Andres Meza
UC San Diego
AlphaChimp: Tracking and Behavior Recognition of Chimpanzees
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:Understanding non-human primate behavior is crucial for improving animal welfare, modeling social behavior, and gaining insights into both distinctly human and shared behaviors. Despite recent advances in computer vision, automated analysis of primate behavior remains challenging due to the complexity of their social interactions and the lack of specialized algorithms. Existing methods often struggle with the nuanced behaviors and frequent occlusions characteristic of primate social dynamics. This study aims to develop an effective method for automated detection, tracking, and recognition of chimpanzee behaviors in video footage. Here we show that our proposed method, AlphaChimp, an end-to-end approach that simultaneously detects chimpanzee positions and estimates behavior categories from videos, significantly outperforms existing methods in behavior recognition. AlphaChimp achieves approximately 10% higher tracking accuracy and a 20% improvement in behavior recognition compared to state-of-the-art methods, particularly excelling in the recognition of social behaviors. This superior performance stems from AlphaChimp's innovative architecture, which integrates temporal feature fusion with a Transformer-based self-attention mechanism, enabling more effective capture and interpretation of complex social interactions among chimpanzees. Our approach bridges the gap between computer vision and primatology, enhancing technical capabilities and deepening our understanding of primate communication and sociality. We release our code and models and hope this will facilitate future research in animal social dynamics. This work contributes to ethology, cognitive science, and artificial intelligence, offering new perspectives on social intelligence.
Reliable edge machine learning hardware for scientific applications
Jun 27, 2024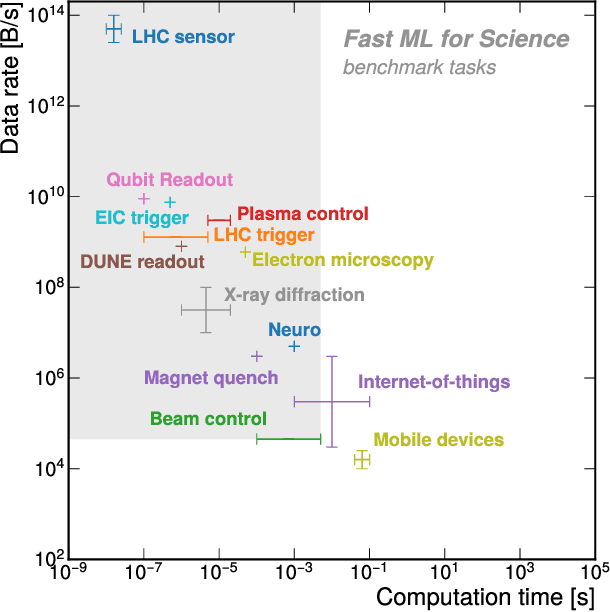
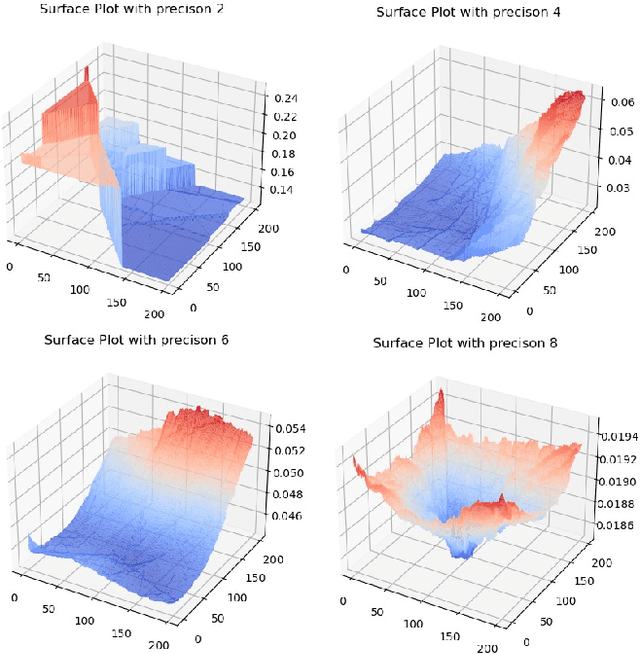
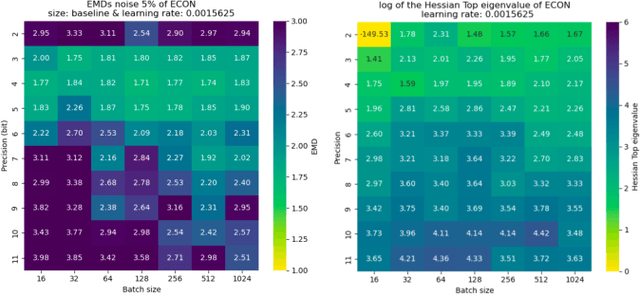
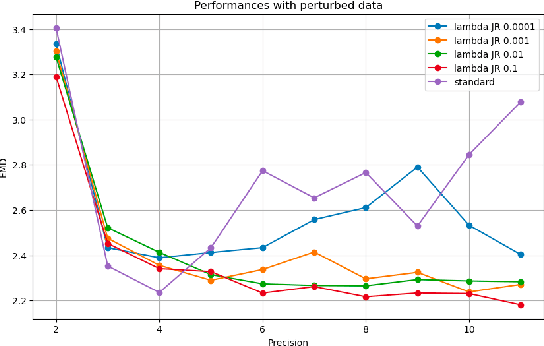
Abstract:Extreme data rate scientific experiments create massive amounts of data that require efficient ML edge processing. This leads to unique validation challenges for VLSI implementations of ML algorithms: enabling bit-accurate functional simulations for performance validation in experimental software frameworks, verifying those ML models are robust under extreme quantization and pruning, and enabling ultra-fine-grained model inspection for efficient fault tolerance. We discuss approaches to developing and validating reliable algorithms at the scientific edge under such strict latency, resource, power, and area requirements in extreme experimental environments. We study metrics for developing robust algorithms, present preliminary results and mitigation strategies, and conclude with an outlook of these and future directions of research towards the longer-term goal of developing autonomous scientific experimentation methods for accelerated scientific discovery.
ChimpACT: A Longitudinal Dataset for Understanding Chimpanzee Behaviors
Oct 25, 2023Abstract:Understanding the behavior of non-human primates is crucial for improving animal welfare, modeling social behavior, and gaining insights into distinctively human and phylogenetically shared behaviors. However, the lack of datasets on non-human primate behavior hinders in-depth exploration of primate social interactions, posing challenges to research on our closest living relatives. To address these limitations, we present ChimpACT, a comprehensive dataset for quantifying the longitudinal behavior and social relations of chimpanzees within a social group. Spanning from 2015 to 2018, ChimpACT features videos of a group of over 20 chimpanzees residing at the Leipzig Zoo, Germany, with a particular focus on documenting the developmental trajectory of one young male, Azibo. ChimpACT is both comprehensive and challenging, consisting of 163 videos with a cumulative 160,500 frames, each richly annotated with detection, identification, pose estimation, and fine-grained spatiotemporal behavior labels. We benchmark representative methods of three tracks on ChimpACT: (i) tracking and identification, (ii) pose estimation, and (iii) spatiotemporal action detection of the chimpanzees. Our experiments reveal that ChimpACT offers ample opportunities for both devising new methods and adapting existing ones to solve fundamental computer vision tasks applied to chimpanzee groups, such as detection, pose estimation, and behavior analysis, ultimately deepening our comprehension of communication and sociality in non-human primates.
Open-source FPGA-ML codesign for the MLPerf Tiny Benchmark
Jun 23, 2022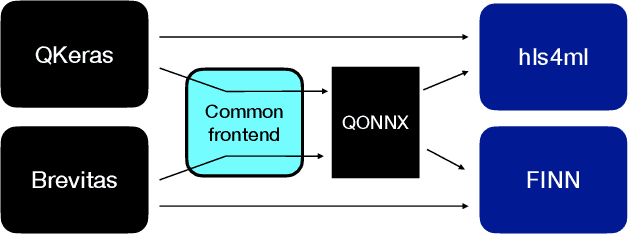
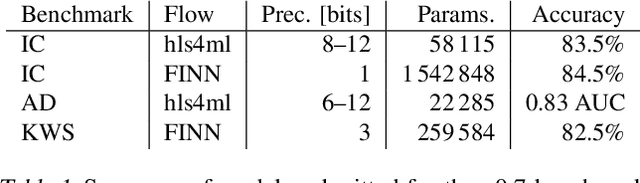
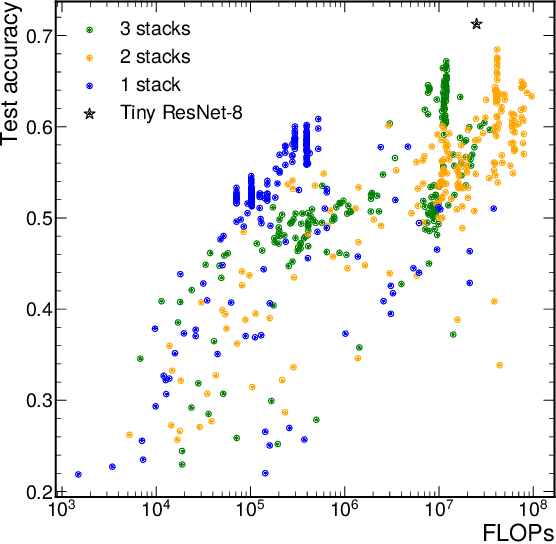
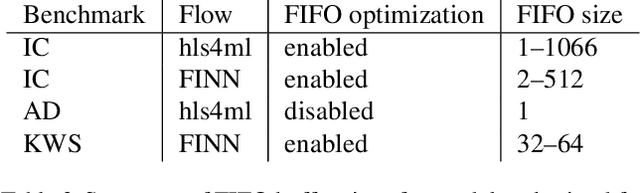
Abstract:We present our development experience and recent results for the MLPerf Tiny Inference Benchmark on field-programmable gate array (FPGA) platforms. We use the open-source hls4ml and FINN workflows, which aim to democratize AI-hardware codesign of optimized neural networks on FPGAs. We present the design and implementation process for the keyword spotting, anomaly detection, and image classification benchmark tasks. The resulting hardware implementations are quantized, configurable, spatial dataflow architectures tailored for speed and efficiency and introduce new generic optimizations and common workflows developed as a part of this work. The full workflow is presented from quantization-aware training to FPGA implementation. The solutions are deployed on system-on-chip (Pynq-Z2) and pure FPGA (Arty A7-100T) platforms. The resulting submissions achieve latencies as low as 20 $\mu$s and energy consumption as low as 30 $\mu$J per inference. We demonstrate how emerging ML benchmarks on heterogeneous hardware platforms can catalyze collaboration and the development of new techniques and more accessible tools.
Applications and Techniques for Fast Machine Learning in Science
Oct 25, 2021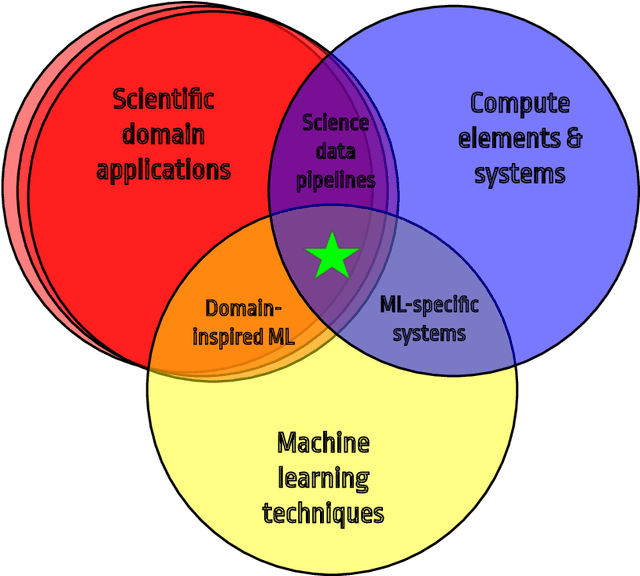
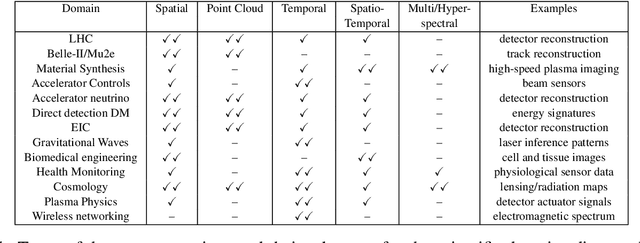
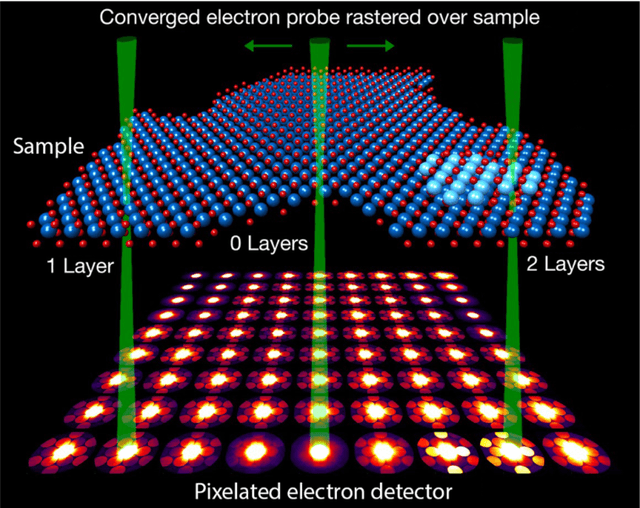
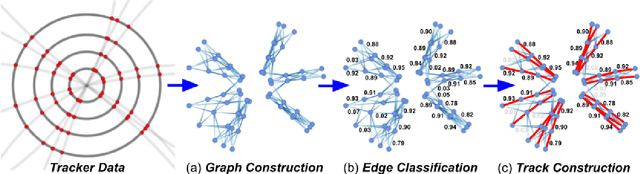
Abstract:In this community review report, we discuss applications and techniques for fast machine learning (ML) in science -- the concept of integrating power ML methods into the real-time experimental data processing loop to accelerate scientific discovery. The material for the report builds on two workshops held by the Fast ML for Science community and covers three main areas: applications for fast ML across a number of scientific domains; techniques for training and implementing performant and resource-efficient ML algorithms; and computing architectures, platforms, and technologies for deploying these algorithms. We also present overlapping challenges across the multiple scientific domains where common solutions can be found. This community report is intended to give plenty of examples and inspiration for scientific discovery through integrated and accelerated ML solutions. This is followed by a high-level overview and organization of technical advances, including an abundance of pointers to source material, which can enable these breakthroughs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge