficiency and strong generalization. On benchmark HLS4ML 150P datasets, JetFormer consistently outperforms existing models such as MLPs, Deep Sets, and Interaction Networks by 3-4% in accuracy. To bridge the gap to hardware deployment, we further introduce a hardware-aware optimization pipeline based on multi-objective hyperparameter search, yielding compact variants like JetFormer-tiny suitable for FPGA-based trigger systems with sub-microsecond latency requirements. Through structured pruning and quantization, we show that JetFormer can be aggressively compressed with minimal accuracy loss. By unifying high-performance modeling and deployability within a single architectural framework, JetFormer provides a practical pathway for deploying Transformer-based jet taggers in both offline and online environments at the LHC. Code is available at https://github.com/walkieq/JetFormer.
On the Existence and Behaviour of Secondary Attention Sinks
Dec 22, 2025Abstract:Attention sinks are tokens, often the beginning-of-sequence (BOS) token, that receive disproportionately high attention despite limited semantic relevance. In this work, we identify a class of attention sinks, which we term secondary sinks, that differ fundamentally from the sinks studied in prior works, which we term primary sinks. While prior works have identified that tokens other than BOS can sometimes become sinks, they were found to exhibit properties analogous to the BOS token. Specifically, they emerge at the same layer, persist throughout the network and draw a large amount of attention mass. Whereas, we find the existence of secondary sinks that arise primarily in middle layers and can persist for a variable number of layers, and draw a smaller, but still significant, amount of attention mass. Through extensive experiments across 11 model families, we analyze where these secondary sinks appear, their properties, how they are formed, and their impact on the attention mechanism. Specifically, we show that: (1) these sinks are formed by specific middle-layer MLP modules; these MLPs map token representations to vectors that align with the direction of the primary sink of that layer. (2) The $\ell_2$-norm of these vectors determines the sink score of the secondary sink, and also the number of layers it lasts for, thereby leading to different impacts on the attention mechanisms accordingly. (3) The primary sink weakens in middle layers, coinciding with the emergence of secondary sinks. We observe that in larger-scale models, the location and lifetime of the sinks, together referred to as sink levels, appear in a more deterministic and frequent manner. Specifically, we identify three sink levels in QwQ-32B and six levels in Qwen3-14B.
Accelerating 3D Gaussian Splatting with Neural Sorting and Axis-Oriented Rasterization
Jun 08, 2025



Abstract:3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently gained significant attention for high-quality and efficient view synthesis, making it widely adopted in fields such as AR/VR, robotics, and autonomous driving. Despite its impressive algorithmic performance, real-time rendering on resource-constrained devices remains a major challenge due to tight power and area budgets. This paper presents an architecture-algorithm co-design to address these inefficiencies. First, we reveal substantial redundancy caused by repeated computation of common terms/expressions during the conventional rasterization. To resolve this, we propose axis-oriented rasterization, which pre-computes and reuses shared terms along both the X and Y axes through a dedicated hardware design, effectively reducing multiply-and-add (MAC) operations by up to 63%. Second, by identifying the resource and performance inefficiency of the sorting process, we introduce a novel neural sorting approach that predicts order-independent blending weights using an efficient neural network, eliminating the need for costly hardware sorters. A dedicated training framework is also proposed to improve its algorithmic stability. Third, to uniformly support rasterization and neural network inference, we design an efficient reconfigurable processing array that maximizes hardware utilization and throughput. Furthermore, we introduce a $\pi$-trajectory tile schedule, inspired by Morton encoding and Hilbert curve, to optimize Gaussian reuse and reduce memory access overhead. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed design preserves rendering quality while achieving a speedup of $23.4\sim27.8\times$ and energy savings of $28.8\sim51.4\times$ compared to edge GPUs for real-world scenes. We plan to open-source our design to foster further development in this field.
ASPO: Constraint-Aware Bayesian Optimization for FPGA-based Soft Processors
Jun 07, 2025Abstract:Bayesian Optimization (BO) has shown promise in tuning processor design parameters. However, standard BO does not support constraints involving categorical parameters such as types of branch predictors and division circuits. In addition, optimization time of BO grows with processor complexity, which becomes increasingly significant especially for FPGA-based soft processors. This paper introduces ASPO, an approach that leverages disjunctive form to enable BO to handle constraints involving categorical parameters. Unlike existing methods that directly apply standard BO, the proposed ASPO method, for the first time, customizes the mathematical mechanism of BO to address challenges faced by soft-processor designs on FPGAs. Specifically, ASPO supports categorical parameters using a novel customized BO covariance kernel. It also accelerates the design evaluation procedure by penalizing the BO acquisition function with potential evaluation time and by reusing FPGA synthesis checkpoints from previously evaluated configurations. ASPO targets three soft processors: RocketChip, BOOM, and EL2 VeeR. The approach is evaluated based on seven RISC-V benchmarks. Results show that ASPO can reduce execution time for the ``multiply'' benchmark on the BOOM processor by up to 35\% compared to the default configuration. Furthermore, it reduces design time for the BOOM processor by up to 74\% compared to Boomerang, a state-of-the-art hardware-oriented BO approach.
* Accepted to International Conference on Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL) 2025
A3 : an Analytical Low-Rank Approximation Framework for Attention
May 19, 2025Abstract:Large language models have demonstrated remarkable performance; however, their massive parameter counts make deployment highly expensive. Low-rank approximation offers a promising compression solution, yet existing approaches have two main limitations: (1) They focus on minimizing the output error of individual linear layers, without considering the architectural characteristics of Transformers, and (2) they decompose a large weight matrix into two small low-rank matrices. Consequently, these methods often fall short compared to other compression techniques like pruning and quantization, and introduce runtime overhead such as the extra GEMM kernel launches for decomposed small matrices. To address these limitations, we propose $\tt A^\tt 3$, a post-training low-rank approximation framework. $\tt A^\tt 3$ splits a Transformer layer into three functional components, namely $\tt QK$, $\tt OV$, and $\tt MLP$. For each component, $\tt A^\tt 3$ provides an analytical solution that reduces the hidden dimension size inside each component while minimizing the component's functional loss ($\it i.e.$, error in attention scores, attention outputs, and MLP outputs). This approach directly reduces model sizes, KV cache sizes, and FLOPs without introducing any runtime overheads. In addition, it provides a new narrative in advancing the optimization problem from singular linear layer loss optimization toward improved end-to-end performance. Through extensive experiments, we show that $\tt A^\tt 3$ maintains superior performance compared to SoTAs. For example, under the same reduction budget in computation and memory, our low-rank approximated LLaMA 3.1-70B achieves a perplexity of 4.69 on WikiText-2, outperforming the previous SoTA's 7.87 by 3.18. We also demonstrate the versatility of $\tt A^\tt 3$, including KV cache compression, quantization, and mixed-rank assignments for enhanced performance.
FW-Merging: Scaling Model Merging with Frank-Wolfe Optimization
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:Model merging has emerged as a promising approach for multi-task learning (MTL), offering a data-efficient alternative to conventional fine-tuning. However, with the rapid development of the open-source AI ecosystem and the increasing availability of fine-tuned foundation models, existing model merging methods face two key limitations: (i) They are primarily designed for in-house fine-tuned models, making them less adaptable to diverse model sources with partially unknown model and task information, (ii) They struggle to scale effectively when merging numerous model checkpoints. To address these challenges, we formulate model merging as a constrained optimization problem and introduce a novel approach: Frank-Wolfe Merging (FW-Merging). Inspired by Frank-Wolfe optimization, our approach iteratively selects the most relevant model in the pool to minimize a linear approximation of the objective function and then executes a local merging similar to the Frank-Wolfe update. The objective function is designed to capture the desired behavior of the target-merged model, while the fine-tuned candidate models define the constraint set. More importantly, FW-Merging serves as an orthogonal technique for existing merging methods, seamlessly integrating with them to further enhance accuracy performance. Our experiments show that FW-Merging scales across diverse model sources, remaining stable with 16 irrelevant models and improving by 15.3% with 16 relevant models on 20 CV tasks, while maintaining constant memory overhead, unlike the linear overhead of data-informed merging methods. Compared with the state-of-the-art approaches, FW-Merging surpasses the data-free merging method by 32.8% and outperforms the data-informed Adamerging by 8.39% when merging 20 ViT models.
MetaML-Pro: Cross-Stage Design Flow Automation for Efficient Deep Learning Acceleration
Feb 09, 2025Abstract:This paper presents a unified framework for codifying and automating optimization strategies to efficiently deploy deep neural networks (DNNs) on resource-constrained hardware, such as FPGAs, while maintaining high performance, accuracy, and resource efficiency. Deploying DNNs on such platforms involves addressing the significant challenge of balancing performance, resource usage (e.g., DSPs and LUTs), and inference accuracy, which often requires extensive manual effort and domain expertise. Our novel approach addresses two key issues: cross-stage co-optimization and optimization search. By seamlessly integrating programmatic DNN optimization techniques with high-level synthesis (HLS)-based metaprogramming and leveraging advanced design space exploration (DSE) strategies like Bayesian optimization, the framework automates both top-down and bottom-up design flows, reducing the need for manual intervention and domain expertise. The proposed framework introduces customizable optimization, transformation, and control blocks to enhance DNN accelerator performance and resource efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate up to a 92\% DSP and 89\% LUT usage reduction for select networks, while preserving accuracy, along with a 15.6-fold reduction in optimization time compared to grid search. These results underscore the novelty and potential of the proposed framework for automated, resource-efficient DNN accelerator designs.
Robust Time Series Causal Discovery for Agent-Based Model Validation
Oct 25, 2024Abstract:Agent-Based Model (ABM) validation is crucial as it helps ensuring the reliability of simulations, and causal discovery has become a powerful tool in this context. However, current causal discovery methods often face accuracy and robustness challenges when applied to complex and noisy time series data, which is typical in ABM scenarios. This study addresses these issues by proposing a Robust Cross-Validation (RCV) approach to enhance causal structure learning for ABM validation. We develop RCV-VarLiNGAM and RCV-PCMCI, novel extensions of two prominent causal discovery algorithms. These aim to reduce the impact of noise better and give more reliable causal relation results, even with high-dimensional, time-dependent data. The proposed approach is then integrated into an enhanced ABM validation framework, which is designed to handle diverse data and model structures. The approach is evaluated using synthetic datasets and a complex simulated fMRI dataset. The results demonstrate greater reliability in causal structure identification. The study examines how various characteristics of datasets affect the performance of established causal discovery methods. These characteristics include linearity, noise distribution, stationarity, and causal structure density. This analysis is then extended to the RCV method to see how it compares in these different situations. This examination helps confirm whether the results are consistent with existing literature and also reveals the strengths and weaknesses of the novel approaches. By tackling key methodological challenges, the study aims to enhance ABM validation with a more resilient valuation framework presented. These improvements increase the reliability of model-driven decision making processes in complex systems analysis.
Optimizing VarLiNGAM for Scalable and Efficient Time Series Causal Discovery
Sep 09, 2024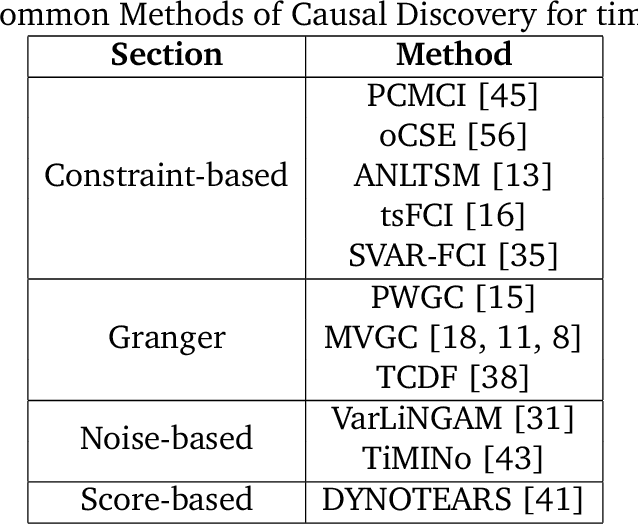
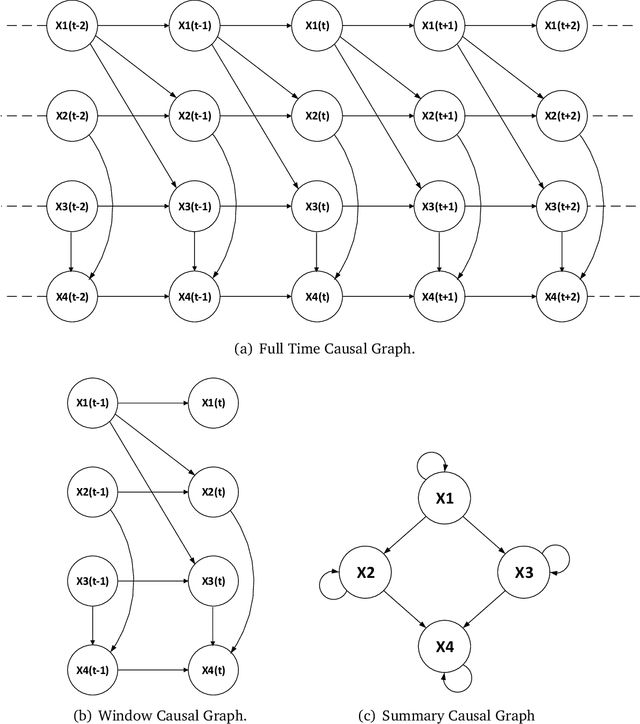
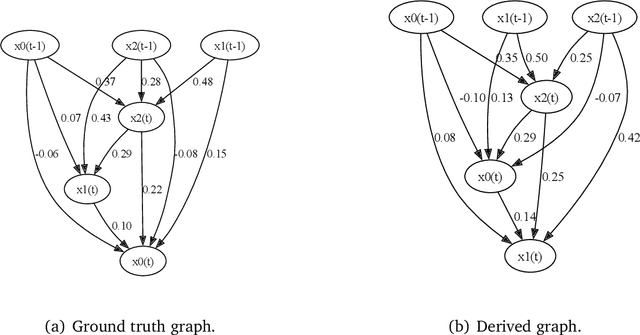
Abstract:Causal discovery is designed to identify causal relationships in data, a task that has become increasingly complex due to the computational demands of traditional methods such as VarLiNGAM, which combines Vector Autoregressive Model with Linear Non-Gaussian Acyclic Model for time series data. This study is dedicated to optimising causal discovery specifically for time series data, which is common in practical applications. Time series causal discovery is particularly challenging due to the need to account for temporal dependencies and potential time lag effects. By designing a specialised dataset generator and reducing the computational complexity of the VarLiNGAM model from \( O(m^3 \cdot n) \) to \( O(m^3 + m^2 \cdot n) \), this study significantly improves the feasibility of processing large datasets. The proposed methods have been validated on advanced computational platforms and tested across simulated, real-world, and large-scale datasets, showcasing enhanced efficiency and performance. The optimised algorithm achieved 7 to 13 times speedup compared with the original algorithm and around 4.5 times speedup compared with the GPU-accelerated version on large-scale datasets with feature sizes between 200 and 400. Our methods aim to push the boundaries of current causal discovery capabilities, making them more robust, scalable, and applicable to real-world scenarios, thus facilitating breakthroughs in various fields such as healthcare and finance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge